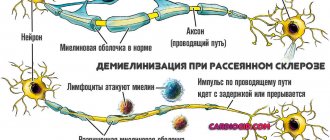
When stage 4 brain cancer is diagnosed, how long do patients live is the most important question. It is impossible to cure the disease at this stage, and the goal of therapy is to maximize human life. With effective intervention, real results can be achieved in almost a quarter of all cases of pathology.
Yes, the fourth stage of the development of the disease can be considered a death sentence, but you cannot give up completely - you have to fight for life, and knowledge of the problem can help with this.
Types of brain tumors
At the last stage of development, many malignant neoplasms are capable of developing into others. At the moment, several types of brain cancer are known, but most are still poorly understood.
Brain tumors are usually differentiated by the cells from which they form:
- neuroma (tumor of the cranial nerves);
- glioblastoma (has subtypes according to localization and degree of benignity) at stage 4 of brain cancer grows into other tissues and becomes multiform;
glioblastoma
- a multiforme tumor (each degree of this type of cancer has new features) is closely related to the circulatory system, which complicates the operation - heavy bleeding is possible;
- gliosarcoma (sarcoma is formed in connective tissues, glioma - from nerve tissues);
- pituitary adenomas (tumors from glandular tissue cells);
- meningiomas (malignant tumor of the meninges).
Also distinguished:
- primary brain cancer (formed from brain cells);
- metastatic (malignant tumors in other organs give metastases to the brain) is more common than primary.
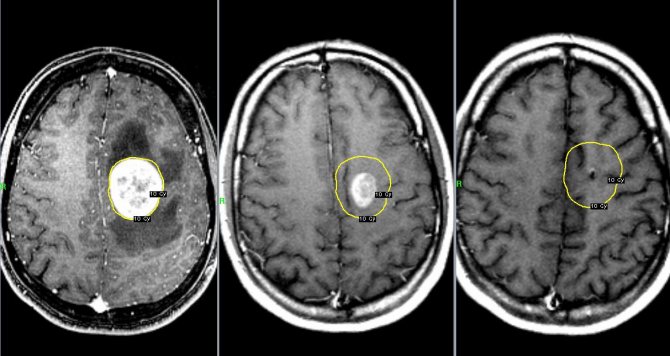
brain metastases
Consequences and prognosis
Once the diagnosis is made, surgery is considered the best treatment option. Excision of the tumor provides a 40% survival rate.
The prognosis of blastoma directly depends on the degree of malignancy, stage and characteristics of the tumor. Benign tumors have a favorable course and can be completely cured. Malignant tumors of the brain most often manifest as metastases to the bones and liver and have an average five-year survival rate, despite treatment.

Clinical picture of the disease
What are the signs of brain cancer?
- focal;
- general cerebral.
Focal symptoms occur due to an increase in tumor in the cranial cavity. The tumor puts pressure on the brain tissue, which can cause it to collapse. General cerebral symptoms occur when the disease begins to progress.
The symptoms and mechanism of development of the disease depend on the location of the tumor in the brain. Each part of the brain controls certain organs and systems of the body, so not all symptoms can be observed in the early stages of cancer development.
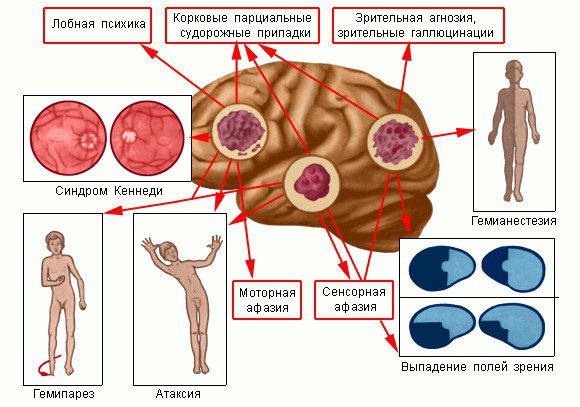
symptoms
Focal symptoms of the disease
- Decreased sensitivity (impossibility to determine body position, decreased pain and sensitivity threshold);
- Memory impairment (memory loss due to destruction of the cerebral cortex, absent-mindedness);
- Personality changes (social characteristics and intelligence);
- Hallucinations (visual and auditory);
- Impaired hearing and speech perception (if the tumor puts pressure on the auditory nerve, the patient is unable to distinguish human speech, he hears only noise);
- Visual impairment (damage to the optic nerve can cause complete or partial blindness, inability to recognize objects);
- Speech disorders (handwriting may change, speech becomes slurred);
- Paralysis (due to damage to the transmission pathways of motor impulses to the limbs);
- Dysfunction of the autonomic system (fatigue, weakness, drowsiness, dizziness);
- Deterioration of coordination (changes in gait, inability to make precise movements);
- Epileptic seizures and convulsions;
- Hormonal imbalance;
General cerebral symptoms of the disease
- Constant headaches (severe, not relieved by non-narcotic medications; the most common symptom of brain cancer);
- Nausea, vomiting (present constantly, the patient cannot drink or eat);
- Dizziness (disturbance of the vestibular apparatus, feeling of body movement at rest).
The essence of pathology
In fact, brain cancer is a set of formations of different nature that affect this organ. It is caused by an abnormal change of healthy cells into malignant ones, followed by their growth and division. They can also be caused by cancer processes occurring in other organs of the body.
The disease itself is accompanied by severe symptoms:
- decreased coordination;
- loss of sensitivity to external stimuli (temperature, pain);
- memory loss;
- epileptic seizures;
- loss of vision and hearing;
- impaired speech, ability to write and speak;
- mental disorders accompanied by abnormal reactions to everyday reactions;
- decreased mental abilities;
- heart and respiratory rhythm disorders.
At the fourth stage, total destructive processes occur. The medulla is subjected to extreme pressure from the tumor. In this case, unbearable headaches arise that cannot be relieved with analgesics. Disorders from the gastrointestinal tract are observed, sometimes complete refusal of food. At the terminal stages of the course, convulsions appear.
INTERESTING fact: Hemlock for cancer, application according to Tishchenko’s method
Diagnostics
Oncology is diagnosed only after a histological examination of the tumor. Diagnosis of brain cancer is difficult due to its location in the cranial cavity. Therefore, the procedure for taking a biopsy sample is a complex neurosurgical operation.
Diagnosis of the disease usually occurs in stages:
- the patient consults a therapist with progressive symptoms;
- hospitalization or outpatient treatment is carried out;
- When neurological symptoms (seizures) appear, the patient undergoes an MRI to identify the source of cancer.
tomography
MRI is a mandatory research method. Only this procedure can reveal the location of the tumor, its size and determine the condition of the tissues around it. The malignancy of a tumor can be judged only by histology; MRI studies provide only approximate results.
What is inoperable cancer?
There are 4 stages of brain tumor. However, head cancer has a peculiarity - it is not necessary for every tumor to go through all 4 stages of development. The first stage is characterized by a benign course. The second is characterized by slow growth and lack of aggressive growth. The third stage of brain cancer is characterized by rapid growth and aggressiveness of the malignant process. The fourth stage of the tumor is characterized by an aggressive course and rapid growth. This stage of cancer is considered the last and the most severe.
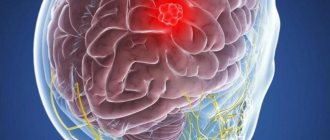
Of the brain tumors at stage 4, glioblastoma is most often recorded. This malignant formation initially belongs to an aggressive form of cancer. It develops from stellate glial cells and is characterized by a severe course and malignant aggressiveness. Glioblastoma forms in the brain primarily or secondarily when tumor cells are carried through the bloodstream from other organs. Stage 4 brain cancer is considered inoperable. This means that the tumor cannot be surgically removed.
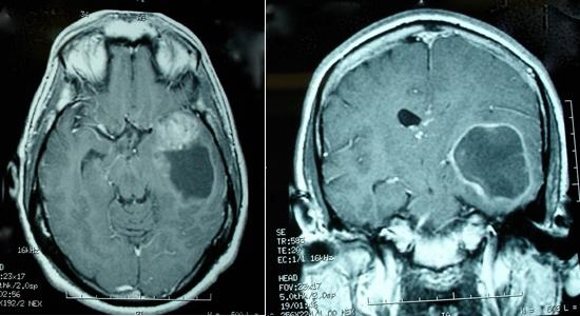
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive form of brain tumor
Treatment
Treatment for brain cancer at stage 4 is carried out, but even at stage 3 it can be considered inoperable. Therapy is aimed not so much at treatment as at alleviating the symptoms of the disease. A person experiences very severe pain, therefore, in the last stages of cancer, the prescription of potent narcotic drugs, which have a sedative and analgesic effect, is indicated.
The main methods of treating brain cancer:
1. Drug therapy (aimed at relieving symptoms):
- prednisolone (reduces brain swelling);
- antiemetics;
- sedatives (for severe mental disorders);
- anti-inflammatory (non-steroidal, relieve pain);
- narcotic drugs (morphine).
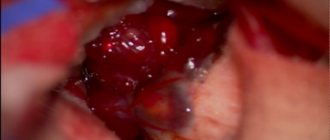
2. Surgery
The most effective method of treatment. Such operations are highly complex and traumatic. Often, surgery cannot be performed due to the large size of the tumor or its proximity to important areas of the brain.
3. Cryosurgery
This is freezing the tumor without harming healthy tissue. Used when surgery is not possible.
4. Radiation therapy
This is the effect of ionizing radiation on malignant brain cells. Irradiation is carried out locally. Sometimes complete irradiation of the entire brain is used when the tumor is very large or has metastasized. The treatment is very difficult for patients to tolerate; accompanying drug treatment is indicated.
5. Chemotherapy
It has a great effect in combination with radiation therapy. For chemotherapy, alkylating drugs (antitumor drugs) are used. Antiemetic therapy is indicated.
Treatment methods for glioblastoma
The main treatments for blastomas include:
- Chemotherapy (the use of drugs that inhibit cell growth);
- Radiation therapy and radiosurgery;
- Surgical removal of the tumor.
Surgery is a common treatment method to prevent the occurrence of metastases. But surgery is considered ineffective in case of tumor metastasis, and it is also not always possible due to the dangerous location of the tumor (if there is a possibility of damaging nearby vital tissue membranes). If the formation is located in a place that allows intervention, then oncologists prescribe surgery.
Radiation therapy and radiosurgery are also widely used in the treatment of the disease. These techniques involve exposing the affected cells to ionizing radiation without affecting healthy brain tissue. The course of therapy is 1 month.
Chemotherapy is also used to treat blastomas. This method blocks the growth of the tumor process and reduces its activity. The most commonly used drug is Temozolomide (well tolerated even by elderly patients), and Avastin is also prescribed, which disrupts the development of neoplasm vessels.
Temozolomide is prescribed daily during radiation therapy, and after completion of the course as maintenance treatment for 5 days every 4 weeks. There are 6 courses in total.
Immunotherapy used for blastoma is aimed at activating the defenses of the affected organism.
To relieve cerebral symptoms, antiemetics, sedatives and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as glucocorticoids and narcotic analgesics are used. Of the NSAIDs, Celebrex (mnn: celecoxib) is considered the most effective; its cheaper analogues include the drug Dilaxa.
When stage 4 brain neoplasm is detected, only maintenance therapy is indicated, since the patient is considered inoperable.

As a rule, complex therapy is indicated, using several methods at once.
Symptoms of inoperable cancer
Signs of advanced stage brain cancer depend on the location and size of the cancer tumor. As the process progresses, many brain functions are disrupted or lost.
As a result, the following symptoms of inoperable cancer are revealed:
- severe headaches that are not relieved by non-narcotic painkillers;
- indomitable vomiting of cerebral origin appears without previous nausea;
- loss of orientation in space and memory impairment. The patient does not recognize close people, does not navigate in the home environment and on the street;
- impairment or loss of pain, temperature or tactile sensation;
- numbness in one or more limbs depending on the location of the tumor;
- asymmetrical pupils – one pupil is wider than the other;
- loss or disturbance of balance, unsteady gait;
- seizures;
- dizziness;
- visual and hearing impairment with the appearance of visual and auditory hallucinations.
Vomiting of central origin is associated with increased intracranial pressure, as well as intoxication due to tumor disintegration.

Brain cancer headaches are often worse in the morning
Headaches due to brain cancer are accompanied by vomiting without subsequent relief.
Patients experience mental disorders that manifest as deviations from normal behavior. Cases have been recorded of patients being thrown out of windows. Impaired consciousness in advanced brain cancer manifests itself in the form of stupor or loss of consciousness up to a coma.
Dizziness in inoperable cancer is associated with intracranial hypertension. When interviewed, it is revealed that during dizziness the patient seems to be spinning, while his position remains unchanged. With brain cancer, paralysis and paresis of one or more limbs develop. In severe cases, convulsive seizures appear.