Why do night headaches occur?
If you experience headaches at night, it may be due to a mental or physical disorder.
While a one-time episode can be treated with pain medication, regular headaches are a serious reason to visit a doctor.
There are many reasons for the development of pain syndrome, here are the main ones:
- Excessive overload and severe emotional fatigue.
- Overexertion, migraine.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Side effect of the drug being taken.
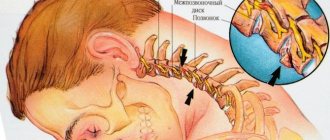
- Cluster disease and cervical osteochondrosis.
- Regular consumption of alcohol, caffeine and smoking.
- Depression, depressed state.
- Uncomfortable sleeping place, posture.
Pain during sleep is a signal of impaired blood supply and metabolic processes in the brain. Since the brain does not have reserves of nutrients, but receives them through delivery through blood vessels, it instantly reacts to a lack of glucose, oxygen and other necessary substances.
The cause will be diabetes mellitus, since it is accompanied by metabolic disorders of several systems at once. Headaches are common in diabetes.
A sudden attack of headache at night in older people will be a signal of a possible stroke or heart attack.
Spasms in the head are complemented by unpleasant pressing sensations in the chest and numbness in the left arm. If you have such symptoms, you should urgently call an ambulance.
↑
Classification of cephalgia
Night headaches can be systematized by time of occurrence and duration:
- Frequent painful sensations are typical with arterial hypertension, Horton's syndrome and vascular atherosclerosis.
- Paroxysmal cramps appear in patients with hemicrania and hypertension.
- Unilateral are observed with hemicrania. Painful sensations are concentrated in the frontotemporal part.
- Repeated ones occur due to inflammation of the 5th pair of cranial nerves.
According to the mechanism of occurrence, cephalalgia is divided into the following types:
- Tension. In this case, the person will feel pressure in the eye area and head. This type usually appears before bedtime and can last from 30 minutes to 5-7 days.
- Cluster - localized in the front of the head. It is considered the strongest of all types of cephalgic syndromes. It is characterized by spontaneous short-term series of outbreaks of painful sensations. The attacks last up to 60 minutes.
- Hypochondriacal appears due to excessive concentration on thoughts about brain diseases and similar ailments. A severe headache occurs in the evening, and a person may wake up feeling unwell at night.
- Organic occurs with pathologies in the brain, for example, hemorrhage, tumors and other neoplasms of brain tissue. Appears after intense exercise during the day. It can occur both before and during sleep.
- Temporal cephalgia appears with temporal arteritis. The pain can radiate to the neck and even to the shoulder. Occurs before and during sleep.
- Cephalgic syndrome due to intracranial hemorrhage is accompanied by speech, visual impairment and ataxia.
Why does my head hurt at night but goes away in the morning?
Often headaches go away by morning. This is due to the fact that the brain still manages to rest and relieve stress. Unpleasant sensations may disappear after waking up due to the fact that the person enters the active phase and the brain is more saturated with oxygen.
If the next morning the discomfort goes away only after breakfast, you need to reconsider your diet and add a vitamin complex to it; during sleep, the brain does not have enough substances to produce the hormone of sleep and awakening.
↑
https://gidpain.ru/bolit/nochnye-golovnye.html
How to eliminate pain
If pain syndrome is caused by increased blood pressure surges, you need to take medications to return it to normal. Osteochondrosis is treated by an orthopedist using preventive physical activity and massage. You need to fight depression by taking antidepressants, they have a hypnotic effect, but for this you need to consult a psychotherapist.
To reduce the risk of unpleasant pain during sleep, follow the rules:
- You should check your room 20 minutes before bedtime, even if it’s cold outside.
- An hour before rest, you need to stop watching TV, using a smartphone, and reading e-books.
- Dinner 2-3 hours before bedtime should be light.
- You should not drink alcohol or coffee 4-5 hours before bedtime.
- Sleep at least 7 hours a day, without oversleeping, and avoid naps during the day.
- Before resting, you need a walk in the fresh air.
- Sleep in a comfortable position.
Which doctor should I contact?
Often, after physical exertion or mental stress, people feel worse. The nature of the pain can be varied. Compressive, pressing, throbbing pain in one side of the head is possible.
Pain during exercise is often functional in nature. They can occur for many reasons:
- Changes in temperature and atmospheric pressure;
- Stressful state during physical activity;
- Heat and stuffiness in the room;
- Dehydration is often the cause of headaches;
- Eat a large meal before training;
- Overweight people often suffer from hypoxia during exercise.
The likelihood of illness is higher in people with specialties: programmer, accountant, driver, who spend many hours at the computer or constantly strain the muscles of the eyes and neck.
Persistent cephalgia, which occurs regularly, requires mandatory consultation with a doctor in order to exclude serious pathology and prescribe the correct treatment in a timely manner.
The initial appointment should be made by a therapist. He will conduct a general examination, measure blood pressure, write out directions for tests and refer you to specialists.
If you have unpleasant sensations in the head and neck area, it is good to have a home blood pressure monitor, with which you can track pressure surges in different life situations. A rise in blood pressure after physical activity can often be the cause of pain.
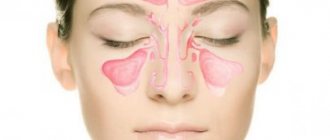
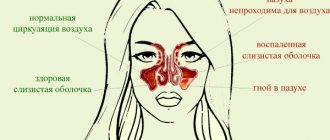
The doctor gives a referral to an otolaryngologist to rule out chronic otitis media, sinusitis or inflammation of the maxillary sinuses (sinusitis).
The doctor can give a referral to an ophthalmologist to identify changes in the fundus and possible vision defects.
Most of the causes of discomfort in the head are associated with neurological symptoms, so diseases accompanied by head pain syndrome are treated by a neurologist.
↑
Medicines
If you have extremely limited time resources and need to get rid of a headache effectively and quickly, you can take a painkiller. The most effective drugs are such compounds as analgin, citramon, Nurofen, Spazmalgon, Nise, Pentalgin. If after sleeping in the morning, when you barely had time to wake up, you have a headache, and it happened just once, pills can help. But if this phenomenon continues on a regular basis, you should urgently contact a medical specialist.
Only by following these recommendations, when you wake up, you can feel just great, and will also ensure that you fall asleep quickly. Therefore, your health in general and the absence of symptoms in particular depend solely on you.
What tests are usually prescribed?
At an appointment with a neurologist, a physical examination of the patient is performed: basic neurological reflexes are checked and the neck muscles are examined.
The doctor writes out a referral for tests: general blood test, biochemical blood test, blood sugar test.
A general blood test with an increase in ESR or an increased content of leukocytes indicates inflammation in the body.
Blood biochemistry may indicate a deficiency of one of the vital elements, which leads to discomfort in the head area.
Low blood glucose levels are often accompanied by cephalgia, dizziness and weakness.
The doctor may write a referral for additional tests:
- The gas composition of arterial blood can reveal cerebral hypoxia.
- A blood test for hormones determines various abnormalities in the functioning of the hypothalamus.
A neurologist can give a referral to one or more diagnostic methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - excludes the presence of various neoplasms (tumors and cysts), aneurysms. The photographs clearly show post-traumatic defects, neurodegenerative abnormalities, and changes in blood vessels affected by atherosclerosis.
- Computed tomography (CT) is the most informative method for studying the brain. It gives a clear idea of pathological changes in the skull and brain, pathology of bone tissue, blood vessels and brain structures. Provides information about the consequences of traumatic brain injuries. The disadvantage of this method is the significant radiation dose during the study.
- Electroencephalography gives an idea of the presence of pathological changes in blood vessels and impaired cerebral circulation.
- Doppler ultrasound (ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck) - shows the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries; narrowing and tortuosity of the arteries, leading to brain hypoxia; peripheral vascular resistance.
- Rheoencephalography (REG) - gives an idea of the tone and blood flow of blood vessels. Using REG, the following are diagnosed: hypertension, atherosclerosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- MRI of the cervical spine - the presence of cervical osteochondrosis can cause pain in the head and neck, which intensifies when turning the head.
- Rheovasography of cerebral vessels (RVG) - shows the quality of blood flow through the great vessels, evaluates collateral circulation.
- Radiography will be less known. In the image you can only see the bone structures of the skull, soft tissues are not visible.
There is no need to panic when scheduling such a serious examination. The doctor excludes rare severe pathologies and looks for the causes of the pain process.
Based on the studies, if no serious organic lesions are found, the cause of the disease is usually diagnosed. It develops as a result of: vascular spasms, cerebral hypoxia, hypertonicity of cerebral vessels, hormonal imbalances, vegetative-vascular dystonia or osteochondrosis, provoked by physical or psycho-emotional stress.
↑
Safe medications and pills
When planning a visit to the doctor, the patient should be prepared to answer questions about how often pain occurs and what its intensity is. This will help the doctor develop the correct treatment tactics.
↑
Groups of drugs effective for episodic attacks of pain
Medicines for the treatment of pathology are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They have an analgesic effect, relieve inflammation, and eliminate swelling.
Often prescribed:
- Ibuprofen-400 mg per day;
- Ketoprofen-100 mg/s;
- Naproxen-500 mg/s;
- Meloxicam-7.5-15 mg/s;
- Celecoxib-200 mg/s.
Most NSAIDs have a negative side effect: with long-term use, they negatively affect the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, including the development of drug-induced gastritis.
Medicines Meloxicam and Celecoxib are new generation drugs that do not have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract. The disadvantages of using these drugs include the relatively high price.
Analgesics are often used at home to relieve an attack. They do not treat the disease, but only relieve pain. Drugs in this group are suitable for stopping episodic attacks, but their systematic use leads to the occurrence of abuse syndrome.
During an attack of pain, you can take Paracetamol-100 mg, Citramon, Analgin-500 mg or Mig 200-400 mg.
If the examination revealed the appearance of cephalgia after exercise as a result of increased blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe medications prescribed at an early stage of the development of hypertension. These include: vasodilators, ACE inhibitors, diuretics, calcium channel blockers.
Self-prescribing antihypertensive drugs is unacceptable. Self-medication leads to serious consequences.
For muscle tension, drugs from the group of muscle relaxants are used as part of complex treatment. They relax the spasmodic muscles of the head and neck, relieving pain of a spastic nature, and help restore blood flow.
Often prescribed:
- Mydocalm-150-450 mg per day;
- Sirdalud (Tizanidine) - 4 mg/s;
- Baclofen-15 mg/s.
Nootropic drugs are often prescribed as part of complex treatment: Phenibut, Nootropil, Glycine. Nootropics have an activating effect on brain function and increase its resistance to damaging factors. The drugs improve cerebral circulation and eliminate the consequences of traumatic brain injuries.
Sedatives in combination with basic drugs lead to muscle relaxation and decreased vascular tone. Taking tranquilizers helps relieve pain, but this type of medication quickly causes drug dependence with withdrawal symptoms.
Sedatives that are not addictive: Afobazol, Atarax; alcohol tinctures of valerian, motherwort, Maryina root.
For severe attacks, a combination of drugs is used: Sirdalud 2 mg + Aspirin 500 mg or Analgin 250 mg + sedative.
The use of vitamin B complexes has proven itself. Vitamins B1, B6, B12 have a beneficial effect on the central nervous system and restore the structure of nerve tissue. Vitamin complexes are often prescribed: Neuromultivit, Milgamma, Neurovitan.
Treating ailments with improvised remedies at home
If a severe pain attack takes you by surprise, and there is no way to get help from a doctor, the following measures will help:
- Short sleep, head slightly raised;
- Rest in a relaxed position with pieces of ice wrapped in a scarf applied to your temples;
- Compress on the head, especially in the temple area, using the pulp of a lemon, grated;
- Light neck massage to relax the muscles;
- Warm sweet tea with lemon;
- Inhalation of essential oils of mint, lavender, lemon, basil, clove, sage, eucalyptus; you can drop a few drops on your forehead and temples;
- Warm (not hot) bath with an extract of soothing herbs or essential oils;
- Foot baths with a temperature of 40 degrees for 15 minutes.
Following a healthy lifestyle helps you get rid of tension pain forever without the help of medications:
- Sound sleep of at least 7 hours with the window open. It is advisable to take an evening walk before going to bed.
- Daily contrast shower strengthens blood vessels, making them more resistant to stress.
- Maintaining water balance. It is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day, not counting soups and drinks.
- Proper balanced and vitamin-rich nutrition.
- Drinking large portions of alcohol and smoking leads to vascular spasms.
- Avoid physical and mental overload and stress.
- While working at the computer, take breaks every hour; Exercises for the eyes and muscles of the cervical region are useful.
- Regular moderate physical activity and an active lifestyle.