What is a nervous eye tic?
Involuntary contraction of small muscles can be observed in almost any part of the human body, but most often they bother the area around the eyes.
This is associated with anatomical features near the orbital region:
- A large number of nerve endings and muscles on the skin of the face;
- The weakest muscles are in the near orbital zone;
- A person's face is directly related to the expression of basic emotions.
Both adults and children suffer from nervous tics. If this disease is permanent and interferes with a normal lifestyle, then you need to consult a doctor to find out the causes and ways to eliminate the problem.
A nervous tic, to some extent, can be a symptom of VSD and osteochondrosis, since nearby nerve endings are involved in this process. It happens that it can provoke insomnia in the early stages of pregnancy. More details...
A nervous tic is an involuntary spasm of muscles in which they make movements of an irregular, but stereotypical nature. Such spasmodic movements often occur in stressful situations and can intensify. As a rule, in children there are several types of this condition, differing in severity, as well as in the need for therapy.
Nervous tics and obsessive movement neurosis in a child: causes of occurrence, what parents should do
The choice of treatment method is made only after the cause of the development of this disease has been determined. For example, if the cause is problems in the family, then the child should attend individual or group sessions with a psychologist.
If the tic does not go away, the doctor recommends drug treatment:
- antidepressants;
- nootropics;
- neuroleptics;
- vitamins.
Drug treatment is carried out for 6 months, combining it with massage, taking medicinal baths and visiting the pool. If a child who is not yet 8-9 years old suffers from a nervous tic, then the treatment will be successful, but early tics, in the absence of adequate treatment, can persist until adolescence.
Causes
Depending on the initial state of the child’s nervous system, they are distinguished:
- primary nervous tics;
- secondary nervous tics.
Primary nervous tics
Primary (
idiopathic
) is usually called a nervous tic, which is the only manifestation
Most often, the first manifestations of nervous tics occur in children aged 7 to 12 years, that is, during the period of psychomotor development, when the child’s nervous system is most vulnerable to all kinds of psychological and emotional overload. The appearance of tics before the age of 5 years suggests that the tic is a consequence of some other disease.
Almost always, these rapid movements (they are also called hyperkinesis) do not indicate damage to the eye and lacrimal apparatus, but show that there are some disorders in the nervous system. Moreover, if a tic affects both eyes, then this process may proceed more favorably, and its treatment will be more successful than a tic of one eye.
The fact is that in this case the normal mechanism of the friendly work of the eyelids is not disconnected, but in the case of an asymmetrical lesion, the separation is obvious.
Eye and lacrimal gland
Much less often, hyperkinesis can be accompanied by lacrimation, conjunctivitis, and swelling of the eyelids. In this case, the baby should first be shown to a pediatric ophthalmologist or pediatrician.
Common causes of tic development include functional weakness of the nervous system and past illnesses, especially acute respiratory viral infections. If they were accompanied by conjunctivitis or blepharitis, then such a tic may be of a residual nature, and the baby should be shown to a pediatric neurologist only after the symptoms do not go away within a month, and should be observed by an ophthalmologist.
Blepharitis - inflammation of the edges of the eyelids
A nervous tic in a child 2 years of age or earlier may be associated with blockage of the nasolacrimal duct. Usually this condition becomes clear when the baby is up to 3-4 months old, but sometimes the blockage is recurrent in nature, and then there is a discharge of pus and the absence of tears in the eye that blinks.
One should not exclude such a factor as heredity. Remember if you had something similar as a child, or with your parents.
The pathology in which the child repeats the same gestures over and over again, twitches, grimaces, slams, stomps and performs other strange actions is reversible. The problem is that parents pay attention to twitching at the wrong time, believing that this is normal pampering and everything will go away on its own.
If the movements are accompanied by insomnia, excessive tearfulness, moodiness, anxiety, it is all the more worth paying special attention to the symptoms. Since the reason may lie in serious illnesses, such as:
- psychological trauma;
- heredity;
- features of brain structure;
- violence, harsh education, moral damage.
The causes of nervous tics in children are considered to be a hereditary predisposition and an imbalance of certain mediators in the central nervous system, for example, dopamine.
It is known that drugs from the group of antipsychotics reduce the severity of tics. These medications reduce dopamine activity in the brain. On the other hand, nervous system stimulants that increase dopamine activity also stimulate the development of tics.
As a rule, the triggering factor for the appearance of tics in children is a stressful situation associated with changes in life, in the very way of existence. For example, when moving, changing the usual composition of the family (when younger children appear in the family, parents divorce, the appearance of a stepmother or stepfather), when usual conditions change.
The reason for the appearance of a nervous tic can even be the first trip to kindergarten or the transition from kindergarten to school.
Moreover, if parents had similar manifestations in childhood (or persisted into adulthood), then the risk of developing a nervous tic in children increases significantly. Almost anything can be a trigger for the disease, including uncontrolled TV watching, as well as constant playing on the computer.
Doctors often forget that the cause of tics is many diseases of the eyes themselves, and not a hereditary or psychological factor. For example, dust gets into the baby's eye or an eyelash falls, which causes discomfort, pain and irritation of the mucous membrane, as well as a natural desire to rub the eye.
At the same time, the baby begins to blink intensely, and if the situation is repeated often, then in the process the usual spasmodic movement is formed.
Later, when the foreign body is removed, muscle contractions can continue for a long time. Some diseases also lead to this, so if any eye twitching occurs, it is important to first consult an ophthalmologist.
Causes of eye twitching
Both psychological and physiological factors can provoke muscle contractions, ranging from overwork and vitamin deficiency to diseases of the nervous system. Before consulting a doctor, parents should remember whether their child had an acute respiratory infection, conjunctivitis or other pathologies caused by bacterial infections the day before. Perhaps the reasons lie in the weakened immune defense of the body. There is a small chance that nervous tics can be inherited. For both teenagers and young children, the problem may be visual fatigue. After all, they spend a lot of free time at the computer and TV. Violent video games and horror films are especially dangerous.
Perhaps the eye twitches due to constant lack of sleep, excessive mental or physical stress, or under stress. A violation may appear if the child is planning a test in some subject, or a competition. The family environment is no less important. Quarrels and conflicts between parents often cause stress in children.
The eye may twitch due to a lack of vitamins. Low levels of calcium, magnesium and glycine in the body cause seizures, shuddering, and lack of impulses. Also, diseases of the central nervous system reduce muscle tone and are accompanied by a syndrome of neuro-reflex excitability.
Classification
To figure out whether a child’s nervous tic will go away on its own or will require treatment, you need to find out the reasons for its occurrence and determine the type. If we give a general definition, then tics are short-term, rhythmic, coordinated movements.
The main distinguishing feature of this disorder is that it can be partially controlled by children. They are usually able to suppress the tic for a short time, but this requires sufficient tension and subsequent release.
Symptoms often intensify when a child sits in one position for a long time (for example, in transport or watching TV). During games or some interesting, exciting activities, they, on the contrary, weaken or even disappear.
But this is a temporary effect, then the symptoms resume again.
Nervous tics in children can manifest themselves in completely different ways. Let's consider the most common forms of this condition:
- motor, during which the child blinks his eyes, raises his eyebrows, jerks his head, shrugs his shoulders, strains his facial muscles, bites his lips;
- vocal, in which the baby may cough, sniffle and make other sounds;
- combined – manifestation of several forms of tic at the same time.
You can find forms of tics in which the child constantly repeats the same action (rubs his hands, walks in a circle, slams the door several times in a row, and others). The condition can be either short-term or chronic - in the latter case, the tic lasts more than 1 year. At the first signs of changes in the baby’s behavior, treatment must begin!
Important! A nervous tic in a child can also be psychological, but in this case, headache, impaired coordination of movements, attention and perception are added to one of the above symptoms.
Symptoms and treatment of nervous tics in a child largely depend on the type of disease. The typology of the disease is based on several basic indicators.
First of all, the etiology is taken into account, i.e. root causes. They are usually psychogenic or somatic in nature.
Based on the duration of their course, nervous tics are classified as transient and chronic, and based on the degree of severity - complex (a complex of uncontrolled movements) and simple (elementary twitching). Hyperkinesis is also distinguished by the location of the muscles involved (limbs, facial expressions, vocal cords, eyes, etc.).
d.).
The most striking symptoms of the disease are:
- motor smacking;
- loud sniffing;
- tongue clicking;
- noisy and deep breathing;
- hissing and snorting;
- repeated utterance of curse words and individual words;
- coughing;
- frowning forehead;
- uncontrolled shoulder movements;
- antics;
- unnatural blinking;
- twitching of limbs or head;
- picking at folds in clothing.
treatment of symptoms, severe eye blinking
Publication date: 10/28/2017
If your baby begins to blink frequently, raise his eyebrows, or perform uncharacteristic actions such as walking in a circle, then most likely he is suffering from a nervous tic. All children from 1 year to 17-18 years old are susceptible to this condition. But most often a nervous tic in a child is observed in the period from 2 to 3 years and from 6 to 11 years.

Classification
Nervous tics in children can manifest themselves in completely different ways. Let's consider the most common forms of this condition:
- motor , during which the child blinks his eyes, raises his eyebrows, jerks his head, shrugs his shoulders, strains his facial muscles, bites his lips;
- vocal , in which the baby may cough, sniffle and make other sounds;
- combined – manifestation of several forms of tic at the same time.
You can find forms of tics in which the child constantly repeats the same action (rubs his hands, walks in a circle, slams the door several times in a row, and others). The condition can be either short-term or chronic - in the latter case, the tic lasts more than 1 year. At the first signs of changes in the baby’s behavior, treatment must begin!
Important! A nervous tic in a child can also be psychological, but in this case, headache, impaired coordination of movements, attention and perception are added to one of the above symptoms.

Reasons for appearance
The cause of this disorder is most often psychological or physiological problems, as well as poor lifestyle and frequent stressful situations. In addition, the source of nervous tics can be:
- Helminths.
- Fright.
- Lack of vitamins or minerals in the body, in particular deficiency of calcium, potassium, magnesium.
- Hours of watching cartoons, playing games on a PC or tablet.
- Poor nutrition and lack of daily routine.
- Lack of sleep or drinking tonic drinks.
- Conflicts with parents or peers.
- Attention deficit or excess (strict parents, many prohibitions, too strict boundaries).
- Hereditary predisposition.
Important! Nervous tics in a child may be secondary. They occur against the background of previous or chronic diseases (herpes, encephalitis, all types of traumatic brain injuries, nervous disorders).
Symptoms and statistics
This disorder is accompanied by uncharacteristic symptoms that depend on the type of nervous tic:
- headache;
- the child’s eyes hurt, he rubs them;
- baby bites his nails;
- the baby constantly twirls a toy in his hands or fiddles with ribbons on his clothes;
- the child constantly makes uncharacteristic sounds;
- the baby has become inattentive and complains of weakness;
- the child is irritable and withdrawn.

If the child is calm or busy playing, then the symptoms are invisible, but any stressful situation leads to their manifestation. It has been proven that boys suffer from this condition more often than girls, but before the age of 18, more than 80% of children experience various forms of nervous tics.
How to cure a child: which doctor should I contact?
Do not make a diagnosis yourself - visit a neurologist, psychologist or local therapist. You can get rid of this nervous disease in just a few weeks! You can be treated with ordinary herbal tea, which perfectly calms the nervous system:
- chamomile drink;
- pharmacy preparations, in which valerian root predominates;
- infusion of anise seeds.
It is also useful to give your baby regular tea and milk with honey, but the amount of chocolate, cocoa and other caffeinated foods and drinks should be reduced. It is also better to exclude all sweets, spicy and fatty foods from the baby’s diet, replacing them with cereals, fruits, vegetables and dairy products.

Advice! If your baby suffers from motor tics, you can treat it with cold water washes and compresses. Nervous tics in a child that were caused by stress are neutralized by eliminating the source of negative emotions and parental care.
What to do if the tic is severe and does not go away?
The choice of treatment method is made only after the cause of the development of this disease has been determined. For example, if the cause is problems in the family, then the child should attend individual or group sessions with a psychologist.
If the tic does not go away, the doctor recommends drug treatment:
- antidepressants;
- nootropics;
- neuroleptics;
- vitamins.
Drug treatment is carried out for 6 months, combining it with massage, taking medicinal baths and visiting the pool. If a child who is not yet 8-9 years old suffers from a nervous tic, then the treatment will be successful, but early tics, in the absence of adequate treatment, can persist until adolescence.

Useful tips
- Light physical activity helps cure a child's nervous tics.
- A favorable atmosphere in the family will be the key to the correct psycho-emotional development of the baby.
- In this condition, water procedures and electrosleep are very useful.
- Regular and acupressure massage will help your baby relax.
- During treatment, it is worth establishing a clear daily routine and ensuring that the child sleeps at least 7-8 hours a day.
- Be sure to reduce the time your child spends at the computer or in front of the TV screen.
Let's sum it up
Most often, children under 6-7 years old blink their eyes or twitch their shoulders, but these changes in the child’s behavior should not plunge parents into panic. Timely treatment, love and care will help your baby get rid of this unpleasant condition in less than 1 month!
I like 1
Related Posts
leave a comment
Features in children
The diagnosis and treatment of nervous tics in children is carried out by a pediatric neurologist (
neurologist-pediatrician
When should you see a doctor?
You should contact a neurologist in the following cases:
- nervous tic is very pronounced;
- multiple nervous tics;
- a nervous tic causes physical discomfort to the child;
- a nervous tic disrupts the child’s social adaptation;
- the nervous tic does not go away on its own within 1 month.
What can a child expect at a doctor’s appointment?
Do not make a diagnosis yourself - visit a neurologist, psychologist or local therapist. You can get rid of this nervous disease in just a few weeks! You can be treated with ordinary herbal tea, which perfectly calms the nervous system:
- chamomile drink;
- pharmacy preparations, in which valerian root predominates;
- infusion of anise seeds.
It is also useful to give your baby regular tea and milk with honey, but the amount of chocolate, cocoa and other caffeinated foods and drinks should be reduced. It is also better to exclude all sweets, spicy and fatty foods from the baby’s diet, replacing them with cereals, fruits, vegetables and dairy products.
For children under one year of age suffering from pathological tremor, massage is mandatory. The timeliness of the measures taken will help to avoid severe complications of the disease in the form of changes in intracranial pressure, hypocalcemia, hyperglycemia and stroke.
You need to carefully monitor the situation and understand when these symptoms appear. The tic in this case will indeed be a blink, but one that attracts attention with the following symptoms:
- fast, paired, or “cluster”, that is, blinking in portions. Instead of a single blink, paired or even group blinking occurs;
- if blinking periodically turns into squinting;
- if there is an extraordinary blinking of one eye, but the other does not blink;
As a rule, most of the nervous tics of the primary group go away on their own after a certain time, without having any particular effect on the health of the baby and without creating serious problems. But if the severity of tics is strong, if they cause discomfort and affect the condition and life of the baby, it is important to carry out treatment, and it should start as early as possible.
Treatment can be carried out using 3 methods:
- Methods of non-drug therapy.
- With the help of medications and medical procedures.
- Using traditional medicine methods.
The priority direction of therapy is always considered a non-drug approach, which is used independently to eliminate the primary type of tics, as well as as part of complex therapy in the treatment of secondary category tics.
Of course, to treat children, it is best to use folk remedies that have a beneficial effect on the nervous system of children. The use of soothing herbal mixtures, infusions and herbal decoctions helps reduce the intensity of nervous tics to a significant extent.
First aid
If a child develops a nervous tic that causes considerable discomfort, it is recommended to take special measures to eliminate it. First aid will consist of the following activities:
- patient distractions;
- massage the twitching area;
- closing the eyes.

To distract a child from negative experiences that provoked pathology, it is worth choosing an interesting activity for him. Interesting games and drawing classes will help to completely absorb the attention of the little patient (watching the computer or TV will not work in this case). These types of activities will create an area of activity in the brain that can drown out provoking impulses.
If the eye twitches, it is recommended to perform a simple massage. Moderate pressure on the brow ridges (the nerve that causes eyelid twitching) is located here to get rid of the pathology. These passes should be performed within 10 seconds. You can also apply gentle pressure on the inner and outer corners of the pathological eye.
If a tic occurs, you should try to close your eyes tightly (for a few seconds). During this exercise, the eyelids should be tense as much as possible. Repeat the passes at least 3 times, with breaks of one minute.
Symptoms
Any attentive parent will notice signs of a nervous tic. Muscle twitching in an area of increased innervation or a constantly emitted sound, especially when the child is excited, are the only symptoms.
Interesting! If a child simply blinks his eyes frequently, this does not always mean he has motor hyperkinesis. The tick always repeats at certain intervals and has a specific rhythm. Simple blinking is irregular, but can be excessively frequent due to eye fatigue or too dry indoor air.
The combination of visually noticeable and vocal manifestations, as well as multiple motor hyperkinesis, require more attention from parents. With such symptoms, it is better to visit a neurologist and undergo additional diagnostics. The presence of local or multiple tics in combination with high fever or lethargy of the child requires urgent medical attention.
This disorder is accompanied by uncharacteristic symptoms that depend on the type of nervous tic:
- headache;
- the child’s eyes hurt, he rubs them;
- baby bites his nails;
- the baby constantly twirls a toy in his hands or fiddles with ribbons on his clothes;
- the child constantly makes uncharacteristic sounds;
- the baby has become inattentive and complains of weakness;
- the child is irritable and withdrawn.
If the child is calm or busy playing, then the symptoms are invisible, but any stressful situation leads to their manifestation. It has been proven that boys suffer from this condition more often than girls, but before the age of 18, more than 80% of children experience various forms of nervous tics.
Signs of a nervous eye tic are especially noticeable to others. Muscle twitching begins unexpectedly for a person; at the initial stage, they can be suppressed by an effort of will, but in the end they will still appear after a short period of time.
Symptoms of the disease do not appear immediately, and sometimes the child may not be aware of them. People around you usually notice strange behavior. Then the sick person himself begins to feel the onset of an attack and can briefly suppress it through an effort of will.
Tics often begin with a growing feeling of tension that you want to get rid of. This feeling intensifies if the child tries to restrain himself. Afterwards there comes temporary relief.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on visual identification of muscle twitching. Since a nervous tic can signal problems in other systems of the body, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination.
The main research methods include encephalography of the brain, ultrasound of internal organs, especially the liver, and detailed blood tests with the determination of trace elements. Children with tics are recommended to be tested for helminths.
Based on the data from the tests performed, the doctor prescribes treatment. In most cases, eliminating the underlying cause also leads to a decrease or complete disappearance of muscle twitching.
It is known that neuropathic pain is a very unpleasant phenomenon. What anti-stress pills are used to treat it can be read in this article. About how the diagnosis of hypertensive type VSD is made.
If nervous tics are not related to eye disease, then their diagnosis, as well as further treatment, will be dealt with by a neurologist, in this case, a pediatric one. You should contact your doctor immediately if:
- A child's tic is very pronounced.
- Tick has a multiple character.
- The condition causes serious physical discomfort to the baby.
- The condition provokes difficulties in the child’s social adaptation.
- Tick is observed for more than one year.
At the appointment, the doctor may ask several questions to clarify the situation and clarify the whole picture of the condition. For example, about when the tic appeared for the first time, in what situation it happened, about the existing medical history, about possible heredity.
As diagnostic measures, the doctor can assess not only the general condition of the child, but also his motor activity, as well as sensory functions and reflexes.
As additional studies, general blood tests, helminth tests, ionograms, as well as electroencephalography and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are often prescribed.
In some cases, additional consultations with other specialists may be required, in particular: infectious disease specialist, geneticist, psychotherapist, oncologist, toxicologist.
Nervous tic as a consequence of emotional shock

Why does a child's eye twitch? The reasons may be related to the psychological and emotional state. Often such problems arise when parents are at the stage of divorce or a misfortune has occurred in the family. Nervous tics can also occur during serious fright. At the same time, it is not so easy to notice eyelid trembling from the outside. Children usually complain of similar symptoms themselves. In this case, you must urgently make an appointment with a neurologist or ophthalmologist.
Treatment
Approximately 10 - 15% of primary nervous tics, being mild, do not have a serious impact on the health and psycho-emotional state of the child and go away on their own after some time (
weeks - months
). If a nervous tic is severe, causes discomfort to the child and negatively affects his psycho-emotional state, it is necessary to begin treatment as early as possible to prevent the progression of the disease.
In the treatment of nervous tics in children there are:
- non-drug treatment methods;
- drug treatments;
- traditional methods of treatment.
They are priority methods of treatment for primary nervous tics, as well as for secondary nervous tics as part of complex therapy. Non-drug treatment includes a set of measures aimed at restoring the normal state of the nervous system, metabolism, and normalizing the psycho-emotional and mental state of the child.
The main directions of non-drug treatment of nervous tics in children are:
- individual psychotherapy;
- creating a favorable environment in the family;
- organization of work and rest schedules;
- good sleep;
- good nutrition;
- elimination of nervous tension.
Individual psychotherapy
Often, to treat primary tics, it is enough to eliminate the factors that cause them. In addition to this, you can use physiological and folk methods that promote rapid recovery of the nervous system. Secondary hyperkinesis requires specialized treatment or cannot be eliminated at all.
Traditional methods
Topical folk remedies include various sedative infusions and decoctions. They can be used instead of drinking or given separately.
Therapy is based on an integrated approach, taking into account the peculiarities of the functioning of the body and the nuances of the course of the disease. In the process of compiling an anamnesis, talking with parents, the neurologist finds out the most likely causes of the development of the disease and discusses options for adjusting the educational methodology. In the initial stages of the disease, the use of drugs is out of the question.
The duration and severity of the pathology is influenced by the patient’s age at which the disease began to develop. It also indirectly indicates the cause of the disease:
- In children under three years of age, a nervous tic is a sign of a more serious illness (brain tumor, schizophrenia, autism).
- At the age of 3 to 6 years - most often the problem is psychogenic in nature, regression occurs only in adolescence.
Consequently, a nervous tic in a 5-year-old child has a favorable prognosis; in the majority of cases, the problem goes away without a trace.
The initial diagnosis of nervous tics is carried out by a pediatric neurologist, then, if necessary, other specialists are involved in the treatment. Typically, a doctor is consulted when a nervous tic of the eye is severe, causes physical and emotional discomfort, does not go away within one month and is accompanied by other symptoms.
What is included in the treatment?
How to treat nervous eye tics in a child at home? First of all, you should not voice your knowledge about nervous tics and your guesses to the child, so that he does not develop an inferiority complex. You need to change your routine, monitor your sleep and rest, which should be active, in the fresh air. You need to limit your time with the computer to 2 hours a day.
You should take vitamin and mineral complexes for children and multivitamins. Glycine works well, as it improves inhibition processes in the central nervous system.
Children's vitamins
And only if the measures taken are ineffective, you should contact a pediatric neurologist.
People suffering from this problem very often ask the question: “How to cure a nervous tic of the eye as quickly as possible?”
Therapy for the disease consists of the use of medications, special exercises and home treatments. Only the combination of these methods will allow a sick person to reduce the symptoms of the disease or completely get rid of it.
Drug therapy
If a nervous tic of the eye is one of the symptoms of another disease, then the treatment of the latter becomes simultaneously the treatment of the tic.
If the development of blepharospasm is associated with a violation of microelements in the body, then a balanced diet enriched with foods containing magnesium and calcium can help in this case. It is recommended to eat nuts, currants, cherries, watermelons, bananas, peas and beans, cheeses, cottage cheese, fish, oatmeal and buckwheat.
It is possible to use drugs such as Magne B6 and calcium gluconate. To reduce eye strain, you should, if possible, reduce the amount of time you watch TV and spend time at the computer.
It is advisable to regularly do relaxing eye exercises.
Among non-drug methods, eye compresses made from bay leaves, geranium leaves, and honey help relieve the condition. Such compresses can be done several times a day, alternating components.
General baths with sea salt and aromatic oils (lavender, lemon balm, cinnamon, basil, ylang-ylang, geranium) help relax the body in general and in this indirect way reduce twitching.
All methods aimed at normalizing the emotional sphere of a patient with a nervous tic of the eye will have a positive effect on treatment. Moderate physical activity, proper sleep, walking, trips out of town, the emergence of new hobbies, “heart-to-heart conversations” - all this helps regulate the functions of the nervous system.
The ability to relax and disconnect for a while from the outside world is something that a patient with a nervous eye tic should learn.
Most tics, including Tourette's syndrome, require only minor intervention. Education is usually necessary for the children themselves and their families.
Most often, the goal of treating nervous tics in children is not to completely suppress symptoms. There is no point in fighting every manifestation. It is enough to cope with the discomfort and teach children to control their tics.
If a child has Tourette's syndrome, family members will need to understand the specifics of the condition.
Tics can change the location, frequency and severity of their manifestation.
It is important for others to understand that tics in a child are not promiscuity, but a painful condition. Over time, obsessive movements and sounds weaken or intensify.
A good example would be the need to blink. All people can go a while without blinking, but sooner or later they will have to blink. Much the same thing happens with ticks. The patient can more or less successfully restrain himself, but there is always a chance that tics will appear.
Nervous tics and obsessive movement neurosis in a child: causes of occurrence, what parents should do
The cause of this disorder is most often psychological or physiological problems, as well as poor lifestyle and frequent stressful situations. In addition, the source of nervous tics can be:
- Helminths.
- Fright.
- Lack of vitamins or minerals in the body, in particular deficiency of calcium, potassium, magnesium.
- Hours of watching cartoons, playing games on a PC or tablet.
- Poor nutrition and lack of daily routine.
- Lack of sleep or drinking tonic drinks.
- Conflicts with parents or peers.
- Attention deficit or excess (strict parents, many prohibitions, too strict boundaries).
- Hereditary predisposition.
Important! Nervous tics in a child may be secondary. They occur against the background of previous or chronic diseases (herpes, encephalitis, all types of traumatic brain injuries, nervous disorders).
Today, nervous tics and obsessive movements (blinking, smacking, coughing, etc.) are considered to be quite common conditions in children.
Often parents do not immediately pay attention to this or do not consider it a serious violation, thinking that soon everything will go away on its own - this is a temporary phenomenon and the child does not need treatment.
Indeed, at first the baby is practically no different from his peers, and frequent blinking, twitching, coughing or swallowing does not bother others, but over time the signs appear more often and more noticeably.
note
Then the parents turn to a specialist, but the otolaryngologist or ophthalmologist does not find any serious pathologies.
And yet, this is a serious disease that needs to be diagnosed and corrected in a timely manner, because quite often a nervous tic is not only a sign of neurosis, but also a symptom of serious diseases of other organs and systems.
What is a nervous tic
Nervous tics occur due to increased stimulation of certain areas of the brain.
In most cases, its appearance is due to dysfunction of the subcortical nuclei, which regulate:
- muscle tone;
- pose;
- facial expressions;
- global motor acts.
The appearance of these movements in a child (often obsessive states) is associated with the need to relieve overexcitation.
Nervous discharge occurs through these actions:
- blinking, winking;
- twitching of lips or eyes;
- smacking;
- nail biting, lip biting, finger sucking;
- nodding head;
- coughing;
- frequent wiping or sniffing in the absence of a runny nose;
- snapping fingers;
- grinding of teeth, and not only at night;
- the child blows on the palm of his hand;
- monotonous rocking or frequent flapping of limbs;
- twitching of the genitals (in boys);
- twirling hair on a finger;
- monotonous pulling or combing of hair.
But besides this, there is another nature of the occurrence of obsessive movements - obsessive-compulsive disorder.
This condition was first described by the French psychiatrist Esquirol; he called this pathology “the disease of doubt.”

Obsessive movement neurosis is associated with a child's obsession with a certain idea or state. In order to prevent this condition and alleviate his situation, the child resorts to certain ritual actions - movements of a symbolic nature (compulsions) repeated over and over again.
Important
Therefore, the neurosis of repetitive movements can be conveyed through the formula: obsessive state - anxiety - repetitive rituals.
Obsessive movement neurosis in children is manifested by motor obsessions combined with fears.
Previously, it was believed that nervous tics arise during age-related crises (new stages of independence), which are observed at 3-4 years and 7-8 years.
It is at this time that children first encounter developmental crises:
- new skills are acquired;
- the child's behavior changes;
- personal characteristics are being formed.
The cause of this condition is, on the one hand, instability of work, immaturity or slight damage to the nervous system as a result of:
- Chronic intrauterine hypoxia:
- significant fetoplacental insufficiency;
- maternal diseases during pregnancy (blood diseases, cardiovascular pathology, diabetes mellitus);
- influence of other factors.
- Intrauterine infections:
- toxoplasmosis;
- cytomegalovirus;
- rubella;
- hepatitis;
- chlamydia;
- herpetic infection.
- Acute hypoxia during childbirth:
- premature placental abruption;
- asphyxia and fetal distress during childbirth.
- Birth injuries.
- Taking certain groups of medications by the mother during pregnancy.
- Prescribing medications for a newborn after birth.
- Bilirubin encephalopathy as a result of prolonged jaundice.
But now experts cannot clearly define the boundaries of age-related crises - in modern society, crises of independence occur earlier and it is impossible to clarify the scope of the occurrence of tics.
Today, it is difficult to clearly determine the specific events that caused the appearance of tic.
In most cases, this pathology is usually provoked by a complex of reasons, which include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- parental behavior;
- acute stress.
The combination of these factors most often leads to the formation of constant obsessive movements (tics).
Tics occur more often in boys, and the pain is much more severe than in girls. Moreover, pathological manifestations in children occur at an earlier age than in parents or other relatives.
An unfavorable balance of communications in the family (speech and non-speech) - both shouting and tugging, and an atmosphere of permissiveness contributes to the emergence of anomalies of behavior and character, and often lead to inhibition of the free physiological activity of the baby or infantilism.
Constant quarrels and a tense psycho-emotional situation are also one of the factors in the formation of a nervous tic.
Lack of attention or increased control, demandingness (overprotection) or uncompromisingness of parents often leads to the onset of the disease.
In addition, the cause of tics can be regular long-term spending of time in front of a TV screen or at a computer - this disrupts the alpha rhythm in the brain, which is responsible for the calm and tranquility of the baby.
As well as low physical activity of the child combined with an excess of intellectual stress. Acute stress is considered the main provoking factor:
- acute or chronic traumatic situation that the child cannot cope with on his own;
- unexpected joy or pleasant surprise in an excitable or emotionally unstable child;
- negative atmosphere in an organized team (in kindergarten or school);
- constant overwork;
- A lot of information;
- constant noise or other irritants;
- psychological trauma in a child;
- too high demands on the child
- constant quarrels between parents, divorce;
- frequent somatic diseases.
- long-term ENT diseases (adenoid vegetations, chronic tonsillitis, labyrinthitis, sinusitis).
When a complex of negative influences begins to affect a child’s body - the baby is in a state of constant stress and has internal anxiety - this is the initial stage of the onset of pathology.
Anxiety is considered a protective mechanism of the brain to prepare in advance for the onset of a dangerous event and speed up reflex activity.
Therefore, during this period, the baby’s brain is in a state of constant anxiety and anticipation of danger. At the same time, the ability to voluntarily suppress the excessive activity of brain cells is gradually lost.
Types of tics in obsessive movement neurosis
Obsessive movement syndrome in children can manifest itself in a wide variety of forms.
The most common symptoms are grimacing and obsessive tics.
Advice
These movements are involuntary and unconscious and intensify with excitement or tension.
Among children, the predominance of this syndrome is noted in boys.
Motor tics:
- facial expressions;
- tics of the limbs (twitching, clapping, stamping);
- tics in other muscle groups.
Non-drug treatments
These methods are considered basic for primary disorders, and are necessarily included in complex therapy for secondary ones. These include:
- Individual psychotherapy. Since the appearance of primary tics in children is mainly associated with stress, visiting a child psychiatrist or psychologist can be very useful. After completing the course, as a rule, the emotional state becomes more stable, and the correct attitude towards the disease is formed.
- Creating a favorable family environment. Parents should realize that a nervous tic is a disease and help their child cope with it. In no case should he be scolded or forced to control the manifestation of symptoms. Relatives and friends should try not to focus on the illness, maintain calm in the family, communicate more with the child, help solve his problems, and, if possible, protect him from stressful situations.
- Organization of the daily routine. It is necessary to ensure a change in physical and mental activity, proper sleep, walks and games in the fresh air. Limit computer games, watching TV, playing too loud music (especially before bed), and reading in poor lighting. You should also try to minimize activities that require excessive concentration, leading to rapid fatigue and increased nervous tension.
- Balanced diet. The diet should be regular and complete, containing all the necessary elements. It is imperative to include in the menu foods that contain calcium.
When a child has a nervous tic, treatment with medications is carried out strictly as prescribed by the doctor, both in the treatment of primary and secondary disorders. They start with the lightest drugs in the minimum dose, prescribing them to children aged one year and older.
Secondary disorders are treated only after eliminating the primary disease, or together with it. Typically, according to indications, the treatment of nervous tics includes:
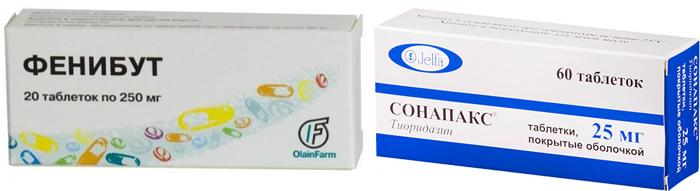
- sedatives: Novo-Passit, Tenoten;
- antipsychotropic: Sonapax, Noofen;
- nootropic: Piracetam, Phenibut;
- tranquilizers: Diazepam, Sibazol;
- preparations containing calcium.
Of the antipsychotropic drugs, the most gentle, with the fewest side effects and contraindications, is Noofen. It shows good results in the treatment of nervous disorders in children, including tics, especially of the facial type (frequent blinking of the eyes, twitching of the eyelids, cheeks, etc.).
How to treat eye blinking in children?
Every mother dreams of her little miracle growing up as a strong and healthy child. Alas, no matter how hard she tries, sooner or later the baby gets sick.
While many are prepared for viral infections and various acute respiratory infections, a nervous tic in a child can frighten even the most experienced parents.
To provide timely assistance, avoid complications and simply save your own nerves, it is enough to know basic information about the disease: symptoms, causes, types and treatment.
Nervous tics can occur not only in adults, but also in children - parents should pay special attention to the symptom
A nervous tic can be described as a sudden and involuntary brief movement of the face or limbs caused by muscle contraction. In certain cases it is accompanied by sounds. Externally you can observe in a child:
- blinking;
- twitching of the corners of the mouth or cheeks;
- wincing and shrugging;
- raising eyebrows;
- head throwing and more.
Tics can appear in children between the ages of 2 and 18, but most often they can be found in children aged 3 and 7-11 years. According to statistics, 20% of children under 10 years of age suffer from a tic disorder—that’s every fifth child.
It is important to be able to distinguish a nervous tic from convulsive muscle contractions that may accompany another disease. These signs include:
- A child's ability to produce, partially control, and temporarily suppress tics.
- The dependence of the frequency of tics on the child’s mood, activity, time of year and even time of day.
- Absence of tics during voluntary movements (drinking from a cup, eating with a spoon, etc.).
- Change of localization. For example, twitching of the corners of the mouth over time can turn into a shrug or blinking. You need to understand: most likely, this is a new attack of an old disease, and not another disease.
When a child is focused and highly engaged in an interesting activity, nervous tics may weaken and sometimes stop completely. After finishing playing, drawing, reading or other activity, the symptoms return with renewed vigor. Also, the child’s prolonged stay in the same position can intensify the manifestation of tics.
Children susceptible to this disorder have noticeable impairments in attention and perception. Their movements cease to be smooth and coordinated; difficulty in performing habitual motor acts can be noted. In particularly severe cases, the child may suffer from impaired spatial perception.
When a child draws or does something else that interests him, the tic often temporarily recedes
Advice
The first type includes tics that affect only one specific muscle group: the eyes or head, arms or legs. Complex tics are a combined contraction of several different muscle groups at once.
Secondly, tics are divided based on their external manifestation:
- motor;
- vocal;
- rituals;
- generalized forms.
The first type includes: blinking, shrugging, throwing the head back, twitching the corners of the mouth or cheeks and other involuntary body movements.
Vocal tics get their name from the sound they produce—sniffing, sniffling, or coughing.
Constantly repeating actions of the same type - walking back and forth or in a circle - are referred to as so-called rituals. With the latter form of tics, the child exhibits several variants of them at once.
Treatment for frequent eye blinking in children is prescribed depending on the cause and does not have universal principles. If this symptom is neurological in nature or associated with stress, then the following therapeutic measures are used:
- family and individual psychotherapy, psychological counseling;
- prescription of sedatives and anti-anxiety drugs (anxiolytics), rarely - neuroleptics;
- use of antipsychotics (Tiaprid, Haloperidol) for a disease duration of 12 months. and more;
- relaxation exercises;
- creating and maintaining a favorable psychological environment;
- normalization of sleep, study and rest patterns;
- massage (facial area, restorative, hygienic).
If the cause of eye blinking is not related to the nervous system, then it is necessary to determine whether the eye disease is of an inflammatory nature or whether foreign bodies are present.
You may need to use anti-inflammatory, antibacterial agents in drops or eye ointments. Keratoprotectors are also often prescribed - drugs that protect the cornea from drying out.
When the twitching is mild, it may be sufficient to eliminate the provoking factor and create a positive microclimate in the house. It is important not to focus attention on the violation that has arisen, to spend more time with the child in various interesting activities, to provide him with fortified nutrition, and to monitor adequate sleep.
For pronounced twitching, a course of medications is indicated:
- Sedatives that improve the general condition of the nervous system and normalize sleep (Valerian).
- Nootropics that normalize blood supply to the brain and increase resistance to stress (Phenibut).
- Antipsychotics that reduce the severity of phobias and eliminate nervous tension (Sonapax).
- Tranquilizers that reduce anxiety, relax various muscle groups (Diazepam).
- Magnesium and calcium preparations (if a deficiency of these substances is detected).
Additional treatment methods in the form of water procedures, aromatherapy, massage sessions, and electrosleep therapy help speed up recovery. Among the folk remedies, compresses with geranium leaves are used, which should be applied to the area where the spasm appears for 1-2 hours before bedtime. A good way to get rid of teak are decoctions of mint, lemon balm, and motherwort (it is recommended to drink them at night). You can enhance the beneficial effects of such drinks by adding a small amount of honey.
Medications and folk remedies
Here is a list of drugs used to treat the disease:
- Neuroleptics. Representatives of this pharmacological group have a complex effect, relieving pain, preventing convulsions, and dulling the gag reflex. These drugs include Tiapride, Risperidone, Fluphenazine, Haloperidol, Pimozide.
- Antidepressants. These drugs are included in therapy in the presence of neuroses, depressive and obsessive states (Prozac, Clofranil, Anafranil, Clominal).
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. Used as aids to maintain general well-being. The most common are “Pentovit”, “Neuromultivit”, “Apitonus P”.
When prescribing drugs, the form of release is taken into account, which is of particular relevance when undergoing a long course of treatment.
Recipes from traditional healers
As an alternative means for the treatment of nervous tics, various herbal tinctures and decoctions are used. You can buy raw materials for home medicines at a pharmacy or collect them yourself.
However, before giving folk remedies to children, it is necessary to consult a doctor in order to avoid unforeseen complications. Among the components that help in the treatment of nervous tics, it is worth noting herbs and roots:
- cucumbers;
- thyme;
- valerian;
- chicory;
- heather
The simplest recipe is mint and lemon balm tea. The preparation is simple: for 1 cup of boiling water you will need one teaspoon of each component. Infuse the drink for 10 minutes, then sweeten it slightly, strain and drink half a glass in the morning and evening.
Recommendations

What can parents do if their child's eye twitches? The main thing is to never scold your child. Positive changes in your condition may not appear as quickly as you expect. Try to create a calm, relaxed environment at home. Offer your child new games. The main thing here is to choose the right hobbies and activities. When treating nervous tics, it is recommended to pay special attention to sports.
Try to constantly monitor the child’s psychophysical well-being. Due to a nervous tic, he may be embarrassed to go out in public and behave with restraint. This leads to serious internal overstrain. Do everything you can to make your child feel comfortable. There is no need to focus on his illness. Let the baby feel like everyone else.
Prevention
The most effective measures to prevent nervous tics in children are healthy relationships in the family, proper nutrition, adherence to a daily routine and adequate exercise.
It is worth spending more time outdoors, be sure to play sports and teach your child how to properly throw out negative emotions, as well as reduce the amount of time spent playing video games. Timely treatment of helminthic infestations also helps prevent the appearance of nervous tics.
In order to prevent the development of a nervous tic in a child, it is extremely important to provide a friendly and calm environment in the family, make appropriate adjustments to the diet, exclude any foods that can excite the nervous system (chocolate, black tea, sweets), limit watching TV and computer games.
The psychological aspect is especially important - all parents, without exception, need to remember this. Listen to your child’s opinion, do not give him difficult and overwhelming tasks, do not forget to praise him for good deeds and help around the house. Be more patient with your baby, take care of his development and upbringing, and don’t let the problem take its course.
Children are highly sensitive to overexertion, since the nervous system has not yet formed and is immature. To prevent nervous tics in a child, you should follow the following rules:
- ensuring regular physical activity;
- avoiding stress and conflict situations in the family;
- regular walks of at least an hour at any time of the year.
It is advisable to avoid watching TV with crime news; parents should keep track of what their child is watching and what they are interested in. It is useful to learn to talk to a child, avoiding control and value judgment.
Quite often, parents notice that the baby’s upper or lower eyelid twitches. Sometimes this happens with one child's eye, and sometimes with the other. Do not rush to make hasty conclusions, for example, “the child has a nervous tic because he blinks his eyes a lot.”
Involuntary twitching of small muscles near the eye can be observed in every person. A minor nervous tic is usually not focused on, but it also happens that this problem does not go away for several days or recurs periodically.
This disease cannot be left without attention, since its cause can be either simple psycho-emotional overload or serious disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system.
A nervous tic of the eye, having appeared once, can return again at any, most unnecessary moment.
To prevent this situation, you need to learn to control your emotions, strengthen your body, and eat right.
Proper relaxation will also help prevent the onset of illness, that is, relaxing the whole body and using the scent of essential oils with a calming effect.
Below you can read how else you can treat nervous tic of the eye.