Physiological reasons
Rare deterioration in health, manifested by symptoms - pain when tilting the head, between the ears, and in the area of the skull above the ear - can well be explained by a number of physiological reasons. By eliminating them, a person can later rid himself of such negative manifestations:
- poor-quality night rest - a stuffy room, a lumpy bed, noise from neighbors, force a person to wake up often, the brain does not have time to rest - in the morning a person feels like the back of his head hurts, it’s like sand was poured into his eyes, he feels dizzy;
- Chronic stressful situations deplete the defenses of the human body, first of all, the structures of the brain suffer, which is manifested by a number of signs - a headache, spots flashing before the eyes, periodic nausea, pain radiates to different areas of the skull - the back of the head, above the ear, in the temple on the right, on the left ;
- The constantly accelerating pace of life does not allow residents of megacities to stop and take a break; many suffer not only from physical, but also from psycho-emotional overstrain - chronic overloads become so common that a person does not notice them, but symptoms gradually accumulate: a headache on the right side, maybe on the left, above the ear, near the eyes, in the back of the head.
A careful analysis of your own feelings and the situations preceding them allows you to independently identify and eliminate factors predisposing to headaches. If discomfort in the head becomes more frequent, it is recommended not to delay consultation with a specialist.
Neurological causes
Nature created the human brain as a complex system that controls all, even the smallest, processes in the rest of the body. That is why, if you notice pain in your head, deterioration of vision, hearing, persistent dizziness, it is not recommended to delay a diagnostic examination.
The symptom - pain on one side of the head above the ear - can be one of the signs of many neurological pathologies. A highly qualified specialist can carry out an adequate differential diagnosis. Self-diagnosis and self-medication are absolutely prohibited.
A headache above the ear can occur with the following neurological pathologies:
- Pulsating, one-sided pain in the head, accompanied by visual, auditory, and olfactory disorders is a sign of a disease such as migraine. The right side of the head is most often affected. Pathology can strike at any age, but is usually detected in childhood. Patients describe pain as a sudden attack of deterioration in well-being; unpleasant sensations are localized in the eye area, above the ear, in the back of the head, on the right or left. Discomfort increases with sudden movements, tilting the head, and attempts to perform work duties.
- Today, many professions are interconnected with the fact that a person is forced to spend the entire working day in one position, for example, at the computer. The shoulder area of the body suffers first, the muscle fibers are pinched and the vessels that deliver nutrients to the brain are compressed - a tension headache is formed. The discomfort intensifies in the evening, when bending over, awkward turns in the neck. It may be slightly stronger on the right side if the person is right-handed. Accompanied by dizziness, flashing spots before the eyes.
- Trigeminal neuralgia - a person experiences severe pain on the left and right when that branch of the nerve fiber that is responsible for innervation of the face in the area of the ear and jaw on the affected side is damaged.
Therapeutic measures should be prescribed only by a specialist - self-medication is absolutely prohibited, the risk of severe complications is extremely high.
ENT pathology
Many diseases of the ENT organs begin with a rise in temperature and local pain, for example, in the ear, in the projection of the sinuses, forehead, purulent discharge joins later:
- Severe headache behind the ear, in the projection of the mastoid process on the affected side - on the right, on the left - with mastoiditis. Characteristically, the intensity of pain increases during night rest hours. The history indicates a previous history of otitis media.
- Boils of the external passage of the auricle also manifest themselves with intense pain. The entire right or left half of the skull hurts - directly depending on the location of the boil; when bending to the side, awkward movement, touching - the pain intensifies significantly. After opening the purulent cavity, the symptoms decrease.
- External and otitis media can occur in a person at any age. Children especially suffer - the slightest hypothermia or prolonged runny nose lead to inflammatory manifestations in the ear area. Patients complain that literally the entire half of the skull hurts - shooting in the ear, making it impossible to eat, sleep, or perform work duties. Accompanied by a significant rise in temperature.
- Every day you can feel pain in the ear area and with such a pathology as dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. The unpleasant sensations are dull, aching in nature, and intensify with movements in the lower jaw, tilting the head, and physical stress on the neck.
After carrying out diagnostic procedures, the ENT specialist will recommend a number of appropriate treatment measures.
Provoking factors
When you have a headache behind the ears, you shouldn’t immediately suspect the worst and look for serious pathologies. First, you should familiarize yourself with the safe causes that can provoke an unpleasant symptom. Often it occurs due to external factors that are in no way related to disease. There is no need to worry if the headache occurs once and is not very intense.
Main reasons:
1. Constant stress, physical and emotional stress. It is difficult for a person who leads an active lifestyle to avoid nervous situations. As a result, the body becomes very tired from stress, and the brain suffers in particular. It also happens that the pain appears and then disappears, and also spots flash before the eyes. In advanced cases, nausea may occur, which can also indicate nervous tension.
- Bad dream. The average person should sleep about 8 hours, and not only quantity is important, but also quality. If a citizen rests in a stuffy room, and is constantly awakened by noise, then he often does not get the opportunity to fully relax. As a result, you should not be surprised by the appearance of pain in the head, since in this case it can be considered a common occurrence. Additionally, you may feel dizzy and experience discomfort in the eyes.
- Fast pace of life. Many people prefer to live actively and try to get a lot done. As a result, their body is exhausted, and they are not even able to rest properly. Fatigue gradually accumulates, and eventually a headache appears behind the ears.
- Injuries. Situations often arise when an unpleasant symptom is associated with TBI. It can be caused by a fall, blow, or other unfavorable situations. It is extremely important to see a doctor immediately if you experience pain in your head and ears. There may be serious complications due to the injury, and other unpleasant symptoms may also appear, such as impaired consciousness, increased heart rate, nausea and vomiting.
If a person has a headache behind the ear on the left or right, he should definitely visit a doctor. Of course, the symptom can be triggered by ordinary factors, and when they disappear, the discomfort in the cranial cavity will also disappear. At the same time, it also happens that unpleasant manifestations do not go away, because they appear due to serious pathologies.
Other pathologies
In addition to the above reasons why a person may have pain behind the ear, there are a number of other pathologies accompanied by similar symptoms:
- an inflammatory process that affects the salivary glands behind the ears - mumps: other symptoms of infection are also present;
- degenerative changes in the cervical structures of the spine - osteochondrosis, intense pain on the affected side, for example, on the right, intensifies with bending, physical strain in the neck;
- carious lesions of dental tissue - can also manifest as a symptom of intense pain behind the ear, aggravated by eating, during night rest;
- neoplasms of the structures of the brain and skull are increasingly being identified - in addition to one-sided pain, a person will experience a decrease in body weight and deterioration in cognitive functions;
- cluster pain – occurs unexpectedly, at the same time, lasts 1-2 days, does not respond well to medication;
- intracranial bleeding - as a consequence of injury, can form unexpectedly, is characterized by a sharp deterioration in well-being, depression of consciousness, different parameters of the pupils are visually noted, hematomas on the skull, hemorrhages in the eyes, emergency hospitalization is required.
Only diagnostic procedures and consultation with a highly qualified specialist can help put everything in its place - why the discomfort occurred behind the ear, in the back of the head, in the neck area, and what therapeutic measures will help improve well-being. Self-diagnosis and self-medication can only aggravate a person’s condition, contributing to the formation of severe complications and disability. So it is better not to listen to advice from friends regarding treatment, but immediately contact a professional medical professional who will prescribe you the correct and necessary treatment.
Similar articles:
- In what cases do you have a headache and feel sick - what measures to take?
- Why does my head hurt and how to eliminate this symptom?
- How to get rid of throbbing headaches forever?
- Constant headaches: what could this be associated with and what do they indicate?
There are hardly people who have not experienced a headache. This problem is the most common among patients. Every year, every person suffers from cephalgia, which is often simply eliminated with the help of painkillers, and its cause remains unknown. Such self-medication does not bring long-term effect, which is confirmed by more and more new attacks.
It is worth noting that every tenth person on the planet who has chronic pain syndrome of this localization suffers from one or another serious pathology in the form of brain damage. Even 70% of children of different ages complain of cephalalgia, but parents often do not pay attention to it. Be careful, because already about 3-5% of the population are disabled due to headaches.
Neurosis, depression - dizziness, noise in the head and ears.
Neurotic disorders, depression, and simply overwork can imitate almost any symptoms of “physical” diseases. Moreover, the only symptom may be dizziness, noise or “fog” in the head, ringing or noise in the ear. Such dizziness is not accompanied by vestibular disorders and this often confuses doctors, and their patients are left without proper help. Returning normal well-being in such situations is quite possible.
Leading symptoms: Dizziness, noise or “fog” in the head without clear vestibular disorders (no illusion of movement, unsteadiness, hearing loss); Involuntary concentration of attention on sensations of dizziness or noise in the head; Fatigue, decreased performance (optional); Decreased mood, nervousness (optional); Decreased or increased appetite, increased or decreased body weight (optional); Decreased or increased sexual activity (optional).
Treatment.
Such dizziness can be successfully treated. Here's how we do it in our hospital:
1. We find out whether you have diseases of the balance organs, whether your condition is really caused by a neurotic disorder;
2. We prescribe medications - vitamins, adaptogens and nootropics. These drugs help improve the supply of oxygen and glucose to brain cells, and therefore increase performance and resistance to stress, and improve physical well-being;
3. We restore a favorable emotional background, find more rational ways to utilize mental stress, and help resolve internal and external conflicts. Our psychologist or psychotherapist will select the most comfortable form of psychotherapy for you.
The main types of headaches localized in the ear area
| Type of headache | Causes and provoking factors | Features of pain syndrome | Intensity | Prevalence |
| Migraine | 1. Heredity. 2. Stress. 3. Lack of sleep. 4. Physical stress. 5. Intense visual and auditory stimuli. 6. Changes in weather conditions. | The headache is severe, paroxysmal. Usually pain occurs in the ear area on one side, right or left. The pain is throbbing and of high intensity. The duration of a migraine attack ranges from 4 to 72 hours. In addition to the ear area, the pain syndrome can be localized in one half of the skull (parietal, frontal region, less often the back of the head), its right or left side. In addition to pain, there are additional symptoms - nausea, vomiting (often), sensitivity to light and sound, and worsening with physical activity. | High | 10-20% |
| Tension headache | 1. Stress. 2. Overwork. 3. Lack of sleep. 4. Visual impairment. 5. Hereditary prerequisites | The head hurts constantly, usually on both sides, right and left, also in the form of a “helmet”. Cephalgia can radiate to the neck. Its peculiarity is monotony and compressive nature in the ear area. It can involve the ear either separately or in combination with other areas of the head. Last from 30 minutes to 7 days. | Average | up to 70% |
| Mastoiditis | Pathogenic microorganisms. | Headache in the ear area, behind it in the projection of the mastoid process. Sometimes cephalgia spreads to half of the head (either side depending on the location of the inflammation). Characteristically, its intensity increases at night. The temperature usually rises, and there is a history of otitis media. | Average | — |
| Boils of the ear canal with lymph node involvement | Infectious agents (staphylococci). | First, itching occurs in the ear area, which turns into a constant aching pain. It increases as pus accumulates. Half of the head hurts on the side of the affected ear. When the boil is opened, the pain syndrome is significantly reduced. | Average | — |
| Temporomandibular joint dysfunction | Stress | A dull pain syndrome is localized in the ear and temple area, radiates along the surface of the cheek, and intensifies with movements of the lower jaw. Headache every day | Moderate | 10-20% |
| External and otitis media | Infectious process. | Patients complain that the ear hurts and radiates to the temple and forehead area. The head hurts on the affected side, and the temperature often rises. Pain syndrome of aching, shooting nature. The right ear is most often affected. | High | 10–15% |
What to do if your ear and right side of your head hurt
Treatment is selected individually, depending on the nature and intensity of the pain syndrome, the exact diagnosis, the patient’s age and other factors. The scheme may include several stages that are combined with each other.
- Drug treatment: in the first stages, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Meloxicam and others) are prescribed. They affect inflammatory processes of any origin, not complicated by bacterial infection. To relieve episodic pain, analgesics are used - painkillers (Analgin).
- Antibacterial therapy: antibiotics are indicated for purulent inflammation, as well as to prevent its development. These drugs are often prescribed for otitis media.
- Muscle relaxants are used in addition to the main treatment regimen (Mydocalm). These drugs help relax muscles and relieve vascular spasms.
- Nootropics are a group of drugs to improve blood supply to the brain (Glycine, Phenibut). The decision about their effectiveness for various disorders is made by the attending physician.
- Surgical treatment - surgery is prescribed only if conservative methods do not bring results. It may be necessary for purulent otitis, some pathologies of the cervical spine, and the consequences of injuries.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of headaches. The center is equipped with the necessary technical facilities for a full examination of patients. Treatment is carried out both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital, with constant supervision by competent specialists. Doctors recommend not to endure pain in the ear and head, especially if it is intense or occurs frequently - timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment will prevent dangerous consequences.
Source:
https://www.neuro-ural.ru/patient/dictonary/ru/b/bol-v-pravom-uxe-i-golove.html
If you have questions about the problem, you can ask our specialists online:
https://www.neuro-ural.ru/patient/consulting/
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of pain syndromes in the area of half the head and ear is given in the table below.
| Type of headache | Features of symptoms | Primary/Secondary |
| Migraine | It is characterized by the appearance of attacks with corresponding symptoms, occurring 1-2 times a month or more often. The patient is initially irritated, and during the attack feels discomfort from intense light and noise. The sensations intensify so much that the patient may feel pain from the sheet with which he is covered. After the attack of pain ends, patients usually fall asleep. | Primary |
| Tension headache | When touching the muscles located near the head, the patient feels pain. Headaches most often occur after physical activity, overexertion, stress, or lack of sleep. | Primary |
| Mastoiditis | Patients also complain of fever and pus discharge from the ear area. When touching or percussing the mastoid process, the intensity of the pain increases. The patient hears worse and notes that there is constant noise in the ear. | Secondary |
| Boils of the ear canal with lymph node involvement | The body temperature rises, and some patients develop a fever. They also note hearing loss, loss of appetite and weakness. Sometimes all this can be accompanied by dizziness. When palpating the ear, patients note increased pain. | Secondary |
| Temporomandibular joint dysfunction | When touching the masticatory muscles, pain is noted on one or both sides (right or left part of the jaw), and movements of the lower jaw are accompanied by a crunching sound. Many patients also complain of tinnitus and dizziness. | Secondary |
| External and otitis media | The disease is accompanied by fever, leukocytosis and an increase in ESR in a clinical blood test. Most often, headaches in the temples hurt at night or in the early morning. There is dizziness and darkening of the eyes. The patient cannot hear anything in the affected ear. | Secondary |
Ear pain radiates to the head - causes and treatment
Since childhood, many of us have had to feel severe pain in the ear, radiating to the head. The reason for this is colds of the ear canal caused by hypothermia, otosclerosis, Meniere's disease, mastoiditis, furunculosis, sensorineural hematoma or allergic manifestations.
Often this is a consequence of the inflammatory process, which the patient does not realize until he consults a doctor. Any unauthorized intervention may cause deterioration in health.
Damage to the jaw joint
It is characterized by the presence of an inflammatory process in the area of the temporomandibular joint, which causes pain in the ears. The nerves adjacent to the organ of hearing are affected. A person feels painful tremors that intensify while talking or eating.
In addition, it is not possible to open the mouth wide; the patient can lower the lower jaw no more than 5 cm. Moreover, if he makes even the slightest attempt to lower the jaw lower, he will immediately feel that his chin sharply begins to move towards the affected side.
Ear pain in a child
Young children under 5 years of age may complain of pain in the ear canal and head. In this case, it is important for parents to quickly show the child to the doctor. Self-treatment is inappropriate; such intervention will cause enormous harm to delicate children’s ears.
If you know that a foreign body has entered your ear, you should not insert tweezers into it. It is better to entrust your baby to a pediatric otolaryngologist. He will examine and select the most suitable treatment method. The same applies to the inflammatory process developing in the ear.
You should not instill anything or warm it up if there is a high temperature and pus is discharged from the child’s ear. It’s worth taking a closer look, perhaps the child’s headache appeared after bathing, then you need to clear the ear canal of water and apply heat.
If the cause is a runny nose, for the first time you can use nasal drops Sanorin, Nazivin, Tizin or Vibrocil, first removing all excess mucus from the nose. Afterwards, be sure to take your baby to the doctor.
Head and ear pain
The problem could arise for the following reasons:
- Formation of sulfur plug. In addition to the unpleasant feeling, it affects hearing loss. An otolaryngologist will help get rid of it, who will clean and rinse the patient’s ear canal.
- Things are much more difficult with inflammatory processes. For example, if the victim has severe swelling of the lymph nodes adjacent to the ear, taking into account neuritis of the facial or ternary nerve.
- Formation of an abscess, lipoma, inflammation of the follicle or damage to the internal cavity of the ear by foreign bodies. If dirt or chlorinated water gets into the ear canal when swimming in a pool without a rubber cap. The symptoms will be unpleasant, jerky, pressing, paroxysmal or stabbing. The entire surface of the head can hurt.
- If an insect has crawled or flown inside your ear. In this case, unbearable pain is felt due to its movement.
- Tumor of the parotid and jaw glands.
Otolaryngological diseases
Ear pain can radiate to the head due to sinusitis or sinusitis. The patient may develop other dangerous pathologies that affect the functioning of the entire body as a whole. A person may experience unpleasant shooting sensations in the ear.
If you recently experienced acute symptoms of a sore throat, or other factors that provoked complications in the throat. To identify this, you will need to undergo several diagnostic techniques at once; an external examination alone will not be enough.
For symptoms of hypertension
Headache is often observed in people suffering from hypertension. The reason for this is a sharp increase in blood pressure. It is necessary to undergo treatment.
Hypertension should never be mistaken for a mild illness. It is important, if you suspect hypertension, to register with a dispensary and undergo treatment strictly following the doctor’s advice.
It is worth finding out why the illness occurred; perhaps the pressure jumped due to prolonged stress and insufficient rest. The body gradually wears out its potential reserve of health, and a person develops various symptoms. Especially, it is worth taking a closer look at the symptoms of pain in the head that radiates to the ear.
What to do if your ear hurts
Avoid quick fixes for ear pain. If you choose the wrong treatment, you can completely lose your hearing. It is important to act according to your doctor's advice.
The following tips will be useful at home:
- Protect your ears from moisture.
- If there is an infection, place a small piece of cotton swab into the ear canal.
- If the pain is unbearable, a painkiller like ketonal will do; you should not abuse them, as there is a risk of causing paralysis of the nerve roots of the face.
- Warming the ear canal should only be done at normal body temperature.
Additional examination methods
When diagnosing a headache and clarifying the diagnosis, you will undergo the following studies:
- Clinical blood test. It will make it possible to determine the presence of inflammation by the number of leukocytes and ESR.
- EEG. A change in the electroencephalogram during a headache may indicate a migraine.
- MRI. Makes it possible to determine the presence of a tumor in the brain as a possible cause of cephalgia.
- EchoEG. Determines the position of brain structures and their displacement.
- Dopplerography. Visualizes blood flow in vessels and their changes, is the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of temporal arteritis.
- Radiography. It will allow you to see changes in the skeletal system, in particular with pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
- Audiometry, otoscopy. To exclude pathology of the hearing organ.
Treatment
The treatment and prevention regimen for migraine and muscle tension pain is presented in the tables below.
To treat temporal arteritis, specific anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed. It contains hormones such as prednisolone and is prescribed in a dose of 60-80 mg. Its action is aimed at reducing pain and eliminating inflammation.
In case of pathology of the temporomandibular joint, the doctor makes a blockade with novocaine, this eliminates the pain. Additionally, NSAIDs (Meloxicam, Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Celecoxib), muscle relaxants (Mydocalm, Sirdalud) are prescribed, and special splints are also used.
With otitis media, mastoiditis, and boils of the ear canal, cephalgia can be cured only by eliminating the symptoms of the underlying disease, that is, ear pathology. To do this, you will have to take antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
If pain occurs in the area of half the head and ear, it is recommended to consult a therapist who can diagnose the disease, relieve pain and prevent its chronicity. After all, pathologies in the initial stages are best treated and corrected.
Sources:
- Grigorova I.A., Sokolova L.I. (ed.) Neurology - 2014 - 640 pp.
- Neurology and neurosurgery A.N. Konovalova - T. 2. - 2009. - 420 p.
- Yakhno N. N., Shtulmana D. R. Diseases of the nervous system - T.2 - 2nd ed. - Medicine, 2001 - p. 744.
A headache is a sensation familiar to every adult. Often the cause is simple fatigue or a sharp turn of the neck, but if accompanying symptoms occur, you should not ignore the malaise. For example, in cases where not only the temples are compressed, but also a shooting headache appears behind the ear on the right or left.
Ears and back of head hurt - what to do
In cases where pain in the back of the head and ears occurs due to exposure to external factors, take a painkiller (Analgin, Templagin, No-shpa) and rest. If your blood pressure increases or decreases, take medications prescribed by your doctor.
If symptoms do not go away within 2-3 days, consult a doctor. First of all, the specialist will listen and analyze the complaints, and then prescribe an examination. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the cause that causes pain in the back of the head and ears. If symptoms are provoked by ENT diseases, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiviral and antibacterial drugs. To eliminate edema, decongestants are prescribed. To reduce body temperature above 38 degrees, antipyretic drugs are used, for example, Paracetamol.
If the cause of pain is purulent forms of otitis or sinusitis, the exudate is removed in the treatment room. Under no circumstances should you remove pus yourself, as this may cause the infection to spread.
Since pain in inflammatory diseases is relieved with anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs, there is no point in using conventional analgesics and antispasmodics.
Also, taking Analgin and drugs based on it, No-shpa and other medications will not have the desired effect during migraine attacks. For migraines, you need to take special medications - triptans. The most popular: Zomig, Sumatriptan, Noramig, Imigran, Rapided.
Painful sensations with low and high blood pressure depend on vascular tone and the presence of obstacles to blood circulation. To improve your well-being during hypotension, take tonic medications, or drink coffee. To lower blood pressure, use antihypertensive drugs, diuretics, motherwort tincture, and mint tea.
To treat cervical osteochondrosis, the doctor may prescribe massage or manual therapy. Doing a massage yourself is prohibited.
You will learn more about ear pain in the following video:
Causes of pain behind the ears
When shooting pain occurs in the ear area, it can be caused by various reasons, from simple fatigue to the presence of serious diseases. Therefore, it is impossible to ignore alarming symptoms, as this can lead to unpleasant consequences. The most likely provoking factors causing pain include the following conditions:
- Overwork . The feeling of a shooting behind the right or left ear often occurs in office workers due to being in one position for a long time, leaning over a table or at a computer monitor. As a result of this body position, muscle spasm appears, which leads to malaise.
- Cold . When exposed to a draft for a long time, when a person can simply be blown through, there is a high risk of severe pain behind the ears.
- Wax plugs or foreign body in the ear . Earwax contains fats and antimicrobial substances that protect the hearing organs from bacteria. But when it accumulates, traffic jams appear, which can lead not only to hearing loss, but also to pain. The same troubles are caused by the presence of foreign small objects in the ear.
- Traumatic injuries . With bruises and fractures of the temporal or jaw bone, unpleasant sensations may be observed in the area of the ears.
- Intoxication . Oddly enough, shooting pain on the left side behind the ear or on the right side of the head can also appear due to poisoning. Each person’s body is individual, and if toxic substances enter, pain can occur everywhere, including in the ear area.
- Diseases of teeth and gums . With the development of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, the pain often “radiates” to the temple or ear.
- Damage to the trigeminal nerve. Pain behind the right or left ear can also be due to hypothermia or an inflammatory process in this appendage, since it is the one responsible for sensitivity in the head area.
- Impaired blood supply to the brain . With such disorders, spasms occur, as a result of which the pain can spread not only to the temples, back of the head and crown, but also to other areas.
- Presence of cervical osteochondrosis . With the development of such a disease, the cervical vertebrae become thinner and blood circulation is impaired, which often leads to pain, including in the ear area.
- Inflammatory processes in the ears . Diseases caused by infection can lead to shooting or aching pain not only in the inside of the ear, but also outside.
- Lymphadenitis . This disease is characterized by inflammation of the lymph nodes that are located behind the ears. When an infection enters the body, the lymph node enlarges, which leads to pain.
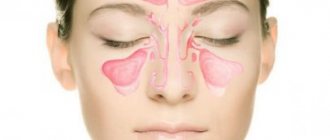
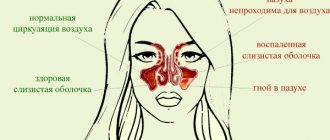
- Sinusitis . With this disease, the paranasal sinuses become inflamed, due to which the outflow of contents is disrupted, which can lead to pain in various areas of the head.
- Rubella or mumps . Since these diseases are caused by bacterial infections leading to inflammatory processes, they can cause pain in the ear area.
- Mastoiditis . Behind the ear is the mastoid process of the temporal bone, filled with air. When bacteria or viruses that provoke inflammatory processes enter the body, pus accumulates here, which causes discomfort.
Many people make a common mistake, preferring to “not twitch” when they shoot in the head on the right side behind the ear, and begin to treat the ailment at home. This should not be done under any circumstances; before using folk remedies, you must undergo an examination and consult with a specialist.
Why does it hurt behind the ear on the right?
Ear and head pain can be related in many ways. In some cases, the source of the problem turns out to be the hearing organ, and cephalgia occurs against the background of intoxication or becomes the result of symptom irradiation into surrounding tissues. Sometimes unpleasant sensations in the ear area, on the contrary, turn out to be one of the manifestations and consequences of cephalalgia.
It happens that pain in the head and ears simply occurs simultaneously, but the symptoms are caused by two separate diseases. It is important to pay attention to: the type and specific localization of the symptom, whether the severity of the sensations increases when you press on the problem area, how long they last and under the influence of what factors they appear.
Can your ear give you a headache?
An inflammatory process affecting the mucous membrane of the hearing organ can cause cephalgia even if the source of the problem is externally located and small in size. A headache will result from intoxication of the body.
The sensations will not necessarily be localized behind the ear. They can affect the entire skull and have an aching, growing, permanent nature. The presence of additional symptoms depends on the severity of the process; they may be absent.
A different clinical picture occurs with serious pathological tissue damage, for example, the formation of an abscess. In this case, the pain is concentrated in the ear, but radiates to the head. It is usually shooting, intense, and intensifies with changes in body position. Often accompanied by fever, general deterioration, weakness, and irritability. Lack of medical care threatens an abscess rupture and blood poisoning, so you need to act quickly.
Cervical myositis
Sometimes people get headaches behind the ears after being in a draft or making sudden head movements. Most often this is the result of local inflammation of the muscles of the neck or back of the head. The condition is not dangerous, but very unpleasant. The pain is absent at rest and appears sharply with any careless movement. It is burning, intense, does not allow you to move, which is why it reduces activity and performance. Pressing on the problem area rarely worsens the symptom. In most cases there are no additional manifestations.
Osteochondrosis
If your head hurts behind your ear, and movements in your neck are accompanied by a crunching sound, this may be a sign of osteochondrosis. Cephalgia results from a disruption in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and brain tissue. This occurs as a result of narrowing of the spinal canal, through which arteries and veins pass, and pinching of nerve endings. The pain is localized in the back of the neck and the back of the head, radiating to the area behind the ears and temples. They are often accompanied by numbness of the skin in the problem area, decreased muscle strength in the upper extremities, and a tingling feeling in the fingers. As the pathological process develops, the picture is complemented by dizziness, decreased performance, and nausea.
Inflammatory lesions of the meninges
Meningitis is characterized by a specific clinical picture, which may include a headache concentrated above the ear.
Most often, cephalalgia is still global in nature. The sensations are intense, bursting, growing. They are so painful that a person tries not to move or open his eyes. Any external factors and even a light touch to the head intensify the symptom. It is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, which does not bring relief. The patient has stiff neck muscles, causing him to throw his head back. Meningitis is characterized by the appearance of a special type of rash, which allows a quick diagnosis.
Trigeminal neuralgia
A chronic pathology in which the patient systematically experiences attacks of intense headaches. The sensations are burning, shooting, radiating across the area of the branching of the trigeminal nerve. They are localized only on one side of the head and can last from 2 minutes to 3 days. Often the temple and ear hurt at the same time; the pain can also affect the lower jaw. During an attack, a person freezes - he is afraid to move and provoke increased cephalgia. Some patients begin to unconsciously rub the affected area, but this rarely brings relief.
Pathologies of the cervical spine
This is an impressive list of diseases: hernias, tumors, arthritis, scoliosis, myositis, infectious lesions and much more. Changes in the structure of the components of the upper part of the spinal column or the tissues surrounding them lead to disruption of the patency of the canals located there. This causes compression of arteries and vessels, irritation of nerve fibers. The muscles and brain stop receiving the required amount of oxygen and nutrients. Violation of the blood outflow process leads to poisoning of cells with metabolic products. The clinical picture depends on the type of disease, but almost always the patient has pain in the back of the head, radiating behind the right or left ear.
Vascular pain
An occipital headache that radiates to the ear on the right or left is characteristic of changes in blood pressure. The symptom can be observed on both sides. Depending on blood pressure indicators, it is accompanied by additional symptoms. With hypertension, these are bursting sensations, pressing on the eyes, dizziness, nausea, and anxiety. Hypotension is complemented by weakness, pulsation and heaviness in the head, drowsiness, lack of appetite, tachycardia and a feeling of lack of air.
Otitis
The clinical picture depends on the severity of the process and the depth at which the inflammation is located. In some cases, the patient’s ears burn (usually one), the temperature rises slightly, and the headache becomes the result of intoxication of the body.
An advanced process in the middle or inner ear is accompanied by severe pain, which spreads to the entire half of the skull and shoots into the hearing organ. At the same time, many patients are unable to do their usual activities, sleep, or even eat. This condition is often accompanied by fever and a general deterioration in the patient’s well-being.
Injuries
A situation where a person with a history of traumatic brain injury has a headache on the right side behind the ear requires immediate evaluation by a doctor. The appearance of a symptom may indicate the formation of a hematoma or the opening of intracranial bleeding.
In the first case, the pain will be the result of increased pressure inside the skull. The condition is characterized by confusion, pressing cephalalgia, nausea and vomiting, fainting, changes in breathing and pulse. When bleeding occurs, a person’s well-being sharply worsens, the pupils take on a different appearance, consciousness is depressed, and hemorrhages may appear on the sclera of the eyes.
Myogelosis
The pathology is characterized by the formation of painful compactions in the muscles as a result of impaired blood supply to the tissues. The condition can be triggered by stress, drafts, osteochondrosis, spondylosis, hypertension, and lack of physical activity in human mode. During the illness, headaches are observed behind the ears and in the back of the head. It is accompanied by limitation of motor activity of the neck and upper shoulder girdle. Sometimes nausea and dizziness occur. Patients often complain of increased fatigue when staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time.
Mastoiditis
The disease is of an infectious nature and is characterized by damage to the mastoid process, located behind the ears. The porous structure of the formation is predisposed to the fact that it can quickly fill with pus from nearby sources of inflammation. As a result of the development of the disease, a person constantly has a headache and radiates to the ears, the temperature rises, and hearing decreases. When you press on the area behind the ear, the pain intensifies and swelling is felt. Pus may come out of the ears. In the absence of professional help, there is a risk of developing a brain abscess, meningitis, and inflammation of the auditory labyrinth.
Diagnostic methods
Since there can be many reasons for pain behind the ears, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination. Diagnostics includes the following activities:
- Studying the medical history and accompanying symptoms (dizziness, nausea, hearing impairment and others).
- Laboratory tests of urine to assess the state of the internal environment of the body.
- General and biochemical blood tests to determine the number of leukocytes and confirm or exclude the development of inflammatory processes in the body.
- Audiometry and otoscopy to exclude hearing diseases.
- X-ray, which allows you to see changes in the temporal and jaw joints.
- EEG and MRI to assess the condition of brain vessels and identify possible tumors and neoplasms.
- EchoEG to determine the condition of brain tissue.
- Consultation with specialized specialists (neurologist, ophthalmologist, ENT specialist, endocrinologist and others).
Based on the results of the studies, treatment is prescribed.
Treatment
After diagnosis, depending on the causes of pain in the ear area, the specialist prescribes treatment. Therapy may include the following medications:
- prescription muscle relaxants;
- antidepressants;
- steroid drugs and blockers;
- antisecretory drugs;
- antibiotics.
When the cause of the illness is neurological diseases, the patient is shown:
- physiotherapeutic methods of treatment;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy;
- massages.
Surgical intervention is required in rare cases, in the presence of serious pathologies, when other methods are ineffective. In such a situation, the following types of surgical treatment can be performed:
- stimulating the occipital nerve to block signals sent to the brain;
- microvascular decompression, which is done to change the location of the vessels that compress the nerve endings, which leads to pain.
As a rule, when treating headaches in the ear area, surgical intervention can be avoided, and the patient feels relief after taking the prescribed medications and performing the necessary procedures.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen for headaches is selected individually. It depends on the type of pain, the frequency and nature of its manifestation, as well as the age of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases. Treatment may include the following steps:
- antibiotic therapy - administration of antibacterial drugs orally or in the form of injections, if the bacterial cause of inflammation is confirmed;
- drug treatment - an individual regimen that includes painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants and other drugs;
- methods of recovery from injuries, including physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises and massage - they are also effective in the initial stages of osteochondrosis;
- specific drugs to increase or decrease blood pressure;
- Surgical treatment is prescribed only when conservative methods are insufficiently effective, including abscesses, hernias, and purulent diseases of the hearing organ.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the treatment of headaches. General and individual diagnostic and therapy programs have been developed here, which are adapted separately for each patient. Modern equipment, competent specialists, the possibility of round-the-clock observation in a hospital setting - these advantages make it possible to timely identify pathology and carry out its comprehensive treatment.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 1 votes
Share article on social networks
Preventive measures
To avoid severe pain behind the ear, you need to follow certain recommendations. Experts advise taking the following preventive measures:
- Regularly undergo medical examination to identify various diseases that may lead to such ailment.
- Avoid overstraining and overworking the neck muscles.
- Monitor your posture and if signs of osteochondrosis appear, carry out the necessary treatment.
- If you stay in one position for a long time, for example, while working on a computer, take regular breaks and stretch your stiff muscles.
- Monitor the condition of the ears to avoid the formation of wax plugs.
- Treat colds promptly and avoid drafts.
- If inflammatory processes occur in the oral cavity, seek medical help immediately.
- Strengthen your immune system and lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Give up alcohol and cigarettes.
- Do exercises regularly and walk in the fresh air.
- If any diseases are detected, strictly follow all recommendations of the attending physician.
Bottom line
It is important to realize that any ailment is caused by certain disorders in the body, and this fact cannot be ignored. Such delay can lead to the development of serious diseases that have serious health consequences.
Similar articles:
Many people face this problem when pain suddenly appears behind the right or left ear. But not everyone knows the causes of the disease and often begin to self-medicate. With improper treatment, various complications arise, so it is necessary to find out the cause of the disease.
Causes
Pain behind the ears indicates various diseases that a person may develop. At the initial stage of the disease, such symptoms indicate the appearance of some disease.
The most common ones are noted:
- Otitis.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Sinusitis.
- Inflammation of the ternary nerve.
- Caries.
- Epidemic parotitis.
- Accumulation of wax in the ears.
There may be other reasons as well. With neuralgia, the trigeminal nerve is affected, often affecting the lower part of the face. Therefore, pain occurs in the ear area. With lymphadenitis, the lymph nodes become inflamed, the inflammatory process affects the head near the ears on the left or right side. With caries, the nerve becomes inflamed, and pain can radiate to the lower parts of the face.
In any case, they seek qualified help from a medical institution. Only with the correct diagnosis and clarification of the cause of the disease, appropriate treatment is prescribed, which contributes to a rapid recovery.
Diagnostics
Usually, if there is pain behind the ear, they refer to a headache and take tablets in the form of analgin or citramon. The frequency of such an illness should be alarming. When examining a patient to determine the cause, the doctor prescribes the following tests:
- Blood donation determines inflammatory processes in the body (leukocytes, ESR).
- Electroencephalogram (to exclude migraine).
- MRI to rule out a tumor in the head, cephalalgia.
- Dopplerography.
- X-ray of the temporal joints.
- Otoscopy and audiometry, hearing problems are checked.
After the examination, the doctor makes a definite diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Possible diseases and their treatment
Often, pain in the head behind the right or left ear indicates a migraine and muscle tension . It is noted that pain occurs above the right ear and radiates to the temple and eye area. To relieve them, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Women often experience throbbing pain to relieve vasospasm by taking nicotinic acid, no-shpa, and baralgin.
Spasms on the left side of the head behind the ear indicate overexertion, uncomfortable posture during sleep, indicates problems with the spine, and hypertension.
With meningitis, the membranes of the brain become inflamed due to infection. Therefore, pain occurs above the ears; this disease requires urgent treatment, since the advanced form of the disease can be fatal. After the examination, drug treatment is prescribed: ear drops, anti-inflammatory drugs and, of course, antibiotics. At the initial stage of the disease, complications can be avoided.
For sinusitis or otitis media, antibiotics and drugs that enhance immunity are also needed. Purulent discharge can enter the brain. With sinusitis, the sinuses become inflamed, and the pain can radiate to any area of the head.
If pain behind the ear is associated with osteochondrosis, then it is recommended to engage in physical therapy and a special massage is prescribed. The cause of the disease may be due to mumps, then antiviral drugs are needed, and in some cases, immunostimulants .
Folk remedies help relieve headaches in the ear area. Tea is prepared from mint, lemon, chamomile, and oregano. Calming and relaxing procedures will help relieve pain. Stress and anxiety negatively affect the human nervous system. They also do a self-massage of the head; the fingers can be lubricated with essential oils: eucalyptus, lemon. Relief occurs within 15 minutes. It is worth noting that if you have tumors, it is not recommended to massage your head. In this case, consult with your doctor.
You can take a shower in the morning and a soothing bath in the evening. Then blood circulation will improve and gradually the headache will go away.
For prolonged pain symptoms, do not self-medicate, because any complications can negatively affect the brain. Only a complete examination can determine the cause of head pain in the ear area. It is important to start treatment as quickly as possible.
If you have constant headaches on the right or left side, it is not recommended to take pain relief pills in the form of paracetamol. Frequent spasms indicate the onset or development of a serious disease.
Safe modern medicines and pills
When planning a visit to the doctor, the patient should be prepared to answer questions about how often pain occurs and what its intensity is. This will help the doctor develop the correct treatment tactics.
↑
Groups of drugs effective for episodic attacks of pain
The main medications for the treatment of this pathology are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They not only have an analgesic effect, but also relieve inflammation and eliminate swelling.
Most often prescribed:
- Ibuprofen—400 mg per day;
- Ketoprofen—100 mg/s;
- Naproxen—500 mg/s;
- Meloxicam—7.5-15 mg/s;
- Celecoxib—200 mg/s.
Most NSAIDs have a very negative side effect: with long-term use, they negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract, even leading to the development of drug-induced gastritis.
Medicines Meloxicam and Celecoxib are new generation drugs that do not have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract. The disadvantages of using these drugs include the relatively high price.
Analgesics are most often used at home to relieve an attack. They do not treat the disease, but only relieve pain. Drugs in this group are suitable for stopping episodic attacks, but their systematic use can lead to the occurrence of abuse syndrome.
During an attack of pain, you can take Paracetamol - 100 mg, Citramon, Analgin - 500 mg or Mig 200-400 mg.
If the examination revealed the appearance of cephalgia after exercise as a result of increased blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe medications prescribed at an early stage of the development of hypertension. These include: vasodilators, ACE inhibitors, diuretics, calcium channel blockers.