Indications
The essence of a biopsy is to extract a certain type of tissue from the brain, the study of which will allow for a more accurate diagnosis of the disease. Since this method is invasive, it can only be performed strictly according to indications.
The procedure is carried out when:
- Neoplasms of unknown origin. In order to determine the severity of the ongoing disease, prescribe adequate treatment, and give the patient prognoses for subsequent life, the doctor needs to know whether the tumor located in the brain is benign or malignant. A biopsy will help answer this question.
Cerebral toxoplasmosis. This pathological condition occurs as a result of the penetration of Toxoplasma into the cells of the human body. The only way to detect the parasite inside the brain is through a biopsy.- Abscesses and bruises that occur between brain tissues.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Hemorrhagic stroke.
- Alzheimer's diseases.
- Diseases of the brain of an inflammatory and infectious nature.
This diagnostic method is used for histological purposes to determine the changes that brain tissue has undergone during certain diseases.
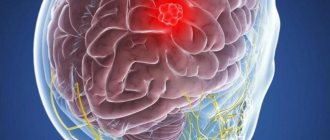
Causes of astrocytoma
The exact causes of brain tumors such as astrocytoma cannot be determined. Experts believe that the neoplasm is multifactorial and appears as a result of the action of several unfavorable factors. The tendency for the growth of astrocytomas is especially pronounced in economically developed countries, whose residents have to breathe exhaust fumes and are daily exposed to waste released into the environment by thousands of industrial enterprises.
The quality of human nutrition also contributes to the development of cancer: food rich in dyes, carcinogens, and animal fats is somehow involved in triggering pathological reactions in the body, including the growth of malignant cells.
Previously, oncological pathologies were diagnosed mainly in older people. Today, brain tumors are increasingly common in young and middle-aged people. The wide capabilities of modern diagnostics and neurosurgery make it possible to detect pathological changes in organs and tissues as early as possible and organize effective therapeutic measures.
Types of biopsy
It was previously noted that certain indications are required for a doctor to prescribe a brain biopsy. The choice of the right type of biopsy will depend on the clinical picture, the pathology occurring in the patient, the severity of its course, as well as other characteristics of the body not related to the underlying disease.
There are three types of brain biopsies:
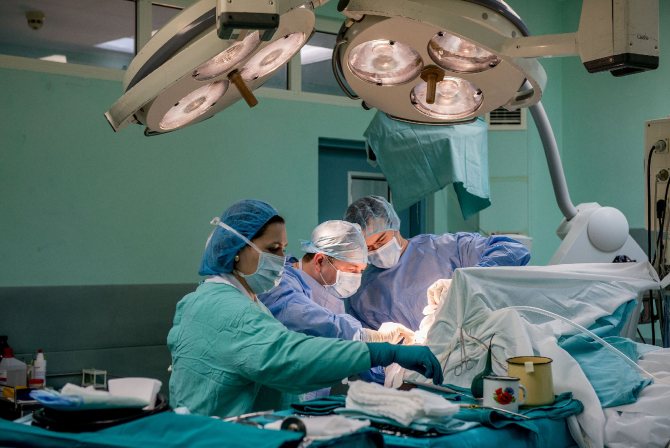
Needle biopsy. It is carried out after the doctor drills a hole in the skull of a sick person through which a thin hollow needle is inserted, followed by the removal of the required amount of material.- Stereotactic biopsy. This procedure is considered minimally invasive because only a small amount of brain tissue is removed. The progress of the procedure is monitored using computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
- Open biopsy. To perform this type of brain biopsy, it is necessary to remove a certain bony part of the skull. This complex surgical intervention, which is performed under general anesthesia, is associated with a high risk to the health of the sick person . Therefore, it should only be carried out by experienced, highly qualified specialists. After a biopsy, long-term rehabilitation measures are mandatory.
Preventive actions
Prevention of the growth of astrocytomas includes protecting the body from radiation exposure, excess ultraviolet radiation and other negative factors, including the consumption of foods and drinks with potentially dangerous chemical components. It is also important to pay attention to working conditions. It is recommended to limit contact with chemicals, objects and equipment that provide a high radiation dose to the body.
Regular preventive examinations and screening studies will allow timely diagnosis of brain cancer processes. The best methods of prevention are timely seeking medical help and regular diagnosis. Today, every person can undergo all the necessary studies and receive detailed information about the state of their health. If an astrocytoma is detected, it is better to remove it immediately. This will prevent the spread of the cancer process to healthy tissue and increase the patient’s life expectancy.
How is a brain biopsy performed?
Neurosurgeons can perform this invasive diagnostic method only in a hospital setting, where all the necessary equipment and drugs are available to ensure the normal implementation of the procedure and the provision of medical care to the sick person in case of complications.
Puncture method
In less complex clinical cases, a puncture biopsy is performed. After performing anesthesia, the doctor makes an incision and drills a hole in a certain place in the patient’s skull. A thin needle is placed into it and gradually moved inwards, at the end of which there is a micro-video camera and a lighting device. They are needed so that the doctor controls the movement of the needle inside the brain tissue. After collecting the material, the needle is carefully and slowly removed.
Public method
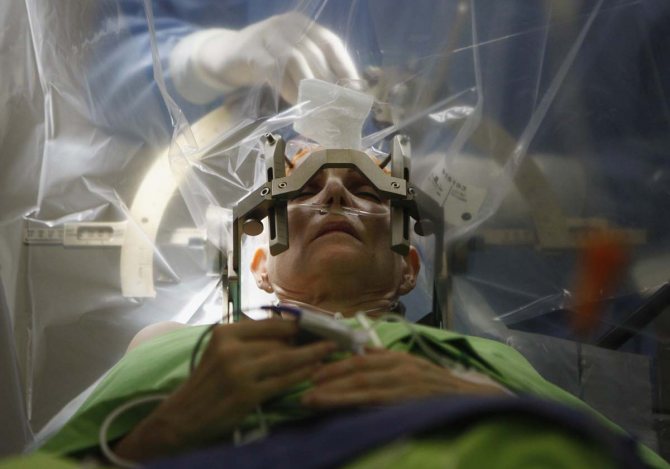
Stereotactic method
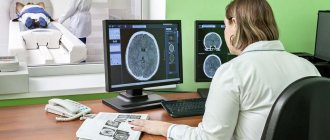
Initially, the stereotactic frame is fixed on the patient’s head. Using an MRI indicator attached to it, the exact location of the pathological area or tumor in the brain is determined. Next, thanks to special software, the trajectory along which the instrument will be inserted into the brain is calculated. Due to this, accidental damage to blood vessels or important centers of the organ can be avoided.
After administering local anesthesia, puncturing the skin and creating a hole using a cutter, the doctor inserts a stereotactic needle into the tissue . Its peculiarity is that the needle does not pierce, but pushes the tissue apart. The required amount of material is extracted from the area that is the subject of the study. He is sent to the histology laboratory. One suture is placed on the human skin. To check the correctness of the procedure and the absence of brain damage, a follow-up examination is carried out using a CT or MRI machine after it.
Important
The risk of complications after a stereotactic biopsy is minimal because it is a minimally invasive procedure. Refusal of it is more dangerous for a sick person than its implementation, because without determining an accurate diagnosis it is impossible to prescribe adequate treatment, which ultimately leads to disastrous consequences
Symptoms of astrocytoma
Astrocytoma of the brain is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure, an irritating effect on brain structures and the formation of toxins as a result of the metabolic processes of malignant cells. Therefore, the main symptoms of the growth of such formations are the following:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- decreased appetite;
- fatigue and irritability;
- decreased cognitive function, deterioration of memory and attention.
The severity of clinical manifestations depends on the degree of malignancy of the tumor, its size and location. The neoplasm compresses and destroys cerebral structures, which is why focal symptoms occur. Hemispheric astrocytomas cause weakening of muscle strength in the limbs and physical weakness.
Some people have problems coordinating movement. Most often, this symptom appears when the tumor is located in the cerebellum. Mental disorders and even aggression are also possible. When the temporal lobe is damaged, speech apparatus disorders appear, memory is noticeably reduced, and hallucinations, taste, and hearing disorders may appear. Astrocytoma, localized between the occipital and temporal lobes, impairs vision. Visual hallucinations may occur. Impairment of fine motor skills and written speech is typical for neoplasms that are located in the parietal zone.
Consequences of a brain biopsy
Modern medicine methods make it possible to minimize the risk of life-threatening consequences associated with a brain biopsy. But surgical intervention may not always be performed correctly and accurately.
As a result, the following may develop:
- acute circulatory disorders in the brain;
- attacks of involuntary muscle contractions;
- secondary infectious processes;
- bleeding;
- swelling of the tissues located around the surgical site;
- comatose states.
Classification of astrocytomas
The main types of brain astrocytomas:
- fibrillar;
- subependymal (glomerular);
- protoplasmic;
- pyelocytic (piloid);
- glioblastoma;
- gemistocytic;
- anaplastic;
- microcystic cerebellar.
The most dangerous form of the tumor is considered to be the pyelocetaceous one. It is classified as the first degree of malignancy. Fibrillar, gemistocytic, protoplasmic astrocytomas are tumors of the second degree of malignancy. They are less life-threatening. But without effective surgical treatment, grade 2 astrocyotoma leads to the death of the patient.
The third degree includes anaplastic tumors and glioblastomas. They account for more than 50% of all malignant brain tumors. Surgery is also used to treat grade 3 astrocytoma. The sooner the tumor is removed, the better the prognosis for life.
Recovery period
After carrying out this diagnostic method, the patient must be under the supervision of medical personnel for a certain time. The duration of this time period is determined by the doctor, who takes into account the complexity of the procedure, the general condition of the sick person after it, and the presence of concomitant diseases in the patient. If we take into account the fact that a biopsy is a diagnostic method that is often prescribed for a pathology that is serious and dangerous to the patient’s health, restorative measures will be more aimed at treating the manifestations of the underlying disease, rather than the consequences of the procedure.
Tulpa V.V., doctor, medical observer
8, total, today
( 187 votes, average: 4.63 out of 5)
Pipelle biopsy of the endometrium with histological examination: what it is, how it is performed, indications, contraindications, complications
Blood test for tumor marker CYFRA 21-1 - laboratory diagnosis of lung cancer
Related Posts
Diagnostics
To select the correct treatment tactics and type of operation, a comprehensive diagnosis is performed. The patient is consulted for neurosurgery by neurologists. Additionally, you can contact other relevant specialists.
The examination includes the following methods:
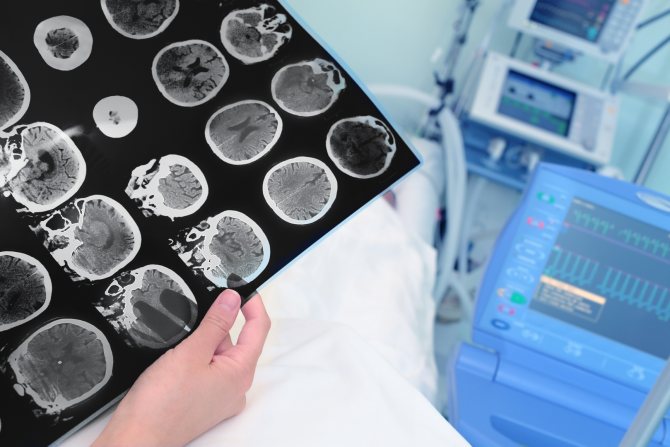
- CT, MRI of the brain;
- electroencephalography;
- study of the vestibular apparatus;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- angiography;
- histological examination of tumor tissue.
Angiography can detect cerebral astrocytoma, plan further treatment tactics and prescribe surgery. The degree of malignancy of the neoplasm is determined by the results of histological analysis. The biomaterial is obtained during a stereotactic biopsy, and then a histological examination is performed.