In addition to the above reasons, poor outflow of venous blood from the head can occur due to a congenital feature of the venous network or connective tissue dysplasia, for example, with Marfan syndrome.
Clinic of the disease
Symptoms of impaired venous outflow of the brain manifest themselves at a young age, mainly with primary altered cerebral hemodynamics. The process is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- cephalgia (head pain) is caused in this case by venous discirculation, intensifies with any movement;
severe weakness and decreased performance, insomnia;
The symptoms are most pronounced in the morning, and sleeping with a high headboard somewhat improves venous outflow from the brain. Visually, a person exhibits a “venous triad” - cyanosis of the skin, dilation of the veins of the neck, which are located directly under the skin, as well as swelling of the face in the morning. Dilation of the fundus veins often allows a diagnosis to be made by an ophthalmologist.
Additional research methods include ultrasound diagnostics, skull radiography, CT or MRI, and angiography of cerebral vessels. In addition to the data, ophthalmoscopy will allow you to determine the dilation of the veins of the fundus.
Treatment and prevention
If a complex of the above symptoms appears, it is necessary to consult a neurologist who will tell the patient what this means - obstructed venous blood flow.
For this pathology, therapy should be comprehensive and cover the main factors in the pathogenesis of impaired cerebral hemodynamics. The goals of treatment are:
- normalization of venous tone;
- preventing or eliminating inflammation;
- correction of microcirculatory disorders;
- increasing the capacity of the venous network.
The earliest possible treatment of the disease in the first stages is aimed at correcting metabolic changes in neurons to prevent their death. To achieve a positive clinical effect, the simultaneous use of several drugs from different pharmaceutical groups is required. Among these, anticoagulants are used, drugs that affect the rheological properties of the blood and the tone of the veins.
Finally, it is worth saying that timely detection and treatment of disorders of the venous outflow of the brain can prevent the development of severe neurological deficits and chronic headache syndrome in patients.
Source: https://neboli-golova.ru/kak-uluchshit-venoznyj-ottok-krovi-iz-golovy.html
Causes
The reasons may be:
Venous discirculation of the brain is usually accompanied by headaches. Very often, patients complain of noise in the head and ears, pain when taking a lying position, or when tilting the head.
Such pain is the first sign of the onset of the disease. However, many patients confuse the pathology with ordinary fatigue.
By supporting the head in a comfortable position, the muscles of the neck and face are subject to tension, blood circulation is disrupted and, as a result, pain occurs.
Symptoms of tension headaches are:
- Pain in the neck upon palpation;
- pain in the temples, forehead;
- heaviness in the eye area
- weakness, nausea;
- labored breathing;
- decreased appetite;
- bad dream.
Factors associated with the occurrence of tension headaches are an improperly organized daily routine, weather dependence, long-term use of analgesics and tranquilizers, alcohol consumption, general fatigue, and emotional stress.
What is the threat of the disease?
Venous discirculation is conventionally divided into 3 stages:
- Latent. Accompanied by minor symptoms such as moderate headache, poor sleep. Often the patient refers to fatigue and does not consult a specialist.
- Cerebral dystonia. This stage is accompanied by an increase in the intensity of headaches, vomiting, insomnia, and fainting may occur.
- Venous encephalopathy. The onset of this stage means that some processes may become irreversible: vision and hearing deteriorate, and epileptic seizures occur. Urgent medical attention is required.
Options for the development of the disease can be:
- Hand tremors;
- epilepsy;
- VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- muscle tissue atrophy;
- hydrocephalus;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- coma;
- stroke.
Symptoms
The first signs of venous stagnation in the brain, as a rule, appear before the disease reaches its apogee. Symptoms to watch out for:
- When tilting or turning the head, the headache intensifies;
- there is noise in the head and ears;
- vision and hearing deteriorate;
- fainting occurs;
- legs and arms become numb, their sensitivity decreases;
- swelling appears on the entire face and on the eyelids in particular;
- frequent dizziness;
- sleep disturbance, insomnia;
- memory problems;
- speech disorder;
- sudden changes in mood, causeless anger, irritability.
In addition to the above, other unfavorable symptoms may occur, such as metabolic disorders. You should not neglect your health; it is better to get examined immediately.
Diagnostics
To diagnose blood stasis in the pelvic organs, legs, brain, lungs, the doctor first questions and examines the patient. Then he directs the patient to the following studies:
- differential diagnosis to exclude the possibility of developing diseases with similar symptoms;
- urine, blood and stool tests;
- hardware diagnostics that help identify pathological processes.
To detect venous congestion in the pelvis in women, an ultrasound is performed; in the brain, phlebography is performed, the pressure in the ulnar vein is measured, an X-ray of the skull, CT or MRI are taken. In the case of the lungs, the doctor prescribes auscultation. When listening to the lungs, wheezing can be detected, especially in the lower regions and behind.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using modern methods, such as:
- Computed tomography of the brain (CT);
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain (MRI);
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and brain;
- Angiography;
- X-ray of the skull (if there is injury or suspicion of it).
The same diagnostic methods are used for adults and children.
Depending on the complexity of the disease, one or more methods are used to detect impaired venous outflow in the brain. A referral for examination can be obtained from a general practitioner and neurologist, or you can contact a paid diagnostic center.
The methods used to identify the disease will help to understand what stage the disease is at and what the future treatment prognosis is.
Asymmetry of blood flow in the vertebral arteries - what is it, causes and treatment
An abnormal uneven blood supply to the vessels of the brain, resulting from their pathological condition, is asymmetry of the vertebral arteries. In medicine, this phenomenon is also referred to by such terminological synonyms as “vertebral artery syndrome” or “vertebrobasilar syndrome”.
General information about the disease
Asymmetry in the area of vertebral blood vessels is a general concept that includes vertebrobasilar syndrome, that is, a violation of the blood supply to the brain as a result of dysfunction of the vertebral arteries.
Of the four major streams that provide blood supply to the brain, vertebrates realize a relatively small percentage of the total amount of blood circulated. The remaining more significant part falls on the share of sleepy ones.
Asymmetry of the vertebral arteries, resulting from exposure to a negative etiology, is caused by obstruction and uneven blood flow in the vertebral arteries.
It occurs as a result of a decrease in the diameter of one or more of them. Reducing the lumen leads to the inability to supply the brain with oxygen and nutrients.
As a result, negative symptoms appear.
The name “vertebrobasilar syndrome” does not accurately reflect the nature of the disease, because such pathology of the spine is not always associated with its diseases or dysfunctions.
The signs of vertebral artery syndrome are similar to those of other diseases, so recognizing it requires a careful diagnostic process. The danger is that the syndrome is only part of a general pathological process, which can be:
- osteochondrosis with accompanying negative manifestations,
- atherosclerosis,
- neoplasms,
- bone and cartilaginous pathologies of the spinal column, leading to compression, narrowing of the lumen and significant deterioration of a person’s condition.
Some of the pathologies that cause impaired blood flow and accompanying negative symptoms can be life-threatening. They require emergency surgery.
Symptoms of asymmetry of the vertebral arteries
The signs that accompany vertebral artery syndrome are often similar to those of other diseases. The patient may experience sudden changes in pressure (increase or decrease), high intracranial pressure, pain in the ears and eyes, blurred vision and hearing, and a burning sensation in the neck.
Along with the progression of the lesion, dizziness, lightheadedness, sometimes fainting, nausea, and less often vomiting, numbness of the fingers and psycho-emotional disturbances may appear. Few people associate all the symptoms, so contacting a doctor occurs already at a late stage of development, when the diameter of the vessel is significantly narrowed.
Any negative symptoms indicating the presence of pathology in the body should not be ignored. Very often attributed to overwork and physical exertion, poor health is a signal from the body about a serious illness.
Causes of the disease
The prerequisites for the occurrence of pathology are conventionally divided into congenital and acquired. The second principle of division is vertebrogenic or non-vertebrogenic. Vertebrogenic are a direct consequence of diseases of the spine (Bechterew's disease, tumors, injuries, osteochondrosis). Nonvertebrogenic suggest:
- external compression (muscle spasm, postoperative scars),
- vascular diseases leading to changes in their natural course (kinks, tortuosity),
- systemic diseases that cause vascular pathologies in the form of thrombosis, atherosclerosis, inflammatory arteritis.
A study of the causes of cerebral ischemia has shown that the largest number of cases occur due to pathologies of the blood vessels that supply it. Vertebral arteries, compressed due to pathological causes, can cause vegetative-vascular dystonia, high intracranial pressure and mental disorders.
The risk group for the disease includes both those who have congenital developmental anomalies and those who neglect their health.
Most of the possible provocateurs of asymmetry arise from systemic disorders of the body’s vital functions, which lead to the appearance of chronic, often incurable diseases.
Destructive processes, metabolic pathologies, and immune system failures also lead to the appearance of vertebral artery syndrome.
What is the danger of violations?
At the initial stage of the disease, in addition to speech and hearing disorders, a malfunction of the vestibular apparatus may occur. In an advanced state, without proper treatment, attacks of angina pectoris appear, leading to myocardial infarction. The prevalence of the disease and its appearance at an increasingly younger age make it necessary to prevent its occurrence.
The resulting dysfunction of the pharyngeal reflex can cause suffocation and spasmodic blockage of the airways. Pathology of brain stem cells causes seizures, drop attacks and loss of consciousness with a sudden fall to the floor. The longer the visit to the doctor, the process of diagnosis and proper treatment are delayed, the worse the manifestations of the disease become.
It is generally accepted that abnormal functioning of the vertebral arteries is not dangerous, but this is an initially erroneous opinion. The forms of this syndrome in the spine, especially the asymmetry of the diameter of the intracranial segments of the vertebral arteries, can lead to loss of functionality of the organs of vision and hearing, as well as to complete disability of the patient.
Diagnosis and treatment of asymmetry of the vertebral arteries
A preliminary diagnosis is made based on the collected history, palpation and external examination to find certain pain points. To confirm the medical conclusion, X-ray examination, Doppler ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain are prescribed.
Identified violations often cause urgent hospitalization. If impaired blood flow and asymmetry of the vertebral artery are caused by any chronic disease, it also requires immediate treatment.
The therapy process is carried out using a complex method using all means that can slow down the development of pathology. Medications stabilize the condition and improve blood flow. A course of vascular therapy is also prescribed.
Further use of medications is dictated by the root cause of the anomaly. Autogravitational therapy, massage, manual sessions, exercise therapy, in some cases - acupuncture, hirudotherapy, reflexology, physiotherapeutic procedures - everything is aimed at improving the patient’s condition.
Surgical intervention may be required if the syndrome is a consequence of neoplasms, intervertebral hernia or osteophytes in the spinal column and if conservative therapy fails.
Loading…
Source: https://medeponim.ru/ortoped/asimmetriya-pozvonochnyh-arterij
Treatment methods
Depending on the speed of the disease and the patient’s well-being, the following treatment methods may be prescribed:
- Medicines;
- physiotherapy;
- massage of the collar area and back;
- physical therapy (physical therapy);
- acupuncture;
- special diet.
Treatment is carried out using one of the listed methods, or in combination.
In addition to taking medications, physical therapy can help you feel better. A general practitioner or neurologist may prescribe:
- Electrophoresis;
- Valerian masks;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Laser therapy;
- Electrical stimulation.
Medication and physical therapy can be prescribed in combination.
Massage of the collar zone is prescribed to a patient with venous stagnation quite often. Massage is prescribed only in the absence of acute inflammation, otherwise this procedure can become extremely painful and harm the patient’s health.
Massage helps improve blood circulation, relieve muscle tension, and eliminate pain. It is advisable that the procedure be performed by an experienced massage therapist or chiropractor. The massage course lasts no more than 10 days.
Self-massage is also possible, 2-3 times a day: light stroking in the direction from the base of the neck to the head. Circular movements are also made from bottom to top to improve blood flow.
Therapeutic exercise is prescribed to a patient if there is a violation of the outflow in the brain, if there are no other contraindications and acute pain symptoms are relieved with the help of medications. Exercise therapy is aimed at strengthening the neck muscles and is initially performed in a sitting position to avoid dizziness and fainting.
Effective exercises to improve blood flow include:
- Smooth circular rotations of the head;
- tilts back and forth, left and right;
- turns the head and neck left and right.
REFERENCE. A course of exercise therapy can be taken at a specialized medical center, where a physical therapy doctor will select the necessary set of exercises, because to improve well-being it is necessary to strengthen the entire body as a whole.
Vertebrogenic headache (cervicocranialgia) is associated with the presence of SCH. The muscles of the neck and back are subject to tension and therefore pain occurs.
The causes of vertebrogenic headaches can be severe physical exertion, injuries to the back muscles, and as a result, protrusions, prolapses or hernias in the intervertebral discs.
The main symptom of vertebrogenic headaches is a noticeable limitation of movements of the head or neck, as well as pain that occurs when palpating areas of the neck.
Treatment is achieved with medications, and after acute symptoms are relieved using the above methods of restorative treatment.
The course of therapy is prescribed by a neurologist or vertebrologist.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! Massage for cervicocranialgia can lead to a deterioration in well-being and is prescribed only at the rehabilitation stage.
Hypertensive type of reg with severe obstruction of venous outflow
Rheoencephalography (REG) is a modern method for assessing the state of the brain, based on the electrical properties of nervous tissue. This procedure allows the doctor to identify abnormalities in the functioning of the central nervous system in the patient, and, first of all, to assess the tone of the vessels and the activity of blood flow in them. In various pathological conditions, for example, in case of impaired blood outflow, a hypertensive type of REG is possible, which has characteristic features on the rheoencephalogram. It is important to note that only the attending physician should interpret the results obtained. When trying to make an independent diagnosis, errors in the prescribed treatment are possible, which can cause not only side effects from the drugs, but also lead to rapid progression of the disease.
Rheoencephalography is performed on patients only in cases where they have certain symptoms and diseases. In all other cases, the study will not show any abnormalities, and the information will not be able to help the doctor decide on further diagnostic and treatment tactics.
REG is performed in the presence of the following conditions:
- persistent headaches that are not associated with any somatic diseases;
- hypertension for a long period of time;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia of any type, both in adults and children;
- transient neurological symptoms (visual impairment, hearing impairment), reflecting disturbances in the blood supply to the brain, etc.
In these situations, conducting an REG can help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis, as well as select the most optimal treatment.
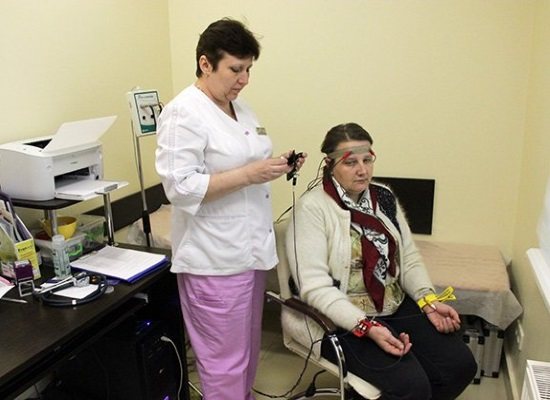
In complex diagnostic situations, when the doctor has difficulty making a diagnosis, REG can significantly simplify this task. To do this, it is necessary to correctly conduct the study according to the following protocol:
- the patient should take a horizontal position to ensure complete comfort. There should be no irritants in the room where the study is being conducted, as they can lead to a change in the resulting picture of brain activity;
- special electrodes that allow weak current pulses to be transmitted are placed on the head in strictly designated places. The surface of the electrodes should always be lubricated with electrically conductive gel;
- During the procedure, the patient should not worry or talk, as this can change the tone of the vascular bed due to an increase in the activity of individual structures of the central nervous system.
The attending physician must discuss the progress of the upcoming procedure with the patient in order to avoid possible distortions of the results.
Many patients ask their doctor a question when identifying a hypertensive type of REG, what is it? In order to get an answer, it is necessary to consider the main options for disturbances in the tone of venous and arterial vessels, which are detected using rheoencephalography.
There are several types of vascular tone patterns with EEG:
- dystonic waves that occur in cases where the outflow of blood through the veins is impaired, however, vascular tone is reduced and pulse filling is weak;
- angiodystonic waves occur during pathological processes in the wall of the vascular bed. Such changes lead to the fact that the elasticity of the arteries is significantly reduced, which is characterized by difficulty in blood flow through them and the appearance of a characteristic type of rheoencephalogram;
- the hypertonic type of waves is characteristic of vessels in which there is increased blood pressure (hypertension) with a simultaneous disruption of the outflow of blood through the veins.
One REG study is not enough to make a diagnosis. The doctor should take into account both the clinical picture of the disease and data from other laboratory and instrumental studies.
Hypertension in the vessels, associated with an increase in blood pressure in them, is characterized by characteristic changes in the rheoencephalogram. The doctor can identify chaotic lines that do not have any common features among themselves, with different shapes and sizes of their peaks.
A distinctive feature of such vascular dysfunction, accompanied by an increase in their tone, is the absence of a rhythm in the appearance of waves.
If a hypertensive type of REG is detected, the attending physician must conduct an additional neurological examination or refer the patient for consultation with a neurologist. As a rule, to identify the immediate cause of increased pressure inside the arteries and impaired venous outflow, angiography or magnetic resonance imaging is necessary. Such studies are completely safe and allow one to assess the state of the vascular bed in the brain, as well as the adjacent structures of the central nervous system.
REG is a modern method for assessing the central nervous system, namely cerebral vessels. Detection of abnormalities on the rheoencephalogram of the hypertensive type is an indication for consultation with a neurologist, followed by the appointment of additional examination methods. Based on the results obtained, a diagnosis is made and further individual therapy is selected for the patient.
For frequent headaches, dizziness, persistently high or low blood pressure, REG of cerebral vessels is prescribed.
Disturbances in the functioning of the brain lead to immobility, loss of ability to work, and a significant decrease in the quality of life. For this reason, it is necessary to identify the pathology as early as possible and begin its treatment.
The doctor writes a mysterious abbreviation in the direction and, without going into too much detail, sends home the patient who forgot to ask what it is - REG.
REG, rheoencephalography, is a non-invasive type of study of cerebral vessels, which is based on measuring the electrical resistance of tissues at the moment a weak high-frequency impulse passes through them. Blood is a conductor of electric current and, filling the vessels, reduces their resistance, as can be seen on the rheoencephalogram.
Clinical rheography is used to show cerebral blood supply. Another type of study, integral, is aimed directly at assessing vascular resistance.
The information obtained from REG allows you to see:
- tone of the walls of blood vessels;
- time of change in their resistance;
- elasticity;
- condition of arteries and veins;
- blood volume;
- viscosity;
- speed of pulse wave propagation.
The rheoencephalogram shows signs of impaired blood flow, but this is not enough to reliably say about the presence of a particular pathology and, moreover, to differentiate between diseases. In this regard, recently there has been a lot of debate about the advisability of conducting REG and replacing it with more informative research methods. So, if REG records a weakening of blood flow and an increase in resistance, then magnetic resonance imaging allows you to see the exact location of a blood clot or a damaged area of a vessel.
However, it is too early to write off rheoencephalography. It is indispensable in cases where MRI and CT are contraindicated: during pregnancy, lactation, the presence of pacemakers or other implants, obesity, claustrophobia, contrast agent intolerance, and the need to avoid radiation. Sometimes, to clarify the diagnosis, this procedure is complemented by echoencephalography.
REG is often confused with EEG. To carry out these studies, electrodes are placed on the head. The main difference is in the purpose: electroencephalography examines brain activity, and REG examines the state of blood vessels.
The rheoencephalographic examination method is absolutely safe and can be performed on patients of all ages, even small children. It is painless, does not require surgical intervention, and does not pose a risk to the patient’s health. The procedure takes a few minutes, and the result can be obtained almost immediately after its completion. REG provides accurate information about the condition of the arteries and veins of the brain.
An important factor is the availability of REG. The survey not only has a low price. Equipment for its implementation is usually available in all clinics and paramedic centers.
If these symptoms are present, the doctor gives a referral for rheoencephalography. This study is also prescribed as a complementary method in diagnosing the following diseases:
- arterial hypertension;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- stroke;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- cerebral ischemia;
- Parkinson's disease.
REG shows the dynamics of changes in the postoperative or post-stroke period.
Excitement and emotional stress affect the examination results, increasing vascular tone. This is a reflex process and is difficult to regulate. Therefore, the main rule is to try not to be nervous and calm down. There is nothing wrong with the planned procedure. Heavy physical activity should be avoided. Go out for research early, don’t run or rush. Plan your arrival time so that you have 15 minutes to recover. It is better to rest before the examination in a ventilated area where there are few people and noise.
The day before the study, the patient needs to stop taking medications that affect the condition of blood vessels. Don't smoke in the evening. You need to sleep at least 8 hours before the examination.
On the day of the examination, do not drink coffee, tea, energy drinks, alcohol, or eat caffeine-containing products (chocolate).
It is better to wash your hair before the procedure, do not use hairsprays or styling foams. Women should remove their hair so it will not interfere. You can take a napkin or towel with you to the procedure to remove any remaining gel after the procedure.
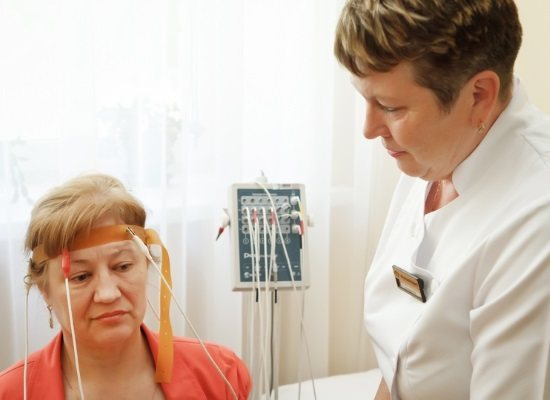
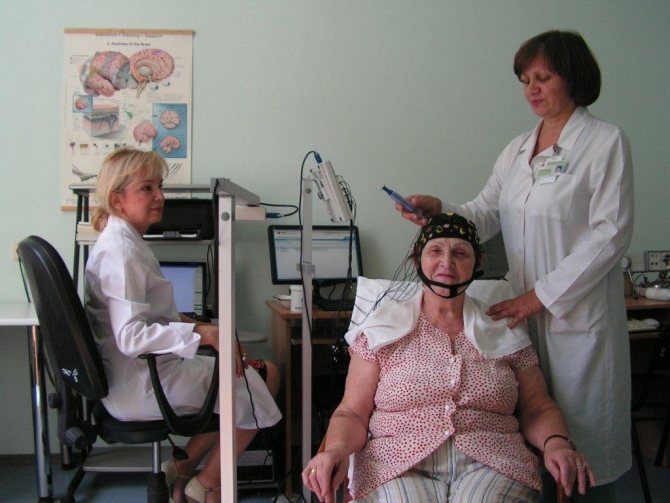
Rheoencephalography of cerebral vessels is carried out in a special room, protected from noise and bright light. For the study, a rheograph device is used, consisting of an electric current generator, electrodes (sensors), a detector for signal recognition and a writing device. The device has from 2 to 6 channels according to the number of areas being tested. Polygraphs are sometimes used. Modern devices are connected to a computer.
The patient is placed on a couch or seated in a chair. It is important that he is comfortable. Before starting, blood pressure is measured. An elastic band securing the paired electrodes is placed on the head so that it passes at the back of the head, above the ears and eyebrows. Instead, a cap with installed electrodes is sometimes used. The sensors conduct current and are usually made of steel, nickel or aluminum. A special gel or paste is applied under the electrodes to facilitate contact with the scalp. During the procedure, it is recommended to sit or lie with your eyes closed and do not move.
The nurse or doctor turns on the rheograph. One of the electrodes emits a signal, which, after passing through the brain tissue, is recorded by the opposite sensor. After this, the data is processed by the rheograph and transmitted to a monitor or paper tape in the form of a curve. The resulting graph, a rheoencephalogram, displays the characteristics of tissue electrical conductivity.
Electrodes are placed on the head depending on the area being examined. They are attached to the bridge of the nose and in the area of the mastoid processes to diagnose the internal carotid arteries. At the temples - to study the external carotid artery. On the back of the head and mastoid processes - to examine the vertebral vessels, on the forehead - to study the blood flow of the middle cerebral artery.
In some cases, when recording a rheoencephalogram, functional tests are performed:
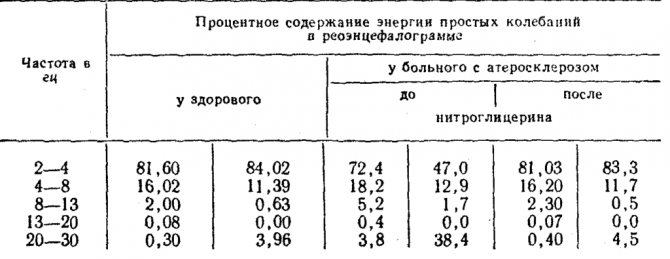
- Nitroglycerin test. The drug dilates the blood vessels, so the amplitude on the rheogram increases and is soon restored. If this happens, they speak of functional damage. Minor changes or their absence indicate an organic abnormality, for example, sclerotic vascular lesions.
- Carbon dioxide test. The patient inhales a 5% mixture of oxygen and carbon dioxide for 5 minutes. It reduces tone, dilates blood vessels, improves blood supply, and reduces peripheral vascular resistance.
- Study with clamping of any main vessel. The rapid restoration of the amplitude of the curve on the graph is a sign of the intact capabilities of the roundabout (collateral) blood flow.
- Hyperventilation test. The patient is asked to breathe deeply for 3-5 minutes. If at this time there are pronounced changes in the amplitude of the curve on the graph, they speak of high reactivity. Minor changes indicate decreased reactivity.
- Test with movement. The patient changes position, perhaps standing up or sitting down from a lying position. The change in amplitude on the rheogram indicates a functional disorder.
- Head turn test. The subject is asked to turn his head to one side for 5 minutes, then to the other. Asymmetry of the curves is a sign of stenosis or other irreversible changes in the vertebral artery.
Time: 10-15 minutes. With additional samples it may increase.
The main function of veins is to drain blood from tissues. Deterioration of such function may be physiological or pathological. The latter indicates the presence of pathology in the body. What to do if venous outflow is obstructed, what does this mean, is it dangerous for human life? The answer to all these questions will be given below.
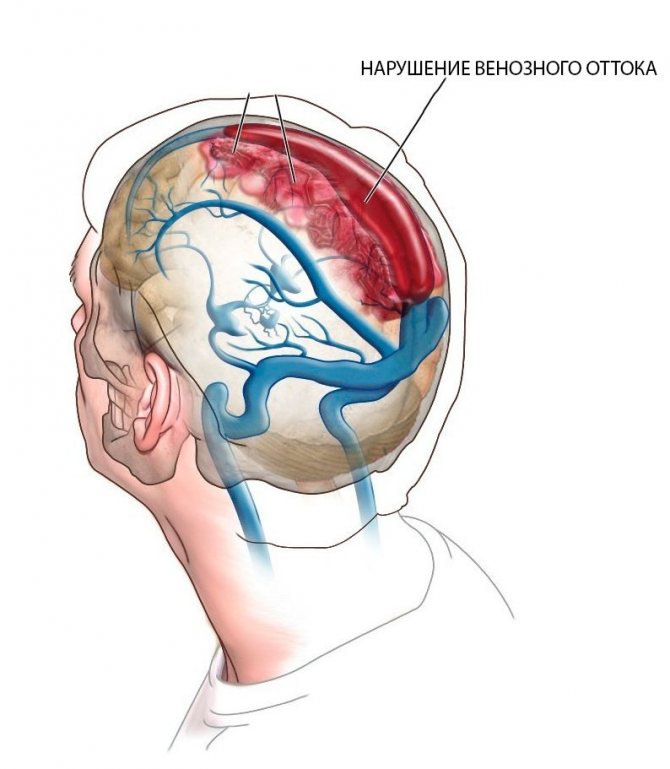
The main function of the circulatory system is to transport nutrients. When cells and tissues have received vital elements, it is necessary to remove all metabolic products. Veins are responsible for this. The main ones are:
Some pathologies lead to destabilization of blood flow. Venous discirculation of the brain is a deterioration in the outflow of blood from organs and tissues. It is a consequence of another disease.
In medical practice, there are three main stages of the disease:
- Primary changes, clinical picture and symptoms are completely absent.
- Typical disorders are accompanied by paraclinical pathology, allowing the patient to lead normal life activities.
- Encephalopathy. This condition requires urgent medical intervention. The microsymptoms of the disease manifest themselves chronically.
In addition, a violation of the outflow of venous blood can be primary or chronic. Chronic stagnation can cause a cessation of blood supply to the brain and damage to parts of the organ.
Venous outflow is obstructed, what does this mean, is it dangerous? This pathology has a very adverse effect on the human body. The reasons for its appearance are mainly acquired.
These include:
- Head injuries – any injury can lead to poor circulation. This includes surgical operations and the consequences of difficult childbirth.
- Internal hematomas - they form after stroke conditions with swelling of the brain of the head.
- Tumors are the most common cause of congestion. As the tumor grows, pressure occurs on various areas of the brain. What causes the venous lumen to be blocked?
- Underdeveloped veins - this may be a consequence of genetic predisposition or secondary factors. But if blood cannot flow normally from the brain to the heart, then discirculation occurs.
- Related diseases - the cause may lie in atherosclerosis, thrombosis or venous insufficiency.
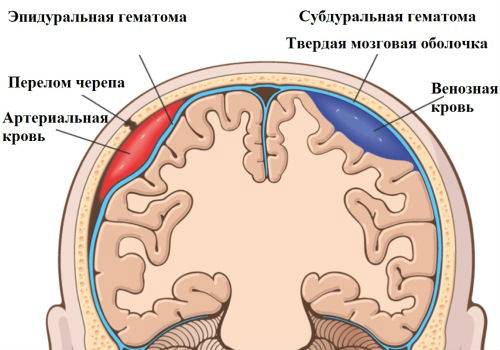
Any therapeutic measures may be temporary if the underlying cause of the disease has not been established.
Each stage of the disease has its own symptoms. Initially, the disturbance of venous outflow does not manifest itself in any way. And over time it becomes brighter:
- Meteopathy – sensitivity to changes in atmospheric pressure. When weather conditions change, the head feels tight and weak.
- High intracranial pressure – This is due to impaired blood flow, which makes blood circulation difficult, and the body tries to make up for the lack of nutrients through its own efforts. Over time, this symptom intensifies.
- Neurological symptoms. Children with impaired venous outflow experience mental disorders, seizures, and epilepsy. When the disease is in a severe stage, lowering the head becomes difficult.
- Adults lose consciousness and their vision becomes dark. If at the same time there is thrombosis of the venous sinuses, then the sense of space is lost, temporary stunning, painful sensations, and dizziness.
- In pregnant women, the disease can occur with symptoms similar to toxicosis.
- These manifestations are a signal that requires immediate contact with a specialist.

Until recently, brain dyscirculation was considered a minor pathology that did not interfere with human life. But today it has been proven that due to improper blood flow, the soft tissues of the brain begin to atrophy.
Also, do not forget that diagnosing this pathology indicates that another disease is present. Which caused this problem.
Treatment of this pathology is carried out by a neurosurgeon or neurologist. Rehabilitation is based on identifying the causes of the disorder and finding the location of the narrowing of the veins. This requires instrumental diagnostics:
- Dopplerography of blood vessels - this technique combines ultrasound and Doppler examination. The method shows the blood circulation rate and pathological changes.
- REG of blood vessels – assesses the general tone and condition of blood vessels. Diagnostics indicates the filling of the veins with blood and the intensity of blood circulation.
- MRI is a technique that makes it possible to find the pathology and the cause that causes it. The procedure is performed with contrast.
After the study, a course of treatment is prescribed. After which the symptoms, causes and consequences of the disease must be stopped.
When the disease just begins to manifest itself, vasodilator tablets can be used. But for patients with low blood pressure, patients with thrombosis or atherosclerosis, they are prescribed very carefully.
After injuries that were the result of stagnation, neuroprotectors, vitamins and substances that increase tone are prescribed intramuscularly.
Patients suffering from this disease should not drink alcohol or junk food, or smoke.
You can also use yoga and Pilates as exercise therapy to improve your condition. Classes must be conducted under the guidance of an experienced instructor.
Video: Exercises for cerebral circulation:
Classification of venous discirculation according to Berdichevsky
The scientist identified two main forms of disturbance of venous outflow.
It is expressed in disruption of circulatory processes in the brain due to changes in the tone of the veins.
This may be a consequence of TBI (traumatic brain injury), hyperinsolation, alcohol or nicotine intoxication, hypertension and hypotension, diseases of the endocrine system, venous hypertension, etc.
It develops when there are mechanical difficulties in the outflow of venous blood. That is, in the cranium, venous outflow is so difficult that this leads to the extinction of the mechanics of the process. In this case, it is impossible to do without outside intervention.
Causes of pathology
The causes of disturbances in venous outflow can be serious traumatic brain injuries with bone fractures, as well as the formation of internal hematomas; previous strokes with subsequent cerebral edema; tumors leading to compression of the brain and blood vessels; reduction or underdevelopment of the network of veins, etc.
If we talk about external causes that lead to difficulty in the venous outflow of the brain, then there may be the following disorders: blockage of the veins, the occurrence of tumors in the cervical region, strangulation lesions, injuries to the abdomen and chest, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, prolapse of spinal discs, etc. d..
In other words, the causes of cerebral venous discirculation can be both in the skull and outside it - in the spine, abdomen, neck. It is important to note here that with any problems with the spine, the consequences are global and disturbances in the functioning of organs appear in the most unexpected ways. After all, when an intervertebral disc protrudes or prolapses, blood flow is disrupted, and this leads to serious consequences.
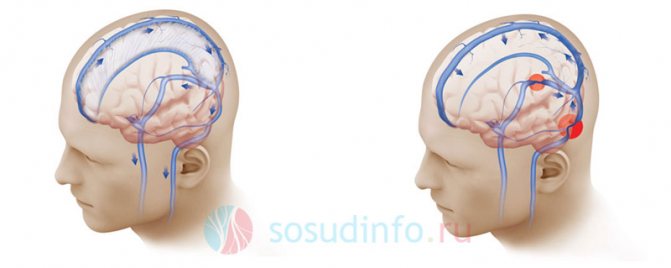
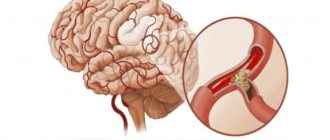
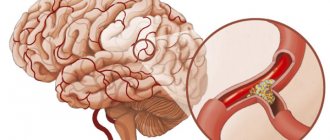
Figure: normal venous circulation of the head (left) and impaired due to vessel narrowing (right). This degree of pathology threatens intracranial hypertension and other severe complications.
Signs of asymmetry of blood flow in the vertebral arteries, diagnostic methods and treatment of pathology
Asymmetry of blood flow through the vertebral arteries is a rather unpleasant ailment. It appears due to improper blood supply to the human brain, as a result of damage to the main arteries.
It also has another name - vertebral artery syndrome, as well as vertebrobasilar syndrome. This disease has become quite widespread lately. Previously, it affected the elderly population, but now this syndrome increasingly affects people between 20 and 30 years of age.
Symptoms of the disease
Hypertension, vestibular disorders, headache are signs of vertebral artery syndrome
Without proper diagnosis, it can be quite difficult to recognize the symptoms of asymmetry of blood flow in the vertebral arteries. This is not due to the fact that such a disease does not manifest itself in any way. On the contrary, the symptoms of vertebrobasilar syndrome are very similar to other diseases.
This begins with osteochondrosis, which is very common among different groups of the population, and ends with diseases that the patient can hardly somehow associate with the spine. That is why, as soon as at least one of the symptoms listed below is detected, you should immediately contact a medical facility for examination.
Very often, people with vertebrobasilar disease may experience a headache. It manifests itself either in attacks that occur with the same frequency or has the same basis. Mostly pain is concentrated in the occipital region.
But besides this, they can spread to the temporal region and even the forehead. Vertebrobasilar syndrome very often begins to increase over time. On the skin, in places where hair grows, the discomfort increases with touching this area.
All this can come together with a burning sensation.
Another symptom of the vertebrobasilar symptom is a strong crunching of the vertebrae in the neck with any turn of the head.
If a patient has this pathology, then first of all, doctors recommend that such patients change their lifestyle to a more active one. It is largely thanks to this method that the majority of those who have asymmetry of blood flow through the vertebral arteries can easily overcome such an unpleasant illness.
Other signs:
- blood pressure rises
- there is a strong noise and ringing in the ears
- the patient periodically vomits
- my heart hurts
- constant feeling of overwork
- dizzy, up to a state similar to fainting
- the patient loses consciousness
- severe neck tension or pain in that area
- vision is impaired
- eyes and ears hurt
Sometimes, in addition to this syndrome, VSD may develop, as well as increased pressure inside the skull. In addition, very often the arms or legs, especially the fingers and toes, go numb.
Among other things, signs such as mild psychological abnormalities in the patient may appear.
But it should be remembered that all these symptoms do not appear immediately, so some patients may delay the treatment of such an unpleasant illness.
Causes of occurrence and risk groups
There are many factors that can cause vertebral artery syndrome
The causes and risk groups for this disease can be completely different:
- The most important reason for this disease is the not entirely uniform development of a pair of arteries, which leads to asymmetry in blood flow. This type of pathology cannot be cured by modern medicine. Often the patient lives with such an illness until death, without feeling the slightest inconvenience.
- Not very stable vertebrae in the cervical spine can also cause this syndrome. They gradually lead to the destruction of the discs in it and to their weakening. It can develop either as a result of an injury in the patient (for example, after an accident) or gradually, due to lifestyle. In the second case, the cause of blood flow asymmetry is a sedentary lifestyle, without sports or regular physical activity.
- Another reason for the occurrence of this disease is associated with extravasal compression. And she, in turn, appears due to hernias and injuries. Also, this pathology can develop into other diseases.
- Trauma received during childbirth is another factor that causes vertebrobasilar disease.
- Osteochondrosis is a very common cause of vertebrobasilar symptoms.
Torn arteries of the spine can also be the beginning of the development of such a disease. This pathology is quite dangerous, and in many cases can lead to strokes.
It is for this reason that patients who have been diagnosed with this syndrome can almost instantly become at risk.
This category of sick people should definitely monitor their health with special scrupulousness. An active lifestyle is especially recommended for them.
If you have any of the pathologies listed above, you should start playing sports or at least exercising. In addition, it is necessary to undergo examination and diagnosis once every few years to identify such a disease at the initial stage.
Diagnostics
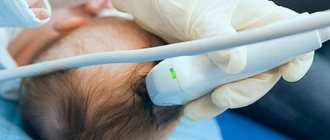
Ultrasound dopplerography of neck vessels - effective diagnosis of pathology
During the initial examination of the patient, the specialist pays great attention to the absence or presence of such a syndrome. To do this, he examines the occipital region, and in particular, checks muscle tension in this place. Asks the patient if the skin on the head or cervical vertebrae is painful during pressure.
Today, the diagnosis of such a syndrome is carried out not only by visual examination, but also by Doppler ultrasound (USDG).
Thanks to this method, vessels and arteries are examined, their condition is revealed, as well as any disorders present in the patient’s body.
Among other things, in some cases the specialist uses radiography to make the correct diagnosis.
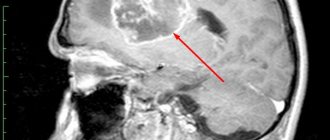
If during such a procedure at least minimal exacerbations are detected, then the patient is sent for an MRI of the brain.
In some cases, after the results of the examination, the patient may be urgently hospitalized.
Pathology treatment method
Only a doctor can prescribe effective treatment for vertebral artery syndrome
Treatment of blood flow asymmetry should occur strictly only under the supervision of a specialist, even if this occurs at the patient’s home.
Therapy in all cases must have an integrated approach. It includes the methods listed below. But the doctor, at his discretion, can add or change anything:
- course of vascular therapy
- prescription of therapeutic exercises
- drugs that improve blood flow
- medications that normalize the patient’s general condition
- a course of manual therapy (preferably carried out by health workers)
- carrying out autogravity
In addition to the methods listed above, other non-drug methods are also practiced. But every patient with such an unpleasant disease must remember that self-medication is fraught with unpleasant consequences. That is why treatment should be prescribed by a specialist on an individual basis. Everything will depend on the cause of the disease and its stage.
If a patient has this pathology, then first of all, doctors recommend that such patients change their lifestyle to a more active one.
It is largely thanks to this method that the majority of those who have asymmetry of blood flow through the vertebral arteries can easily overcome such an unpleasant illness. But we should not forget that such therapy must be used in combination with other methods. It is then that the treatment will have the desired effect.
Source: https://DiagnozLab.com/analysis/immunolog/antiphospholipid/asimmetriya-krovotoka-po-pozvonochnym-arteriyam.html
Symptoms of cerebral venous circulation
Any disease manifests itself with certain symptoms. If we talk about venous discirculation, it manifests itself as a dull headache, which is most pronounced in the morning. A person suffering from this disease has difficulty getting out of bed. It seems to him that his body is not listening, he feels lethargic, as if he had not slept at all. Painful sensations increase while moving the head in different directions. When changing atmospheric pressure, as well as temperature, pain can also intensify. Excitement, stress, and alcohol consumption also often cause pain. The pain is accompanied by noise or buzzing in the head, cyanosis of the cheeks, lips, nose, ears, mouth appears, the lower eyelids swell, and the veins in the fundus dilate. These symptoms are most pronounced in the morning immediately after waking up.
As for venous pressure, it is in the range of 55-80 mmH2O. Art., and the arterial value most often corresponds to the normal value.
Symptoms of impaired venous outflow may include dizziness, a feeling of dizziness, darkening of the eyes, numbness of the limbs and fainting. In some cases, seizures of epilepsy and mental disorders occur. If venous congestion is pronounced, then the patient will not be able to lower his head or take a horizontal position.
If the doctor decides that there is a possibility of a violation of the venous outflow, the pressure in the ulnar vein is measured, and an X-ray of the skull and venography are also performed.
Currently, most adults exhibit symptoms of this disease, even in a mild form. It manifests itself especially strongly in the spring-autumn period, when the season changes. Some endure the inconvenience, trying to live their previous lives, while others resort to injections of special drugs that help dilate the blood vessels on their own. We'll talk about some drugs a little later.
Symptoms and manifestations of the disease
When the first symptoms of impaired blood flow in the head appear, you should consult a specialist and begin treatment. Timely therapy will help avoid serious deviations and complications.
Any brain pathology is accompanied by severe symptoms:
- Headache (cephalgia). It can intensify with slight turns of the head.
- Intense headache (cephalalgia) that occurs due to stressful situations or after drinking alcohol.
- Unpleasant sensations and pain near the ears.
- Noise and unpleasant sounds in the head.
- Dilated veins of the eyeball.
- Headache that occurs without any reason, mainly before lunch.
- The face becomes bluish.
- There is swelling of the legs.
- The patient often loses consciousness.
- There is numbness in the arms and legs.
- Frequent mental disorders.
- Legs and arms lose their sensitivity.
Not all symptoms that may arise due to a violation of the venous outflow of the brain were presented above. Signs of pathology will depend on the general condition of the patient and the progression of the disease. Dementia is very common in elderly patients, but this symptom is also a sign of many other abnormalities, so it is necessary to undergo a professional evaluation.
Venous outflow of the brain can provoke ischemia of brain tissue and other serious complications.
What to do if symptoms of venous outflow disturbance are detected?
If you have symptoms of the disease, do not panic. In the early stages, you can easily correct the functioning of the blood vessels in the brain. Moreover, sometimes it is enough to change the lifestyle that leads to a deterioration of the general condition in order to get rid of the disease. In any case, there is no need to delay, but if possible, turn to specialists. With their help, the necessary examinations will be carried out and a course of treatment will be prescribed.

Treatment
To make an accurate diagnosis of whether the patient’s venous outflow from the brain is impaired or not, studies must be carried out. The most accurate data can be obtained after undergoing an MRI. This drug is located in every major city, it is served by a specialist trained in specialized courses. If abnormalities are found in the jugular veins, then this may be the reason why headaches and some associated symptoms occur. When diagnosing blood flow disorders, attention is paid to the fundus of the eye, where stagnation may occur.
Drugs that improve venous outflow
Currently, there are drugs that improve venous outflow. They can help not only improve outflow, but also normalize the functioning of blood vessels. Venotonics are modern drugs that help improve blood flow. They are also good for prevention.
What effect do venotonics have on the human body:
- Strengthening blood vessels. The permeability of blood vessels is normalized, their fragility decreases, swelling decreases, microcirculation improves;
- Strengthening the general tone in the veins, giving them greater elasticity;
- Fighting inflammatory processes with their further prevention;
- Increased overall tone.
At the moment, the most common herbal venotonics are:
In any case, these drugs should be used after consultation with a doctor. Do not neglect to follow the instructions for use of the drugs.
- Massage;
- Phytotherapy;
- Relaxation;
- Full sleep;
- Regular contrast shower;
- Frequent and moderate exercise;
- Long walks outdoors.
Exercises to help improve venous drainage
In some cases, when venous outflow is impaired, simple and accessible exercises can help. Sometimes it is enough to work on your neck to get rid of pain within a few weeks. In this case, exercises to improve venous outflow can be done several times a day, without particularly disturbing your rhythm of life. They will take about ten minutes to complete.
The purpose of the exercise is to improve venous outflow from the head. You need to sit on a chair, resting your hands on the back. The muscles of the legs and arms are relaxed, the head is thrown back freely. Try sitting in this position for a minute. Breathing is free and deep. After you finish the exercise, walk a little and repeat it twice.
The exercise can be performed standing or sitting. The main thing is to relax and lower your head to your chest. As you inhale, begin to lift your head up, looking at the ceiling. Then stretch your neck, as if an invisible thread is pulling you up. When you lower your head, exhale. The exercise is repeated up to eight times depending on how you feel.
The exercise is performed in a relaxed state. Start drawing an imaginary figure eight using the top of your head. One circle to the left, the other circle to the right. Breathing is free, the body is relaxed. The exercise is repeated up to six times.
Sit straight on a chair and clasp your fingers under your chin. While exhaling, tilt your head down, pressing on it with your palms and the back of them. As you inhale, tilt your head back, resisting the movement with your palms placed on the back of your head. The exercise is repeated up to twelve times. It is not recommended to hold your breath.
These exercises help a lot with asymmetry of venous outflow, as it often occurs when the neck is incorrectly positioned or pinched in the cervical spine. These four common exercises can bring a lot of benefits.
Yoga classes are good for improving venous outflow. In this practice there are many asanas aimed at strengthening blood vessels and improving blood flow. In addition, specific breathing through the larynx during exercise helps pump air, which in itself increases blood flow.
Running is great for improving overall blood flow. Considering that running is not accessible to everyone, you can start with regular long-distance walking. It’s good if walking and running are done in a place with clean air and beautiful views of nature. This will have a double effect.
Some argue that lifting weights can not only help prevent venous dyscirculation, but also cure it. Most likely, those who affirm this postulate mean the early stages of the disease, when everything is not yet advanced. In any case, before you start practicing physical activity, consult your doctor.
What about the bathhouse? In a bathhouse, a sharp change in maximum heat and cold has a strong effect on the blood vessels. Yes, blood flow increases, but if the vessels are weak, then harm can be done to the body. Still, the bathhouse is more suitable for prevention, as a means of pumping blood and strengthening the vascular system.
About the benefits of exercise
Impaired venous outflow with cervical osteochondrosis, as well as in some other cases, may require the patient to perform special exercises.
Important: their frequency, duration and quantity should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Examples of such exercises:
- Number 1: sit on a chair or stand, trying to relax. We lower our head to the sternum. As you exhale, we try to stretch our neck up as much as possible and also raise our head as high as possible. As you exhale, on the contrary, we lower our head to our chest, but without straining.
- Number 2: sit on a chair, rest your hands on the back. Having relaxed, we tilt our head back, hold it for 60 seconds, get up and walk for several minutes. We sit down again and do the exercise, repeat several times.
- Number 3: Make a figure eight with the top of your head six times. The body should be relaxed, the eyes should be closed, and we try to maintain even and calm breathing.
Violation of venous outflow is a serious problem, but by correcting your lifestyle, paying enough attention to physical activity and performing special exercises, as well as taking medications prescribed by an experienced doctor, you can live for years and decades, and a full life.
Vessels
Superior (Inferior) Thyroid Artery: Embolization, Thyrocervical Trunk
Feb 03, 2020 Kokh V. A.
2976
Vessels
Vasodilators for Osteochondrosis of the Neck: Medicines, Tablets
Feb 03, 2020 Kokh V. A.
7466
Vessels
Problems at an early age
Unfortunately, situations where venous outflow is significantly obstructed in a child occur frequently. The child suffers greatly from this, especially if he is not yet a year old. He often screams in response to pain. Parents do not always think of contacting a specialist who can conduct an examination. In the early stages, some diseases are treated easier and faster.
If the cause of the baby’s frequent cries is not recognized in time, he will subsequently be forced to limit himself in exercise. In modern schools you can often find healthy-looking children who study well, but often experience severe headaches, especially during sudden changes in weather. Often during physical education classes they are forced to recover for a long time after performing exercises, since venous outflow is difficult and they have to wait some time for the dizziness to pass.
Prospects

Since humanity discovers new diseases every year, it is difficult to imagine what will happen to our health and medicine in ten to twenty years. Cerebral venous dysfunction is already causing a lot of problems, as the number of patients with this disease is growing. As mentioned above, there are many reasons. One of the main reasons is difficult childbirth. Children who have suffered a difficult birth often have many deviations in health and further development. They have to try too hard to feel normal compared to others. Medicine can help here, but not completely. Still, impaired lymphatic drainage is not always completely restored. Treatment requires a bit of luck and the patient’s perseverance. Not everyone will be able to take charge of themselves, change their previous harmful lifestyle - give up alcohol, tobacco, eat huge amounts of junk food, start playing sports.
Venous dysgemia is observed even in athletes who perform in professional sports. The desire to achieve high results and perseverance help them achieve their goals. Only occasionally do you find information in newspapers and on the Internet that another young athlete lost consciousness during a competition or was out of action for an indefinite period of time.
We are all at risk, so it is extremely important to lead a healthy lifestyle, but without much fanaticism. Then the risk of cerebral venous discirculation disease will be reduced to zero.
Asymmetry of cerebral vessels
Asymmetry in the area of vertebral blood vessels is a general concept that includes vertebrobasilar syndrome, that is, a violation of the blood supply to the brain as a result of dysfunction of the vertebral arteries.
Of the four major streams that provide blood supply to the brain, vertebrates realize a relatively small percentage of the total amount of blood circulated. The remaining more significant part falls on the share of sleepy ones.
Asymmetry of the vertebral arteries, resulting from exposure to a negative etiology, is caused by obstruction and uneven blood flow in the vertebral arteries.
It occurs as a result of a decrease in the diameter of one or more of them. Reducing the lumen leads to the inability to supply the brain with oxygen and nutrients.
As a result, negative symptoms appear.
The signs of vertebral artery syndrome are similar to those of other diseases, so recognizing it requires a careful diagnostic process. The danger is that the syndrome is only part of a general pathological process, which can be:
- osteochondrosis with accompanying negative manifestations,
- atherosclerosis,
- neoplasms,
- bone and cartilaginous pathologies of the spinal column, leading to compression, narrowing of the lumen and significant deterioration of a person’s condition.
Some of the pathologies that cause impaired blood flow and accompanying negative symptoms can be life-threatening. They require emergency surgery.
The signs that accompany vertebral artery syndrome are often similar to those of other diseases. The patient may experience sudden changes in pressure (increase or decrease), high intracranial pressure, pain in the ears and eyes, blurred vision and hearing, and a burning sensation in the neck.
Along with the progression of the lesion, dizziness, lightheadedness, sometimes fainting, nausea, and less often vomiting, numbness of the fingers and psycho-emotional disturbances may appear. Few people associate all the symptoms, so contacting a doctor occurs already at a late stage of development, when the diameter of the vessel is significantly narrowed.
Any negative symptoms indicating the presence of pathology in the body should not be ignored. Very often attributed to overwork and physical exertion, poor health is a signal from the body about a serious illness.
The prerequisites for the occurrence of pathology are conventionally divided into congenital and acquired. The second principle of division is vertebrogenic or non-vertebrogenic. Vertebrogenic are a direct consequence of diseases of the spine (Bechterew's disease, tumors, injuries, osteochondrosis). Nonvertebrogenic suggest:
- external compression (muscle spasm, postoperative scars),
- vascular diseases leading to changes in their natural course (kinks, tortuosity),
- systemic diseases that cause vascular pathologies in the form of thrombosis, atherosclerosis, inflammatory arteritis.
A study of the causes of cerebral ischemia has shown that the largest number of cases occur due to pathologies of the blood vessels that supply it. Vertebral arteries, compressed due to pathological causes, can cause vegetative-vascular dystonia, high intracranial pressure and mental disorders.
The risk group for the disease includes both those who have congenital developmental anomalies and those who neglect their health.
Most of the possible provocateurs of asymmetry arise from systemic disorders of the body’s vital functions, which lead to the appearance of chronic, often incurable diseases.
Destructive processes, metabolic pathologies, and immune system failures also lead to the appearance of vertebral artery syndrome.
At the initial stage of the disease, in addition to speech and hearing disorders, a malfunction of the vestibular apparatus may occur. In an advanced state, without proper treatment, attacks of angina pectoris appear, leading to myocardial infarction. The prevalence of the disease and its appearance at an increasingly younger age make it necessary to prevent its occurrence.
The resulting dysfunction of the pharyngeal reflex can cause suffocation and spasmodic blockage of the airways. Pathology of brain stem cells causes seizures, drop attacks and loss of consciousness with a sudden fall to the floor. The longer the visit to the doctor, the process of diagnosis and proper treatment are delayed, the worse the manifestations of the disease become.
It is generally accepted that abnormal functioning of the vertebral arteries is not dangerous, but this is an initially erroneous opinion. The forms of this syndrome in the spine, especially the asymmetry of the diameter of the intracranial segments of the vertebral arteries, can lead to loss of functionality of the organs of vision and hearing, as well as to complete disability of the patient.
About pathology
Asymmetry of blood flow through the vertebral arteries is a phenomenon in which the blood supply to the brain is disrupted due to dysfunction of the vertebral arteries.
Reference. The pathology is also known under such terms as vertebral artery syndrome, vertebrobasilar syndrome.
The blood supply to the brain is provided by 4 large blood vessels (carotid and vertebral). The vertebral arteries account for a relatively small volume of the total blood flow.
Source: https://golovnoj-mozg.ru/zabolevaniya/krovoobraschenie/asimmetriya-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga