Information from anatomy
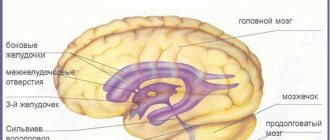
The lateral ventricles are designed to accumulate cerebrospinal fluid. They should not differ from each other and have the same dimensions. The lateral ventricles can be called a container for storing cerebrospinal fluid. They are large in size compared to others. The left formation is the first, and the one on the right side is the second. The third is connected to two lateral openings located between the column of the fornix and the thalamic ending, located in front and connected to the third element of the interventricular body. The fourth ventricle is located near the cerebellum and has an oblong appearance, similar in appearance to a rhombus. This is where the name diamond-shaped fossa comes from. The lateral ventricles consist of the body, as well as the posterior, anterior and inferior horns.
There are 4 ventricles in total:
- two of them are lateral, which are symmetrical and arranged in pairs;
- two located sequentially along the midline.
The fourth ventricle is directed through the cistern into the central canal, which ends in the terminal cistern.
According to the standards, they must have the following parameters:
- the horns located in front should have a depth of no more than 2 mm;
- if we consider the area of the body, then their depth should be twice as large and be 4 mm;
- The dimensions of the tank should be within 3 – 6 mm.
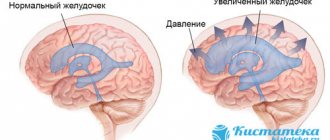
The ventricles of the brain grow in proportion to the growth of the baby and are combined with the size of the skull bone, provided that this is a normal process. Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain is possible at any age, but this will be assessed as a pathology. In medical terms, this phenomenon is called “occlusive hydrocephalus.” This happens due to a violation of the liquor flow. The intervention of specialists is mandatory here.
But when the ventricles of the brain are enlarged, this causes great concern among parents. Is there really any reason to worry? To do this, it is worth understanding the reasons for this manifestation.
If a fifth ventricle is detected during an ultrasound examination of the fetus, then do not worry: this is normal.
The function of the ventricles is not only to accumulate cerebrospinal fluid, but also to secrete cerebrospinal fluid. If everything is normal, then the cerebrospinal fluid flows into the subarachnoid space. If this process fails, it is noted that the ventricles of the brain are dilated. When this function is impaired, dropsy develops or, according to medical indications, it is called hydrocephalus.
Diagnostic methods
Expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain in children is one of those pathologies that cannot be left to chance. To prescribe competent treatment, you must first make a diagnosis. Modern medicine knows several methods for diagnosing the condition of the brain. Radiation diagnostics is considered the most informative, but it is suitable for children after the fontanelles have become overgrown with bone tissue (more details in the article: when and how do the fontanelles overgrow in children?). Other methods include:
READ ALSO: how is NSG performed on a baby's brain?
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging. It allows you to get a complete picture of the condition of soft tissues, including the brain, but has many contraindications. It is prescribed to small children only in extreme cases, since for a reliable result it is necessary for the patient to lie still for at least 20 minutes, which infants cannot do. There is a solution - general anesthesia, but it negatively affects the baby’s health.
- An alternative to MRI is diagnosis using a computed tomography scanner - CT. It is carried out much faster and does not require anesthesia, therefore it is the most preferable way to diagnose the condition of the brain in an infant. It has a significant drawback compared to MRI - lower quality of images, especially when it comes to small shooting areas. CT scans best show hemorrhage in the interthecal spaces, so a diagnosis can be made quickly and treatment can be prescribed.
- NSG, or neurosonography. The procedure allows you to estimate only the size of the ventricles, but does not provide a visual picture. The device is capable of capturing organ sizes from 1 mm, no less.
- An additional diagnostic method is to assess the condition of the fundus. During the process, dilated vessels can be seen, which will indicate that the patient has increased intracranial pressure.
- Cerebrospinal fluid puncture, which is performed in the lumbar spine. By analyzing the taken material, the state of the cerebrospinal fluid is assessed.
Cause of pathology
Dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain, or ventriculomegaly, should be especially carefully studied if asymmetry is present. With symmetrically located lateral ventricles of the brain, this can be diagnosed as either hydrocephalus or a normal condition. With asymmetry, it turns out that the ventricles are different sizes and disproportionate to each other. Perhaps these are the consequences of a skull injury. In this case, a neurosurgical operation is necessary for the newborn so that there are no unexpected consequences. Also, asymmetrically located ventricles can be a normal condition, but if all this is observed in a mild form. As a rule, their difference in size should not exceed 2 mm. Although this option is not recognized as a pathological condition, dynamic monitoring is still necessary so that this number does not increase.
An increase in horns in the back of the head is considered abnormal. To recognize this in a timely manner, screening, ultrasound examination of the brain, and neurosonography are carried out. All examinations are carried out through the newborn's fontanel. Moreover, if the ventricles are not clearly visible, this does not mean that expansion of the ventricles of the brain has occurred.
For newborns, dilatation of the ventricles of the brain is recorded only when the dimensions of the diagonal sections at the level of the foramen of Monroe exceed 0.5 cm, and the smoothness of the contour of the fundus is completely eliminated.
The causes of this phenomenon can be congenital or acquired over time. List of congenital causes:
- abnormal course of pregnancy;
- difficult childbirth;
- acute hypoxia of the fetus while in the placenta;
- deviations from normative indicators of the central nervous system;
- developmental deficiency;
- early birth;
- perinatal trauma.
Specialists pay special attention to hemorrhages, both external and internal. For this reason, deviation from ventricular symmetry often occurs. Filling with blood, changing in volume, causes a change in their size. Also included in the category of acquired pathology are:
- viral infections that affected the fetus;
- septic complications;
- a long period of time spent on the birth of a child and the breaking of waters;
- maternal pathologies (for example, prophets of the heart, as well as diabetes).
The accumulation of fluid in the newborn's brain causes symptoms that affect the entire brain and can cause negative conditions.
Hydrocephalus does not contribute to the enlargement of cerebrospinal fluid cavities in a short time. It is possible that intracranial pressure may initially rise, followed by expansion of the lateral ventricles. The latter are not located relative to the center, as a result of which they experience great pressure.
The need for neurosonography
Neurosonography is performed on a newly born child if they find:
- convex or sunken fontanel;
- pulsation in the fontanelle;
- infection of the fetus in the womb (including infection from the mother);
- absence of the baby's first breath.
Abnormalities of fetal development, such as chromosomal pathologies, detected during pregnancy may also be a reason for a brain examination.
If the child’s mother, while pregnant, took drugs or alcohol, she will also have to send the baby for neurosonography.
Neurosonography of newborns is mandatory if the child was born prematurely (before the 37th week).
Neurosonography may be required when the mother and newborn have different Rh factors. It is important to examine the newborn’s brain even when hypoxia is suspected.
The reason for performing neurosonography may be a difficult or pathological birth. It is also necessary if doctors assessed the condition of the newborn as low on the Apgar scale.
The child will be asked to be brought in for neurosonography after a month if seizures, epilepsy or problems with the nervous system occur.
Other reasons for the need for an ultrasound examination of the child's brain may include:
- violation of proportions or non-standard head size;
- delay in growth and development;
- suspicion of strabismus;
- hemorrhage inside the eyeball.
Neurosonography of newborns is often done as an additional procedure after obtaining an encephalogram.
In this case, an ultrasound of the brain is necessary to clarify the presence of trauma in the newborn due to a fall or diagnoses such as cerebral palsy, encephalitis, rickets, ischemia, meningitis, autoimmune disease or Apert syndrome.
The need for neurosonography may also arise when a newborn has increased intracranial pressure or there is a suspicion of cancer.
Neurosonography is also needed if the child is hyperactive and has genetic developmental disorders.
Blood poisoning, complications after viral diseases and problems with organs are also indications for neurosonography.
What could be the consequences?
To recognize by external signs whether a baby has intracranial pressure, you should pay attention to:
- lack of appetite and lethargy;
- protrusion of blood vessels on the forehead because venous blood flow is obstructed;
- changes in muscle tone, with tendons becoming more active;
- trembling of limbs;
- decreased sucking and swallowing reflexes;
- frequent regurgitation;
- swelling and protrusion of the fontanel;
- an increase in the size of the head, disproportionate to the body.
It is possible that headaches, nausea, and in some cases vomiting may occur due to compression of certain areas of the brain.
It is possible that the above points are not related to ventriculomegaly, however, parents should monitor the changes that occur.
Diagnosis of pathology
After the fontanelles are completely overgrown, which usually happens within a year or two, the disease can be monitored using an x-ray or tomograph.
MRI is much better at this task. With its use, you can clearly examine the contours of soft tissues, as well as the ventricles of the brain in all projections. But there is one caveat: you need to stay in the magnetic field of the topographer for at least 20 minutes, and it is unlikely that every child will withstand such a load. It is not always possible for an adult to cope with such a task, and even more so for a small person. Therefore, medicated sleep is used for children, unless, of course, it is contraindicated for them.
If for a number of reasons MRI is not possible, then tomography is used. Thus, it is possible to determine the expansion of the ventricle of the brain. But this survey also has its drawbacks:
the radiation dose enters the baby’s body;
poorly conducted examination.
However, in this case there is no need to use anesthesia. In case of subarachnoid hemorrhage, a topographer will be able to more accurately determine the location of blood accumulation than a magnetic tomograph.
Treatment of the disease
When the ventricles in the head are enlarged, parents are faced with the question: should this pathology be treated? Or maybe it will go away on its own over time?
If there are no changes in the child’s development and he eats, sleeps and develops well, this means that there is no need for treatment, everything will go away on its own. This is what experts say. Treatment will be required only if the cerebrospinal fluid pressure increases. This is checked using a tomograph, and the diagnosis is clarified when a puncture is taken. But doing the latter is a last resort. Manipulation is indicated for diseases of meningitis, although they do not cause dilatation of the ventricles.
To treat the pathology, vitamins, diuretics and antihypoxants are prescribed. As a rule, massage and physical therapy are prescribed as an addition to the main treatment. To avoid complications caused by treatment, potassium-rich drugs should be used.
2What does a patient with left atrial dilatation experience?
"Trained Heart"
Dilatation of the left atrium may not manifest itself clinically. Among people involved in professional sports and heavy physical activity, this condition is considered physiological and does not require treatment, the so-called “trained heart.” It happens that patients find out that the chambers of the heart are dilated only during a medical examination and do not pay due attention to this because they feel well.
When dilatation of the left atrium occurs, at a certain stage insufficiency in the pulmonary circulation develops. In this case, the patient complains of the appearance of shortness of breath, first during physical activity, then with its minimal degree, and then shortness of breath may appear at rest. In addition to shortness of breath, a dry cough occurs, which may be streaked with blood - hemoptysis, chest pain of a pressing, aching or squeezing nature, general weakness, sweating, surges in blood pressure.
Interruptions in heart function
A common symptom is rhythm disturbances, which the patient feels as attacks of rapid heartbeat, interruptions in heart function, and a feeling of “fading” of the heart. As the disease progresses, not only the left, but also the right parts of the heart expand: the left ventricle dilates first, and then the right atrium dilates. In this case, severe circulatory failure develops, which is characterized by the addition of edema of the legs, enlarged liver, and ascites.
Other cases of pathology
In some cases, pathology is observed when the ventricles of the brain are enlarged in adult relatives, that is, the disease is inherited. Also, do not panic if there are dilated ventricles in the brain compartment. Perhaps this phenomenon is due to the fact that the baby has a large head. This pathology is typical for children aged one year. In this case, the content of all cerebrospinal fluid in their cavity should be diagnosed.
If cerebrospinal fluid is produced in excess, then for this reason the ventricles may also be dilated. With poor outflow of cerebrospinal fluid due to an obstacle in its path in the form of dilatation of the system. Pathology also becomes noticeable in newborns born prematurely. If a change in the parameters of the ventricles is suspected, this condition is assessed by specialists, and the indicators are compared with normal sizes.
When the ventricles present in the human brain are dilated, this requires decoding and description by doctors.
Left atrium dilatation: what is it and how to treat it?
Determination of treatment method
If the patient does not complain, no other diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine or other systems that can lead to dilatation have been identified, treatment is not indicated; observation by a cardiologist and control echocardiography at least once a year is sufficient. When identifying the cause leading to the expansion of the atrium, it is necessary to directly influence it.
If such causes are complications of infectious diseases leading to inflammation of the heart muscle and changes in its chambers - anti-infective treatment; if the reason is a change in the valve apparatus - consultation with a cardiac surgeon about the advisability of replacing the valve; if dilation occurs due to consistently high blood pressure numbers - adequate antihypertensive therapy, if the cause of dilatation lies in endocrine disorders - treatment and normalization of the endocrine glands.
Eliminating the cause prevents the progression of dilatation. Also, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the complications of the enlarged cavity of the left atrium, which include rhythm disturbances, heart failure, and thromboembolism. If there is a tendency to form blood clots, antiplatelet agents are prescribed, and antiarrhythmogenic therapy is carried out if rhythm disturbances are detected. To improve nutrition and myocardial oxygenation, metabolic drugs are prescribed.
In modern medicine, dilatation is an increase in the volume of any internal organs. If we are talking about changes in the size of the atria, the patient undergoes a number of examinations to clarify the diagnosis.
Often additional, more serious cardiac disorders are discovered, which were the original cause of the expansion of one of the heart chambers.
Early diagnosis is the key to a successful and quick recovery.
The heart is one of the most important organs in the human body, as it performs the function of a pump. It consists of four chambers: the left and right atria, the left and right ventricles.
Violation of the process of enriching the blood with oxygen can be the first cause of heart dilatation.
Enlargement of multiple chambers of the heart is extremely rare. However, if the pathology is not treated for a long time, the disease will affect the right side of the heart. This is fraught with more serious consequences. A threat to life appears if the pathological process is too advanced.
The situation is aggravated by the fact that for a long time such a cardiac disorder does not manifest itself in any way. Signs of underlying medical conditions may be present, such as:
- stenosis;
- atrial fibrillation;
- tachycardia;
- Mitral valve insufficiency.
Dilatation of the cavity of the left atrium becomes a consequence of obstructed outflow of blood into the cavity of the left ventricle. The reason for this is most often a malfunction of the valve.
As a result, large quantities of fluid accumulate in the atrium cavity and burst the muscle walls. In modern medicine, this process is called regurgitation, which means the reverse flow of blood.
Such pathological processes negatively affect the functioning of the body as a whole, so it is better not to delay treatment.
Causes
Not a single disorder in the human body appears just like that. The primary task of the cardiologist is to understand what prompted the expansion of one of the chambers of the heart. It is quite difficult to identify the cause of this violation.
Dilatation of the left atrium may be a consequence of other diseases, alcoholism. Medicine also knows of cases where such a diagnosis was the only deviation from the norm in a patient.
In any case, you can live with the presence of such a disorder if you monitor the dynamics of its development.
In most cases, atrial fibrillation provokes the occurrence of pathology. In this case, chaotic work of each of the atria is noted. They contract at different rhythms.
This leads to an increase in the volume of one of the cavities of the heart muscle.
At best, the consequence of this is a rapid pulse and shortness of breath, but often such a pathology threatens a person with cerebral thromboembolism.
Systolic dysfunction almost always provokes the development of dilatation. Incorrect or insufficient operation of the valve itself is a pathology. Blood does not completely flow into the aorta.
Most of the fluid returns from the ventricle to the left atrium, accumulates there and stretches the walls. Often, against the background of such disorders, venous hypertension of one or both lungs also develops.
The nature of dilatation is not fully understood. Sometimes the disease develops due to alcohol abuse.
In addition, various autoimmune diseases or disorders of the endocrine system can provoke expansion of the left atrium.
Pathology is not always viewed negatively, since it performs a compensatory function. With the help of dilatation, the heart adapts to new operating conditions. However, people with a similar diagnosis need to remember that any load is performed due to the additional reserves of the heart. The more you load the myocardial muscle, the more it stretches.