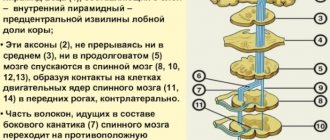
Causes
Hyperkinetic syndrome is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of pathologies, therefore the factors predisposing to its occurrence are varied. The main reasons are considered:
- Deviations in the development of the central nervous system, laid down during the period of intrauterine formation of the fetus, gene and chromosomal abnormalities.
- Hereditary diseases characterized by the slow destruction of nerve cells. Parents with neurodegenerative pathologies are highly likely to give birth to children with anomalies, one of the signs of which is hyperkinesis. Diseases of this kind are diagnosed at an early age. This group includes metabolic disorders such as iron deposition in the brain (in the basal ganglia), copper metabolism disorders, Huntington's and Minor's diseases.
- Traumatic brain injuries resulting in damage to the central nervous system. In infants, hyperkinesis may occur as a result of passage through the birth canal if the mother’s labor was difficult. In older children, muscle contractions are caused directly by injury, leading to the destruction of cells in the central nervous system.
- Intoxication with drugs: antipsychotics, anticonvulsants and other drugs that have the ability to accumulate in nervous tissue, bypassing the barrier between capillary blood and neurons of the central nervous system. Stopping taking such medications leads to the disappearance of involuntary muscle contractions.
- Endotoxicosis due to hyperthyroidism, high concentrations of bilirubin in newborns, with insufficiency of kidney and liver function.
- Abnormalities in the movement of blood through the vessels supplying the brain. Vasoconstriction leads to oxygen starvation and cell death in the centers responsible for coordination of movements and muscle tone, which leads to the appearance of hyperkinetic syndrome.
- Inflammatory diseases of an infectious nature. Meningitis and encephalitis provoke cell death in the parts of the brain that coordinate movements. Viruses lead to the destruction of myelin fibers, which provokes chaotic unintentional muscle contractions and a number of other symptoms.
- Emotional and mental overload. The child’s central nervous system, which has not yet formed, cannot withstand excessive stress, which leads to mental disorder, which is also expressed in sudden involuntary movements.
In addition to common causes, the following factors are also identified: the development of tumor formations in the brain, systemic autoimmune diseases (rheumatism, lupus and others). Hyperkinesis in cerebral palsy is included in a separate group.
Features of HS in childhood
Hyperkinetic syndrome that develops in children causes a lot of difficulties for parents and teachers - such children are very often aggressive.
The prognosis for the development of this pathology is disappointing, and most patients experience serious problems with social adaptation among their peers, which persist in the future. You can distinguish a child with hyperkinetic syndrome by the following characteristics:
- Children with HS experience an increased level of activity , which is very pronounced. Such children are unable to sit still and their behavior is particularly fussy.
- Hyperkinetic syndrome can be differentiated from the state of anxiety and emotional arousal inherent in all children by degree of severity and connection with severe disorders . The disease begins to manifest itself at the age of 3-4 years, but it is often diagnosed when the child goes to school.
- Such a child is characterized by a small attention span , the inability to concentrate on any activity for a long time, and a high level of distractibility when any stimulus causes a response.
- Hyperkinetic syndrome in childhood causes a defect in attention , which persists as the child grows older.
- Hyperactivity may disappear, and even, on the contrary, during puberty there may be a decrease in it, as well as a lack of motivation. This pathology is also characterized by developmental delay .
- usually not easy for such children to study , due to the fact that their intellectual abilities are at an average level or equate to mental underdevelopment. Sometimes hyperactivity can be an indicator of temperamental properties or manifest itself as a result of brain damage.
Treatment of HS in childhood will consist of a traditional approach with the prescription of medications, the formation of a system of behavioral control for parents, as well as the provision of professional correctional assistance.
Combining all these therapeutic methods is very effective.
Classification and main symptoms
The classification of the disease is based on various signs, and one of them is how the movements of a child diagnosed with hyperkinetic disorder are modified. In accordance with this division, there are the following types:
- Rapid, or hypotonic, hyperkinesis. Caused by a decrease in long-term persistent tension in muscle fibers. This group includes tic hyperkinesis, chorea, myoclonus, and tremor.
- Slow or dystonic. Caused by instability of tone: some muscles experience excessive tension, while others are hypotonic. This type of involuntary contractions is characterized by unnatural body positions in space and includes torsion and cervical dystonia, contractions of the orbicularis oculi muscle, and athetosis.
In accordance with the frequency, duration, intensity of abnormal contractions and their localization, the following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Tremor. It manifests itself in the form of trembling of the limbs and head, and is a symptom of pathologies such as parkinsonism, Huntington's disease.
- Extrapyramidal form - disorders of this group are caused by damage to the system of the same name and are represented by a variety of types: rhythmic, tonic, phasic. Clinically manifested in grimaces, abnormal movements of the eyeballs, involuntary utterance of sounds and words, twitching of the limbs.
- Athetosis. Slow tonic convulsions localized in the muscles of the trunk, limbs, and face. Lack of treatment leads to joint contracture.
- Oral type. This type includes hyperkinesis of the tongue in children, contractions of the muscles of the soft palate and larynx, which occur due to infectious diseases.
- Tiki. In newborns they often go away on their own. Treatment of tic hyperkinesis in children is delayed if there is a violation of cerebral circulation.
- Choreic form. Diagnosed very rarely in children, it presents with erratic movements of the limbs, and the facial muscles may also be involved.
- Dystonia. Affects the muscles of the upper and lower extremities; this type of hyperkinesis in children under one year of age is the most common.
- Chill-like type. It is expressed in the form of trembling, the appearance of goosebumps on the skin, accompanied by a rise in body temperature.
- Hysterical form. It is characterized by a wide range of movements in the absence of muscle hypertonicity, manifests itself in a state of nervous excitement and goes away when the child calms down. Diagnosed in school-age children.
The main symptoms of hyperkinetic syndrome in children, which should alert parents:
- trembling;
- unintentional twitching of the limbs, head, torso;
- trembling of facial muscles, eyes;
- cardiopalmus;
- absence of symptoms during sleep.
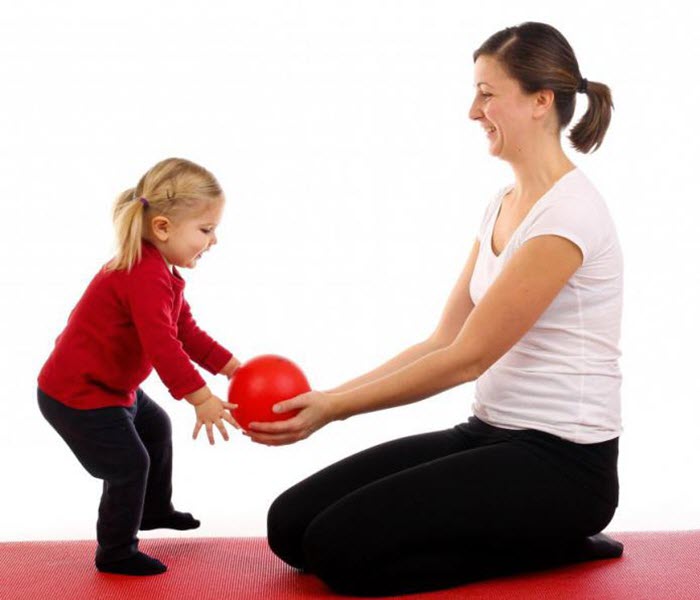

What triggers the development of cerebral palsy?
The factors causing the disease are different. The most common of them:
- Brain injury before, during or immediately after childbirth. Most often, trauma occurs during childbirth when the mother’s body is unable to properly develop labor (quick or too long labor, cesarean section). If a child is born with a bluish marbled body, cyanotic asphyxial lips, and often entwined with an umbilical cord, this indicates brain hypoxia.
- Previous infectious diseases (rubella, jaundice), vaccinations during illness cause postpartum damage to areas of the brain.
- Rhesus conflict of parents. Conflict between mother and fetus blood groups.
- Early placental rejection.
The neural tube and brain tracts of the fetus are formed in the first weeks of pregnancy, and by the end of the first trimester motor reflexes appear. About 50 factors influence the formation of a child’s body and can lead to diffuse brain damage. Therefore, a woman should take care of the health of her child long before conception: undergo an examination, give up bad habits and the use of alcohol, narcotic drugs, and unnecessary use of medications, especially hormonal, sedative, and psychotropic ones.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to constantly be monitored by an obstetrician-gynecologist and come for consultations in a timely manner, especially if there are chronic diseases of the endocrine and cardiovascular systems, or toxicosis.
Take preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of inflammatory processes of viral and bacterial infections. Particular attention should be paid to the diet. The mental and emotional state during pregnancy is also important.
Necessary research
Diagnostics takes place in several stages:
- Examination and interview of the patient and his relatives.
- Examination of the brain using ultrasound.
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
- Electroencephalography of the brain.
- Electromyography.
- Blood tests: general, biochemical.
Based on the research, the doctor draws a conclusion about the nature of the hyperkinetic disorder and the primary disease, which allows him to make a decision regarding the treatment of the syndrome.
Recommended treatment
Correction of hyperkinetic disorders is carried out in accordance with the diagnosis. There is no specific therapy that would be the same for all cases of hyperkinesis in children. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the syndrome, which entails regression of symptoms, but often this is only a temporary measure. In addition to medication, some physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, and teaching parents the basics of physical therapy for children are recommended.
Drugs
To eliminate pathology in children, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Anticonvulsants. Shows effectiveness in the treatment of myoclonus and tic disorders.
- Anticholinergic drugs. Prescribed for hypotonic forms of the disease.
- Muscle relaxants. Have a relaxing effect on muscles.
- Adrenergic blockers. They alleviate the patient’s condition with such a form of pathology as chorea.
- Neuroleptics. They block dopamine receptors on striatal neurons and are used for any form of hyperkinetic syndrome.
- DOPA drugs that relieve tremor are prescribed in early childhood.
Children with diagnosed syndrome are advised to take vitamin-mineral complexes.
Certain diseases require specific medical intervention: surgical for spastic torticollis and early (juvenile) parkinsonism, rheumatological for chorea of a rheumatological nature.
Unconventional methods
Therapy with traditional medicine should be carried out in parallel with traditional treatment and under the supervision of a physician. To relieve muscle tension and stop attacks, use:
- A decoction of plantain, rue herb, anise seeds.
- Compresses from geranium leaves.
- Mumiyo.
Hardening and playing outside are recommended as general strengthening therapy for children.
Behavioral therapy
Behavioral therapy should be used to treat hyperkinetic syndrome. It is aimed at reducing the impact of stress, reducing anxiety, developing responsibilities, and adapting to the social environment.
This treatment involves working with a psychologist or psychotherapist. A specialist will be able to help the patient increase self-esteem and teach him to adapt to society.
With behavioral therapy, it is important that an adult learns to relax, achieve goals, and draw up a clear plan of action. The support of family and friends is mandatory.
Behavior therapy is individually selected for each person and a course of medications is prescribed.
A person begins to rethink his life, behavior, relationships with people and copes well with the manifestations of this disease.
Source: FeedMed.ru
Measures to prevent pathology
There is no specific prevention of hyperkinetic syndrome in children. If a child is at risk of developing a disease (hereditary pathologies), it is recommended:
- A balanced diet enriched with vitamins and minerals, potassium, magnesium, glycine.
- Moderate physical activity - therapeutic exercises, walking at an average pace.
- Favorable psycho-emotional environment.
- Lack of mental and physical overload.
Prognosis for recovery
The prognosis for the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy is largely determined by the severity of the pathology, the presence of concomitant health problems, and adequate and timely treatment. The disease cannot be completely overcome. However, with a competent approach and rehabilitation, developmental defects can be compensated as much as possible.
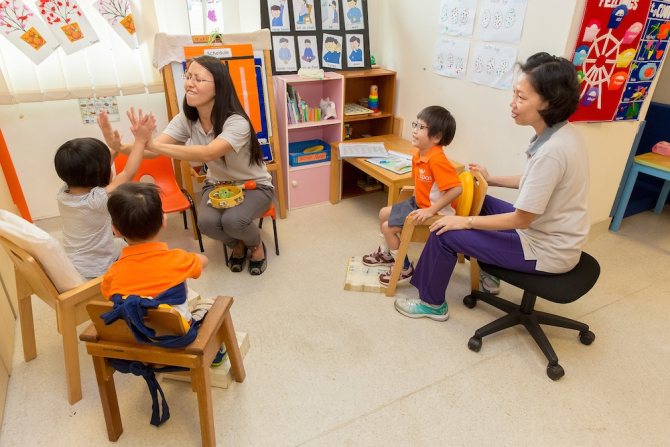

In the absence of seizures, the disease practically does not progress. Children can move independently from the age of 5-6 years with a mild or moderate severity of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy. Their mental development suffers less than physical development. Therefore, in most cases, they master the school curriculum and receive secondary or higher education.
Forecast
In cases where the disease is genetically determined or caused by pathologies of the central nervous system, the prognosis is unfavorable. Often the syndrome develops into a chronic disease. The consequence of the lack of timely treatment is disability.
If the anomaly is caused by overload (psycho-emotional or physical) against the background of age-related immaturity of the nervous system or some other factors, with timely treatment it is possible to eliminate the symptoms.
( 4 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)