Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disease manifested by paresthesias in the lower extremities and their excessive motor activity, mainly at rest or during sleep.
Restless legs syndrome was first described by Thomas Willys in 1672: “In some people, when they are about to sleep and go to bed, there is immediately after a stirring of the tendons, arms and legs, accompanied by colic and such restlessness that the patient cannot sleep, as It’s like he’s under torture.” The modern definition of this syndrome was proposed by the Swedish scientist K. Ekbom in 1945:
Restless legs syndrome can be primary (idiopathic) or secondary.
One of the most likely causes of the development of primary restless legs syndrome is considered to be a deficiency of dopaminergic systems in the subcortical structures of the brain involved in inhibitory processes.
Secondary restless legs syndrome can develop during pregnancy and various pathological conditions.
The main causes of secondary restless legs syndrome are:
- Iron deficiency. Lack of iron disrupts the production of dopamine in the brain, which in turn provokes the development of secondary RLS. A patient's iron stores may become depleted even without clinically significant anemia. Research has shown that decreased iron stores, defined as ferritin levels falling below 50 mcg/L, may cause or worsen symptoms of RLS.
- Neurological disorders. Secondary RLS is often observed with injuries to the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system, as well as peripheral neuropathies of various origins (diabetic, alcoholic, toxic).
- Pregnancy. RLS occurs in 15-20% of women during pregnancy. Symptoms can be quite severe but usually disappear completely within a few weeks of delivery. It is assumed that the causes of RLS during pregnancy may be iron deficiency anemia, folic acid deficiency, hormonal changes and venous congestion in the lower extremities.
- Uremia. Up to 50% of patients with end-stage renal disease have RLS. A correlation was shown between the frequency of RLS and blood urea levels, anemia, peripheral neuropathy and a decrease in parathyroid hormone levels in this category of patients. Particularly severe symptoms are observed directly during dialysis, when the patient is forced to lie motionless for several hours. RLS symptoms have been shown to improve or disappear after kidney transplantation.
- Use of medications. Symptoms of RLS can develop or worsen due to the use of various medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, azaphene, etc.), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (trazodone, Prozac), lithium preparations, metoclopramide (Reglan), calcium channel blockers (Corinfar, finoptin). Caffeine also makes RLS symptoms worse.
Clinical manifestations of RLS can be grouped into several main symptom complexes:
Unpleasant sensations in the legs. They are usually described as crawling, trembling, tingling, burning, twitching, electric shock, movement under the skin, etc. About 30% of patients characterize these sensations as pain. Sometimes patients cannot accurately describe the nature of the sensations, but they are always extremely unpleasant. These sensations are localized in the thighs, legs, feet and occur in waves every 5-30 seconds. There are significant variations in the severity of these symptoms. In some patients, symptoms may occur only at the beginning of the night, while in others they may continuously disturb throughout the day.
Symptoms are worse with rest. The most characteristic and unusual manifestation of RLS is an increase in sensory or motor symptoms at rest. Patients usually report worsening when sitting or lying down and especially when falling asleep. Usually, it takes from several minutes to an hour for symptoms to appear when you are in a calm state.
Symptoms are relieved by movement. Symptoms are significantly weakened or disappear with movement. Simple walking often has the best effect. In some cases, stretching, bending, exercises on an exercise bike, or simply standing can help.
Symptoms are circadian in nature. Symptoms increase significantly in the evening and in the first half of the night (between 18 pm and 4 am). Before dawn, symptoms weaken and may disappear altogether in the first half of the day.
It should be noted, however, that diagnostic difficulties can sometimes arise in the differential diagnosis of primary and secondary restless legs syndrome. Since there are no accurate biochemical markers of primary RLS, it is not possible to say definitively whether the above condition is the cause of secondary RLS, or whether it merely provoked the clinical manifestations of primary RLS.
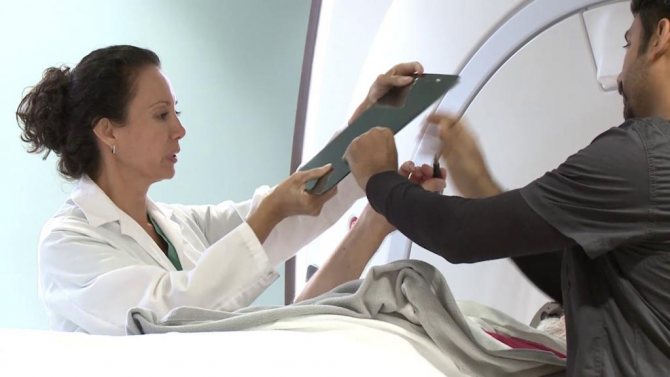
Valuable diagnostic information to confirm the presence of restless legs syndrome can be obtained by performing polysomnography, a method of long-term recording of various physiological parameters during sleep.
If you or your relatives want to fully relax during sleep, we are waiting for you at the somnology department of the Diagnostic and Treatment Center of the International Institute of Biological Systems named after S.M. Berezina.
Give yourself a healthy sleep!
What is leg tremors
Physiological tremor is caused by physical and psychological fatigue, alcohol intoxication, stressful situations, hypothermia, etc. This disease is easy to treat. Subject to compliance with the doctor’s requirements, it is minimized or reduced to zero.
In contrast, pathological tremor accompanies a number of serious diseases. These include Parkinson's disease (usually occurs in older people), multiple sclerosis, etc.
Both newborns and elderly people can suffer from tremor.
- Emotional. Appears at moments of change in emotional state (for example, bad news).
- Senile. It occurs in older people, usually over 60 years of age.
- Hysterical is caused by nervous overstrain.
- Tremor of movement.
- Popping or alcoholic. Manifests itself in cases of alcohol poisoning or liver failure.
- "Mercury". Appears in case of mercury vapor poisoning or other acute or chronic poisoning.
- Rubral tremor is caused by pathologies of the brain. Manifests itself both in a state of rest and movement.
Depending on the number of oscillations, there are:
- Fast (frequency of movements reaches 6-12Hz).
- Slow tremor is accompanied by fluctuations not exceeding 3-5 Hz.
On this topic
All about essential tremor
To understand why the tremor appeared, it is necessary to analyze the situation that existed before the tremor appeared.
Depending on the symptoms, the following types of tremor are distinguished.
Postural
The appearance of tremors is caused by narcotic, toxic, alcohol or drug poisoning, as well as an overdose of heavy metals.
Intentional
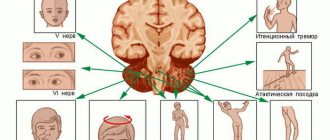
The appearance is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the cerebellum. This organ is responsible for coordination and balance of movements. If it is damaged, trembling of the legs and arms may appear as a primary symptom.
Asterixis
The cause of asterixis is the accumulation of copper in the blood, medulla and liver. This is due to pathologies of internal organs.
Parkinson's disease
Most often common among the elderly. Its appearance is due to disturbances in the functioning of the brain.
Hereditary tremor
Can be passed on to descendants.
Physiological
It occurs as a slight deviation from the norm and does not pose a danger.
Hormone
This type of tremors occurs in adolescents and people suffering from diseases of the thyroid gland, which is responsible for hormonal balance in the body. Tremors may be accompanied by increased sweating, irritability and other changes.
Infant
It is observed in many newborns, especially premature ones. This is due to the imperfection of the nervous system. Within 3 months the symptoms disappear. If they remain, additional examinations are required, since tremor may indicate serious illnesses and abnormalities that require immediate treatment.
The list of causes of tremor is open. With the development of medicine and science, new causes for the appearance of such a symptom are being identified.
Drinking alcohol
Shaking when drinking alcoholic beverages is considered a pathology:
- alcohol, entering the blood, disrupts the conduction of nerve tissue from the spinal cord to the brain, which causes tremors;
- trembling occurs in people in the morning after an evening feast, as well as in alcoholics - regardless of whether they drank in the evening or not.
The symptom usually goes away after the person drinks again.
Symptoms
The main symptom is trembling of the limbs. Depending on the reasons, tremor can appear in a state of psycho-emotional overload, in a state of rest, constantly, etc.
- In newborns, mild leg tremors may last for 3 months. This should be reported to the observing pediatrician so that if the symptoms do not go away, the necessary examinations and subsequent treatment can be prescribed.
- In case of poisoning with alcohol, drugs, etc. manifests itself during the decay of toxic substances. After cleaning from the breakdown products of harmful substances, the symptoms of trembling disappear.
- Intentional and asterixis appear as the disease progresses, intensify and require immediate treatment.
- Hormonal symptoms manifest themselves, as a rule, when the mental situation changes. So, in case of excitement, anxiety, or stress, twitching of the limbs may appear.
- Physiological tremor can occur in any person. He poses no danger. Caused by physical stress on an unprepared body or stressful situations. When the causes affecting the appearance of tremor are eliminated, the symptoms disappear.
- One of the symptoms of Parkinson's is trembling of the limbs in adults, usually over 60 years of age. Tremor is a slight vibration at first in one limb; as the condition worsens, the second and other parts of the body join.
When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist for advice.
Walking in heels

Legs often tremble due to constant walking in high heels:
- the load is distributed unevenly, going to the calves and the front of the thigh;
- shaking occurs due to tension in the legs, back and the need to constantly maintain balance.
Girls who regularly wear low-heeled shoes will not experience trembling legs.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out by a specialist of a certain profile. When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
The doctor will conduct a visual examination and interview the patient. If a diagnosis can be made during the initial visit, treatment will be prescribed. If the etymology of the trembling cannot be established immediately, then additional tests and examinations are prescribed.
If there is a suspicion that the tremor has arisen due to changes in hormonal levels, then a blood test for hormones is prescribed. If it is suspected that the tremor is due to damage to the cerebellum, a brain examination is prescribed. The survey helps the specialist determine the causes of symptoms and, based on the data obtained, he prescribes examinations.
source
Treatment
After a thorough examination, the doctor prescribes treatment. If twitching occurs due to a deficiency of some nutrients, then treatment will consist of changing the diet and taking multivitamins. Everything is much more complicated if the cause of unpleasant symptoms is hidden in pathologies of the nervous system. First of all, the neurologist uses conservative treatment methods: drug therapy, physiotherapy, acupuncture, massage, gymnastics. Surgery may be necessary for brain or spinal cord injuries. In severe cases, one specialist does not have the right to make a decision on his own, so a group of specialists is assembled (consilium).
What is meant by the term “tremor”
Trembling of the limbs is provoked by rhythmic, uncontrolled movements of individual muscles caused by their contraction. This disorder can affect one or both arms at the same time and spread to other areas of the body:
If tremor of the legs, arms, etc. develops, the patient experiences oscillatory movements with a frequency of up to 10 repetitions per second. The amplitude is determined by the causes and degree of damage to the nervous system.

Trembling can develop in any state - during physical activity or rest. Most often, it intensifies against the background of strong emotions and increased stress.
Medical statistics confirm that hand tremors are being detected more and more often, and are included in the list of the most common disorders of the motor function of the human body.
Types and symptoms of tremor
There are several types of tremors:
- Rest tremor.
- Popping tremor.
- Senile.
- Rubral tremor.
- Hysterical.
- Essential.
Rest tremor (parkinsonian) is manifested by trembling, which tends to decrease with movement and increase during periods of rest. The pathology mainly affects the upper limbs, chin, lips. Legs or head shake less often. This condition is mainly one-sided, asymmetrical in nature.
Flapping tremor (asterixis) is characterized by involuntary trembling of the wrists, reminiscent of the flapping of bird wings. A similar disorder can affect the tongue, causing it to alternately retract and protrude while the eyes blink convulsively. A flapping tremor can develop in the feet, causing them to flex and straighten involuntarily. Bilateral asterixis develops more often, and unilateral forms of the disorder develop less frequently. Its distinctive feature is the ability to lead to the accumulation of copper in the blood and internal organs (kidneys, liver, lungs).
Causes of tremors
Body tremors are often associated with the following processes:
- dysfunction of areas of the brain responsible for muscle function;
- neurological disorders;
- traumatic brain injuries.
Muscle tremors often accompany neurodegenerative diseases. Often, causes such as Parkinson's disease, Wilson-Konovalov's disease, atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, and osteochondrosis lead to the development of the disorder.
The cause of tongue trembling is neurasthenic syndrome, pustular or tumor-like formations in the cerebellum, multiple sclerosis. This phenomenon may indicate thyrotoxicosis (hyperfunction of the thyroid gland), side effects of drugs used for increased anxiety and other psychological problems.
Body tremors at rest are provoked by excessive emotional stress, alcohol abuse, and drug withdrawal. Often this condition is aggravated by overwork and severe anxiety.
Among the causes of chills and trembling in the extremities, experts name kidney and liver failure, mercury poisoning, sodium valproate, hypoglycemia (low blood glucose).
Diagnosis of pathology
For tremor of the upper extremities, a neurologist performs a diagnosis consisting of several stages.
- Examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis. The doctor conducts a conversation to identify the circumstances and causes of the disorder, the presence or absence of a hereditary predisposition.
- Functional tests during which a person is asked to stretch out his arms and hold them straight. This allows you to determine the degree of finger tremor.
- Finger test, assessing the patient’s gait condition.
- Thermography, recording vibrations in various projections.
- Electromyography, which helps determine the quantity and quality of oscillatory movements.
- Electroencephalography, which determines brain electrical activity and deviations from normal values.
- CT and MRI, revealing structural changes in the intracranial space.
Patients with signs of thyrotoxicosis are examined for the presence of atrial fibrillation, and the pattern of movements of the eyeballs is determined. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to a neurosurgeon or medical geneticist.
How to treat tremors caused by various reasons
To prescribe treatment for hand tremors or trembling in other areas of the body, a specialist needs to know the exact cause of the development of the pathology. After clarification, the following therapeutic measures are carried out:
- for Parkinson's disease, MAO inhibitors (Selegiline) and the combination drug Levodopa are prescribed;
- for essential tremor, they resort to the use of beta-blockers (Penbutolol, Sandinorm);
- in case of increased activity of the thyroid gland, taking thyreostatics (Tyrozol, Propicil) is indicated;
- patients with chronic cerebrovascular accidents are prescribed nootropics and antiplatelet agents (Pantogam, Anaprilin, Dipyridamole).
If the cause of the disease is multiple sclerosis, the patient is prescribed hormonal drugs from the DMT group. A complete abstinence from strong drinks and a course of B vitamins help eliminate the pathology that has arisen due to alcoholism.
Additional therapeutic measures include taking baths with soothing herbal infusions, breathing exercises, and relaxation procedures.
How is this related?
At the moment of fear, a person experiences many unpleasant physiological symptoms. The most common are increased heart rate, increased blood pressure and increased heart rate. The thing is that, sensing danger, the body begins to prepare for the upcoming battle. Blood begins to flow intensively to the head and heart, “forgetting” about the gastrointestinal tract. To warm the body, the abdominal muscles begin to contract intensely. A person perceives these spasms as trembling. Gradually, if the body does not receive enough heat, the “shaking” spreads to the limbs. In some cases, a person’s legs even give way from trembling, and their hands become unable to hold one or another object. The condition when legs tremble with fear is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- feeling of instability, loss of balance;
- severe weakness in the legs, fog in the head;
- fever or chills, increased sweating;
- pain and tension in the chest area;
- dizziness, noise or ringing in the ears;
- a strong urge to urinate or have a bowel movement;
- respiratory disorders (shortness of breath, feeling of suffocation, inability to take a full breath);
- panic attacks, derealization.
When you are afraid, in most cases it is not only your knees or hands that tremble. Often patients feel shaking inside the body, and sometimes the trembling even spreads to the face.
Disease prevention
Prevention is based on a healthy lifestyle and avoidance of stressful situations. Measures to help minimize the risk of developing pathology include:
- Minimizing the consumption of alcoholic beverages and strong coffee (best is complete abstinence).
- Healthy eating, excluding salty, fried and spicy foods from the diet.
- Constant monitoring of blood pressure indicators.
- Moderate physical activity, participation in accessible sports.
- With increased emotionality and a tendency to worry, take medications that prevent the development of physiological tremors.
Regular baths with essential oils and drinking soothing herbal teas (from lemon balm, verbena, mint) before bed are helpful. It is important to harmoniously alternate periods of work and rest, to avoid psychological and physical overload.
source
Symptomatic treatment
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, medications from the beta blocker group are used in medicine. They are also used in the treatment of hypertension, arrhythmia and heart attack. These drugs block the connection of adrenaline with other hormones and reduce the reaction to stress. The drug commonly used is Propranolol. Anticonvulsant medications may also be prescribed. But such medications should not be taken while pregnant and breastfeeding. In addition, there are some contraindications. Therefore, only a doctor can prescribe the appropriate drug.
Medicines can be supplemented with alternative medicine. Your doctor may recommend taking soothing herbal teas, valerian, or motherwort. Ginseng tincture has proven itself well. It is recommended to use twenty drops three times a day, this will help reduce the manifestation of pathology. All traditional medicine that is intended to be used must be approved by a specialist.

Tremor
Tremors are rhythmic, rapid contractions of the muscles of the trunk or limbs of an involuntary nature. Literally, the term muscle tremor means “trembling.” Trembling can occur during rest or exclusively during voluntary movement. Muscle tremors allow for rougher work. Fine motor activities are often difficult. For example, it is often difficult to thread a needle through the eye, or handwriting deteriorates significantly. Hypothermia, fatigue, increased concentration, and excessive muscle tension usually increase trembling. Most often, the described disorder affects the upper extremities, less often the proximal parts of the body. Tremors are most susceptible to people of older age, but it can also arise at a fairly young age.
Stress or fear
Tremors in the limbs can be a consequence of stress or severe fright:
- mobilization of the body's defenses leads to a lack of oxygen and a decrease in body temperature;
- after a spasm occurs in the intestines and stomach area, the trembling spreads to the limbs.
When fear disappears or the stressful condition passes, blood will begin to flow to all parts of the body, the temperature will stabilize and trembling will disappear.

Causes of tremor
Before finding out the factors that cause involuntary muscle contractions, it is necessary to answer the question: “tremor, what is it?”
Tremors are involuntary rhythmic contractions of muscle groups in certain parts of the body. More often, trembling is a signal of some kind of problem occurring in the body, and not a separate ailment.
Involuntary muscle contractions may be a symptom related to dysfunction in the areas of the brain that control muscles. In addition, tremors can occur as a result of a number of neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, stroke, traumatic brain injury, and some neurodegenerative diseases that damage certain areas of the brain or cerebellum, such as Parkinson's disease.
There are a number of other factors that provoke the development of trembling of the body and limbs:
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels (due to the accumulation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of capillaries, narrowing of arterial vessels occurs), leading to the development of chronic pathology of cerebral circulation;
- Minor's disease or essential tremor, which is a hereditary benign disease and manifests itself as non-progressive tremors, most often of the neck muscles;
The baby spits up a lot, I heard that this could be due to neurological disorders. Is it so?
Regurgitation is a very common complaint in the first months of life.
Most healthy children burp up to 3-5 times a day. For infants, regurgitation is the norm rather than a pathology, since the structure and functioning of the gastrointestinal tract predispose them to regurgitation. The stomach of newborns is located horizontally, has a round shape and a small volume - only 5-10 ml: this is why a few drops of colostrum are enough for a newly born baby to eat. The entrance to the baby's stomach is relatively wide, and the sphincter (the muscle that closes the entrance to the stomach) is underdeveloped. Therefore, the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract is somewhat slower. The immaturity of certain enzymes and lack of coordination in the processes of breathing, sucking and swallowing, which are more typical for premature and low birth weight babies, also predispose to regurgitation. Regurgitation can also be associated with overeating, frequent feedings, and aerophagia (swallowing air). Yes, they can be a manifestation of some kind of neurological pathology, but this happens very rarely, especially if there are no other symptoms of the disease. Reasons for shaking legs
Tremor symptoms
To find out the symptoms of tremor, it is necessary to define tremor, what it is and its forms.
As was written above, trembling is most often a symptom of an illness, and not a separate disorder. It manifests itself in the form of involuntary rhythmic muscle contractions. There are two main types of this condition: pathological trembling and physiological. The first occurs as a result of serious dysfunctions of certain parts of the nervous system.
Pathological tremor is one of the symptoms of the disease. The second is a slight shaking that occurs under certain conditions in the outstretched upper limbs. This condition usually goes away quite quickly after the cause is eliminated. Such reasons include: excessive physical activity, various stress factors, use of certain medications, etc.
Tremor during excitement is considered one of the types of physiological tremors. The appearance of involuntary muscle contraction during excitement is a fairly common phenomenon that can manifest itself in different ways. Most often it occurs as a result of a stressful situation or depression. Trembling with excitement is manifested by twitching of the hands and fingers, head, limbs or larynx. This type of trembling during excitement is just the body’s response to anxiety, excitement and usually goes away on its own.
If trembling is observed for several weeks, if it is not associated with taking medications, physical activity, stress, or excessive alcohol consumption, then there is a possibility that muscle contractions are caused by serious pathologies in the functioning of the body.
You can also classify trembling according to its prevalence - local and generalized trembling. The first is observed in certain areas of the body (tongue, head, limbs). Generalized muscle contraction is distributed evenly throughout the body.
Based on amplitude, tremors can be divided into the following forms: small-sweep and large-sweep.
Based on the characteristics of the manifestation of tremor, static and dynamic forms can be classified. The first form is a resting tremor, since this form is observed and most manifested in an unstrained muscle. The second form is action tremors, which manifests itself or intensifies during active movements. It, in turn, can be postural, intentional, or contractive. Postural trembling occurs or worsens when maintaining a position (for example, holding straight arms in front of you). Intentional muscle contraction occurs when performing small precise movements (for example, touching your nose with a fingertip).
Contraction tremor occurs or is aggravated when the muscle is held in a contracted state (for example, clenching the fingers into a fist for a long time).
Body tremor often occurs with abuse of alcohol-containing drinks or chronic alcoholism and is called alcoholic. The described type of trembling is manifested by “shaking” of the spread fingers, often spreading to the head or torso of the individual. This symptom is more often observed in patients in the morning and goes away after the next consumption of alcohol-containing liquids. The same situation is observed in drug-dependent individuals with withdrawal syndrome.
When using drugs or taking certain medications incorrectly, irregular small-scale trembling is observed in the fingers or hands. To eliminate this symptom, you must stop taking the drug.
Postural tremor is characteristic mainly of people suffering from autonomic dysfunction, excessively anxious and suspicious individuals. This form of the disease can be a consequence of pathologies of the thyroid gland, taking a number of drugs and alcoholic beverages, and may also have hereditary roots. This form of tremor is caused by withdrawal symptoms, chemical poisoning.
Postural tremor is small-scale and more pronounced when the arms are extended and the fingers are spread out. It intensifies when trying to concentrate, when the individual tries to reduce trembling, and does not disappear when moving.
Intentional oscillation occurs due to damage to the brain stem or cerebellum. With this form of trembling, large-scale muscle contractions are noted, which are absent at rest, but occur during purposeful movements, especially when achieving a goal. The patient, standing in a standing position with his eyes closed, arms straight and outstretched, is unable to touch his nose.
This form of trembling can be caused by tumor processes in the body, trauma, Konovalov-Wilson disease, vascular diseases, multiple sclerosis.
Tremor of the hand muscles, caused by lesions of the cerebellum, pathologies of the structures of the subcortex and brain stem, is characterized by constantness.
The most dangerous type of involuntary muscle vibrations is asterixis. Its distinctive feature is its sweep, arrhythmia, and asymmetry of contractions. The shaking resembles the flapping of wings. This form is observed exclusively with voluntary muscle tension.
The described type of trembling is caused by a periodic paroxysmal decrease in the tone of the muscles responsible for maintaining a certain posture. That is why outwardly asterixis resembles a non-rhythmic, flapping trembling that appears when the hand is extended and the arm is straightened. A few seconds after straightening the arm, sharp tremors are observed, followed by an immediate return to its previous position. Similar twitching is detected during tonic tension of other muscles.
You can often observe bilateral asterixis, which appears against the background of a darkened consciousness. This is the main symptom of metabolic encephalopathy. Unilateral asterixis often occurs with a stroke.
Rhythmic myoclonus is characterized by widespread trembling of the entire body, which intensifies with muscle tension (during movement) and completely disappears with muscle relaxation. This form of tremors often accompanies the following ailments: various pathologies of the brain and vascular diseases, Wilson's disease, multiple sclerosis.
Parkinsonian tremor is a consequence of damage to the subcortical areas of the brain. Parkinson's disease is characterized by trembling at rest, which disappears or significantly decreases with the onset of activity.
Parkinsonian muscle tremor is often asymmetrical. This manifests itself in unequal intensity of shaking, for example, the left hand shakes more than the right. In this case, the oscillation decreases or completely disappears if the individual tries to perform a spontaneous action with this hand. With parkinsonism, movements are noticeably slower, but distinct.
Hereditary predisposition causes familial tremor, or as it is also called essential tremor. Most often it is observed in elderly individuals, less often in children. This type of trembling most often appears when trying to maintain a certain position. Essential tremor is characterized by fluctuations of small or medium amplitude with unchanged muscle tone. The twitching persists but is not aggravated by flexing the upper limbs without support. Tremors at rest are observed much less frequently than in Parkinson's disease.
Symptoms and signs of pathology
Having considered what tremor is, it is necessary to study the symptoms that may accompany it. In diabetes mellitus, when the concentration of sugar in the blood drops, not only the lower but also the upper limbs tremble, weakness and sweating appear. When eating sweets, the trembling goes away.
With alcoholism, the cerebellum is damaged, causing tremors, which intensifies when trying to tense the leg muscles. At rest, this phenomenon is not observed. The same symptoms are inherent in intoxication with mercury vapor.
With Parkinson's disease, the legs and arms shake at rest, but when a person performs any actions, the trembling is not so noticeable or stops altogether. The disease is also accompanied by hypokinesia, stiffness, and numbness. When walking, a person places his feet parallel to each other, he moves in small steps, while shuffling his feet, his torso is tilted forward.