Results
The problem of neurological syndromes worries many people, and, unfortunately, doctors are not always able to completely neutralize the impact of the disease. For this reason, it makes sense to periodically do preventive diagnostics of the state of the brain and nervous system in order to identify possible problems at the stage of their inception.
As mentioned above, many children with primary speech underdevelopment showed focal or diffuse neurological microsymptoms. In general, among the 670 children with HP we examined, this occurred in 89% of cases. Similar data were obtained by I.F. Markovskaya (1993) in a group of children with mental retardation (72% had focal neurological symptoms). Similar data are provided by Z. Tresohlava (1986), who studied children with mild brain dysfunction. In most cases, neurological symptoms did not develop into any specific syndromes and were scattered in nature. The most common symptoms were disorders of cranial innervation - in 81% of children. Among them, the first place in frequency is asymmetry of the nasolabial folds (36%), followed by restlessness of the tongue (19%) and SYMPTOMS of facial nerve insufficiency (12%). Other symptoms were much less common (Table 5). As can be seen from the table, manifestations of hemisyndrome are rare among the children we examined.
Finger apraxia syndrome
A possible explanation for the identified differences in the performance of these two groups of tasks may be that the first two require a high degree of conscious kinesthetic control of movements and operational learning when performing. The last two use motor skills that have already been developed and are automated to one degree or another. In other words, our subjects suffered more from the coordination of voluntary actions requiring a high degree of kinesthetic control.
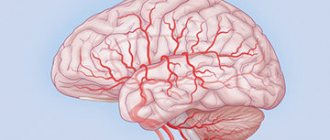
Focal neurological symptoms, or focal neurological deficits, are a set of problems characteristic of local damage to certain structures of the central and peripheral nervous system. This affects a specific area of the body, for example, the right or left arm, or a certain part of the face.
These symptoms include disturbances in vision, hearing and speech, and the appearance of abnormal sensations, for example, numbness in some area of the skin. A focal neurological deficit can cause changes in movement without the person being able to control them - tremors, loss or increase in muscle tone, even paralysis. The location of the problem indicates which areas of the nervous system are affected, since each part of the brain or spinal cord controls a specific function of the body.
In contrast to focal neurological deficits, general cerebral symptoms occur with diffuse damage that extends over a wider area. In this case, the problem concerns not a specific area, but the nervous system as a whole. The symptoms of these disorders also differ; they can include both emotional disturbances and general loss of consciousness.
Residual encephalopathy with diffuse neurological symptoms
The concept of encephalopathy implies the presence of abnormalities in the functioning of the brain, which are a consequence of exposure to damaging factors of various natures. The residual form of encephalopathy is residual effects that can appear after a long period of time after direct damage to the nervous tissue.
Reasons for development
Residual encephalopathy can be caused by all factors that damage brain cells.
- Various traumatic injuries: concussion, brain contusion.
- Complicated course of pregnancy and childbirth in the mother.
- Exposure to toxic substances: high doses of alcohol, salts of heavy metals, toxic compounds, certain medications.
- Taking narcotic and psychotropic drugs.
- Liver and kidney diseases accompanied by high levels of bilirubin or urea.
- Previous cerebrovascular accidents (stroke).
- Atherosclerotic lesion of cerebral vessels.
- Arterial hypertension with uncontrolled rises in pressure.
- Diabetes.
- Attacks of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Inflammatory diseases of the nervous tissue of the brain.
- Long-term exposure to ionizing radiation on the body.
Under the influence of negative factors, damage or death of some brain cells occurs. Over a long period, the brain can compensate for this loss, but after some time the compensatory capabilities weaken, and symptoms characteristic of encephalopathy appear.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this pathology is sometimes difficult due to the fact that the appearance of the first clinical manifestations may occur after a long period of time after the action of the damaging factor. Often the disease has signs of other diseases, which causes incorrect diagnosis.
A major role in identifying residual encephalopathy is played by a detailed interview with the patient, during which the history of possible causes that led to damage to brain cells is clarified.
In order to identify the lesion, all patients are required to undergo the following:
- EEG (electroencephalography)
- CT (computed tomography)
- NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance)
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
From laboratory tests, a biochemical blood test, clinical blood and urine tests, and cerebrospinal fluid examination play an important role in diagnosis.
Treatment
For each patient, an individual set of treatment measures is selected, which will depend on the causes that caused the development of encephalopathy, symptoms and the severity of their manifestation.
Drug therapy includes:
- Drugs that improve blood flow in the brain.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: hormonal and non-steroidal.
- Vitamin complexes.
- Anticonvulsant medications.
Of great importance in successful treatment is the appointment of sessions of manual therapy, reflexology, acupuncture, physiotherapeutic procedures, and therapeutic exercises. In addition, all patients are advised to adhere to a daily routine, regular walks in the fresh air, and give up bad habits.
Disease prognosis
With early detection and adequate treatment, complete recovery and disappearance of clinical symptoms are possible. Or it is possible to stabilize the process without progression of the manifestations of the disease. If the pathology is detected at a late stage, the prognosis is unfavorable, since complete restoration of brain function is impossible in this case.
Prevention
Preventing the development of residual encephalopathy is associated with the prevention of all causes that can cause a negative effect on the brain, as well as their timely and complete treatment.
How we save on supplements and vitamins . probiotics, vitamins intended for neurological diseases, etc. and we order on iHerb (follow the link for a $5 discount). Delivery to Moscow is only 1-2 weeks. Many things are several times cheaper than buying them in a Russian store, and some goods, in principle, cannot be found in Russia.
Source: //headnothurt.ru/jencefalopatija/rezidualnaja-jencefalopatija-s-rassejannoj.html
Examples
The patient may have language difficulties, such as problems understanding or producing speech (aphasia), and an inability to name objects (anomia) or produce sounds (dysarthria). Sometimes there is a loss of coordination and difficulty performing complex movements.
Damages to other structures of the nervous system lead to changes in vision - double vision (diplopia), a decrease in the field of vision, or sudden blindness. In some cases, there is a strong gag reflex, frequent choking and difficulty swallowing. When the cortex of the frontal lobe of the brain is damaged, a change in personality occurs, which can manifest itself as causeless rage or inappropriate jocularity, apathy, and a tendency to engage in antisocial behavior.
Other examples of localized brain damage include Bernard-Horner syndrome, which is caused by disorders of the sympathetic nervous system.
It is found in humans, dogs, cats and horses. There is unilateral drooping of the eyelids, cessation of sweating on a certain side of the face, and a sunken eyeball.
Anything that harms or destroys the nervous system can lead to focal damage. Among the most common causes of this symptomatology are:
- diseases of one nerve or a group of them;
- various infections;
- brain tumors;
- blood vessel abnormalities, such as vascular malformation;
- strokes;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- degenerative nerve diseases;
- cerebral palsy;
Depending on the mechanism of action, the nature of the lesion and its location, various motor and sensory disorders occur.
If symptoms of focal neurological deficits appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. To make an accurate diagnosis, in addition to the patient’s medical history, you will need to provide the following information:
- where loss of function or abnormal sensations are located;
- when the problem began and how quickly it changed;
- whether there were increases or decreases in symptoms;
- what kind of violations are observed;
- other symptoms should be indicated, even those not directly related to the nervous system;
If a stroke occurs, it is very important to get the patient to the hospital as soon as possible. Intense and sudden movements should be avoided. Before the ambulance arrives, the patient should not be allowed to eat or drink, since paralysis of the swallowing organs can cause suffocation.
It is recommended to lay the person so that his head and neck form one line, the angle of which should be about 30° to the horizontal.
If focal neurological disorders are detected, a diagnostic examination of the nervous system is necessary. Tests and tests should identify the affected areas, with the type of test depending on the symptoms observed. As a rule, the following research methods are used:
If there is a suspicion of a tumor lesion, the patient is sent to the oncology center at the place of residence, where a set of examinations is carried out to confirm and refute the diagnosis.