What is external replacement hydrocephalus of the brain?
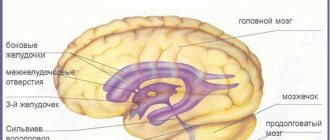
Brain tissues do not come into contact with bone tissues, since they are in the cerebrospinal fluid. This is cerebrospinal fluid that protects the brain from mechanical injury. It provides a stable temperature and supplies nutrition to the cells. The standard volume of cerebrospinal fluid is 150 ml. Several times a day, the composition of the liquid is completely renewed.
The fluid is absorbed by the ventricles, which begin to put pressure on the brain.
If this process is disrupted, cerebrospinal fluid is poorly absorbed and accumulates between the membranes, causing dropsy. Sometimes the fluid is absorbed by the ventricles, which will put pressure on the brain. As a result of the development of microadenoma, brain activity is disrupted and alarming symptoms arise.
Forms of the disease
There are several types of moderate hydrocephalus:
- External - fluid accumulation is observed mostly in the subarachnoid space, that is, on top of the cerebral hemispheres.
- Internal - a disease caused by impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, accompanied by the accumulation of fluid in the cerebral ventricles.
- Mixed - accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid both inside the brain, in the ventricles, and under the membrane of the hemispheres.
- Replacement - a gradual reduction in the volume of the brain matter with filling of the voids with cerebrospinal fluid. This type of dropsy is diagnosed mainly in elderly patients.
On this topic
- Hydrocephalus
How is shunting performed for cerebral hydrocephalus?
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- March 26, 2020
In some cases, the replacement form accompanies degenerative diseases of the central nervous system, in particular Alzheimer's disease.
External moderate hydrocephalus is also divided according to its origin:
- acquired - occurs as a result of injuries and other external factors, in addition, frequent human illnesses can be the cause;
- congenital - develops as a consequence of a difficult birth process or intrauterine infection.
Classification
Moderate external replacement hydrocephalus can have different degrees. For example, it is characterized by different pressure indicators. It increases, decreases, or remains normal. Also, the pathology is acute, subacute or becomes chronic.
There is another classification of the disease:
- the closed form means that the ducts that remove cerebrospinal fluid are blocked. The liquid cannot circulate normally. In most cases, the duct is clogged due to a blood clot after a hemorrhage;
- open. Absorption by the venous system is impaired;
- hypersecretory. Cerebrospinal fluid production occurs at a rapid rate;
- external - cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in one of the areas instead of the brain, which decreases in volume;
- internal. The fluid is absorbed by the ventricles;
- mixed type - cerebrospinal fluid fills not only parts of the brain, but also the membranes.
Diagnostics
This disease and its other forms are diagnosed in two ways:
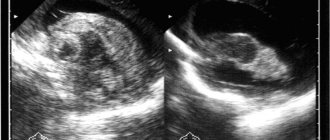
- Magnetic resonance imaging is the most effective method due to the high level of accuracy of images of cavities inside the skull.
- X-ray of the skull in two projections.
On this topic
- Hydrocephalus
What is the danger of open hydrocephalus?
- Ekaterina Nikolaevna Kislitsyna
- March 26, 2020
In addition to these basic methods, the doctor may prescribe other procedures:
- Ultrasound;
- angiography - MRI with the introduction of a contrast agent, which allows you to clearly see all the disorders and anomalies in the circulatory system, such as damage to blood vessels, narrowing of their walls, aneurysms, etc.;
- CT scan;
- lumbar puncture - analysis of cerebrospinal fluid, makes it possible to detect harmful microorganisms in the cerebrospinal fluid;
- General blood test
In addition to these measures, ophthalmological, neuropsychiatric, and endocrinological examinations are often prescribed.
Why does pathology appear?
In a newborn child, pathology is most often provoked by infections that the woman suffered during pregnancy. At risk are infants who become infected with infectious diseases in the first months of life. Another factor is head and neck injuries, such as during childbirth. Hypoxia in newborns increases the risk of developing hydrops.
In adults and older children, the development of hydrocephalus can be triggered by strokes, infectious diseases affecting brain tissue, and mechanical injuries in the head and neck area (for example, fractures). At risk are people who have suffered a concussion, have metabolic disorders, other cystic formations, vascular problems, parasitic infections and bad habits.
What it is
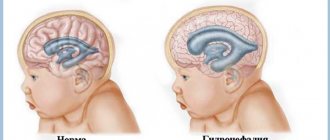
HC is an abnormal increase in CSF (or cerebrospinal fluid) in the cavities of the brain. Moderate external hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult or child is a mild form of the disease associated with a disorder of the CSF flow. Accompanied by:
- increase in subarachnoid space;
- thinning of blood vessels and medulla;
- fibrosis of the arachnoid membrane.
People of any age are susceptible to the disease. But it is more common in children and appears from birth.
Symptoms in children and adults
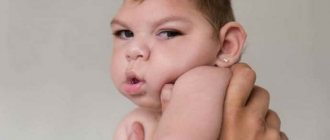
Symptoms of moderate external replacement hydrocephalus are usually distinguished between children and adults. In children, the disease provokes more unpleasant and acute symptoms:
The child spits up very often.
- tremor (chin, hands trembling);
- the head is thrown back;
- the newborn has seizures;
- regurgitation occurs very often, and in large quantities;
- eyeballs do not move as they should;
- the child constantly screams due to pain in the head;
- there are delays in development, in which the baby does not hold his head up, does not learn to roll over, etc.
If parents ignore these signs, dropsy will manifest itself as deformation of bone tissue. The head will grow disproportionately to the rest of the body.
In adult patients, the signs of the disease depend on the form in which it occurs. For example, at the initial stage there are usually no symptoms. As the problem worsens, the person will feel discomfort:
- constant migraine, which cannot be controlled with medications;
- nausea (especially in the morning), vomiting;
- feeling of weakness, constant fatigue;
- there will be double vision, sweating will increase;
- the sleep-wake pattern will be disrupted, in which you will suffer from insomnia at night and want to sleep during the day;
- Memory failures occur. Sometimes patients cannot remember their own day of birth;
- intellectual abilities are greatly reduced, inattention develops, and speech becomes incoherent.
Establishing diagnosis
A simple examination of the patient will not make it possible to diagnose and confirm internal replacement hydrocephalus. This will require additional diagnostic procedures. But first, the doctor determines the sensitivity of the limbs and also conducts a coordination test. During the examination, information about previously received injuries (primarily brain injuries) and previous infections is clarified. To clarify the diagnosis, the following types of examinations are prescribed:
- MRI of the brain - allows you to determine whether dropsy is present and at what stage the pathology is;
MRI of the head. - A CT scan is an alternative test in which the doctor gets a complete picture of what is happening to the brain;
- X-rays are usually intended to clarify the size of the increased cerebrospinal fluid, as well as to detect clogged ducts;
- neurosonography. In fact, this is an ordinary ultrasound performed on children. The study of brain tissue takes place through the fontanelle, which does not close until a certain age;
Study of brain tissue. - angiography. The vessels in the area of the skull and neck are examined. Possible deviations from the norm and circulatory disorders are identified.
Causes
Normally, CSF, which is located in the subarachnoid space, is absorbed by the arachnoid membrane of the brain and spinal cord and enters the bloodstream. Excessive accumulation of CSF in this brain system is associated with 3 pathogenetic factors: the production of excess CSF, a violation of its absorption or circulation. Pathology can be caused by one of these mechanisms or a combination of them.
Mild HC can be congenital or acquired.
Causes of congenital HC:
- malformations of the central nervous system, cerebrospinal fluid system (for example, arachnoid cysts, spina bifida, etc.);
- intrauterine infections, including parasitic ones (toxoplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, cytomegaly, etc.);
- chromosomal pathologies;
- subarachnoid hemorrhages;
- delivery before PDR.
Causes of acquired HC:
- obstacles along the liquor pathways (inflammation, tumors);
- neuroinfections;
- lifetime or birth trauma.
There are also several factors that increase the likelihood of developing an acquired pathology: diseases of the vascular system (stroke, hypertension, atherosclerosis), musculoskeletal system (especially in the cervical region), oncology, untreated infectious diseases.
Treatment options
In most cases, doctors try to treat replacement hydrocephalus using conservative methods. This is due to the high risk of tissue damage during surgery. Medicines are used if the pathology has not yet caused significant deformations in the internal tissues.
Treatment of mixed replacement hydrocephalus of the brain is aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms and improving blood circulation in the tissues. Patients are advised to massage the collar area, limit physical activity and take certain groups of drugs:

Painkillers.
- painkillers that reduce migraine and cope with its attacks;
- anticonvulsant medications are prescribed if the patient already has severe seizures or convulsions;
- diuretics are required to remove excess fluid from the body. They help reduce tissue swelling;
- agents that improve blood supply to brain cells;
- with increased intracranial pressure, medications are prescribed to stabilize its indicators;
- if there is a focus of inflammation in the brain tissue, you will need to take corticosteroids;
- If there are significant changes in the psychological state, tranquilizers or other sedatives are prescribed.
Surgical methods
Hydrocephalus in adults does not always respond to conservative treatment, so in rare cases it requires surgical intervention. Typically, surgery is prescribed only in cases where the pathology is rapidly progressing and medications do not improve the person’s condition.
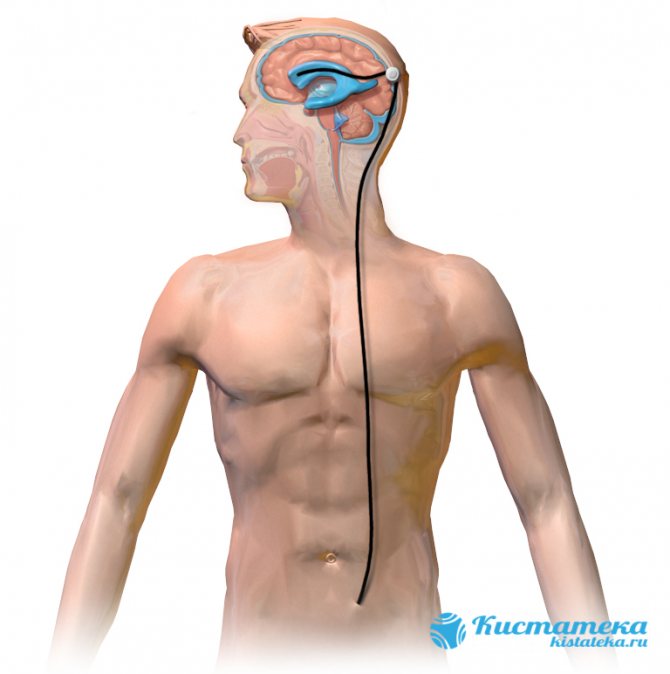
Excess cerebrospinal fluid is removed into the abdominal cavity through a special shunt.
Until recently, the most common type of surgery was bypass surgery. To perform the operation, a special shunt is installed to connect parts of the brain with other tissues of the body. Most often, excess cerebrospinal fluid is removed into the abdominal cavity. When the valve opens, cerebrospinal fluid is released. However, this method has many disadvantages. First of all, this is the danger of the intervention itself, which risks harming healthy tissue. In addition, after installing a shunt, it sometimes needs to be replaced, which also causes a lot of inconvenience.
Therefore, recently doctors prefer to use endoscopic surgery. The fluid is removed using an endoscope, which is inserted into the holes in the ventricles.
Description of the disease
Violation of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, its balance in the process of formation and absorption provokes an excess of secretion, its production remains at the same level, and absorption sharply decreases. This phenomenon provokes an increase in intracranial pressure and causes hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome.
As a result, there is a sharp decline in visual function, weakness in the arms and legs, and frequent convulsions. Since the brain stem is compressed, oculomotor disorders are observed, such as strabismus, “setting sun” syndrome, when when looking up the pupil rolls back strongly, etc.
Such phenomena often provoke a decrease in mental abilities, severe neurological disorders, and sometimes death.
Consequences and complications
The main danger lies in the lack of therapeutic measures. Replacement hydrocephalus requires mandatory medical supervision, as it leads to health-threatening conditions. It provokes dementia, in which the patient is unable to objectively assess current events.
Subsequently, motor functions are impaired, the person ceases to maintain balance and falls when he tries to stand up. The next stage of complications is impaired speech function. There is trembling in the limbs, convulsions, seizures resembling epileptic ones. The patient is unable to control his own body, which leads to urinary incontinence.
In essence, a person ceases to control himself and can no longer provide for his own needs. Therefore, serious stages of pathology usually lead to some degree of disability.
In case of cerebral dropsy, it is necessary to adequately assess the patient’s condition and visit a doctor at the first alarming symptoms. Lack of treatment leads to a person’s complete loss of all basic functions. If a rehabilitation course is started in time, the patient will be able to return to their normal lifestyle.