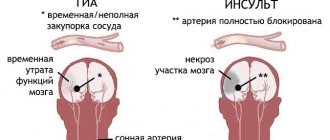
Symptomatic focal post-traumatic epilepsy develops in 11-20% of patients who have suffered traumatic brain injury (TBI); its frequency and severity depend on the severity of the primary TBI, the location of the post-traumatic focus, the state of the premorbid background (the presence of repeated TBIs and genetic predisposition) [18]. The disease in most cases is the result of the action of vascular, toxic and other factors that cause the development of intellectual-mnestic disorders [1].
The basic principles of treatment of post-traumatic epilepsy are the following: treatment of traumatic brain disease, aimed at correcting vascular, autonomic, cognitive, motor and other disorders caused by trauma; antiepileptic therapy itself; treatment of concomitant somatic pathology.
In post-traumatic epilepsy, the use of antioxidant and nootropic drugs in combination with basic antiepileptic therapy is considered justified.
However, there are currently no clear recommendations for the use of nootropic therapy in patients with symptomatic epilepsy [10]. There is an opinion [23] that the use of nootropics for epilepsy can cause an increase in epileptiform activity and aggravate the course of the disease with an increase in attacks.
In this aspect, the use of phenotropil for epilepsy should also be considered. The domestic drug phenotropil (N-carbamoyl-methyl-4-phenyl-2-pyrrolidone) has been used in clinical neurological practice since 2003. It is a phenyl derivative of pyrrolidone, i.e. has a phenyl radical in its structure, the presence of which somewhat changed the spectrum of pharmacological activity of this drug compared to other pyrrolidones. Phenotropil has nootropic, anxiolytic, antiasthenic, antiepileptic and neuromodulatory effects. Although the mechanism of pharmacological action of phenotropil has not been fully studied, the following features of its action have been established today: 1) binding to n-ACh receptors of the hippocampus [24] (presynaptic n-ACh receptors modulate the release of dopamine, serotonin, glutamate, GABA and acetylcholine itself in the brain) [4]; 2) lack of affinity for dopamine D1, D2 and D3, serotonin 5-HT2 and glutamate NMDA receptors [4]; 3) the ability to reduce the density of D1 and 5-HT2 receptors compared to control by 20 and 18%, respectively [4]; the ability to increase the density of D3, n-ACh and NMDA receptors by 30, 58 and 67%, respectively [4].
Significant positive experience has been accumulated in the use of phenotropil in clinical practice in individuals with various diseases of the central nervous system. In terms of this study, the previously established [3, 7, 8, 14, 15, 17, 20] antiepileptic activity of the drug is of particular interest.
As for Mexidol, its mechanism of action is associated with the influence of lipid peroxidation processes, which play a large role in the development of traumatic disease and post-traumatic epilepsy in particular [9]. This role justifies antioxidant therapy in post-traumatic epilepsy.
It was found [1, 2, 5, 12, 13, 19] that Mexidol has a pronounced anticonvulsant effect. Particularly effective is the combined use of Mexidol with other antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) [15, 19], for example, with carbamazepine [2, 6].
The purpose of this study is to study the clinical effectiveness and safety of the use of the nootropic drug phenotropil and the antioxidant Mexidol in patients with symptomatic focal post-traumatic epilepsy.
What are nootropic drugs?
Nootropic drugs contain chemical compounds that enhance brain activity, stimulate the nervous system and metabolic processes in general. Increased stress on the nervous system slows down brain activity and leads to poor circulation.
These drugs can increase energy, speed of thinking and memorization of information. It’s not for nothing that they are also called “smart drugs.”
Nootropics with proven effectiveness affect the activity of nerve impulses, accelerating brain function. Piracetam (the first nootropic substance) was invented in 1964 in Belgium as a derivative of pyrrolidone. From this stage, the synthesis and development of neurometabolic stimulants began.
Nootropics with proven effectiveness help with neuralgic diseases. The list of drugs will help you choose the best ones.
The most common nootropics:
- pyrrolidone derivatives;
- diaphenylpyrrolidone derivatives;
- amino acid derivatives;
- neuropeptides.
Complex preparations have been developed that contain a combination of stimulating substances.
Mechanisms of action

Photo: https://pixabay.com/illustrations/brain-mental-health-psychology-3441536/
The first nootropic drug (Piracetam) was synthesized back in 1964 by Belgian pharmacologists. It increased mental activity and had virtually no side effects.
The active substances gently and very carefully act on nerve cells and help them become a little more “happier”. Initially, the drugs were developed to help not the damaged brain, but the “chronically tired” or developmentally delayed one.
How do nootropics affect a person? Their action is due to the following processes:
- improvement of cerebral circulation;
- providing the brain with energy due to faster absorption of glucose;
- saturation of brain tissue with oxygen;
- stimulating communication between the prefrontal cortex and other areas of the brain;
- influence on the accelerated production of certain neurotransmitters, thanks to which cognitive functions are activated, information is more easily processed and absorbed;
- strengthening the membrane of nerve cells;
- increase in the speed of impulses in the brain;
- improvement of nucleic acid metabolism.
As a result, metabolic processes in the brain accelerate, memory becomes “stronger”, perception is more “alive”. For this reason, nootropics are popularly known as “cognition stimulants” and “brain vitamins.”
However, there are several myths that would be useful to dispel.
You should not think that nootropics “accelerate” the brain to a new level - a person will not have any superpowers. Everyone’s intelligence and level of development are individual; a drug can help facilitate the completion of a particular task, but its solution will entirely depend on the available knowledge.
A single dose or a large dose will not increase the brain's potential and capabilities. Nootropics are taken as a course because they have a cumulative effect. Swallowing a pill before an important exam or difficult work, in the hope that “your brain will fall into place,” is useless. You need to take the drug at least a month before the session.
Reception features
Since nootropics work in brain cells, they use drugs with great caution, based on the basic principles of using neurometabolic drugs:
- feasibility, since the nootropic effect is not needed so often: a complete clinical and laboratory examination of the patient is needed, an accurate diagnosis, prediction of the desired result, analysis of possible risks and side effects;
- the prerogative of a neurologist in prescribing nootropic drugs;
- systematic course of administration - occasional use of drugs is pointless, nootropics have accumulation and the effect becomes noticeable only against the background of long-term use of drugs;
- complexity - nootropic drugs are not able to solve therapeutic problems, concomitant diseases are treated simultaneously as part of combination therapy (sometimes cerebral ischemia or hypoxia requires an integrated approach to treatment);
- Constant monitoring is a necessary measure in therapy, since there is a possibility of adjusting the dose or duration of the course during treatment, and sometimes discontinuing the drug.
Indications for the use of nootropics for memory
Drugs to improve memory and brain function are not a harmless remedy, so it is necessary to take into account the indications for their use. The remedies differ in strength, duration and mechanism of action.
They help in the following conditions:
- If the ability to remember new information has deteriorated;
- With a decrease in mental activity;
- For inflammatory diseases of the brain;
- For encephalopathy caused by poisoning with toxic substances;
- Impaired brain activity as a result of alcohol abuse;
- Consequences of TBI;
- Hyperkinetic activity;
- Age-related dementia, dementia.
Nootropics for improving memory are not prescribed in a number of cases:
- Intolerance to active components;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Acute or chronic renal failure;
- Stroke (acute period).
In some cases, the patient has no contraindications to the prescription of nootropic drugs, but when used, adverse reactions occur.
It can be:
- Allergic reaction;
- Dyspeptic disorders (stool disorders, nausea, vomiting);
- The appearance of drowsiness;
- Irritability;
- Sleep disturbance;
- Blood pressure fluctuations.
The appearance of these conditions suggests that you need to replace this drug with another with a similar effect, but you cannot do this on your own. Due to the fact that the active ingredients of different drugs may belong.

Side effects
Medicines have low toxicity, so the detected negative phenomena can be considered as consequences of non-compliance with instructions and restrictions. According to the instructions, the following may appear:
- sleep problems;
- increased mental or motor activity, or vice versa, lack of vigor, lethargy;
- noise in the head;
- nausea;
- headache;
- constipation;
- allergic reaction, itchy skin.
If the medicine provokes such side effects, then the dose should be reduced; in case of allergies, stop taking it.
Types of nootropics
Nootropic drugs are not classified as a separate class; they are combined with psychostimulants.
Depending on the active substance, clinical effectiveness, and mechanism of action, they can be divided into two groups:
- “true” nootropics with a predominant mnestic effect, that is, affecting memory;
- neuroprotectors (broad-spectrum) that protect brain neurons from various damages.
The first group includes:
- racetams (drugs whose names end in “-tam”) - piracetam, pramiracetam, phenylpiracetam and others. They improve cerebral blood flow and enhance metabolic processes;
- cholinergic drugs. They have a vasodilating effect;
- neural peptides. Regulate the physiological functions of the body;
- amino acids. They are “building materials” that form proteins.
Neuroprotectors include:
- substances that activate metabolic processes in the brain;
- strong vasodilators;
- calcium antagonists that lower blood pressure;
- antioxidants that protect the body from toxins and aggressive environmental influences;
- a group of substances that affect inhibitory neurons.
Basic nootropic drugs
Which ones are better in the treatment of neurological diseases? The use of nootropic drugs can be combined or independent. Typically, nootropics are used as stand-alone therapy for minor disorders. The following drugs with proven effectiveness are widely used in neurological practice:
- Piracetam.
Probably the most popular nootropic. The drug enhances metabolic processes in the brain. Used for the treatment of systematic dizziness and correction of dyslexic syndrome. In adult patients, the drug is used as a complex therapy for myocardial infarction, withdrawal syndrome for addictions of any origin. Doctors prescribe a remedy for the treatment of neuroinfections caused by viral agents. - Memoplant One of the best herbal nootropics. The German drug Memoplant contains highly purified extract of Ginkgo biloba EGb 761®. Many preparations of ginkgo biloba contain a significant amount of harmful impurities - ginkgolic acids. Memoplant does not have this drawback, since it is cleaned during 27 production stages. The drug increases the resistance of nervous tissue to oxygen deficiency and improves cerebral circulation. Effective for dizziness, noise in the ears or head, as well as decreased memory and performance.
- Vinpocetine.
With constant use, the blood vessels of the brain dilate and microcirculation increases. The active substance of the drug ensures complete transport of oxygen to brain tissues and increases the absorption of nutrients. Vinpocetine has a pronounced neuroprotective and antioxidant effect. The treatment regimen changes from first administering intravenous solutions and then switching to tablet forms of the drug. Used as an adjuvant in antihypertensive therapy. - Phenibut.

High effectiveness is noted for functional disorders of the vestibular apparatus, sleep disorders, neurasthenia, and asthenic syndrome. Long-term use normalizes metabolic processes in brain tissue at the cellular level. The strengths of the drug are its psychostimulating ability and antioxidant effect. The drug is characterized by low toxicity and few side effects. - Fenotropil.
The drug belongs to a new generation of nootropics with a pronounced adaptogenic effect. Patients show resistance to stressful situations without causing drug dependence. Phenotropil is prescribed to patients with strong emotional and mental stress. - Fezam.
A nootropic directly intended to treat impaired blood circulation in the brain. Effective for serious diseases of the nervous system, circulatory disorders in the vascular system of the brain. In complex therapy, headaches with increased intracranial pressure are relieved, and the functioning of the organs of hearing and vision is improved. Fezam is prescribed for amnesia and is highly effective in hypoxic syndrome. - Cinnarizine.
A drug intended to strengthen the vascular walls of the brain during their dilatation (stretching). At the same time, blood pressure indicators remain within the usual norm. Effective in the prevention of motion sickness and vestibular disorders. Prescribed for chronic migraines, increased hypertension, accompanied by dizziness, tinnitus, and headache. Cinnarizine is used in adult women to reduce the symptoms of menopause. - Cerebrolysin.

The safety and effectiveness of the drug has been proven by numerous studies. Used as an adjuvant therapy against serious mental and neurological disorders. When the dosage is prescribed correctly, mental processes are activated, concentration and mood increase. Long-term use improves memory and increases learning ability. - Actovegin.
A drug classified as an antihypoxic nootropic. Used to treat metabolic disorders in the brain, promotes rapid healing of wounds. The drug is used as a complex therapy for radiation-induced skin lesions and diabetic polyneuropathy. Actovegin is available in the form of tablets, intramuscular, intravenous solutions and intra-arterial injections. There is also a form of the drug for topical use.
Nootropic drugs for the treatment of serious neurological disorders are used in adult neurological practice. When used as complex therapy, the likelihood of a decrease or increase in the activity of other drugs is taken into account.
Combined products
Among nootropics, there are drugs with a combined composition. Such products include two or more active components, which to one degree or another enhance or reduce the effect of each other. The main drugs in the series are:
- Gamalate B6 (composed of pyridoxine hydrochloride, magnesium glutamate hydrobromide);
- Omaron, Fezam, Evriza, Noozom (Piracetam and Cinnarizine, auxiliary components);
- Neuronorm (active ingredients Piracetam and Cinnarizine);
- Olatropil (Piracetam and GABA);
- Thiocetam (Piracetam and Thiotriazolin).
All products are similar in effectiveness to Piracetam. Combination drugs are used for severe problems; similarly to popular drugs, they are used in monotherapy and in combination with other drugs.
All medications, despite the absence of side effects, require a doctor's prescription. Only on the basis of medical examination data can an accurate diagnosis be established, which will determine further adequate treatment.
Old and new generation drugs
Old-generation nootropics are derivatives of Piracetam, the very first synthesized drug of the group. The essence of the action of drugs is to improve the condition of existing neurons. Such drugs not only affect the psychophysiological reactions of the body, but also correct the general state of the nervous system, improving perseverance and the process of memorization.
A feature of such nootropic drugs is a positive effect on the thinking process, increased criticality of the perception of the surrounding reality, and the patient’s own behavior.
The drugs are well tolerated, quickly absorbed, and easily cross the blood-brain barrier, penetrating neurons.
Drugs derived from Piracetam get along well with antidepressants, stimulating the activity of the latter. The disadvantage of old nootropics is the feeling of drowsiness after taking them and a rather weak therapeutic effect, which manifests itself only with long-term use of the drugs (after discontinuation, the result quickly goes to zero).
The list of old nootropic drugs today includes:
Name of medicine Price in rubles
| Nootropil | 239 |
| Omaron | 126 |
| Tanakan | 518 |
| Glycine | 30 |
| Thiocetam | 575 |
| Olatropil | 260 |
| Piracetam | 25 |
| Cerutile | 191 |
| Bemethyl | 499 |
| Phenibut | 43 |
New nootropics are drugs of the third or latest generation of drugs. The list of such drugs is constantly expanding, but not every new drug has proven effectiveness. All new medications are divided into three types:
- mediator - suppliers of neurotransmitters responsible for transmitting signals from one nerve cell to another (Lecithin);
- stim-like - drugs have a neurometabolizing and tonic effect at the same time (Phenotropil);
- neuropeptide - drugs do not stimulate old neurons, but create young ones (Semax).
New generation nootropic drugs are able to stimulate the synthesis of mediators and stabilize the work of biologically active substances, improving the transmission of nerve impulses from one neuron to another. This allows the nervous system to perform its functions fully. Nootropics help produce energy within the body and correlate its level with increased or decreased physical activity.
Medicines improve the functioning of the immune and cardiovascular systems, affecting the blood supply and oxygen supply to nerve cells. Due to the mild vasodilating effect, regional blood flow is normalized, the effect on metabolic processes allows nootropics to participate in the resorption of atherosclerotic plaques, restoring the lumen of blood vessels that nourish neurons.
The disadvantages of new generation nootropics include irritability and possible insomnia, which are quickly neutralized by sedative drugs.
The main disadvantage remains the lack of knowledge of new drugs, the incompletely clear features of their effect on the central nervous system, and side effects. However, the emergence of modern drugs is a guarantee of the treatment of neurophysiological and neurometabolic disorders in the future.
By and large, the result of the action of all nootropics is a younger and healthier brain. And this is important for the future.
The list of third generation nootropic drugs includes:
Name of medicine Price in rubles
| Lecithin | 300 |
| Carphedon | 1 350 |
| Fenotropil | 1 036 |
| Sydnogluton | 1 000 |
| Fezam | 259 |
| Diapiram (Diaperid) | 140 |
| Cerebrolysin | 996 |
| Cortexin | 766 |
| Semax | 335 |
| Ginkum | 262 |
| Noben (Idebenone) | 526 |
| Cerepro | 265 |
| Noopept | 320 |
Latest generation nootropics: indications, contraindications, side effects
The main branches of medicine where the use of nootropics for the brain is indicated are psychiatry, neurology, gerontology and pediatrics. Drugs of this clinical and pharmacological group are prescribed for the following diseases and pathological conditions:
- Decreased mental and physical activity;
- Deterioration of thinking abilities;
- Problems with memory and concentration;
- Neuroinfections (for example, encephalitis or polio);
- Impact of toxic substances on the brain;
- Cerebral blood flow disorders;
- Senile dementia;
- Encephalopathy and withdrawal symptoms due to regular alcohol abuse;
- Stuttering;
- Consequences of TBI (brain damage);
- Ischemic stroke;
- Enuresis;
- Hyperkinesis.
Nootropics are not prescribed to patients diagnosed with:
- Hypersensitivity to the active component or intolerance to auxiliary ingredients;
- A marked decrease in the functional activity of the kidneys (acute or chronic renal failure);
- Hemorrhagic stroke (acute period);
- Gettington's chorea (hereditary degenerative disease of the central nervous system).
The vast majority of patients tolerate therapy with nootropic drugs well. In some cases, the following side effects may develop:
- Unmotivated feeling of anxiety;
- Night sleep disturbances;
- Daytime sleepiness;
- Increased irritability;
- Instability of blood pressure;
- Dyspeptic disorders;
- Allergy.
How safe are memory enhancing medications?
If you have insomnia, bad mood, problems with memory and concentration, pills will not be able to remove the causes of these disorders. The most they will do is reduce the symptoms a little. However, you need to be prepared for side effects. It is recommended that you first understand the reasons behind your memory problems.
A tooth hurts, what to do at home to make the pain go away quickly, tablets for toothache, folk remedies
In most cases this is:
- - poor nutrition;
- - sedentary lifestyle;
- — oxygen starvation;
- - psychological injuries;
- - lack of sleep.
First, find out the cause of the problem, and then try to deal with it!
The best nootropics with a calming effect
Phenibut
350 (tablets 0.25 No. 20)
Phenibut is able to relieve tension, fear, in complex therapy improves sleep, enhances the effect of sedatives and hypnotics. Has a slight sedative effect.
The drug is able to facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses in the central nervous system and has an antiplatelet effect, preventing red blood cells from sticking together. Able to improve some psychological indicators, for example, reaction speed, memorization time.
It is used in complex therapy of encephalopathy, in the early recovery period of ischemic stroke, and can be successfully used even in old age, since it does not cause an inhibitory effect. It fights well against fears of various causes. It is used to prevent seasickness in air passengers, as well as when traveling by other modes of transport. The distinctive effect of the drug is the lack of influence on cholinergic receptors and histamine receptors. Therefore, it does not cause dry mouth and other symptoms characteristic, for example, of first-generation antihistamines.
Minuses:
In case of long-term use, it is necessary to monitor liver enzymes; it may enhance the effect of alcohol. In case of overdose, drowsiness and hypotension may occur.
9.8/10Rating
Glycine
30 (tablets 0.1 No. 50)
Glycine, the most accessible and safe nootropic, is a truly “folk” drug, which, due to its cheapness and availability, can successfully compete with the most expensive drugs. This medicine differs from all others in that it is a purified amino acid, which, among other things, makes up our proteins. It is glycine that is part of GABAergic receptors, one of the inhibitory mediators in the central nervous system.
This drug is used for encephalopathies, in the treatment of memory disorders, for strokes in the elderly and as a preventative measure in schoolchildren and students.
Glycine is well tolerated and is used in all situations in which “mental burnout” occurs. It helps with stressful situations in both adults and children. Glycine relieves mild neurosis-like conditions and is able to relieve manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia, both in hypertonic and hypotonic variants.
Minuses:
In some conditions, glycine may not be a strong enough drug. But this disadvantage has its continuation in the form of an advantage - glycine has practically no side effects, and it is very difficult to cause an overdose. This drug is able to activate inhibition processes in the cerebral cortex.
9.7/10Rating
Dosage regimen
Nootropics are designed for long-term use, but the duration of treatment and dosage are limited. They are different for adults and children and are indicated for each specific drug. Uncontrolled long-term use should not be allowed. This is fraught with the development of drug-induced parkinsonism. Repeated courses are allowed, but a break in treatment should be taken (1-3 months).
Attention: For effective and safe treatment, it is important to strictly follow the instructions; when choosing an over-the-counter product, you must follow the doctor’s recommendations.
There are therapeutic and prophylactic doses. It is preferable to take the drug in the morning, afternoon, early evening hours (no later than 17-18 hours).
Nootropics for children
The composition of nootropics for children is absolutely safe; tablets or injection solutions include vitamins, amino acids, and neurotransmitters. There are no toxic components. These medications a priori do not cause negative side effects; they are prescribed to improve memory, develop creativity, increase activity and curiosity. Nootropics increase the resistance of neurocytes to hypoxia and nutritional deficiency.
The advantages of nootropics for children include the possibility of prescription at different ages, ease of administration, complex action, affordability (analogs). When using medications, the child’s rhythm of life does not change.
The disadvantages include relative contraindications and the risk of side effects. On the list of the most popular:
- Glycine;
- Pantogam;
- Cogitum;
- Picamilon;
- Encephabol;
- Cerebrolysin;
- Cortexin.
Some drugs are already familiar to the reader; let’s look at the properties of others.
Picamilon

A nootropic with a stimulating effect is Picamilon, which is prescribed to children from the age of three. The drug is well absorbed, helps to cope with whims, tearfulness, emotional lability, nocturnal enuresis, improves psychomotor skills and cognitive abilities of the child. The medicine supports physical and mental activity while studying. Combines with B vitamins and magnesium. Price – 80 rubles.
Pros Cons
| Has a complex effect on neurons | Possible allergic reaction |
| Relieves anxiety | There are contraindications: functional failure of the liver and kidneys, individual intolerance |
| Normalizes sleep | Reduces the effect of barbiturates, enhances narcotic analgesics. |
Cogitum
Cogitum is a nootropic that activates the brain. The drug has a general tonic effect, enhances neuronal metabolism, relieves asthenia, increased fatigue, mild neuroses, depression, and speech delay. Prescribed to school-age children in individual dosages. Cost – 4,500 rubles.
Pros Cons
| Quickly restores nerve functions | Causes tearfulness |
| Improves overall well-being in cerebral palsy | Provokes hyperactivity |
| Suitable for long-term treatment | May cause increased excitability |
Cortexin

Cortexin was originally created for the treatment of brain pathologies, therefore it is combined with many drugs from other pharmacological groups. Used for developmental delays in children, it contains a combination of neuropeptides. The drug exhibits the properties of an antioxidant, neuroprotector, and improves brain trophism. The cost of the injection solution is 766 rubles.
Pros Cons
| Stimulates stress resistance and concentration | Painful injections, lack of tablet forms |
| Has a complex but gentle effect, recommended from birth | Risk of infiltrates at the injection site and secondary infection |
| Reduces intoxication from psychotropic treatment | Price/quality ratio with a minus sign |
Contraindications
Nootropics, in addition to individual contraindications, which are prescribed in each instruction for the prescribed drug, have general restrictive frameworks:
- individual intolerance;
- development of allergies, anaphylaxis against the background of sensitization of the body (you need to take polypeptide medications and amino acids with particular caution);
- brain tumors, including a history (cysts are not taken into account, they are not capable of proliferation);
- impaired liver and kidney function;
- pregnancy, lactation;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- psychomotor agitation.
The naturalness of drug components dictates a minimal list of contraindications for use, but sometimes the situation forces nootropics to be prescribed if there are relative restrictions on use. In this case, side effects occur.
The effectiveness of nootropics has been proven in many cases, but do not forget about contraindications to taking neurostimulants.
Depending on the type, nootropic drugs should not be taken by patients with:
- severe vascular and heart diseases;
- pronounced psychomotor activity;
- diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of the urinary system;
- hypotension;
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug;
- stomach ulcer.
Also, nootropics are not advisable to take during pregnancy or during muscle cramps.
The best nootropic drugs for the elderly
The list of nootropic drugs includes drugs intended to maintain the health of older people. Due to age-related changes, past diseases and disorders, they also need protection of the nervous system, stimulation of brain and physical activity, maintenance of blood circulation, and improvement of memory. The best proposals selected by experts and reviews from specialists will be able to cope with this.
Enerion
This product contains only one component - sulbutiamine (a modified molecule of vitamin B1), it is designed to regulate biochemical and metabolic processes in the central nervous system. It can only be used by adult patients, since it is a synthetic substance. Doctors recommend Enerion to patients suffering from fatigue and low performance. Take the pills for no more than 1 month, since they are a pure psychostimulant, even if they have a mild, moderate effect. The nootropic drug is available without a prescription, which is its great advantage. Prohibited for patients under 18 years of age.
Advantages
- Psychostimulating properties;
- Over-the-counter sale;
- Soft delicate impact;
- Short course of therapy;
- Clinical researches;
- No depletion effect.
Flaws
- Risks of side effects;
- Price.
The drug is in great demand in medical practice, as it has repeatedly proven its effectiveness in clinical trials before its release. When used correctly, it does not deplete the body and does not provoke addiction. If you overdo the dose, undesirable manifestations are possible - excitement, euphoria. Buyers consider the price tag to be a downside.
DMAE
The main substance in this product is a molecule extracted from fish - dimethylaminoethanol. Since the 70s, pharmaceutical product developers have been researching the medicinal properties of such a component. As a result, positive dynamics were established in increasing life expectancy. DMAE is a powerful antioxidant, a substitute for the vital neurohormone in the human body, acetylcholine, which is a memory molecule, and also part of phosphatidylethanolamine, that is, cell membranes. This allows you to improve memory function and cleanse blood vessels of lipofuscin (aging pigment). You can use this medication from the age of 18 and as prescribed by your doctor and in the dosages prescribed by him.

Advantages
- Natural origin;
- Pronounced antioxidant effect;
- Protection of cells from toxins;
- Improving blood properties;
- Memory stimulation;
- Prevention of cell aging.
Flaws
- Long course of admission;
- Price.
Having proven the effectiveness of dimethylaminoethanol, today not only capsules for the elderly are produced on its basis, but also dietary supplements, cosmetology products, vitamins, etc.
The list of contraindications and side effects is minimal. But the downside is the cumulative nootropic effect, due to which you will have to take the product from 1 to 6 months, as well as its price.
Theanine
It is based on a molecule extracted from tea. Its main effect is a sedative effect. The molecule is natural, safe, it is 100% absorbed by the body, without causing any harm to it even in large dosages. The substance relaxes, helps cope with stress and nervous tension. This in turn normalizes the processes of excitation/inhibition in the brain. The use of Theanine guarantees calm, relaxation, freshness of thinking, and ease of coping with any problems and difficulties.

Advantages
- Natural relaxant;
- Safety;
- Sedative effect;
- Eliminating the effects of stress;
- Full digestibility;
- Convenient shape.
Flaws
- Price;
- Not always on sale.
This is one of the safest, natural nootropics. It can be used without a doctor's prescription. There are practically no contraindications, and the risks of side effects are minimal. The range of beneficial properties is wide. Buyers consider the price as a disadvantage, as well as difficulties in finding the product on sale.
The best nootropic drugs for adults
For adult patients, neurometabolic stimulants are recommended, which are used to improve memory and increase performance, both mental and physical. In medical practice, they are used to restore patients after strokes, traumatic brain injuries, neuroinfections and other serious diseases. The best nootropic drugs for adult patients were selected after analyzing reviews and studying test results.
Piracetam
The very first nootropic, which was synthesized in 1964. The list of indications for Piracetam includes more than 50 diseases and patient conditions. It demonstrates the greatest effectiveness in accelerating metabolic processes and improving the conductivity of impulses in the cerebral cortex. When used correctly, tablets are even suitable for treating mental retardation and maintaining a person’s performance in old age. The active component is gamma-aminobutyric acid, it also improves cerebral circulation without dilating blood vessels, increases resistance to toxins, improves glucose absorption, etc. Piracetam can be used from the age of 1 year.

Advantages
- Good degree of tolerability;
- Inexpensive price tag;
- Availability;
- Safe chemical formula;
- No effect on blood vessels;
- Cumulative effect.
Flaws
- Possible side effects;
- Long course of treatment.
In Russia, this is one of the very first, reliable drugs of this kind, widely used to maintain the health of people from 1 year to old age. Patients note good digestibility of the composition and relative safety. Side effects occur extremely rarely if you do not follow the instructions. But to feel the positive dynamics, you will have to take the pills for at least a month.
Nootropil
This drug belongs in its composition to pyrrolidine derivatives, the main substance is piracetam. It increases norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain, which provokes an increase in the action of acetylcholine. It is most often used in the complex treatment of diseases of the central nervous system, atherosclerosis, frequent dizziness, in the field of pediatrics, narcology, etc. You can see different forms of release on sale - capsules, syrups, solutions, tablets. Testing has repeatedly proven that Nootropil effectively affects the functions of the nervous system and cognitive function. Age limit – from 3 years.
Advantages
- Safe composition;
- Complex impact;
- Various release forms;
- Cumulative effect;
- Wide scope of application;
- Inexpensive price tag.
Flaws
- Contraindications, serious side effects;
- Pain when injected into a muscle.
This is almost a complete analogue of Piracetam in composition, principle of operation, and other features. But the nominee in question offers more forms for convenient use, including an intramuscular solution. Patients consider the downside to be the pain from the injections, as well as the inadmissibility of taking it in case of kidney disease or hemorrhagic stroke.