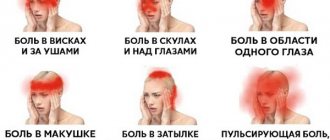
The appearance of a feeling of heaviness in the head rarely manifests itself.
Usually it is accompanied by other pathological signs, which also cannot be ignored:
- Frequent depression.
- A pressing sensation in one or another area of the skull or neck.
- Balance imbalance.
- Nausea.
- Deterioration of smell and hearing.
- Nasal discharge.
- Dizziness.
- Stiffness in neck movements.
- Heaviness in the head and drowsiness are often combined; in the morning you want to sleep even after a long sleep.
It is imperative to report these symptoms to the doctor, because complaints like “heavy head”, “cotton head”, “I walk like the plague” do not really clarify the situation, they accompany many conditions and do not have a clear link to the diagnosis. If such sensations arise, you need to observe your body before visiting a doctor and identify any deviations in your health.
Diagnostics
After clarifying all the patient’s complaints, the doctor sends him for examination.
The patient may need to undergo:
- MRI.
- X-ray.
- Cardiogram.
- CT.
You also need to take blood tests, including an immunogram.
Consultation with a cardiologist or rheumatologist or neurologist is necessary. If you suspect inflammation of the ear or sinuses, you should visit an otolaryngologist.
Associated symptoms
Often, confusion and brain fog occur suddenly, without warning symptoms. Just a minute ago the person felt great, and suddenly began to experience dizziness, blurred vision, and impaired concentration.
Depending on what pathological or physiological process contributed to the appearance of the symptom, another clinical picture arises:
- increased sweating;
- increased or decreased blood pressure;
- headache;
- decreased ability to work;
- sleep disturbance (insomnia or drowsiness);
- increased heart rate.
If confusion is due to a psychological reason, there is unreasonable fear, a feeling of lack of air, noise and ringing in the ears, discomfort in the sternum.
Methods for eliminating discomfort
To eliminate unpleasant sensations in the head, you should definitely contact a specialist, because some of the causes of this condition are indeed very dangerous. Only after the causes and treatment have been determined can discomfort in the head be treated in a targeted manner.
Independent selection of methods and techniques, irrational use of folk methods can harm the patient and contribute to a waste of time when effective necessary measures can be taken. Without a full diagnosis and following the doctor’s instructions, it is impossible to determine how to get rid of heaviness in the head.
So, a heavy head: what to do, and what methods can doctors offer to make life easier?
- Psychotherapy and psychopharmacotherapy (use of medications to eliminate psychological stress and depression).
- Massage (after special consultation with a doctor and massage therapist, you can perform self-massage at home).
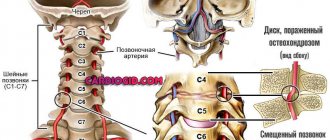
- Manual therapy (in the presence of osteochondrosis).
- Methods for eliminating or inhibiting the growth of tumors, if present (radiation therapy, chemotherapy).
- Operations (for tumors and anatomical defects in the skull, back and neck).
- Drug therapy.
- Breathing exercises and physical therapy.
- Individually developed relaxation methods.
- Physiotherapy.
If nothing is done, a cloudy, heavy head will be felt more and more often, and others will be added to this symptom. Therefore, you should take any instructions from your doctor with the utmost responsibility and always follow them.
Possible diseases
Headache in the frontal region (the causes often remain unspecified) can occur as a result of various diseases:
- Tension headache. Muscle contractions in the head and neck area are triggers for headaches in the forehead area. Main symptoms: dull pain in the front of the forehead, increased sensitivity of the skin of the head and forehead. Causes:
- smoking;
- eye strain;
- alcohol;
- caffeine;
- incorrect posture;
- colds.
- Temporal arteritis. A disease caused by damage to medium and large arterial vessels. The temporal and ophthalmic arteries are predominantly affected. It occurs due to a compromised immune system; provocateurs are often herpes and hepatitis viruses. Characterized by recurring pain in the frontal region, increased sensitivity around the temples. It occurs more often in women over 50 years of age.
- Refractive disorders of vision. Disorders that affect the eye's ability to focus on an object. Fatigue and eye diseases can also cause forehead pain. Working on a computer for several hours every day, visual defects or diseases such as glaucoma, cataracts. Additionally, there are many other causes of forehead pain, such as muscle tension, lack of sleep, side effects of medications, lack of fluids, neurological disorders, brain tumors, and accidental injuries to the forehead.
- Sinusitis. The frontal sinus belongs to the paranasal sinuses and forms a cavity in the frontal bone. The cause of infection is viruses and bacteria. Frontal sinusitis is often accompanied by fever, runny nose, headache with a feeling of pressure in the front of the skull, general fatigue, and can be acute or chronic. Symptoms: nasal discharge, dull pain with throbbing, toothache, fever.
- Cluster headache. The disease is accompanied by watery eyes, drooping eyelids, nasal congestion, sweating in the forehead, as well as sensitivity to light, noise, and nausea. Painful attacks are very severe, can last from 15 to 180 minutes and are repeated several times a day. Characterized by very long, sometimes for many years, periods of pain-free condition until the next attack of headache. Exacerbations occur more often in autumn and spring.
- Tightness in the frontalis major muscle can also cause headaches in the forehead. More common, however, is the contraction of the smaller muscles of the forehead, the mechanical ones, which are located between the eyebrows. Frequent contraction of the eyebrows leads to tension in this muscle, the formation of corrugations and, consequently, headaches in the forehead.
- Migraine. The disorder occurs suddenly and resolves in characteristic phases. For example, many patients in the precursor phase primarily suffer from psychological, neurological and autonomic symptoms, such as fatigue or sensitivity to noise, food cravings. In some cases, this is followed by an aura phase that is associated with perceptual disturbances. During this period, vision and speech may be impaired, and symptoms of paralysis may appear. Therefore, it is especially important to clearly classify symptoms and distinguish them from other diseases such as stroke. Then comes a phase of severe headache, especially in the forehead, temples and eyes. Other symptoms may also occur, such as loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, and increased sensitivity to light, noise and odors.
Excessive alcohol consumption is also a possible cause of forehead headaches. Rare causes of forehead pain include cancer or nerve damage.
Drug therapy
Constant heaviness in the head can be eliminated with the help of various medications in each individual case:
- Remedies for hypo- and hypertension with pathological changes in pressure.
- Drugs for the treatment of VSD.
- Antispasmodics and analgesics so that a constantly heavy head does not hurt from spasms.
- Vitamins and restorative medications to strengthen the body's defenses.
- Muscle relaxants for prolonged muscle strain.
- Phlebotonics for insufficient blood flow from the brain.
- Antibiotics for inflammation of the inner ear or sinuses.
- Antihistamines for severe allergic reactions.
Taking any drug must have good reasons. You cannot take painkillers uncontrollably without eliminating the root cause of the discomfort.
Such an incorrect approach can only lead to problems with the liver and kidney filtration, as well as to the development of intoxication of the body.
When to see a doctor
Headache in the frontal part (the reasons for its occurrence must be correctly identified by a specialist) is dangerous in the following cases:
- A concussion leads to a dull pain in the temples and forehead.
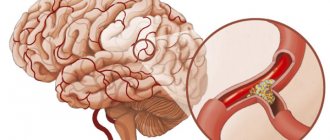
- If a sudden disorder is accompanied by other symptoms: dizziness, nausea, vomiting. In this case, the cause of pain may be a cerebral hemorrhage.
- Severe headache that occurs on one or both sides of the temples (arteritis), which is typical for inflammation of the temporal vessel. This symptom often occurs in combination with rheumatic disease. May be accompanied by numbness and blurred vision.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a neurologist, neurologist or therapist.
How to relieve the condition
When it is precisely determined why the heaviness in the head occurred, the causes of the disorder are identified, you can use some home remedies to eliminate the discomfort, but only after agreeing with your doctor.
Recommendations that may be helpful:
- Hypothermia and staying in places where there are patients with respiratory infections should be avoided.
- It is necessary to develop optimal physical training that will prevent (or treat) spinal diseases, physical inactivity, and venous congestion.
- It is useful to change your type of activity, relax, and select the most suitable methods of active recreation.
- If a person sleeps for a sufficient amount of time (precisely enough, because excessively long sleep also harms the nervous system), he does not have a headache, or attacks of morning weakness occur much less frequently.
- You should always be optimistic and try to avoid depression.
- A person who eats poorly (irregularly or monotonously) runs the risk of developing various vitamin deficiencies and metabolic failures, due to which he will feel a constant sensation of cotton head. Therefore, your diet needs to be adjusted, preferably with your doctor or nutritionist.
- If heaviness in the head and lethargy are associated with hypo- or hypertension, you need to learn to live in such a way as not to encounter provoking factors (eliminate harmful work, overload, physical inactivity).
- Some foods (chocolate, hawthorn, black currant) also help normalize blood pressure with slight deviations. However, severe hypertensive and hypotonic attacks with large deviations in indications, in which “the head is like cotton wool” or “cast iron”, should be stopped only with the help of medications prescribed by a doctor.
- A heavy headache with VSD may be less likely to bother you if a person tries to lead a healthy lifestyle that minimizes negative effects on blood vessels.
- You should consume an amount of water sufficient for the normal functioning of all tissues, blood vessels, brain matter and maintaining the normal structure of the intervertebral discs.
- If the doctor sees no contraindications for hardening, you should definitely do it. But the mode and intensity of each lesson must be selected individually, taking into account weak points in the body that may suffer from sudden influences.
Prevention
What to do to prevent heaviness and pain in the head:
- sufficient relaxation, rest;
- daily 8-hour sleep;
- physical exercises - yoga, swimming;
- balanced diet, eating small portions; low glycemic levels, which result from not eating during the day, are one of the causes of problems;
- correct posture - try not to hunch over or walk at an angle;
- The cause of heaviness and pain in the head is a sharp withdrawal from caffeine, so a person accustomed to consuming it should eliminate the stimulant slowly;
- walk in the fresh air.
Please note that heaviness and pain in the head may be caused by the consumption of certain foods, in particular cheese, chocolate, ice cream, and processed foods. Try to identify your trigger and eliminate it from your diet.