Side effects
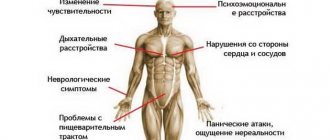
Negative side reactions during treatment with antipsychotics occur infrequently and depend on the overdose, violation of the duration of the course, age, health status, physiological characteristics of the patient, and the compatibility of the antipsychotic with other medications. Most often noted:
- endocrine disruption due to long-term use of drugs;
- lack of appetite;
- weight fluctuations, more often in the direction of sudden weight loss;
- constant drowsiness, apathy, especially on the first day of admission;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- slurred speech;
- uncontrollable tics;
- temporary blindness;
- dyspepsia;
- dysuria;
- acute urinary retention;
- dry mucous membranes;
- tonic spasm of the masticatory muscles (trismus);
- ejaculation disorder.
Problems disappear with discontinuation or replacement of the drug.
List of drugs
There are many antipsychotics, they are all different. Every neurologist, psychiatrist, psychotherapist always has his own list of the most popular antipsychotic drugs at hand, but uses it only after a complete examination of the patient and an accurate diagnosis.
There are several generations of drugs. Typical antipsychotics are old-generation medications that are used only for inpatient therapy and are quite difficult to purchase in pharmacies (only with special prescriptions). Prescribed for the treatment of schizophrenia and serious mental disorders. Typical antipsychotics are:
| Name of drugs | Cost in rubles |
| Chlorpromazine | 124 |
| Haloperidol | 21 |
| Molindon | 106 |
| Thioridazine | 247 |
New generation
The list of new generation antipsychotics is updated every year. Their action is correlated by their chemical structure and clinical effect. Modern medications have less effect on the brain, do not provoke addiction, and have a minimum of adverse reactions. They can rather be called antidepressants; they are not suitable for the role of means for serious treatment of severe psychogenic disorders. The most popular drugs without side effects:
| Name of drugs | Cost in rubles |
| Abilify | 4 900 |
| Moditen | 1 200 |
| Quetiapine | 1 099 |
| Fluanxol | 349 |
| Triftazin | 34 |
| Tizercin | 215 |
| Closasten | 1 332 |
Over-the-counter
There are no antipsychotics available without a prescription. But there is a group of drugs of borderline action with a predominant sedative effect. You can buy them at the pharmacy yourself (without a prescription). List of the most available:
| Name of drugs | Cost in rubles |
| Olanzapine | 215 |
| Serdolect | 1 850 |
| Ariprizole | 2 784 |
| Etaperazine | 345 |
| Chlorprothixene | 179 |
The most effective and safe
When it comes to neuropsychiatric disorders, an important characteristic of the drugs intended for use is their safety and effectiveness. Such antipsychotics are among the new generation of drugs. These include:

| Name of drugs | Cost in rubles |
| Sertindole | 1 901 |
| Solian | 3 410 |
| Zeldox | 5 760 |
| Lakvel | 1 385 |
| Azaleptin | 1 246 |
| Prosulpin | 104 |
| Betamax | 289 |
| Limipranil | 1 754 |
Mechanism of action
Neuroleptics are antipsychotic drugs that affect higher nervous activity by correcting the functioning of all brain structures, in which the mediators are dopamine, norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin.
Due to these substances, antipsychotics inactivate dopamine receptors, calming a person, relieving anxiety, panic, and aggression. The group's drugs are used for the treatment of psychotic, neurological and psychological disorders of varying severity: schizophrenia, oligophrenia, senile dementia.
The mechanism of action of antipsychotics is the blocking of nerve impulses in the limbic, mesocortical systems of the brain, which are responsible for the production of dopamine and serotonin. Antipsychotics have a short half-life, are well absorbed by any route of administration into the body, but do not act for long, so they are always prescribed in combination, potentiating each other.
Penetrating the blood-brain barrier, antipsychotics are localized in the liver, where they are metabolized, and then excreted with bile and urine. The maximum half-life is 70 hours (Haloperidol). However, there are long-acting medications that, when administered intravenously, have a therapeutic effect for up to 3 weeks.
The neuroleptic effect on the brain is:
- hypothermic effect;
- sedative;
- antiemetic;
- hypotensive;
- antitussive;
- anti-hiccup
In addition, neuroleptics correct behavior, minimize autonomic reactions, potentiate the effect of drugs, alcoholic beverages, sleeping pills, and tranquilizers.
Restoring the body after taking pills
As you know, it is quite difficult to “get off” antipsychotics after many years of using the pills. The drugs inhibit the production of dopamine. After stopping taking antipsychotics, emotions often become dulled.
In most cases, it is possible to restore the normal state of the emotional sphere with the help of special medications. The production of dopamine is also activated when walking in the fresh air. Regular physical exercise also contributes to the patient’s recovery.
Some of the most effective drugs for improving dopamine production include:
- Tyrosine;
- Dopamine.

In order not to leave the path of recovery and not fall into depression again, you need to watch your diet. Foods rich in tyrosine are beneficial. The diet should include seafood, green tea, bananas, and chicken eggs.
Ginkgo biloba after taking antipsychotics
Taking care of your health too late can lead to unwanted complications. Therefore, after completing the course of taking antipsychotics, it is recommended to take ginkgo biloba. The medicinal plant helps improve peripheral and cerebral circulation.
In this simple way you can achieve changes such as:
- improved sleep;
- restoration of normal blood circulation in the lower extremities;
- memory improvement.

Ginkgo biloba is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to its components. A plant with this name should not be used for severe diseases of the digestive tract. The use of ginkgo biloba is not recommended for those with reduced blood clotting.
Some representatives of the group
Risperidone is probably the most prominent representative of the 2nd generation antipsychotics. Being a powerful dopamine receptor blocker, it exhibits a strong, effective antipsychotic effect. But, along with this, the list of its side effects is quite wide. Compared to other “atypists,” it causes depression, increased prolactin and extrapyramidal disorders to a greater extent, provokes nausea and vomiting, weight gain, drowsiness and other undesirable reactions. But no one writes him off, since he most effectively fights psychotic agitation.
Quetiapine . One of the safest atypical antipsychotics. Shows a pronounced anti-anxiety effect and normalizes mood. It has a weak effect on serotonin and dopamine receptors, and has a greater effect on adrenergic receptors. Used for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Fluphenazine . The drug is for injection use. It has a moderate effect on the noradrenergic system, and a pronounced effect on the dopamine system. Eliminates irritability and has a psychoactivating effect. Used for hallucinations and to treat neuroses.
The drug is administered intramuscularly in a dose of 0.25 or 0.5 ml with further consideration of the administration regimen. It can enhance the effects of other psychotropic drugs and alcohol, so their simultaneous use is undesirable. When used in parallel with narcotic analgesics, it causes depression of the central nervous system and respiration.
Clopixol was developed more than 20 years ago. It is actively used abroad, but in Russia it was introduced into practice relatively recently. The drug acts on 3 types of receptors: serotonin, dopamine and adrenergic. Available in two forms: injections and tablets.
Injectable forms are Acufase and Depo.
Clopixol-Acupaz is used for acute psychosis, exacerbations of its chronic forms, as well as for mania. It eliminates the nuclear symptoms of schizophrenia: hallucinations, mania, disturbances in mental activity, relieves anxiety, aggressiveness, and reduces manifestations of hostility.
One injection of the drug is enough to relieve acute symptoms. The effect lasts up to three days. After this, they will probably appear again, so it is advisable to prescribe Clopixol in the form of depot or tablets.
Clopixol-Depot provides a prolonged sedative effect. The maximum effect is achieved after the first week after administration of the drug. A single injection of 1 ml of Clopixol-Depot for two weeks or 2 ml for four weeks replaces the daily intake of tablets of the same name for 14 days.
Classification
Antipsychotic drugs are differentiated into typical and atypical antipsychotics.
In addition, there is a division according to therapeutic effect into:
- drugs with a predominant sedative effect;
- stimulants;
- true antipsychotics.
By duration of impact on:
- neuroleptics with short-term effects;
- prolongators.
Typical
Such drugs belong to the old generation of antipsychotics and are characterized by strong effects and a large number of side effects. These are derivatives of phenothiazine, thioxanthene, butyrophenone, indole, benzodiazepine, diphenylbutylpiperedine - different in chemical structure. Neuroleptics in this group treat serious mental disorders, depression, and severe phobias. Prescribed only by a doctor, prescription drugs.
Atypical
Drugs of this type are new generation neuroleptics that can improve memory, concentrate a person’s attention, relieve neurological problems, and exhibit a sedative effect. Atypical antipsychotics have advantages:
- absence of uncontrolled motor activity during administration;
- minimizing complications;
- inertness to prolactin;
- no inhibition of dopamine metabolism;
- good tolerability and rapid elimination from the body (prescribed to children).
Only a specialist can recommend atypical antipsychotics; the drugs are prescription drugs.
Differences between typical old drugs and new generation atypical antipsychotics
| Typical antipsychotics | Atypical antipsychotics |
| Potent to moderate antipsychotic effect | Quite pronounced antipsychotic effect |
| Significant side effects in large quantities | Almost complete absence of unwanted side effects |
| Act exclusively on positive symptoms of schizophrenia | Drugs correct positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia |
| Cause depression, worsening overall health | Improve overall well-being by correcting cognitive properties |
| Poorly tolerated by patients | Well tolerated by patients |
| Poor compliance (disposition to treatment) | Good compliance |
| Impair quality of life | Improve quality of life |