According to statistics, every third child regularly experiences headaches. Unlike adults, children cannot always understand the cause of their condition and inform their parents about it, and children in the first years of life cannot even articulately talk about their complaints.
Snoring, apnea, insomnia or other problems? Contact the Sleep Medicine Center at the Rehabilitation Clinic in Khamovniki. We will definitely help you! Ask questions and schedule a consultation by phone.
Why might a child have a headache? And how do you understand what exactly needs to be done?
The main causes of headaches in children
The causes of unpleasant sensations in the head include a number of pathological processes, mental disorders and constant overwork of the child. It is important to establish the correct cause in order to select a rational treatment. Without diagnostic measures, it is impossible to make a diagnosis yourself.
The main causes of headaches in children:
- Migraine (childhood or teenage).
- VSD syndrome (vegetative-vascular dystonia).
- Tension headache.
- Tumor-like processes in the brain and its membranes.
- Diseases of ENT organs and eyes.
- Meningitis and encephalitis.
- Violation of intracranial pressure.
- Infectious and viral pathologies.
- Poisoning.
- Inflammatory process in the trigeminal nerve.
- Head and brain injuries.
If a child complains of a headache, do not try to drown out the illness with analgesics. First, find out what the nature of the pain is, how long it torments the child, and the frequency of occurrence. If accompanying symptoms occur, such as nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, call an ambulance immediately. Before the ambulance arrives, it is better to refrain from taking any medications, as the clinical picture may be blurred, which makes it much more difficult to make a diagnosis.
Help and treatment for headaches in children
The first step when children complain of headaches should be to find out the cause of its occurrence. Let's consider options for providing assistance when children have headaches:
- To prevent children from contracting the infection, the Ministry of Health provides vaccinations and other preventive measures. By the way, fever, diarrhea and headaches can also be a reaction to professional vaccinations. If the child does become ill with an infectious disease, then it is necessary to immediately contact a pediatrician. For each infectious agent there are certain, destructive drugs: antiviral and antibacterial. To relieve the accompanying symptoms of dyspepsia, you can give your child painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- If a child has suffered a head injury, then, first of all, you need to calm the baby down and provide assistance. For minor damage, you can apply a cold compress and lubricate the injury site with Heparin ointment to quickly resolve the hematoma. If the injury is bleeding, then it is necessary to stop it with hydrogen peroxide and treat the wound with iodine or brilliant green. If there is a headache, put the child down and give a pain reliever, such as Ibuprofen. In more serious injury situations, try to stop the bleeding and go to the hospital;
- For hypertension, epilepsy and migraine in childhood, a course of treatment is prescribed only by a specialist who observes the child and registers him. In these cases, as a rule, anticonvulsants and vasodilators are prescribed with a certain dosage and frequency;
- In case of poisoning of children, assistance can be provided in the form of cleansing the gastrointestinal tract by inducing vomiting with a solution of manganese, and also, depending on the age of the child, giving activated carbon or other adsorbent agents: Smecta, Enterosgel;
- If a child’s headache is caused by an allergic reaction, then it is necessary to protect the baby from the allergen and carry out immunity-strengthening therapy:
- A healthy lifestyle for the baby (exercise, sleep, walks);
- Compliance with the diet (the necessary complex of vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates and proteins);
- Loving and caring for your children will help prevent many situations that cause them pain and illness.
Clinical picture and nature of pain
So, if a child has a headache, first of all, we provide him with complete rest and find out the main clinic, based on the complaints. Children 10 years old can quite clearly describe their condition. The nature of headaches in a 5-year-old child is more difficult to determine; usually children either turn to the wall, not wanting to communicate, or cry loudly, which further increases the intensity of the pain.
Headache in children can be:
- piercing;
- pulsating;
- pressing;
- bursting;
- aching.
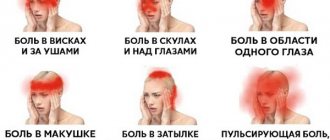
Localization can be observed in the occipital, parietal, frontal, and temporal lobes. It may hurt in the eye area or throb in the temples. If you managed to find out the nature of the child’s headache, this is already good. All that remains is to figure out how headaches occur in pathological conditions.
Migraine
The disease most often affects children from 7 to 11 years of age. Migraine pain is characterized by:
- Pulsation in the area of the eye or temple, on one side.
- Irritation and increased pain from bright light and noise.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Reaction to odors.
The condition improves after the child vomits and falls asleep.
A 10-year-old child, as a rule, has less intense pain than a seven-year-old child. The older the patient, the richer the vessels. This is why teenage migraines usually subside by age 18.
Migraine headaches in children have their own characteristics, in contrast to the course of the disease in adults:
- paroxysmal pain lasts from 30 minutes to 5 hours;
- cephalalgia is directly related to fatigue and psychological stress;
- may be accompanied by fainting and severe dizziness;
- The child will definitely have a stomach ache, diarrhea and vomiting.
If a child often has a headache and the cause is migraine, it is important to eliminate the provoking factors. The child should not get tired; nutrition and rest should be observed and adjusted. Mental stress should be distributed, and physical stress should be supervised by parents.
Behavior of a five-year-old child with headaches
- Tearfulness;
- Moodiness;
- Refusal to eat;
- Indifference to games and communication;
- Apathy or agitation;
- Complaints of headache.
With such manifestations of behavior in children, you need to pay attention to the circumstances of the occurrence of such complaints, the duration and accompanying symptoms of malaise. The factors influencing headaches in children under five years of age and the causes of its occurrence are very diverse.
Refusal to eat
Causes of headaches in children 5 years old
Change of environment, climate and biological time of day . At this age, it is difficult for a child to cope with a change of place of residence, adaptation to the kindergarten team, frequent moves, trips to other countries and resort areas. With such factors, changes in the psycho-emotional state of the child and possible deviations in the biorhythm of the child’s body occur. Violation of the child’s usual routine and diet, as well as non-compliance with the child’s activity and rest time, can lead to headaches and malaise.
Stress and childhood fears. Very often, the vulnerable child’s psyche reacts negatively to family scandals, aggressive and frightening programs on television. Children often witness threats and criminal situations, which leads to mental disorders that cause headaches. Mental disorders in a five-year-old child, that is, in a child who has certain life experience, arise as a result of fears. This feeling can be observed in the form of:
- constant threats from adults;
- fear of the dark;
- fear of insects and animals;
- fear of illness and death;
- fear of medical workers;
- fear of rain, ponds, fire.
When a child is in this state, one can expect different reactions from his body: hysteria or stupor, nausea and vomiting, involuntary urination, headache and even convulsions.
Stress as a reason!
Headache in a child as a consequence of illness
At the age of five, children are susceptible to many infections, and also often get injured due to increased activity and mischief. Head contusions in children are the most common injury, as the child often falls and gets bumps. The resulting hematoma of the head in the forehead or back of the head causes pain and takes a long time to heal. In some cases, a child may suffer a mild concussion, which is not always accompanied by pathological symptoms.
Hypertension in children is not a rare phenomenon. Changes in blood pressure at a young age are associated with child illnesses, emotional and physical stress. The cardiovascular system in small and active children does not always keep up with muscle tone, so disruptions in the blood supply to the vessels may occur, that is, an increase in blood pressure. At the same time, the child complains of dizziness, pain and pulsation in the temporal and parietal parts of the head, nausea and darkening in the eyes. As they grow up, children can sometimes observe such phenomena, but if hypertension is permanent, then it is necessary to show the child to a pediatrician and undergo an examination.
Epileptic syndrome is a disease associated with impaired cerebral vascular function. In children, this pathology may have a congenital or acquired factor. In anticipation of and at the end of an epileptic seizure, the child often has a headache and dark vision.
Migraine . According to statistics, children up to puberty, especially boys, suffer from periodic headaches. The phenomena of migraine pain occur after stressful situations, physical and mental stress and changes in climatic conditions. Also, the appearance of migraines in young children is observed after head and spinal injuries.
The development of infectious diseases in young children occurs with certain symptoms that are characteristic of viral infection. These are diseases such as:
- angina,
- measles,
- rubella,
- diphtheria,
- mumps (mumps),
- whooping cough,
- flu.
The main symptoms of such pathologies are: high body temperature, headache, nausea, cough, vomiting, nasal congestion, hyperemia and sore throat, skin rashes, photophobia, enlarged parotid glands and cervical lymph nodes.
Neuritis and trigeminal neuralgia . Inflammation and disruption of innervation in the back of the head, temples and face is one of the causes of headaches in a child. This pain is of a sharp nature and is especially felt when moving the facial muscles of the face, tilting and turning the head, when sneezing and coughing.
Anemia, rickets and hypoxia. Such pathologies in children at a young age arise as a result of disturbances in diet and rest. For the normal physiological development of a child, a nutritious diet rich in vitamins, proteins and minerals is necessary. It is also considered important that children spend enough time in the fresh air and sunbathing, which prevents oxygen starvation and calcium deficiency. The child's active lifestyle should alternate with a break for rest (sleep). Otherwise, the occurrence of anemia and rickets in children entails problems with the brain and the body as a whole.
Poisoning. Young children often put everything in their mouth, and this can end in disaster. If you come across tablets or other products or liquids that can harm the child’s health, then poisoning with subsequent complications is inevitable. Symptoms of this condition are expressed in the form of vomiting, hyperthermia, pain in the head and gastrointestinal tract, low blood pressure, convulsions and loss of consciousness.
When children consume large amounts of sweets and other foods with food additives, the body is also poisoned with the corresponding phenomena of headache, diarrhea and vomiting.
We measure the child's blood pressure!
If your baby often has a headache, this may be a reaction to nicotine when his parents smoke in the living room.
VSD syndrome (vegetative-vascular dystonia)
Frequent headaches in a child aged 7–10 years are often associated with changes in vascular tone. The reasons may lie in brain hypoxia, a clear sign of which is constant yawning. In addition to oxygen starvation, the development of VSD syndrome can be influenced by diseases associated with dysfunction:
- Of cardio-vascular system.
- Kidney.
- Liver.
Medical statistics claim that VSD affects children exposed to constant stress and overwork. The atmosphere in the family plays an important role in the development of the disease. With constant scandals in the house, the child gets a severe headache. VSD syndrome resolves when the underlying disease is eliminated and the patient’s emotional background is stabilized.
Head pain is accompanied by disturbances in heart rate and blood pressure. Such children are subject to frequent mood swings and excessive irritability.
What are the reasons for headaches at night?
In schoolchildren, pain in the head area can be from mental or physical overload received during the day, while newborn children are aggressively affected by various external irritants. The cause of a sore head can be an error in eating, an incorrect physiological position of the body during sleep, which can lead to poor circulation, and ultimately to headaches.
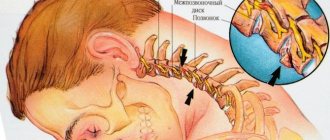
Even a poorly chosen pillow or a scratchy blanket can lead to insufficient oxygen supply to the child’s body, or a long stay in an unventilated room. Headache at night due to medications taken before bedtime, with osteochondrosis (dystrophic changes occurring in the joints, compression of the nerve endings of blood vessels in the spinal column)
Depressed children who have experienced stress the day before also have headaches at night, also when their blood sugar levels rise. With diabetes, the patient often wakes up at night from sharp and burning pain.
TTH (tension headaches)
The peak of such pain occurs between the ages of 7 and 10 years. Approximately 75% of cephalgia are the result of tension headaches.
The problem happens with children:
- spending a lot of time at the computer and watching TV;
- with crooked posture;
- with tension in the neck muscles.
The main complaint is localization of pain in the frontal or parietal region. Pressing pain that calms down after the patient rests. Children have severe headaches, but by the time they reach adulthood, the disease goes away.
Who is at risk?
The main and most common cause of tension-type headache is considered to be an emotional state. Constant anxiety, stress, depression, and psychological stress are the “pebbles” that injure the nervous system. An irrational approach to planning the day leads to fatigue, irritability, and poor diet. All this depletes the body as a whole and the nervous system cannot withstand the load.
The pathogenesis of muscle tension headaches is based on contraction of the muscles of the shoulders, neck, and head. This occurs under poor working conditions. These include:
- uncomfortable workplace (table, chair), which forces you to take an incorrect position;
- prolonged visual strain (working at a computer, with small parts);
- constant monotonous action;
- night shifts;
- mental stress.
But the source of the problem can be not only working time, but also rest. For example, sleep is of great importance. An uncomfortable bed or pillow contributes to incorrect posture during sleep, especially after taking sleeping pills or alcoholic beverages. In this case, the muscles of the shoulder girdle will be in constant tension.
Doctor's note: Long-term and independent treatment of headaches with analgesic drugs can also cause deterioration in well-being.
Tension headaches often occur against the background of a depressive state (constant feelings of guilt, fear, experiences that are depressing in nature).
Meteorological weather conditions can also affect a person's state of mind.
Pathogenesis (mechanism of development) of tension headaches
Summarizing the risk factors, we can identify possible victims of tension headaches: office workers, drivers, jewelers, schoolchildren, individuals suffering from depression, etc. The lion's share of potential patients with this problem belongs to females and people over forty years of age.
Photo gallery “At Risk”
This disease is not inherited. However, it is classified as a disease with a genetic predisposition.
Intracranial pressure disorder
The concept of intracranial pressure disorder refers to hypertension, that is, a change in pressure in the vessels of the brain. This disease usually affects young children. Vascular incompetence and a sharp drop in pressure causes activation of pain receptors. The accumulation of intercellular fluid puts pressure on the vessels and pain occurs. The danger of hypertension lies in the possible development of convulsive syndrome.
With increased intracranial pressure, the baby constantly has a headache when the weather changes or overwork. By the age of five, the disease usually subsides. Bursting pain may be accompanied by vomiting, in some cases uncontrollable.
Intracranial pressure can be not only increased, but also decreased. Fluid deficiency leads to tension in the membranes of the brain. It is stretching that leads to increased pain. The unpleasant feeling goes away when you change the position of the head and body.
Why is there a knocking in my temples?
Pain, pulsating and pressing on the temples, leads to irritation, nervousness, loss of appetite, dizziness and even blurred vision and stuffy nose in the child.
There is a knocking in the temples when:
• migraine with a duration of 1.5 hours to 2 days in young children;
• arteritis with swelling of the temporal artery;
• development of inflammatory processes in the body;
• cephalalgia (head pain is observed, accompanied by nausea and radiating to the temple area);
• intracranial hypertension due to increased pressure in blood vessels, expansion and compression of the brain;
• abscess with the accumulation of pus in the areas of the alveolar processes (prolonged, shooting, aching pain is observed);
• neuralgia (pulsates, shoots and radiates in the temples);
• inflammation of the tonsils of the nasopharynx (in children 3-5 years old it usually has an acute course);
• anemia due to a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood;
• lack of iron in the body (headache for a long time, more than 5 days, accompanied by dizziness, shortness of breath).
Viral and infectious diseases
Any viral and infectious diseases begin with pain in the head. Intoxication is the main cause of the disease. Toxic substances formed during the life of viruses and microbes poison the child’s body. Common symptoms of intoxication also include:
- Weakness.
- Fatigue.
- Drowsiness.
- Nausea.
Along with the above symptoms, body temperature increases, body aches and muscle pain appear. Therefore, if a child has a severe headache and is shivering, it is likely that he has an acute respiratory viral infection or acute respiratory infection. A pediatrician can make a diagnosis when examining a small patient.
Injury
Injury to the skull entails severe pain in the head area. If a child receives such an injury, there is a risk of brain damage.
Therefore, in this case, he should be hospitalized immediately.
The need for hospitalization arises even if the baby does not complain of feeling unwell. Symptoms such as nausea, dizziness and pain may occur over time.
One of the most noticeable signs of a head injury is loss of consciousness. Parents should also be wary of the fact that their child complains of darkening of the eyes.
What needs to be done before the ambulance arrives if the baby is injured? Firstly, he needs to be provided with complete rest. The child is placed on a bed in a room where bright light does not flicker.
To prevent the formation of bruises and swelling in the bruised area, it should be rubbed with your hands. It is also recommended to apply something cold to the injury site.
Even if the child is not hospitalized, it is not recommended to play outdoor games with him for several days after the injury, as this can cause pain.
If a few days after the injury the baby complains that his head area hurts, this is an alarming symptom.
Parents should immediately take him to the nearest medical facility for medical diagnosis.
Symptoms such as vomiting, severe dizziness and pain in the back of the head indicate a concussion.
Meningeal headaches
Inflammation of the membranes of the brain caused by viruses and bacteria is always accompanied by pain in the head.
Meningitis is characterized by:
- severe pain in the head;
- vomit;
- fear of light and sounds;
- increased sensitivity of the skin;
- forced position of the patient in bed.
A patient with meningitis lies on his side, his head thrown back, and his legs tucked to his stomach. If you try to bring your head to your chest, muscle spasm occurs (stiff neck). It is dangerous to treat such a patient at home; only timely help from doctors will help relieve inflammation from the membranes of the brain.
Poisoning
Acute food poisoning is characterized by severe headaches in children. This symptom is a consequence of intoxication of the body. If a child complains of soreness in the head, nausea and weakness, it is important to find out what he ate at school or at a party. Later, vomiting and diarrhea occur. The worst thing about poisoning is dehydration. Only replenishing lost fluid will help you recover quickly. Give the patient food often and in small portions. You must tell your doctor about what happened.
Diagnostic measures
If a child has a severe headache, what should you do? The very first step parents take is going to the doctor. Diagnostics will reveal the true cause of the disease.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following will be prescribed:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- X-ray of the cervical spine.
- Angiography.
- Duplex of cerebral vessels.
- REG.
If meningitis is suspected, the patient is indicated for a spinal puncture, with examination of the cerebrospinal fluid for the presence of pathogens.
Only after diagnosis will the doctor announce the verdict on why the headache hurts and how to deal with it.
When to sound the alarm
Calling an ambulance or going to the doctor is urgent if your child has:
- severe and sudden headache;
- unusual, shooting pains, accompanied by noise in the ears and head;
- when changing body position, the pain intensifies;
- pain is observed in the morning;
- during an attack, consciousness becomes confused;
- severe pain after a previous injury.
There are many types and forms of headaches in children; only a doctor can identify the true cause. It is very difficult to recognize what is bothering a child if he is still very young. Infants react to discomfort in the head with anxiety, refusal to eat, insomnia, and frequent regurgitation. With intracranial hypertension, “fountain” vomiting may occur. The fontanel pulsates and bulges.
Older children complain of fatigue, holding their heads and trying to lie down. Some people try to distract themselves from discomfort by fiddling with their hair or scratching their face.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Associated symptoms may indicate the nature of the pathology, but even an experienced doctor is not always able to determine the nature of the disease. For this purpose, laboratory and hardware studies are carried out.
Acute and chronic forms
If the phenomenon was momentary, but strong, it is an acute form. Periodic occurrence indicates an established, chronic form.
Bunch pain
Develops when the trigeminal nerve becomes inflamed or irritated. It is more common in boys and can last up to several hours, especially severe at night.
First aid for a child
Treatment of headaches in children at home begins with creating complete peace. Television and other external irritants must be eliminated immediately. Place the patient in bed, soak a towel in cool water and apply for 5 - 7 minutes. The room should be well ventilated. Very often, children suffer from pain due to stuffiness in the room.
Offer the patient a warm drink, especially if vomiting occurs. Ascorbic acid relieves cephalalgia well. You can give 2 - 3 tablets of ascorbic acid or tea with lemon. Decoctions of soothing herbs - motherwort, valerian - will relax the blood vessels and help the child fall asleep. Do not give chocolate under any circumstances - this product provokes even greater pain.
If rest and sleep do not help, it would be a good idea to consult a doctor. Children can only take Paracetamol and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Ibuprofen.
Do not overuse medications. The only thing that differentiates a medicine from a poison is the dose. Failure to comply with the frequency and exactly specified dosage can cause significant harm to health.
Create the most comfortable conditions if the pain is not frequent and is associated with overload at school. If attacks are repeated with a certain frequency, and the child turns pale, loses consciousness, or does not remember the events taking place, call an ambulance immediately.
Preventive actions
To reduce the intensity of pain and protect as much as possible from relapses, follow simple rules that are very easy to follow:
- The child must have a clear daily routine.
- Meals are timely and rich in microelements.
- Regular walks in the fresh air.
- Protecting the child from stress and overwork.
- Ventilation of the children's room.
- The family environment should be as comfortable as possible for children.
- Communication and participation in the life of a small family member.
- Active lifestyle.
- Limitation on computer games and hours of sitting in front of the TV.
If your child suffers from frequent cephalgia, you should be regularly monitored by a neurologist. This is especially true for children aged seven. Primary school completely changes the daily routine, mental and emotional state of the student. Excessive mental stress should be corrected by the attending physician and distributed in a rational manner.
Source