Neurogenic dysfunctions occur regularly in patients. The number of sufferers, according to statistical estimates, is more than 30% of the people on the planet.
For the most part, these are relatively mild deviations from the norm, which are not even always noticeable, up to a certain point.
Numbness of the face is one of the possible neurological symptoms of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, processes in the brain, blood vessels of the neck and other structures.
The symptom is diverse and is present in a large number of pathological processes. The cause of the deviation can be identified through instrumental diagnostics.
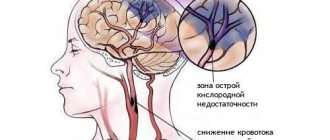
In some cases, sensory loss indicates an emergency condition, such as a stroke. Therefore, when such a symptom develops, especially if it is combined with paresis or paralysis, an ambulance must be called to exclude necrosis of cerebral structures.
Therapy depends on the case. Numbness itself does not require correction; it is necessary to influence the provoking factor. This is the basis.
Migraine
It is still considered a mysterious disease. Mainly found in women, the ratio of the number of patients m/f can be determined as 3:1 and even more.
It has a clear hereditary nature, if one of the parents had a disorder, with a probability of over 70% the disorder is transmitted to children and manifests itself at some point.
Why migraine develops is not known for certain. It is assumed that the disorder is caused by spasm of cerebral vessels against the background of autonomic dysfunction. That is, we are talking about a purely neurological disease, but whether this is true or not is a moot point.
The symptomatic complex is always approximately the same. In classic cases, the following signs of the condition are found:
- Severe headache. On the one side. Left or right. Baling, shooting, bursting. Accompanies the patient throughout the entire episode of the disorder. It radiates into the orbit and can move towards the crown and back of the head, initially located in the frontal region.
- Nausea, rarely vomiting.
- Disorientation in space. A person cannot move normally, the world is spinning and spinning before his eyes.
- Numbness of the entire head or part of the face as a result of a disorder of nerve conduction at the level of cerebral structures. This is a temporary phenomenon that does not indicate either the severity of the problem or the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
Cyanosis in a newborn
Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle is very common in infants. The weakest cyanosis, which manifests itself when the baby cries, is of respiratory origin (the child inhales little oxygen and exhales a lot). Turning blue in this area when straining or screaming is considered normal.

Cyanosis that occurs in a child during prolonged crying does not cause serious concern if it goes away after the baby calms down
Other causes of blue skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle, which is considered normal:
- The baby's superficial blood vessels dilate, becoming more visible, during breastfeeding.
- In case of hypothermia, which can occur during the period of changing clothes or swimming. But after the baby warms up, the color of his skin above the upper lip returns to its original color.
A serious threat to the life and health of the child is posed by any dysfunction of the cardiovascular and respiratory organs, which are manifested by the same symptom.
Attention. If, after the nasolabial triangle turns blue, its color does not return to normal after some time, and the fingers and tip of the tongue also turn blue, you must definitely seek help from a medical facility.
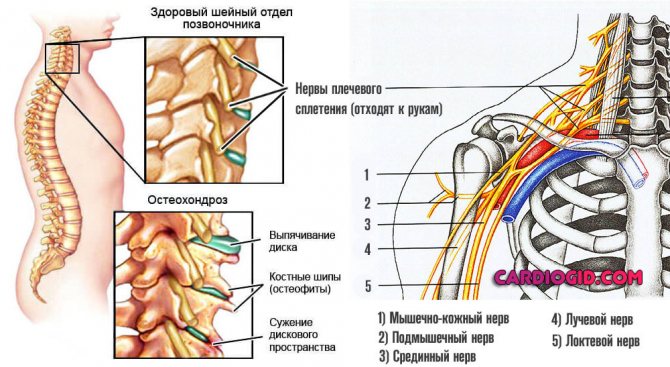
Osteochondrosis
It is an inflammatory, degenerative-dystrophic disorder of the spine, in particular, the cervical region suffers.
The pathology develops and progresses gradually and steadily. Detecting the moment when the disorder reaches a dangerous level is not easy.
Neurological symptoms, such as impaired facial sensitivity and others, also do not develop overnight, over many years.
Signs are specific:
- Pain in the neck area. Popping, burning or bursting. Fickle. Intensifies after physical activity.
- Dizziness. Accompanied by the inability to navigate in space. Develops sporadically.
- Cephalgia. Pain in the back of the head, crown.
- Problems with motor activity of the cervical spine. It is impossible to turn, motor abilities decrease gradually but steadily.
- Numbness of the face, lips, tongue and head with osteochondrosis is common, along with a decrease in sensitivity in the hands. This is a late sign. In the initial phase, it is present when the nerve endings are pinched, then, when the roots die, it remains permanently.
- Nausea. Vomiting is less common.
- Problems with cardiac activity. Like tachycardia. Relatively rare.
Disruption of the musculoskeletal system provokes characteristic manifestations due to compression of nerve endings at the local level.
It is necessary to differentiate from hernias of the cervical spine. As a rule, both processes occur in parallel.
Features of the manifestation of the disease in adults and children
According to pediatric practice, a slight discoloration in the nasolabial area of a newborn is often considered normal. A slight bluish tint may be caused by the baby crying a lot and continuing for a long time. This skin color appears due to the way the baby’s lungs work.
Due to loud crying, the normal flow of oxygen into the blood is disrupted, which contributes to the appearance of blueness. With age, this symptom disappears on its own. If, when the baby is 1 year old, blueness of the skin after crying can still be observed, it is advised to consult an experienced pediatrician on this issue.
Also, non-alarming cyanosis in a baby can occur due to such a natural feature as too light or thin skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle. Small veins are clearly visible through the thin layer of skin, and the fold above the lip appears slightly blue. As you grow older, this symptom disappears without a trace.
According to medical practice, very often cyanosis in a baby appears as a result of a protracted labor process. According to experienced pediatricians, this condition is not considered life-threatening for the baby; it goes away on its own after a few days.

Among the physiological reasons that can cause cyanosis in both an adult and a small child are:
- severe hypothermia of the body;
- staying at altitude for a long time;
- lack of oxygen entering the body.
Blueness of the skin caused by these reasons is usually harmless. After normalization of the functioning of the organs and systems of the body, it goes away by itself.
Hernias of the cervical spine
A dangerous complication of osteochondrosis. Less commonly it develops as a result of injury or sudden movement. For example, after a car accident, an unfortunate fall, a fracture, etc.
The essence of the disorder is the displacement of the intervertebral disc beyond its normal anatomical position. Then it breaks and completely loses its own structure and function.
This leads to abrasion and degeneration of adjacent vertebrae and even greater limitation of activity and severe discomfort.
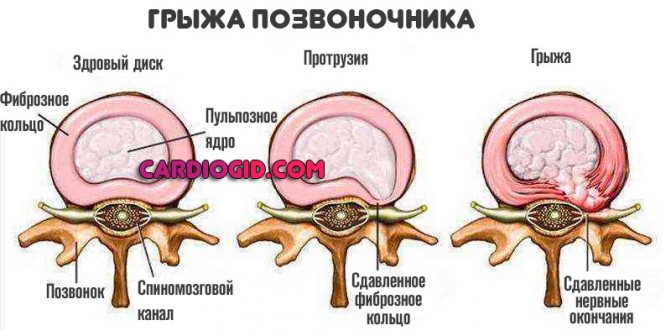
The clinical picture is typical. Disorders of the musculoskeletal system are accompanied by severe, sometimes unbearable pain in the neck (in an acute state they do not go away at all), problems with orientation in space.
The patient cannot hold his head up because the muscle corset is weak.
In almost 100% of cases, a clinical picture of vertebrobasilar insufficiency is detected; due to instability of the spinal column, compression of local arteries occurs.
The therapy is surgical, but doctors are delaying the moment as best they can. They stop attacks and prevent new ones.
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
A common disorder. Usually develops as a complication of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
The essence of the disease is a sharp disruption in the nutrition of cerebral structures due to compression of the arteries localized in the neck.
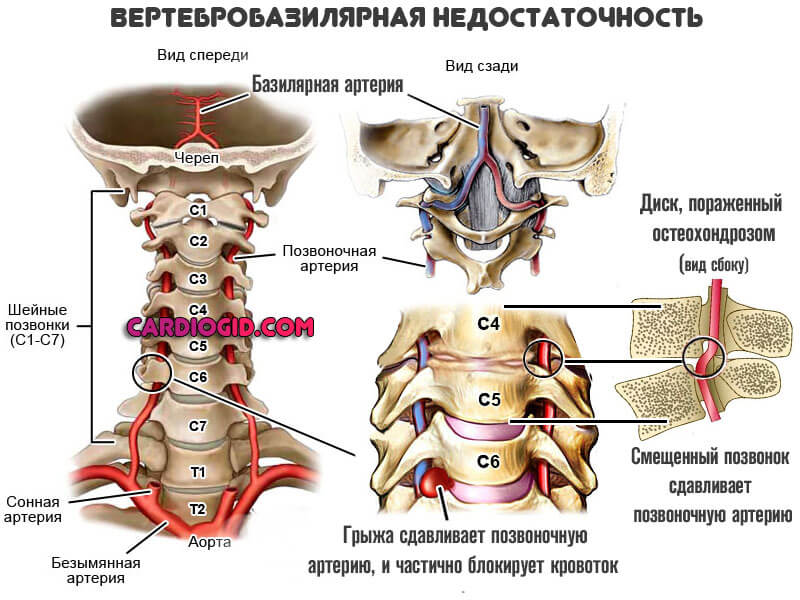
There are many variants of the clinical picture of the disease. Basically, the symptomatic complex comes down to a group of deviations:
- Headache. Expressed, strong. Migraine attacks are possible during the course of the disease.
- Dizziness and inability to navigate in space. The person is in a forced position. Lying on his side, he moves little.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Visual impairment. Loss of areas of visibility, sensation of bright flashes (simple hallucinations), temporary total blindness is possible. In late, advanced stages.
- Decreased hearing acuity.
- Inability to move smoothly. Unsteadiness of gait. This is all due to disruption of the extrapyramidal system.
- When the lobes of the brain on the left side are affected, the right side of the head (and the body in general) goes numb and vice versa.
Also other clinical signs. VBI is considered a significant factor in the development of stroke in the future. The cerebellum and occipital region of the brain are affected.
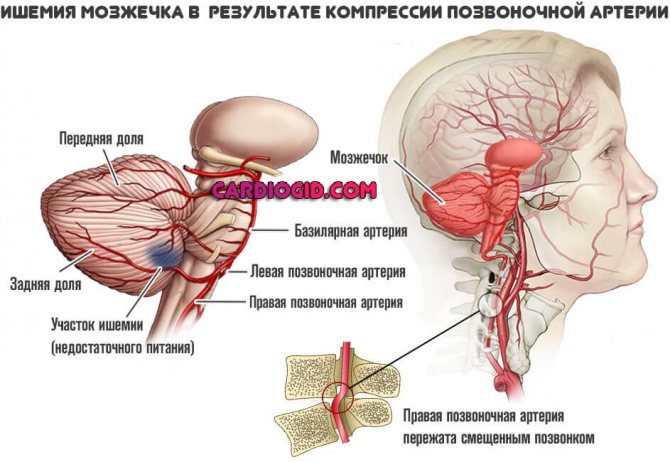
With timely treatment, it is possible to stop the progression of the disease and take control of the situation.
Types of disease
Variants of the algorithm for the development of lip cyanosis divide it into 3 pathological groups:
- The permanent type is of central origin. In addition to the cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, it is characterized by a sluggish sucking reflex. Pathology occurs as a result of abnormal development of any part of the brain, increased intracranial pressure or trauma during childbirth.
- Respiratory nature of the disease. Additional symptoms of this group:
- pale skin color;
- blueness in the eye area;
- When you inhale, the small intercostal muscles retract.
Cluster headaches
An extremely rare neurological condition. However, it is very difficult. Accompanied by unbearable, painful attacks of discomfort in the frontal region.
Unpleasant sensations radiate to the eyes. The clinical picture is complemented by pronounced numbness on the left side of the face or vice versa, depending on the exact localization of vascular spasm.
The etiology of the disease is unknown. It is believed to be a related condition to migraine, with some differences.
A typical symptom is a severe headache that cannot be relieved by any medications. The intensity of the discomfort is so great that suicide attempts are known among patients during an attack.
Treatment is not possible; the only thing doctors seek is to prevent relapses in the future. Reducing the risks of developing such.
Transient ischemic attack
A common phenomenon. It is mistakenly called a microstroke. In fact, we are talking about an acute but temporary disruption of brain nutrition. Develops as a precursor to an emergency condition.
The main patient population is people with a history of arterial hypertension, often elderly.
The clinical picture is identical to that of a typical stroke. The only difference is the duration of the violation and its outcome.
Transient ischemia does not lead to necrosis of nerve tissue; moreover, it regresses spontaneously, independently, even without the help of a specialist. If I may say so, this is a rehearsal for a stroke.
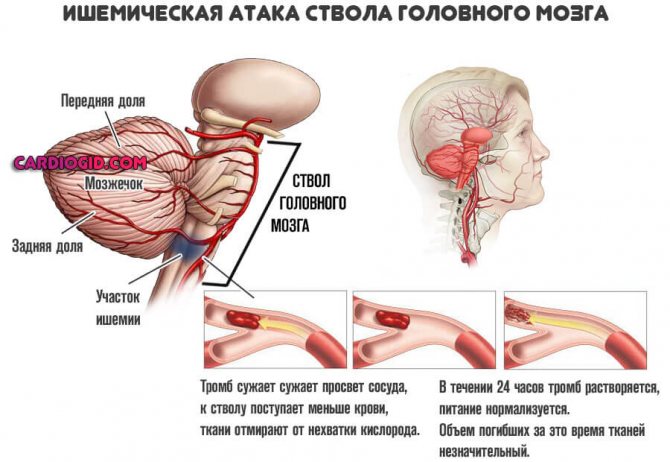
Among the manifestations:
- Severe headache in one area or another. Bursting, baling. Intense.
- Disorientation in space.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Discomfortable sensations on the skin: goosebumps, tingling. A typical patient complaint is that half of the face or arm is numb. This is an indication of a disruption in the conductivity of nerve endings, but not the death of them.
- Confusion.
- Dysfunctions of the sense organs.
If your head goes numb, it could be a transient ischemic attack or a chronic brain disorder.
Differential diagnosis is mandatory. It is aimed at distinguishing between different conditions.
Stroke
Acute cerebrovascular accident. According to statistics, it is somewhat less common than a heart attack and is the second most important factor in deaths around the world.
The essence of the disorder is necrosis of cerebral structures. Nerve fibers die and irreversible changes occur in the brain.
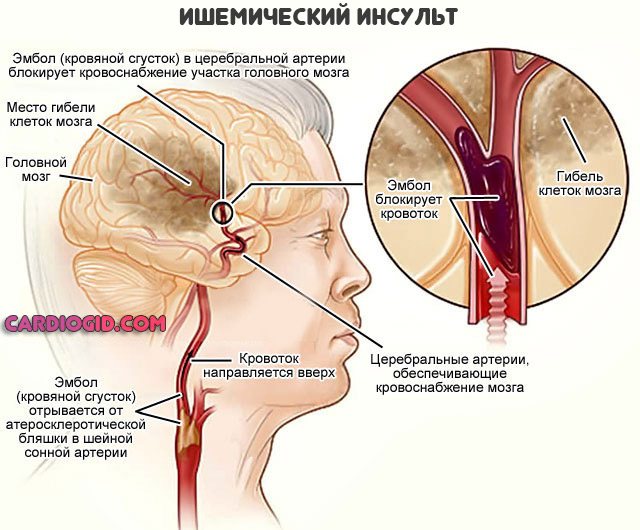
The condition is extremely unfavorable in terms of its course; without medical care it leads to death.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the brain
Among these, two can be named: meningitis and encephalitis. Both develop against the background of a previous disease (the focus does not matter), or after bites from vectors (for example, ticks).
They occur acutely and are accompanied by pronounced deficit neurological phenomena.
It is not always possible to determine the nature of the disorder even through MRI.
The only reliable diagnostic criterion is the presence of an infectious agent, possibly blood, in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Doctors obtain a sample through puncture. However, this is a dangerous procedure; it is used relatively rarely and only when necessary.
The clinical picture resembles that of a stroke, but the symptomatic complex develops less rapidly.
If help is not given in a timely manner, the disorders persist for a long period and cannot be corrected. Diseases can result in profound disability.
What else causes cyanosis to develop?
Cyanosis can develop on any part of the body, but is most often observed in the area of the nasolabial triangle. Some patients suffer from this disease only during the cold season. It happens that the appearance of symptoms begins in a person who has been at high altitude for a long time. Lack of oxygen in the air affects the body in exactly this way.
The nasolabial triangle is more noticeable in young children. In adults, the symptom appears in cases of severe condition. In some patients it manifests itself as a result of poisoning, diphtheria, asthma, tuberculosis, thrombophlebitis.
Multiple sclerosis
Common neurological disease. It is of autoimmune and metabolic origin.
Accompanied by destruction of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers. For this reason, the speed of impulse transmission drops, and then the possibility of this is lost completely. The disease affects the brain, less often the spinal cord.
Such degeneration progresses constantly, but does not lead to critical disorders at one point. This is a rather lengthy process. It takes more than one year before disability, often much longer.
Timely treatment can reduce symptoms and significantly slow down the pathological process.
The clinical picture is varied and depends on the location of the area of nerve fiber destruction. Typically, motor dysfunctions, a feeling of numbness of the face and limbs, decreased visual acuity, and cognitive disorders are detected.
Intelligence, however, suffers only slightly, at least in the early stages. Without treatment, there is a high chance of rapid disability.
Causes of the disease
With a change in blood composition, namely with an increase in the amount of deoxyhemoglobin (hemoglobin deprived of oxygen), skin color changes. Blood, almost deprived of oxygen, becomes darker and translucent through the skin. The normal hemoglobin concentration is 3 g/l. If it becomes more than 30 or 50 g/l, this disease occurs.
Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle in a child indicates that the baby may suffer from neuralgia, heart or lung disease. In an adult, such a triangle appears as a result of diseases of the respiratory system or due to cardiovascular failure.

The severity of cyanosis depends on the density of the subcutaneous capillary network and the thickness of the skin, so it is much more noticeable in children
Note. The bluish color of the skin around the mouth and nose in a small child does not always indicate the presence of serious causes, since children's skin is very thin and the venous plexuses are very noticeable.
Inflammation of nerve fibers
Against the background of hypothermia or other infectious diseases. It occurs in one form or another in almost 40% of people; at least once in their life, every second person has encountered a similar problem.
It develops spontaneously and is accompanied by unbearable pain, especially if the trigeminal nerve is affected.
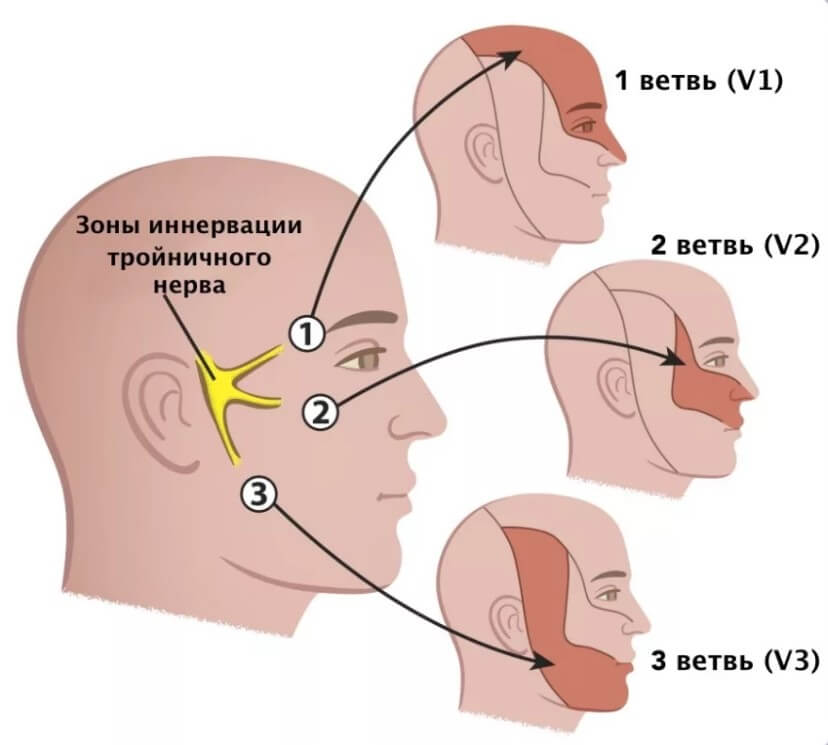
The use of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs gives minimal effect. Medical attention and combinations of drugs to relieve discomfort are required.
Numbness and severe pain are the main symptoms. As an addition - an increase in body temperature.
How to get rid of facial numbness
If numbness of a part of the face occurs due to prolonged exposure of the body to an uncomfortable position, treatment is not required. After changing your position, this condition goes away on its own; to speed up the process, you can rub the skin in this area with light movements.
Urgent medical attention is required if, in addition to the face, limbs become numb so that a person cannot move his fingers, and also if this condition is accompanied by weakness or dizziness. Among the alarming symptoms, in addition, involuntary emptying of the bladder or bowels, loss of the ability to speak and move. If numbness is the result of a back, neck, or head injury, immediate medical attention is needed.
Sometimes this condition appears after dental procedures, and if it does not disappear on its own after some time, you should consult a dentist. If facial numbness is caused by vitamin deficiency, treatment is prescribed aimed at replenishing the vitamin deficiency. In this case, the drug regimen must be determined by the doctor.
In situations where the feeling of numbness is caused by severe multiple sclerosis, the patient is prescribed a course of corticosteroids and B vitamins. Sometimes this manifestation is associated with certain external conditions, such as air temperature. In this case, exposure to unfavorable factors should be avoided if possible. Massage, acupuncture, yoga or meditation may have some effect.
For facial neuralgia, unpleasant symptoms are relieved with the help of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and treatment is prescribed individually. Typically, treatment for neuralgia of the facial nerves is carried out using prednisolone, and a course of special gymnastics for the face is also prescribed. In some cases, you can relieve pain and numbness of the face by wiping the skin on the affected area with an alcohol solution.
Prevention of this condition lies in taking good care of your health: it is necessary to avoid drafts and hypothermia, promptly treat chronic diseases, and regularly take vitamin and mineral complexes.
In some cases, facial numbness goes away on its own. For example, when a person is in an uncomfortable position. Changing the position helps blood flow to the problem area and returns normal sensitivity. You can speed up the process by rubbing the skin. If numbness is accompanied by stiffness of movement, dizziness, pain, and weakness, emergency assistance may be required.
Alarming signs also include involuntary bowel or bladder emptying, loss of the ability to move or speak. If numbness occurs as a result of a head or back injury, help should be provided as quickly as possible. If paresthesia is a sign of a disease, treatment is aimed at eliminating the pathology.
For example, with multiple sclerosis, the patient is prescribed a course of B-vitamins and corticosteroids. For trigeminal neuralgia, therapy is aimed at reducing pain. For this purpose, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are used. As a rule, for this pathology the drug Prednisolone is prescribed.
How to contact whom and what needs to be examined
Diagnostics is carried out by neurologists. In some cases, the help of several doctors is required, depending on the situation.
The research is almost always the same:
- Oral questioning of a person to clarify symptoms.
- Anamnesis collection. To better understand the likely origin of the disease.
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate.
- Assessment of basic reflexes.
- X-ray of the cervical spine.
- Dopplerography of blood vessels to exclude VBI and impaired cerebral trophism, duplex scanning. Shows the quality and speed of blood flow.
- MRI of the same area. For the diagnosis of hernias, advanced osteochondrosis.
- Tomography of cerebral structures. Perhaps the reason is multiple sclerosis or tumors. In both cases, contrast enhancement with gadolinium is required. This will increase the information content several times.
- General blood test, biochemical.
If necessary, a lumbar puncture is performed to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid. Basically this is enough.
As needed, doctors prescribe additional diagnostic measures.
Actions to take if cyanosis appears in a child
If cyanosis appears, it is recommended to monitor the baby’s further behavior. If the symptom appears not only after hypothermia, then it is necessary to show the child to the pediatrician to prescribe additional studies.
Procedures that are usually prescribed by a doctor:
- Ultrasound of the heart muscle;
- X-ray of the chest area;
- electrocardiogram.
For a complete examination of the baby, you need to visit a neurologist. It is very important to maintain comfortable conditions in the apartment, because this is a mandatory requirement for proper development. Temperature and humidity must comply with the standards. It is necessary to regularly walk with him in the fresh air.

Already from the second week of a child’s life, you can start 15-minute walks in the fresh air, gradually increasing their duration
Daily massage stimulates the nervous system and normalizes the respiratory system.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the disease. Conservative methods are mainly practiced. Medicines from several pharmaceutical groups are used.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs of non-steroidal and hormonal origin. The first ones are Nimesulide, Diclofenac and others. The second is Prednisolone and more powerful analogues. They pursue identical goals and are used according to indications.
- Chondroprotectors. To protect the vertebrae. Structum as an option.
- Cerebrovascular, nootropics. Normalizes brain nutrition. Actovegin, Piracetam, Glycine.
More can be said knowing the specific situation.
Surgery is a last resort. It is practiced for tumors, advanced hernias and in some other cases. When there is no other way out.
What needs to be treated is not numbness, this is impossible and makes no sense, but the underlying pathological process.