Heart and vascular diseases are often the cause of death for many people. By knowing the signs of stroke and heart attack in women, the negative consequences of the disease can be significantly reduced. Often, a cerebral stroke is confused with a myocardial infarction; it’s all about the similarity of causes. Myocardial infarction is one of the most terrible manifestations of coronary heart disease. Women are half as likely to be susceptible to this disease as men.
Nature of diseases
Heart attack and stroke belong to the group of cardiac disorders. Until recently, such ailments were considered the scourge of old people, but diseases are getting younger. Recently, the percentage of cardiac disorders in patients aged 35 to 45 years has increased significantly. Usually these are young, purposeful people. They try to build a successful career without particularly taking care of their health, working around the clock. A description of these diseases will help you understand whether a stroke or heart attack is worse.
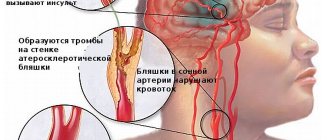
A heart attack is a partial or complete damage to the heart caused by thrombosis of an arterial vessel. It feeds the muscle, but when the channel is blocked by a blood clot, its transportation is interrupted. Tissues suffer from a lack of oxygen and other elements - they gradually die. Moreover, a heart attack is a disease that affects not only the heart. In practice, there are disturbances in the vessels of the kidneys, intestines and even the brain.
The reasons are the same:
- atherosclerotic effect on the arteries transporting blood to the organ;
- hereditary coagulation disorders, the development of abnormalities in blood vessels, leading to the formation of blood clots.
To prevent heart disease, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and undergo regular (at least once a year) examinations.
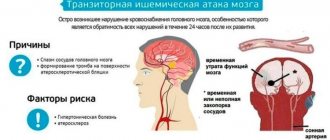
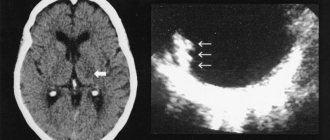
Stroke is an acute disorder that occurs in the blood circulation of the brain. Emu can be caused by narrowing or blockage of blood vessels (ischemic stroke) and hemorrhage into the organ, as well as into its membranes (hemorrhagic stroke). Stroke is an even younger disease than heart attack. It occurs in young people starting from 20 years of age.
The most common causes of pathology include ischemia (poor blood flow) and deformation of the walls of blood vessels. Thrombosis causes a blockage in the blood vessel (which brings blood and nutrients to the brain), causing tissue swelling. During a hemorrhage, a rupture of an artery in an organ is detected - this can happen regardless of the person’s age. During embolism, a clot of fat-like elements cannot pass through the vessel, forms a blockage and stops blood flow. Often this type of stroke develops after cardiac surgery or arrhythmia.
Differences in manifestation
Knowing the nature of the formation, it is not difficult to understand how a stroke differs from a heart attack. However, diseases are different not only because of their development, but also in the nature of their manifestation.
Load and heart attack
Problems with blood flow are, first of all, indicated by low physical activity and exercise, not even the heaviest. For example, a person is walking. During a normal walk, he began to experience chest pain. It’s as if my heart is squeezing. Symptoms are accompanied by shortness of breath. Everything disappears as soon as the body stops moving and goes into a state of rest. Even more often, problems appear when walking quickly or moving uphill: unpleasant/painful sensations begin behind the sternum, further movements are difficult. Again, relief comes when you stop.
An unusual manifestation of the location of pain is also possible - in the area of the joints of the elbow and shoulder, as well as the detection of “starting pains”: after leaving the house (in the morning), unpleasant sensations begin, which soon subside, and cardiac pain does not bother you for the rest of the day.
The most dangerous signal should be the appearance of squeezing or burning in the chest at night, as well as an increase in angina attacks during the day. In this case, it is recommended to go to the doctor as soon as possible. If severe, constant pain in the chest begins, which is accompanied by sudden weakness and cold sweat, you need to quickly call an ambulance.
The number of deaths associated with cardiovascular diseases is the leader in statistics. Therefore, it is recommended to regularly carry out preventive procedures to prevent the development of ischemic heart diseases, chronic disorders manifested by absolute or partial damage to the blood supply systems due to damage to the coronary arteries.
The unpredictability of stroke
It is possible to diagnose a stroke in connection with the abnormal development of cerebral vessels, arterial hypertension that cannot be controlled, and atherosclerotic damage to the arteries that transport nutrients to the organ.
Main features:
- speech disorder;
- sharp asymmetry of facial muscles;
- poor sensitivity, weakness in the limbs.
Most of the symptoms of acute stroke are associated with impaired blood flow and the development of acute ischemia of a certain area of the organ (responsible for a separate set of functions in the human body).
In patients at a young age, an acute ischemic attack in the brain or heart is very harmful to the body and can lead to death or disability. This is due to the fact that with age, the number of thin vessels that conduct nutrients to the organs increases. In case of danger, these “workarounds” - small vessels - begin to work. They will allow the brain not to be completely deprived of nutrition, and at least a little to compensate for the lack of oxygen. This saves cells from complete death. Young people have much fewer such “helpers” or none at all.
Separately, it is necessary to note the subjective sensations of each patient. Manifestations of a stroke are associated with problems in the functioning of the muscles of the head and the body as a whole. It turns out that if a person has an unnatural smile (the corners of the lips are asymmetrical due to disturbances in muscle contraction), he is not able to fully raise his arms, clench his palm, speak clearly and clearly, he needs to go to the doctor as soon as possible. It is very important that in the event of a stroke, assistance is provided within several hours, otherwise the risk of death is high.
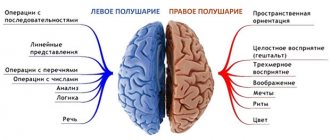
In general, the symptoms greatly depend on the nature and location of the disorder. It must be taken into account that the hemispheres control the opposite halves of the body, and paresis and paralysis will spread to the side of the body opposite to the lesion.
For example, disorders of the speech apparatus are not a mandatory manifestation of a stroke. This only happens when there are disturbances in the area where the speech center is located. Aphasia in right-handed people develops when the left hemisphere is damaged, since the apparatus is concentrated there. In this case, the person loses the ability to express his thoughts out loud, but can still communicate using gestures and facial expressions (motor aphasia). Oral speech may not go away, but the patient forgets words, pronounces them with distortion, and therefore those around him do not understand him.
Cerebellar ischemic stroke initially affects coordination. Manifestation:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- vomit;
- instability of movements;
- lack of coordination of actions;
- The eyeballs "run"
Signs of a heart attack
The first signs that are typical for women that appear before a heart attack:
- constant unnatural fatigue that does not go away even after proper rest;
- sleep disturbance leading to chronic insomnia.
Before a heart attack, circulatory disturbances often occur, which leads to the formation of swelling.
Symptoms of a heart attack in women also include:
- difficulty breathing;
- dyspnea;
- presence of discomfort in the chest;
- pain in the heart area radiating to one arm or both;
- vomiting or nausea;
- the appearance of cold sticky sweat.
If these signs occur, proper diagnosis and treatment must be immediately carried out to avoid a heart attack.
First aid
Brain infarction and stroke are very dangerous. When a painful attack not only does not disappear, but continues to increase (compression in the sternum, pain), accompanied by body malaise, cold sweat, severe shortness of breath, or speech and musculoskeletal system disturbances begin to appear, you need to immediately call an ambulance. Don't hesitate! In such a situation, time is a valuable resource, the waste of which leads to death. The sooner specialized medical care begins, the greater the person’s chances of survival.
Most often, urgent surgical intervention is used to treat acute coronary pathology. The doctor’s goal is to restore blood supply as quickly as possible. Today, most, if not all, large hospitals are equipped with all the necessary equipment.
Rules for preventing stroke:
- getting rid of cigarettes if you smoke;
- taking at least 7-8 thousand steps a day;
- maintaining a rational food diet;
- monitoring the water balance in the body (at least 1-1.5 liters of regular still water per day);
- avoiding alcohol consumption;
- control of the ratio of proportions and body weight (for men the maximum waist size is 94 cm, and for women - 80 cm);
- blood pressure control;
- monitoring glucose and cholesterol levels;
- passing the commission once a year.
If the pathology has already been diagnosed, you must regularly take medications prescribed by your doctor.
What to do after a stroke?
Poor cerebral circulation affects the functioning of all internal organs and systems. If we talk specifically about what happens to a person after a stroke, then everything depends on the duration of exposure to the pathological factor and the speed of first aid. A stroke requires a long recovery process, which must be multifaceted, helping to restore brain cells and normalize its function. A set of rehabilitation measures may include:
- massage – aimed at normalizing muscle tone;
- physiotherapy – increase blood circulation in damaged organs and tissues;
- therapeutic exercises – helps restore muscle function;
- sessions with a psychotherapist;
- rejection of bad habits.
Prognosis and consequences of stroke
The consequences of the disease, as well as the main symptoms, depend on the type of stroke and help to understand the difference between a stroke and a heart attack. Thus, neurological disorders, numbness of the limb, pain, and cell death occur.
A stroke can develop in three directions:
- favorable (after a few minutes, hours, consciousness returns to normal);
- intermittent;
- progressively severe (consciousness appears after a day, several days).
If the course is favorable, and if treatment is approached correctly, over time, all damaged areas of the brain can be completely restored. An intermittent outcome will allow you to return only part of the “lost”; moreover, a repeated attack and the development of additional diseases (heart problems, pneumonia) cannot be ruled out. Unfortunately, the progressive form leads to an increase in symptoms, which fall in a “clump” on the patient. This often ends in death.
Among the neurological disorders standard for stroke, the most common are
- complete or partial paralysis;
- speech problems/complete loss of ability to speak;
- poor vision, hearing;
- loss of memory fragments.
It is impossible to avoid the consequences of a stroke, but it is wise to take care of the conditions for recovery after it. Among these processes are:
- accurate and quick diagnosis of the problem;
- emergency hospitalization;
- compliance with the rehabilitation regime prescribed by the doctor.
A person cannot influence a number of factors, these are: strength, type of stroke, location of the lesion and extent of the lesion. The only thing that is within the patient’s control is attentiveness to the prerequisites and prevention.
First aid for stroke and heart attack
In the old days, only older people suffered from heart attacks, however, in recent years, attacks often occur in young men and women. Men are most susceptible to symptoms of the disease and are in the first risk group. In women, the phenomenon of a heart attack occurs mainly in adulthood, since the production of the sex hormone estrogen prevents the formation of cholesterol in the body.
The typical form of a heart attack manifests itself in the form of an acute attack of pain in the chest area that occurs for no obvious reason. The sensations are characterized by pressure on the heart, compression, sometimes pain reflexes spread to the back and shoulder muscles. The symptom is similar to angina pectoris, but unlike this heart disease, it can occur not as a result of stress, but at rest.
During an attack, people near the victim should immediately call an emergency medical team. If a person becomes ill, one should perform the basic steps one by one. What are they:
- lay the victim on a horizontal surface, place a cushion under the head;
- loosen, remove things and accessories that impede the flow of oxygen;
- if you lose consciousness, place your head to one side to prevent mucus and vomit from entering the respiratory tract;
- If the victim has dentures, they must be removed.
The actions themselves when providing first aid also differ; it is important to note the nature of the symptoms. If you have a stroke, you should not give the victim liquid, food, or medications in tablet form. Paralyzed arms and legs can be rubbed with medical alcohol. The main thing is to control the parameters of pressure and breathing. In the absence of experience, it is better not to take other actions on your own.
During a heart attack, the victim can be given nitroglycerin by placing it under the tongue. Taking aspirin will help dilute blood clots in the arteries before the ambulance team arrives. There is no point in dealing with the crisis on your own. Only experienced doctors can save a person’s life.
The main difference between a heart attack and an ischemic stroke is the danger that one of the pathological conditions poses to a person. When the first alarm signals appear, it is necessary to take pre-medical measures and call an ambulance. A competent doctor will help prevent the onset of a stroke or heart attack - in the future this can save the patient’s life.
Each disease has its own definition, by which you can understand the difference between a heart attack and a stroke:
- Stroke (cerebral infarction) is a disease of the nervous system that is characterized by impaired blood circulation in the brain. It is divided into ischemic stroke, which is caused by an acute, pronounced deficiency of blood supply in the basin of a certain cerebral vessel with the formation of a focus in it similar to a brain infarction, and hemorrhagic stroke is a consequence of an acute hemorrhage into the substance and ventricles of the brain or into the intrathecal spaces.
- A heart attack is a stoppage of blood flow, cessation of blood supply due to blockage or spasm of the arteries, as well as the occurrence of a focus of necrosis and tissue necrosis. An attack can develop in any organ: lungs, myocardium, spleen, kidney, brain. Most often, infarction is observed in the myocardium, brain and lung.
- Myocardial infarction is a heart disease that is caused by an acute insufficiency of its blood supply with the appearance of a focus of necrosis in the heart muscle.
- Pulmonary infarction is a disease caused by embolism or thrombosis of the branches of the pulmonary artery.
The most dangerous and undesirable consequences of any disease are complications. In case of heart attack and stroke, they are more dangerous and can be fatal. What is more dangerous - a heart attack or a stroke, why they are terrible, what are their differences, what is worse, can be determined by the complications that arise after the disease.
1. Complications of a heart attack. Some patients, before reaching the hospital, die in an ambulance from the following complications of a heart attack:
- Left ventricular failure.
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Pericarditis.
- Dressler's syndrome.
- Aneurysm in the left ventricle.
- Rupture of the interventricular septum.
2. Complications of stroke. The following complications occur during a stroke:
- Bedsores.
- Paralysis.
- Pneumonia.
- Coma.
- Vascular thrombosis.
- signs of a stroke - the patient cannot speak clearly. The muscles on his face are paralyzed, which makes him unable to smile and asymmetry is visible. It is not possible to raise two hands at once (only one is effective). In appearance, a person “hangs” and sinks down;
- signs of a heart attack - severe pain occurs in the middle of the chest, also accompanied by a burning sensation and squeezing (a sharp increase in pressure when the heart beats). The pain radiates to the neck, left arm, shoulder and back (usually under the left shoulder blade). The patient may experience shortness of breath and difficulty breathing (dyspnea). When the pain radiates to the stomach, vomiting may occur.
Harbingers:
- stroke - slowing down of the patient, paralysis of the face and parts of the limbs, dizziness and disorientation in space;
- heart attack (pre-infarction state) - sharp heart pain, a feeling of depression and anxiety, shortness of breath, a feeling of pain spreading to different parts of the body.
First aid:
- In case of a stroke - if there are warning signs of the disease and the patient cannot fulfill your requests (answer questions, smile and raise his hands), then you need to urgently call an ambulance. Before the ambulance, help the patient take a sitting position or recline; if there is shortness of breath, provide a flow of fresh air. A stroke requires calling an emergency ambulance; self-medication with any medications is prohibited. Restoration of the body occurs under the treatment of neuroreparants. Folk remedies include additional herbs for general strengthening - tincture of pine cones, decoctions of calendula, yarrow, thyme and St. John's wort. The prognosis after the disease can be disappointing - it all depends on the damage to the area of the brain, some may recover from the blow, and some may experience paralysis of the body and speech. Long-term rehabilitation and therapy are required.
- In case of a heart attack, quickly measure the pressure with a tonometer (if you have it on hand), take blood pressure medications (for example, nitroglycerin, captopril), you need to put the tablet under your tongue until it completely dissolves; if it does not decrease, you can chew half an aspirin tablet and call an ambulance. In case of loss of consciousness and pulse, we provide first aid - indirect cardiac massage and mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration, done before the doctors arrive (try to remove all constricting clothing from the patient, the depth of pressure on the chest is five centimeters). Folk remedies are good for restoring the body after a crisis - this is an addition to the main treatment. For example, decoctions against edema, to normalize blood pressure, vasoconstrictors and to strengthen the immune system. The most common are tinctures of motherwort, hawthorn, and chamomile. Reduce pressure and remove swelling - rowan fruits, mint and garlic. The prognosis after damage to the heart muscle can be varied - restoration of the affected area is impossible, in the future you will be plagued by pain and restrictions in physical activity.
1. Chest discomfort - most heart attacks are accompanied by a feeling of discomfort in the central part of the chest that does not go away within a few minutes (pressure, squeezing or pain). 2. Discomfort in other areas of the upper body - pain or discomfort in one or both arms, back, neck, jaw or stomach.3. Difficulty breathing (whether accompanied by a feeling of discomfort or not). 4. Cold sweat, nausea or dizziness.
The main sign of a heart attack in both men and women is pain or discomfort in the chest. However, women are more likely than men to experience other signs of a heart attack: difficulty breathing, nausea/vomiting, and back or jaw pain.
Timely provision of first aid is the key to successful treatment and recovery. If brain cells do not receive nutrition in the first hours after a heart attack, they begin to die. In the case of cerebral hemorrhage, the situation is worse, since destructive processes are launched immediately after the rupture of the vessels. In most cases, such a stroke leads to death, less often to lifelong disability.
The first thing your loved ones need to do during an attack is call an ambulance. While the team of doctors is traveling, you can try to alleviate the patient’s condition. To do this, you should put him in bed, raising the head of the bed and opening the window for air access. If a person is conscious, it is necessary to monitor his well-being and provide emotional support.
Signs of stroke and heart attack develop suddenly, rapidly and can take you by surprise at home, at work or on vacation. Providing first aid for a heart attack and stroke begins with calling an ambulance.
At home in case of a heart attack you need to:
- calm down;
- provide access to fresh air;
- give a comfortable position with the head end of the bed raised;
- let chew 300 mg. aspirin (“aspirin cardio”, “magnicor”).
With a stroke, everything is more complicated. Without knowing the mechanism of development of the disease, you should not start any measures. Medicines for stroke and heart attack are different. Using the same medications at home can be dangerous.
A patient with stroke symptoms must be provided with complete rest, access to fresh air, and high blood pressure reduced, but not more than 10% of the initial level (tissue hypoperfusion can lead to a worsening of the condition).
Prognosis and consequences of a heart attack
The differences between a stroke and a heart attack are expressed in the consequences. The disease greatly affects physical condition and overall quality of life. We are talking about necrosis of an area of the heart - the myocardium, caused by poor blood supply. The dead cells will no longer be restored, which means that part of the muscle completely falls out of work, affecting the body as a whole. In order for other areas to take over the functions of the deceased, it is necessary to undergo a whole course of rehabilitation.
The consequences are:
- early;
- sharp;
- remote;
- late.
Early - acute heart failure, leading to pulmonary edema, sometimes death. This also includes muscle rupture, pericarditis, aneurysm, and thrombosis. The latter can lead to congestion in blood vessels and the development of a stroke.
Long-term – development of chronic failure due to scarring of the damaged myocardial area. They are characterized by post-infarction syndrome, which includes a complex of diseases - pericarditis, pneumonitis and pleurisy. More often they form within 2-5 weeks after an attack caused by autoimmune processes. Pericarditis is chest pain, sometimes accompanied by leg swelling, ascites, distended jugular veins, enlarged liver and general malaise. Pleurisy is a similar chest pain. It is accompanied by blue discoloration of the skin and shortness of breath due to poor blood flow.
Don’t forget about a healthy lifestyle: give up bad habits and exercise – then you will live a long and happy life without encountering most common diseases along the way.
The occurrence of a heart attack and its manifestations
A heart attack can occur when, for some reason, a blood clot forms. It blocks the flow of blood because it clogs a certain branch of the coronary vessels.
The blockage causes the oxygen supply to a specific area of the heart muscle to be cut off for 20-30 minutes. During this time, profound changes in heart tissue occur in the body. The affected cells subsequently die. In the body, in a state of myocardial infarction, acute circulatory failure of the heart tissue occurs.
The state of a heart attack, depending on the concentration of the area in which there is a lack of blood circulation, is:
- large-focal;
- small-focal.
In many cases, it happens that a person feels quite normal, and suddenly a prolonged attack of heart pain begins. It has features that indicate myocardial infarction:
- the duration of the attack is more than 15 minutes;
- after taking nitroglycerin, only weakening is observed;
- the nature of the pain is intense, sometimes wave-like;
- spread to the left arm, shoulder blades, neck and lower jaw;
- the main pain occurs on the left side of the chest or behind it;
- There is compression and strong pressure in the sternum.
Precursors of myocardial infarction in women are:
- dizziness;
- blueness of lips and limbs;
- marble skin color.
The reasons for the severity of symptoms during a heart attack depend on:
- area and location of the affected area;
- stages of the disease.