Symptoms and treatment of cervical myositis
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for Joint Treatment: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your joints by taking every day...
Read more "
The term myositis refers to damage to different muscle groups under the influence of a wide variety of negatively affecting external or internal factors.
Myositis of skeletal muscles in the cervical region can develop in almost any person; the disease can be triggered by working conditions or sports training.
Cervical myositis also occurs for a number of other reasons; treatment of the disease depends on the factor provoking the pathology. In the absence of an effective course of treatment in the acute phase, the disease quickly becomes chronic with periods of exacerbation of varying duration and intensity of symptoms.
Causes of disorders in skeletal muscles
Myositis of the cervical muscles develops quite quickly, the first signs of the disease are recorded three to four hours after the negative impact. It was found that a large group of diseases, injuries, and toxic lesions can lead to damage to skeletal muscles.
- Infections - myositis often develops after acute respiratory viral infection, tonsillitis, tonsillitis, against the background of chronic rheumatism. Post-infectious myositis occurs due to an imbalance of the immune system.
- Professional activity – patients of a neurologist with myositis often become computer operators, violinists, pianists, that is, people who spend several hours a day in an extremely uncomfortable position.
- Injuries – direct blows to the cervical spine, bruises and fractures of the upper extremities, SGM.
- Often neck myositis occurs after long-term psycho-emotional stress.
- Hypothermia, influence of drafts.
- Parasitic infections. Infection with various helminths leads to general intoxication and allergies, which affect not only organs, but also muscles.
- Joint diseases – osteochondrosis, herniated intervertebral discs. With these ailments, a person strives to achieve a body posture in which pain is less pronounced. In this case, the skeletal muscles remain in an anatomically incorrect position for a long time, causing them to stretch and become damaged.
- Toxic effects arising from metabolic disorders in chronic gout, diabetes, general poisoning of the body with various substances. Cocaine addiction and alcoholism lead to myositis. Short-term myositis can develop when taking certain groups of drugs.
- Often the cause of acute myositis is a combination of several provoking factors, such as hypothermia and viral infection. Young people and teenagers experience muscle pain after intense training, emotional stress, and during exams.
Classification of the disease
Several classifications of myositis are used in medicine. The most basic division is based on the location of muscle damage. There are cervical, lumbar, thoracic, and gluteal myositis rarely occurs. Doctors also use the classification of myositis according to the provoking cause:
- Purulent myositis is one of the most severe, caused by various types of bacteria, mainly staphylococci and streptococci. This form develops when an infectious agent enters an open wound; this can happen during surgical interventions on the neck or with various injuries. Purulent myositis can lead to very serious complications - cellulitis, abscesses, therefore, effective antibacterial therapy is selected for its treatment.
- Infectious myositis develops during or after influenza, ARVI, lupus erythematosus, rheumatism. Infectious non-purulent lesions are characterized by less severe symptoms compared to purulent myositis.
- Neuromyositis is a form of myositis that affects not only the neck muscles, but also the peripheral nerve fibers. Neuromyositis often occurs chronically, which leads to dystrophic changes in the muscles. The occurrence of damage to nerves and muscles occurs with the simultaneous influence of significant physical overexertion and the action of cold temperatures or drafts.
- Münchmeyer's disease or myositis ossificans is characterized by the appearance of foci of large amounts of calcium in the skeletal muscles. The etiology is not fully understood; the disease is often defined as congenital; it happens that foci of ossification occur after injuries.
- Polymyositis is a simultaneous lesion of several muscle groups. Typically, this form develops in autoimmune diseases; the disease is characterized not only by pain, but also by increasing weakness in the muscles, which subsequently develops atrophy. If a disease is detected in a child, then it is necessary to examine the lungs and heart - pathological processes are also observed in these organs. A male patient over 40 years of age diagnosed with myositis often suffers from tumors of internal organs. Polymyositis is one of the most severe forms of muscle damage.
- Dermatomyositis affects several systems - muscles, skin, internal organs. This type of myositis is most often detected in young women; hormonal disorders and hereditary predisposition can contribute to the disease. Skin symptoms are determined by the appearance of pinpoint rashes, swelling of the eyelids and lips. All symptoms can appear either rapidly or gradually increase over several days.
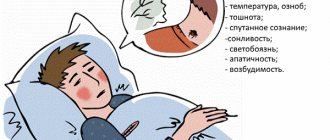
Symptoms that are characteristic of the disease
Acute myositis develops only a couple of hours, in rare cases days, after exposure to an unfavorable factor, in this it differs from osteochondrosis and radiculitis, in which sharp pain can occur at the moment of the highest physical exertion. Cervical myositis has characteristic symptoms:
- Intense and increasing pain. The pain intensifies with movements and at the time of palpation. Palpable pain is observed throughout the hand to the phalanges of the fingers.
- The neck muscles are tense, and the usual movements in the joints are limited.
- Swelling is detected above the affected muscles.
- With purulent myositis, the skin turns red, local and general temperature rises.
- Fever may occur.
- With myositis of the neck, a headache occurs, fixed in the back of the head and temples. The masticatory muscles are tense, sometimes to such an extent that the patient cannot move his jaws.
- With chronic myositis, atrophy develops, pain intensifies at night, when weather conditions change.
- Parasitic myositis leads to pain in the chest, limbs, and soreness of the tongue.
With mild symptoms, the disease may go away on its own within a few days. But under the influence of hypothermia, weather changes, stress, the disease will again manifest itself with all its acute symptoms.
Diagnostic techniques for identifying signs of disease
The diagnosis is made based on all complaints from the patient, anamnesis, palpation and external examination of the cervical spine. A specific clinic already makes one suspect myositis.
If purulent myositis is suspected, it is necessary to identify the causative agent of the disease by culture. For neuromyositis, electromyography is performed - a procedure aimed at identifying damage to nerve fibers.
In case of polymyositis, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination with a mandatory ECG. Myositis also requires differential diagnosis with diseases with similar symptoms - osteochondrosis, hernias. For this purpose, radiography and MRI are performed.
Treatment options for the disease
How and with what exactly to treat myositis of the cervical muscles depends on the identified cause. All treatment should be comprehensive, including medications, massage, diets, and special exercises in the treatment regimen. Complete recovery is achieved only with a combination of all procedures recommended by the doctor.
- Drug treatment includes a course of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pharmaceuticals and painkillers. Analgesics are prescribed for the entire period of pain, anti-inflammatory drugs until the inflammation completely goes away. If the origin of myositis is parasitic, it is necessary to use anthelmintics depending on the identified pathogen. Purulent myositis requires opening the abscess and using highly effective antibiotics.
- Warming ointments are necessary to warm up the muscles. Warming up improves blood circulation and partially eliminates pain. These include Alizartron, Viprasal, Vipratox ointment.
- – a manual technique aimed at relaxing muscles after voluntary tension. Relaxation methods are taught by specially trained physiotherapists; after mastering the technique, the patient can then carry out the exercises independently.
- Treatment in Tibetan medicine for muscle damage is based on the use of acupuncture, various methods of massage, and manual therapy. Local impact is necessary to eliminate muscle tension and return them to their normal anatomical position. The course of procedures for each patient is selected strictly individually.
- Diet – in case of acute myositis, it is recommended to follow a special diet with the exception of too salty, spicy and fried foods. The introduction of foods with fiber promotes the rapid elimination of toxins; it is also necessary to consume a sufficient amount of liquid.
- Exercise therapy – the use of a set of physical exercises greatly enhances the effect of the main therapy. Regular exercise relieves tension, reduces soreness and stretches muscles. Classes are selected by the doctor based on all the symptoms and pathologies identified in a particular patient.
Traditional medicine in the fight against disease
Along with treating cervical myositis with medications, traditional methods of restoring mobility in tense skeletal muscles can also be used.
“Grandma’s recipes” partially relieve pain, prevent further inflammation and allow you to reduce the period of use of medications.
- A compress made from white cabbage leaves will relieve pain from myositis. Clean leaves must be generously rubbed with laundry soap, sprinkled with soda and applied to the neck, secured with a scarf. You can leave the compress on overnight.
- Bay oil, which can be purchased at the pharmacy, eliminates pain and muscle spasms. A few drops of oil are dripped into a liter of warm water, and a towel is soaked in this liquid. Then it is wrung out, rolled into a tourniquet and applied to the back of the head. Laurel oil effectively relieves neck and head pain.
- Burdock leaves have an anti-inflammatory effect. Six leaves of the plant must be doused with boiling water, folded in a pile and applied to the neck, secured with a scarf.
Neck myositis is a fairly serious disease with a tendency to be chronic. The success of treatment depends not only on the literacy of the attending physician, but also on the persistence of the patient, who will regularly carry out all the necessary procedures.
The same banned issue for which Ernst fired Malakhov!
Joints and cartilage will be cured in 14 days with the help of ordinary...
Video: Neurologist talks about the main causes of neck pain
Symptoms of hand neuritis
Numbness of the hand
Symptoms of the disease directly depend on the degree and area of damage. Common features include:
- Loss of sensitivity. Patients often complain of numbness and tingling in the upper extremities.
- Partial decrease in strength or paralysis of muscle tissue. Atrophy may develop.
- Swelling of the skin.
- Blue discoloration of the upper layer of the epidermis.
- Thinning skin and dryness.
- The appearance of ulcers on the surface of the skin.
In cases of injury to the armpit or upper third of the shoulder, the pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Partial or complete loss of sensation.
- Inability to move the index and middle fingers.
- Violation of flexion and extension functions.
- Inability to straighten the arm in the wrist area.
When the middle third of the shoulder is affected, the same symptoms are observed. At the same time, motor activity and sensitivity of the shoulder are preserved. A distinctive feature is the “falling” brush. The patient is unable to straighten his fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joints.
The main symptoms of neuralgia and methods of its treatment
Neuralgia most often occurs in people whose immunity is weakened. The disease is considered more common in older people. But cases when young patients turn to doctors for help and complain of pain spreading in the lumbar region or concentrated in the area of the shoulder blades are also often encountered in everyday medical practice.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes can affect various parts of the spine. Any type of disease is characterized by pain symptoms. According to experts: cervical neuralgia has become significantly younger in recent years. This is due to the fact that young people spend a long time in a static position while working at computers. The cause of the disease is also impaired metabolism, which is closely related to the problem of proper balanced nutrition.
Who is at risk?
Neuralgia is usually classified based on the area of the body where nerve damage and dysfunction occur. Few people know that the disease can be caused not only by injuries and bruises of the spine, but also by allergies, which are directly related to impaired metabolism. No less dangerous for the spine are infectious diseases and hypothermia, the treatment of which was not carried out in a timely manner. Degradation of the muscle corset is one of the most common causes of the disease, as is physical inactivity. That is why, before treating a disease, the first priority for medical specialists is to establish its causes.
In some cases, diagnosis and treatment of neuralgia can be difficult due to diseases that occur in parallel with it. This spinal disease affects people with diabetes. In women, the risk of onset of neuralgia increases significantly during menopause. Those people whose body has a metabolic disorder do not absorb or do not receive sufficient amounts of B vitamins, so these patients are also at risk.
Neuralgia can begin due to malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract. People who abuse alcohol are also at risk. As medical studies show: neuralgia progresses much faster in them, covers large areas and its treatment is much more difficult.
General symptoms
Various types of neuralgia of the spine have specific and general symptoms, the main of which are pain.
The pain is concentrated along the affected nerve in the neck, lower back and other parts. It is not necessarily only hot and sharp. A person along the spine may feel a dull aching pain, but he thinks that it is a manifestation of osteochondrosis, but this will be a completely different disease. Neuralgia of the lumbar region is also often mistaken for a disease of the kidneys or genitourinary system. That is why, before starting to treat the kidneys, it is necessary to check the condition of the back, which can significantly worsen due to the presence of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
If a person begins to experience muscle spasms along the spine, they may be one of the manifestations of neuralgia. Why is it still often mistaken for kidney disease? Because in the area of the sacral region and above its region, tissue swelling may be observed. Neuralgia significantly complicates a person’s motor activity; the slightest movement causes pain. But the fight against the disease and its full treatment is impossible without physical activity.
Neuralgia is quite easy to identify independently by its following symptom: with gentle pressure on areas along the back, for example, in the area of the sacral region, discomfort and pain will be felt, which are noted to the right and left of the spine.
When the neck is affected
If the functioning of the nerves in the neck area is impaired, neuralgia is often mistaken for migraine and its treatment can be mistakenly started, since the symptomatic picture of both ailments has significant similarities. In this case, the pain is not concentrated only in the neck area. The back of the head and head hurt, often pain symptoms are observed in the eye area. When the nerves of the neck are affected, any rotation of the neck is associated with the appearance of uncomfortable sensations of pain. The same condition is caused by touching the back of the head. Neuralgia may not always be accompanied by pain; in certain cases, numbness in parts of the body will indicate it.
Impaired functioning of the nerves in the neck is often accompanied by photophobia. This neuralgia is often confused with cervical osteochondrosis, whose treatment can be much more difficult if it is accompanied by nerve disease. People suffering from both diseases often complain of general weakness and dizziness. Neck disease can cause various conditions. These include:
- fainting;
- nausea;
- vomiting
Patients' condition may worsen during physical activity or when the neck remains in a static position for a long time. This condition is due to the fact that the disease affects not only the neck area, but also the occipital nerves, whose condition is closely related to them.
If your back hurts
When pain symptoms spread to the lumbar region, this indicates a disruption in the functioning of nerves in another part of the back. If there is damage to the sacral area, the pain will be intermittent. They will appear and disappear. As with neck problems, people often experience dizziness and nausea.
When you press on the affected area of the back, the symptoms will be immediately noticeable. If the lower back or neck is affected, another common symptom will be observed - muscle spasms. The functioning of muscle tissue during neuralgia also changes significantly. With it, a visually noticeable involuntary muscle contraction may occur, which is noted in the lumbar region.
Increased sweating will occur in the affected area of the sacral region. In addition to swelling, there may be excessive redness or paleness of the skin. It is likely that this is how neuralgia declares itself. If treatment is not started in time and care is not taken to protect the lower back from hypothermia, then the disease of the sacral region will turn into neuritis. What does this mean?
Neuralgia itself is not considered a dangerous disease, but this does not apply to the complications that it brings with it. If neuritis progresses in the sacral region, it can lead to paralysis of the back. An equally serious complication is considered when neuralgia of the sciatic nerve progresses.
How to deal with the disease?
If pain begins in the head, sacral or cervical region, you should immediately consult a doctor. There are various types of diagnostics that can determine nerve disease. If pain is felt in the lumbar region, then you should definitely check the condition of your kidneys and back. For diagnostics the following are used:
- computer diagnostics;
- ultrasonography;
- X-ray;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
They will quickly help establish the correct diagnosis if the nerves of the back are affected in the lumbar region. It makes sense to undergo a spinal cord examination, because if the pain is felt in the lumbar region, then it may be the one that is affected. Treatment of neuralgia is largely determined not only by the stage of the disease, but also by its accompanying diseases.
When the disease spreads in the lumbar region, it also affects the functioning of the musculoskeletal system. One of the causes of neuralgia is stress, which can also cause pain symptoms spreading to the lumbar region. This is why it is so important to create a calm environment for therapeutic activities. Traditional medicine advises in such cases to treat with medicinal herbs:
- St. John's wort;
- valerian;
- mint;
- anise;
- fennel.
Painkillers are used if acute pain spreads to the lumbar spine or in any other way. Traditional drugs: analgin and novocaine also successfully cope with this task. Treatment must include vitamin complexes that strengthen the body's immunity.
In the fight against neuralgia, it is important not only to determine how the pain spreads (lumbar or in the area of the shoulder blades), but also to find the factors that provoke it. Only then can treatment be effectively carried out using massage, ultrasound, acupuncture, laser therapy, infrared, ultraviolet radiation and electromagnetic fields.
How is glossopharyngeal neuralgia diagnosed?
The basis of diagnosis, of course, is a thorough questioning, the patient’s complaints, and a characteristic clinical picture. The following methods are used to confirm the diagnosis:
- X-ray of the skull (upper and lower jaw). Using this method, it is possible to identify changes in the styloid process (its size and structure), which plays an important role in the development of the disease;
- High-resolution MRI of the brain to detect a volumetric process in the brain, as well as computed tomography;
- Electroneuromyography. Allows you to determine damage to the nerve trunk of the glossopharyngeal nerve itself, compare it with the same nerve on the opposite side, and evaluate the quantitative parameters of excitation;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck. Allows you to evaluate the quality of the vascular wall of the carotid arteries, the presence of aneurysms, atherosclerosis, calcifications and other formations.
In the photo: this is how an ultrasound of the larynx happens
. As you can see, diagnosing this type of neuralgia can take 1-2 days, and is impossible without modern research methods (neuroimaging, electrophysiological methods).
Intercostal neuralgia on the left: causes, symptoms and treatment
The older we get, the more often we feel pain. Middle-aged people get used to living with pain and do not pay attention to it, but some types of pain frighten them. What scares people the most is the pain caused by intercostal neuralgia on the left.
Fear is based on the misconception that a person’s heart is located in the left side of the chest, so intercostal pain is very often confused with pain in the heart. In fact, intercostal neuralgia can be caused by diseases of the spine and various pathological processes in the body. According to doctors, it does not pose a serious threat to human health, but it reduces the quality of life. Therefore, neuralgia must be treated.
- What is “intercostal neuralgia”
- Symptoms of the disease
- Differences between intercostal neuralgia and other diseases Gastric diseases
- Pneumonia with pleurisy
- Diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia
- Medicines
What is “intercostal neuralgia”
This is pinching or irritation of one of the spinal nerves. Due to the location of the pain (on the left, under the heart), many people tend to confuse it with symptoms of cardiovascular disease. The acute nature of the pain makes patients think that they are having a heart attack.
Often, when describing pain, one can immediately suspect intercostal neuralgia, but in reality, it turns out that the patient has a stomach ache or renal colic. Therefore, it is very important to be able to distinguish between pain from neuralgia and other pathologies.
For example, there is a difference between a heart attack and left intercostal neuralgia. The symptoms of an attack are quite specific: in addition to pain, the patient experiences changes in pulse and blood pressure. Painful sensations are eliminated by nitroglycerin. For neuralgia, nitroglycerin is not effective and blood pressure does not change.
Intercostal neuralgia can cause pain not only on the left side of the chest. They can be localized in other parts of the body located near the spine: center of the chest, right half of the body, back, under the shoulder blades. Quite often, patients complain of girdling pain.
Infringement of the vertebral nerves most often occurs due to spinal diseases such as osteochondrosis, scoliosis, various tumors, and vertebral displacement. In addition, the development of intercostal neuralgia can be triggered by the following factors:
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Hidden inflammatory processes.
- Traumatic injuries to the ribs, sternum and spine.
- Spinal cord oncology.
- Toxic damage to the body.
- Damage to nerve tissue.
- Severe pathological curvature of the spine.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Stress factors.
- Herpes.
- Chest deformity.
- Aortic aneurysm.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Menopause in women.
I would like to warn readers against making an independent diagnosis for intercostal pain, because similar symptoms may hide dangerous diseases that require immediate serious treatment in a hospital.
Symptoms of the disease
Intercostal neuralgia on the left has no specific symptoms. All the symptoms of the disease are found in other diseases, but since the disease is characterized by pinched nerve endings, we can say that acute painful attacks are a characteristic symptom of intercostal neuralgia.
Attacks of pain have the following characteristics:
- Sharp pain shoots through the chest on the left. Many patients describe it as an electric shock or heartache. The person cannot move, since any movement leads to increased pain.
- The attack does not last long. After a few minutes, the discomfort goes away. The attack develops unexpectedly. The pain during it can change intensity.
- Pain with intercostal neuralgia increases significantly with any contraction of the chest caused by coughing, sneezing or a change in body position.
- After the attack is over, the pain may remain, but its intensity decreases sharply. Aching pain is localized in the spine or in the heart area.
Attacks of intercostal neuralgia may be accompanied by accompanying symptoms:
- spasmodic muscle contractions;
- goose bumps;
- difficulty breathing, the patient is afraid of provoking more acute pain, so he breathes shallowly and frequently;
- semi-fainting condition caused by lack of oxygen;
- sweating;
- numbness in the part of the body where the nerve was pinched;
- hyperemia and hyperthermia of the skin.
During attacks of neuralgia, points of increased pain sensitivity appear on the human body. If you press on them during an attack, the intensity of the painful sensations increases greatly. As a rule, such points are located above the pinched nerve.
Differences between intercostal neuralgia and other diseases
Since intercostal neuralgia on the left is very similar in symptoms to other diseases, you need to be able to determine the true cause of the pain. Signs of pathologies with similar symptoms will help us with this.
Heart diseases. Heart attacks are always accompanied by chest pain, which is a source of confusion. You can distinguish neuralgia from a heart attack by the duration and nature of the pain.
If there are disturbances in the functioning of the heart, the pain is constant in nature. Its intensity does not change when the patient moves. Heart pain can be relieved with the help of specific medications that are ineffective for neuralgia.
Stomach diseases
Painful sensations from ulcers and gastritis are often localized behind the sternum and in the left hypochondrium. In this case, the pain can have a different nature and intensity, which complicates the differentiation of the source of the problem.
However, if you remember that pain from ulcers and gastritis always occurs after eating, then you can easily distinguish them from an attack of intercostal neuralgia. In addition, pain due to stomach diseases is very often accompanied by nausea and stool disorders.
In some cases, vomiting comes along with pain. When a person vomits, the intensity of pain will begin to decrease. In case of gastric diseases, pain can be relieved with the help of enveloping and antacid medications.
Pneumonia with pleurisy
Pain during pneumonia occurs only if it is complicated by pleurisy. The fact is that there are no pain receptors in the lungs, so the lungs themselves do not hurt. Pleurisy becomes the main source of pain. Pain sensations are localized in areas where the pleura is affected.
Pleural pain intensifies when coughing, sneezing, or turning the body. Intercostal neuralgia on the left shows the same thing. The symptoms of the diseases, however, have one important difference: with neuralgia, the pain intensifies when tilting towards the affected side, and with pleurisy - in the healthy direction.
Also, pain from pneumonia is always accompanied by a wet cough, hyperthermia, shortness of breath and general malaise. Painful sensations during pleurisy can be eliminated with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics.
Infectious herpes. Herpes zoster or herpes zoster is an infectious type of intercostal neuralgia. These illnesses have similar symptoms and similar pain characteristics. The only sign that allows you to distinguish herpes zoster from typical intercostal neuralgia is skin rashes in the area of the pinched nerve root.
Diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia
When diagnosing neuralgia, doctors are forced to use additional research methods to exclude the possibility of other diseases with similar symptoms. When making a diagnosis, an ultrasound of the heart and internal organs is performed. When doctors have doubts, they can prescribe a computed tomography scan with myelography.
During this study, a special substance is injected into the spinal canal of a sick person, which allows you to see a more accurate picture of the condition of the spinal cord and the nerves extending from it.
Contrast discography allows you to exclude or identify pathologies of the intervertebral discs. In recent years, electrospondylography, which allows assessing the condition of the spinal column, has become especially popular in diagnosing left intercostal neuralgia.
Treatment of left intercostal neuralgia
Treatment measures can be started only after an accurate diagnosis has been made. Let us remind you that self-diagnosis is unacceptable. This should be done by specialists. Treatment of intercostal neuralgia takes place in several stages. Each of them can use different methods.
The first step is to relieve the patient of acute pain. This can be done with the help of specific analgesics. However, they will not be effective if they do not simultaneously try to eliminate the cause of the disease. For this, the patient is prescribed appropriate therapy.
You can reduce the intensity of pain with the help of a supportive corset. It allows you to relax your back muscles and relieve pressure on pinched nerves.
Dry heat can and should also be used to combat pain. This method is suitable even for those people who, for some reason, cannot use medications for treatment.
Treatment of neuralgia is conservative. It is based on the use of medications, physiotherapy, massage, and acupuncture. The use of traditional medicine methods is not prohibited.
Trigeminal neuralgia – Spine Pathology Center
At our Center, we can offer comprehensive treatment for trigeminal neuralgia in combination with radiofrequency ablation.
This technique will save you from suffering for a long time. We will answer all your questions by phone. You can also ask a question by filling out the request form below. Trigeminal neuralgia is a disorder caused by unilateral inflammation of one of the three existing branches of the nerve originating from the temporal part of the skull and ending in the forehead, cheek and lower jaw area.
Disruption of the nerve occurs as a result of its compression by a nearby vessel.
Experts strongly call this disease one of the most insidious. It causes a lot of discomfort to the patient.
If you do not identify the symptoms in a timely manner and do not begin proper treatment, you can develop many more serious problems.
Causes
In many cases, the cause of the disease remains unknown, but more often, after conducting a full medical examination, the doctor can determine the etiology of the disease. The main precursors of nerve inflammation are:
- damage to part of the face by a herpes viral infection;
- trauma that damages the trigeminal nerve;
- atherosclerosis, impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the brain;
- abnormal placement of blood vessels, leading to compression of the nerve;
- aneurysm;
- multiple sclerosis;
- formations in the brain (tumor (meningioma), scars);
Symptoms
Most often, the first attacks of pain begin in the jaw area. Pain may appear spontaneously or be provoked by external factors (laughter, chewing movements, articulation). The pain has a shooting character, similar to an electric shock.
To determine the diagnosis, the doctor first of all pays attention to the symptoms that appear, which often appear during sleep:
- one side of the face periodically twitches;
- pain that begins in the jaw area spreads to the cheek, nose, ear, frontal area, eye, throat and tonsils;
- the appearance of red spots on the face (usually on the right);
- copious nasal discharge;
- eyes often water.
Due to pain in the jaw, a person uses only the healthy side to chew food. A lump may form in the muscle on the affected side.
To make an accurate diagnosis and exclude other possible diseases, it is necessary to examine the ENT organs and the oral cavity. An MRI and CT scan should be performed to rule out cluster headache, atypical neuralgia, myofacial pain, jaw pain, and temporal pain.
Treatment
Basically, trigeminal neuralgia is eliminated using conservative treatment methods. The main anticonvulsant drug used, Carbamazepine, is prescribed only by a doctor.
The patient must be monitored throughout the entire treatment period. At the same time, the doctor may prescribe antispasmodics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
If the pain does not go away after taking an anticonvulsant drug for two days, doctors consider it appropriate to reconsider the diagnosis.
Along with medications, physiotherapeutic treatment is used. Pulsed currents with low frequency, ultrasound with ultraviolet and infrared radiation, laser puncture, acupuncture, electrophoresis, and acupressure are used.
If tumors or vascular changes are detected, surgical decompression is prescribed. During surgery, the affected nerve branch is blocked, and a gasket is placed between the nerve root and the vessel compressing it.
A less painful surgical method is radiofrequency root ablation, performed through the skin. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, and the body recovers in a short time.
Conservative and surgical (superselective radiofrequency thermocorrection of the sensitive portion of the Gasserian ganglion) treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
Radiofrequency ablation
Minimally invasive surgery
The principle of radiofrequency deinervation is based on the physical method of thermocoagulation and is based on the effect of the release of thermal energy when ultra-high frequency currents pass through biological tissues.
An electrode connected to a current generator is brought to the anatomical area, the site of destruction, through an insulated cannula needle. The intensity of heating of the fabric depends on its resistance.
A STRYKER Multigen radio frequency generator is used, which provides voltage to the circuit and is connected by wires between two electrodes. Electric current passes between an active or damaging electrode immersed in body tissue and an indifferent or scattered electrode.
Heat production, and as a result, nerve ablation, occurs only around the non-insulated tip of the active electrode.
Technique
Radiofrequency deinervation is carried out with insulated needles 100 mm long with a working bare end at a 5 mm cut. Under visual control, the tip of the needle is placed into the foramen ovale through the 3rd division of the trigeminal nerve into the Gasserian ganglion.
After needle placement, low current stimulation is applied at a frequency of 100 Hz for sensory fibers and 2 Hz for motor fibers, with a tingling sensation at less than 0.5 V indicating optimal proximity of the needle to the affected nerve.
The nerve is stimulated with current and the desired branch of the trigeminal nerve is searched. After identifying the branch, the ablation procedure is carried out - the tip of the needle is heated to 70 C for 90 seconds or in pulsed radiofrequency ablation mode 42 ° C for 120 seconds. Low temperature conditions do not cause burns.
This leads to healing of the inflamed nerve.
Indications
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve with long-term pain syndrome and frequent recurrent exacerbation when conservative treatment is ineffective.
The procedure lasts approximately 40 minutes under intravenous sedation. The needle is inserted through a puncture. A visit to the clinic is not required.
In the postoperative period, you need to observe bed rest for up to 5-6 hours, then without restrictions. The operation is effective in approximately 90% of cases.
Radiofrequency treatment has 2 effects
1) pain decreases or disappears immediately after the procedure.
2) delayed effect - developing over 6-8 weeks. The latter is associated with synaptic restructuring of the sensory fibers of the trigeminal nerve (the gate of pain). But the radiofrequency ablation technique is captivating with its simplicity, effectiveness and low invasiveness.
Source: //backlanov.ru/nevralgiya-troynichnogo-nerva/
How the disease develops
Hand damage
Neuritis is an inflammatory process that develops in the peripheral nervous system. Hand involvement most often means radial neuropathy. The disease develops against the background of compression of nerve endings, which is accompanied by pain, loss of sensitivity and some other symptoms. In some cases, severe pinching may cause paralysis of the arms.
The arms are connected to the central nervous system by the bundles of the radial, ulnar and median nerves. A disease when the pathological process spreads to several bundles of nerve endings at once is called polyneuritis in medicine.
Pathology causes dysfunction of muscle tissue, and the inflammatory process is accompanied by loss of tendon reflexes. Depending on which nerve is damaged, the functioning of a certain area of the hand or arm is impaired.
Types of radial neuritis
All neuritis of the radial nerve of the hand is usually divided into three types depending on the traumatic effect. These include:
- Axillary. Also called crutch palsy. Diagnosed in rare cases. A distinctive feature is the weakness of the flexion function of the forearm. In addition, there is a loss of extensor mobility.
- "Tennis Player Syndrome" It is characterized by injury to the posterior branch of the nerve in the elbow area. The causes of development are heavy physical exertion, when pressure was placed on the elbow. This is exactly what can be observed when playing tennis, for which this type got its name. All changes that occur with radial nerve neuritis lead to chronic disease of the nerve bundle. It manifests itself as painful sensations when moving the arm or moving the fingers.
- Nerve damage in the middle third of the shoulder, as well as on the outer back surface. Happens quite often. The causes include fractures, sleeping in an awkward position and incorrectly administered injections.
Radial neuritis in some cases may be the result of previous infectious diseases, when a person received insufficient or no treatment. Most often, due to infection, damage to the middle third of the shoulder develops.
Methods for diagnosing neuralgia
The diagnosis of brachial neuralgia is made by exclusion.
The doctor must first make sure that the patient does not have another disease with similar manifestations (neuritis, osteochondrosis), and then identify the cause of neuralgia - i.e. determine what exactly caused the pinched brachial nerve. It will be impossible to cure the patient without eliminating this cause. Even if the pain syndrome is relieved, if the underlying disease is not treated, the pain will return again and again. For diagnosis, the patient will need to undergo basic tests, and also, as prescribed by the doctor, take an x-ray, undergo an ultrasound examination, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.