One of the most pressing neurodegenerative diseases is Alzheimer's disease. Plaques form between neurons in the brain, connections are disrupted, and as a result, nerve cells stop functioning and die. In the last 10-15 years, mortality from this disease has been growing rapidly, and there is no radical treatment for Alzheimer's disease.
Numerous clinical studies have not confirmed the effectiveness of any modern drug. Drugs such as memantine, cholinesterase inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, and psychotherapy methods can only improve the transmission of nerve impulses between surviving neurons and improve the patient’s quality of life. Modern medicine cannot restore broken connections between cells and stop the pathological process.
Alzheimer's disease - causes, risk factors
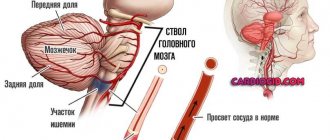
Alzheimer's disease (or AD) is a degenerative disease of the brain in which the structure of nerve cells is disrupted and pathological foci are formed outside the cells. Instrumental diagnostics reveals diffuse atrophic changes, which manifest themselves as a decrease in the volume of the gyri with the expansion of the furrows between them. The most common location of the lesion is the temporoparietal region.
Intracellular changes are represented by the deposition of proteins, destroying the structure and connections between organelles. Extracellular lesions consist of plaques containing beta-amyloid and other proteins. Neurologists note that the severity of symptoms directly depends on the number of plaques, and the amount of intracellular deposits determines the rate of disease progression.
Hereditary predisposition plays an important role in the development of AD. Family inheritance occurs in every fifth patient. Most individuals from this group have abnormalities in the structure of 14, 19, 21 pairs of chromosomes.
Genetic predisposition plays a major role in the onset of the disease before age 65 (so-called early-onset asthma).
Experts warn that people with mild cognitive impairment are more likely to develop Alzheimer's if the main symptom is amnesia.
When starting the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer's, the doctor clarifies the presence of risk factors. The main factors are the patient’s age (the likelihood of atrophy increases several times over time) and family history. Other negative reasons that indirectly affect the occurrence of the disease include:
- female;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- hypothyroidism;
- estrogen deficiency in women.
The likelihood of developing asthma is also increased by such somatic diseases as arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia.
Treatment methods
Effective treatment of the pathology will require accurate diagnosis to identify the stage and spread of the disease. Therapy includes not only medication, but also psychological assistance to the patient. It is important to correct concomitant pathologies, for example, diseases of the thyroid gland and heart.
Medicines
The difficulties of this method lie in the fact that the patient’s body is too sensitive to medications and is quite weakened. The drugs are prescribed in minimal dosages with gradual adjustment of the regimen. In psychiatry, the following groups of medications are indicated for the treatment of the disease:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors. This group of medications increases the level of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Thanks to this, irreversible processes in the brain are inhibited. Commonly prescribed drugs are Galantamine, Donepezil, and Revastigmine. Galantamine enhances attentiveness, enhances attention, and strengthens human memory. It is characterized by low toxicity and is well accepted by patients. Donepezil is considered the most effective among all drugs. The rate of inhibition increases 1000 times compared to other medications. The latter drug is used in cases of advanced forms of pathology.
- Memantine. The drug helps reduce the activity of the mediator glutamate. It is this that has a detrimental effect on cells. It is characterized by moderate effectiveness in the middle and advanced stages of the disease.
- Tranquilizers. Medicines of this group are prescribed for increased excitability of a person. The drugs eliminate aggression and prevent the progression of psychosis. Among the newest drugs, Clozepine, Olanzapine, and Risperidone are actively used. If hallucinations occur, then Haloperidol is indicated.
- Combined agents. The drugs combine the properties of neuroleptics, antidepressants, and tranquilizers. The best are Phenibut and Sonapax. They fight depression, strengthen memory, and enhance attentiveness.
It is advisable to use Actovegin and Cerebrolysin. Medicines normalize cerebral circulation and saturate brain cells with oxygen.
The effectiveness of therapy is achieved through prolonged use of medications. The first changes are observed after a few weeks.
A new method of therapy is the use of stem cells. Damaged cells are replaced with completely healthy ones, thanks to which brain functions are recreated. But this method is very expensive and not fully studied.
Folk remedies
In order not to wonder whether Alzheimer's is being treated, it is necessary to take care of the patient at the first symptoms and prevent the symptoms from developing. Traditional medicine will help with this. At the initial stages, you can slow down the progression of pathology using the following means:
- Products based on ginkgo biloba leaf extract. They normalize the functioning of the brain.
- To stimulate and maintain memory, use hawthorn infusion.
- Dandelion, calamus and chicory enhance the functioning of the hypothalamus.
- Motherwort and valerian are characterized by a sedative effect.
- A mixture of ginseng root and schisandra berries is characterized by a supporting effect. The ingredients are taken in equal proportions and boiled over low heat. Use a couple of times a day.
- Add 10 grams of dried withania root to 0.2 liters of water. Afterwards, cool and drink a cup of the drink in the morning.
A useful supplement is soy lecithin, which is rich in vitamins. Dietary supplement improves brain functioning. Taking Omega-3 regularly has good results.
It has been proven that drinking three cups of coffee a day, strong natural coffee, reduces the risk of progression of the pathology several times.
Devices
At present, attempts are being made to develop effective and harmless ways to combat pathology. Recently, such a device as “Biomedis M” has appeared on the market. It is a bioresonance device that emits high-frequency electromagnetic waves. They have an effect on the brain, thereby supporting its functioning.
This method is considered controversial. Doctors do not recommend using this method as an independent remedy. Dementia is the result of natural damage to nerve cells. The apparatus is simply not able to resume this destructive process.
Help from doctors
In the initial stages of progression, the use of psychotherapeutic methods is very effective and improves the patient's condition. The progression of the disease is slowed down. Psychological assistance is provided in the form of:
- music therapy;
- art therapy;
- ensuring presence.
In case of illness, a speech therapist can also provide assistance. At more severe stages, speech impairment occurs. The support of loved ones plays an equally significant role. It is important to reward a person for any action.
It is forbidden to separate the patient from people and not allow contact with them. He must visit cinemas, attend clubs, perform various mental exercises, learn poetry, draw, solve puzzles, read books. Be sure to go for walks in the park every day.
The behavior of loved ones plays a special role. Relatives need to accept that the person is sick and will never be the same again. There is no need to be offended by him or accuse him of something. If a person cannot care for himself, then proper care will be required. It is important to assess your strengths, and if this is not possible, then ask for help from qualified specialists.
Treatment is aimed at prolonging the first stage, preserving thinking and mental skills for as long as possible.
Alzheimer's disease: symptoms through the eyes of loved ones
Based on the time of onset, there are 2 variants of the onset of the disease:
- Early-onset asthma – up to 65 years of age;
- Late-onset asthma – after 65 years.
In 50-60% of patients, the disorder initially manifests itself in the form of memory loss, in the rest – with behavioral disorders. What does it look like? Everyday memory begins to suffer - for recent actions, events, while old skills and knowledge are still preserved.
Patients with AD can engage in mental work and easily reproduce information from textbooks and encyclopedias. With this disease, the core of personality is often preserved for a long time: patients behave in accordance with previously learned social norms.
Experiences about forgetfulness and the ability to “correctly” (adequately to the context of the situation) answer questions related to memory gaps remain. For example, an old woman who no longer remembers how old she is can retort with dignity that asking women about their age is indecent. Likewise, a patient who forgets to call relatives will say that “he was busy.”
Such formal responses and fairly orderly behavior cause Alzheimer's treatment to begin very late.
Often, even specialists miss the symptoms of the disease, suspecting depression in such patients. It actually occurs in a third of patients in the early stages of asthma. Relatives may notice symptoms such as:
- decreased interest in work and loved ones;
- mental, motor retardation;
- apathy, lack of initiative;
- reducing self-criticism.
Gradually, dementia (or the “three A” disease: aphasia, agnosia, apraxia) actually leads to the loss of speech, cognitive and practical skills. As dementia progresses, relatives notice how the patient's personality changes. He becomes rigid, unspontaneous, his circle of interests narrows, egocentrism and suspicion grow. Disinhibition may occur. These manifestations occur in 75% of patients with asthma.
Professional and social skills are retained for a long time. After their loss, behavioral disorders come first:
- episodes of verbal aggression (swearing, threatening);
- physical aggression (the patient swings his arms, attacks);
- loss of neatness;
- increased appetite;
- sexual disinhibition;
- self-harm.
Thus, relatives may notice that a short time after the meal the patient sneaks into the kitchen, finds food and eats it, without worrying about their combination or table setting. He reacts negatively to comments and tries to take a swing at him. Changes in behavior at a late stage of the disease occur in 80% of patients. This can lead to relatives becoming unable to cope with care, medications, and planning temporary treatment for Alzheimer's in a psychiatric hospital. You can get a free and anonymous consultation about hospitalization procedures by calling the clinic.
Behavioral disorders in some cases are accompanied by the development of psychotic disorders:
- delusions of damage;
- delusions of persecution;
- illusions;
- auditory, visual or olfactory hallucinations.
Deterioration of cognitive abilities leads to impaired social functioning. Such patients do not understand how they can make a phone call, get somewhere by public transport, or pay bills. The progression of the disease is indicated by the inability to dress, comb your hair, brush your teeth or shave on your own. Patients cease to understand the simplest things - how to lie on the bed, take a spoon, a glass. Speech is impaired to the point of mutism.
Changes in gait (shuffling steps, unsteadiness), tremors in the hands, epileptic seizures occur in the later stages of the disease, when the mental state of patients already requires constant care.
Principles of drug therapy
The main treatment for Alzheimer's disease is medication. However, therapy can only slow down the progression and reduce the intensity of symptoms, but not completely eliminate the pathology. Since the majority of patients are people over 60 years of age, drugs must be chosen with caution, because they pose an additional threat to an elderly person. The selection of medications and dosage is determined by the doctor; only with the help of a good specialist can the consequences be minimized.
Rules for choosing drugs
The effectiveness of drugs is about 70%; individual tolerance of the components plays an important role in their selection. To evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen drug for a particular patient, it is necessary to use it for at least 3 months, during which the doctor will monitor his condition. If it is necessary to change the medication, take a break for 3-7 days.
A person will drink a medicine that is suitable in composition throughout his life. They are produced not only in the form of tablets, but also drinking solutions and even patches. According to medical observations, the good effect of treatment in most situations lasts for a year from the start of therapy, then the disease progresses again. Acetylcholinestrase inhibitors are treated according to a number of rules, which include:
- constant monitoring of the patient by a doctor or relatives;
- assessment of side effects by a specialist;
- excluding combined use with alcohol, tonic drinks, NSAIDs or medications that lower the heart rate.
You cannot stop taking medications on your own; this is done only at the last stage of the disease, when therapy is no longer effective. Stopping medications can cause rapid progression of dementia.
What drugs are used?
The choice of medications is determined by the stage of the pathology and the present clinic; at the very beginning, the effect can be provided by: Glycine, Actovegin, Ginkgo Biloba extract. Early and moderate dementia is treated with acetylcholinestrase inhibitors; if for some reason their use is impossible, they are replaced with Piribedil, Vinpocetine, Pentoxifylline. The last degree is treated with Memantine. Other medications may also be involved in therapy:
- Exelon;
- Aricept;
- Reminyl and many others.
In addition to basic medications, it may be necessary to eliminate symptoms. Glycine helps improve cerebral circulation and prevents the patient from becoming depressed; the same functions are performed by Carbamazepine. If the patient experiences hallucinations or delusional states, the use of antipsychotics and tranquilizers will be required. Taking any drugs together can be dangerous; only a doctor can decide on the possibility of combining drugs.
Contraindications
All contraindications to components of Alzheimer's medications must be identified before their prescription. They should not be taken by people with individual intolerance to the components, with impaired functioning of the liver and kidneys, as well as in the presence of:
- bronchial asthma and chronic respiratory disease;
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- obstruction of the urinary ducts;
- epilepsy;
- intestinal obstruction;
- ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract and so on.
In such situations, the advisability of taking medications is determined by the doctor.
Side effects
Because the medicine for Alzheimer's disease will be taken for life, there should be no side effects. As a result of use, you may experience:
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness and headaches;
- loss of appetite and abdominal pain;
- increased sweating;
- hand tremors;
- drowsiness and fatigue;
- increased excitability;
- insomnia;
- depression;
- loss of consciousness;
- hallucinations;
- changes in blood pressure;
- stomach ulcer.
Side effects appear immediately after the start of therapy and may result from exceeding the dose.
Early signs of Alzheimer's disease
If the development of the disease is suspected, relatives or the patients themselves can assess their condition. Identification of at least one of the ten signs of cognitive impairment is the basis for contacting a psychiatrist to begin examination and treatment for Alzheimer’s.
- Decreased memory for recent events. This may be accompanied by attempts at compensation - notes, electronic notes. This also includes forgetting the names of loved ones, the names of actions, and surrounding objects.
- Errors in the financial sphere: loss of ability to plan expenses, monthly payments. If the patient is still coping with this issue, he spends more time on calculations and makes mistakes.
- The patient stops solving routine tasks at work: he makes mistakes, and cannot even go to familiar places on business (for example, to a conference, to a warehouse).
- The account of time is disrupted, confusion arises with dates and the definition of the season. At times, a person does not orient himself in a place: he gets lost, does not understand where he is.
- The perception of visual images is disrupted: color, shape, spatial relationship. Difficulties arise with reading and driving; the patient with asthma does not understand road signs.
- Speech disorders. The person does not know how to join the conversation or continue it after a pause, calls objects in other words.
- Loss of personal belongings and the inability to remember under what circumstances they disappeared (he walked from the room to the kitchen, got distracted and left them on the table). To explain the disappearance of objects, patients accuse their relatives of theft. Sometimes treatment for Alzheimer's begins with complaints about this behavior.
- Ridiculous actions related to finances. Thus, people with cognitive impairments can invest large sums of money in dubious enterprises: purchasing dietary supplements, “miracle devices” for the home.
- Giving up hobbies, familiar company, new responsibilities at work. It is worth paying attention to these behavioral features if they were not characteristic of the patient before.
- Changes in psychological state: confusion, depression, mistrust, suspicion. Manifestations increase in an unfamiliar environment when a person is stressed.
These signs may also indicate the development of dementia in other brain lesions.
Diagnostics
What to do if you suspect Alzheimer's disease in your parents or other relatives?
If others have clearly noticed a syndrome of memory impairment for recent events, difficulties in finding words, problems paying bills or controlling expenses, problems with orientation in a familiar area, then this is indeed a reason to suspect the initial manifestations of Alzheimer's disease. In this case, the neurologist at the appointment will test higher brain functions using special scales and offer to supplement it with a full-fledged neuropsychological study. Testing to rule out other causes of dementia, especially those that require different treatments or may be reversible (eg, normal pressure hydrocephalus), will be essential. Therefore, a complete blood count, vitamin B12 levels, thyroid hormone levels, reactions to HIV and syphilis in the blood, positron emission tomography or single photon emission tomography (SPECT) may also be needed. In complex atypical cases, studies of biomarkers in the cerebrospinal fluid, examination of the level of apolipiprotein-E and apolipoprotein-Eε4 in the blood may be required. If a rare familial form is suspected, genetic testing for mutations in the presenilin 1 and 2 protein genes.
If you suspect Alzheimer's disease, you can undergo a full examination at the Neurology Clinic of the European Medical Center in Moscow.
Disease progression
The dynamics of cognitive decline and decline in a patient with Alzheimer's disease are conventionally divided into stages. The MMSE scale is used for diagnosis. The examination is carried out by a doctor. He assesses the patient’s orientation in time and place, asks him to count in his head, repeat words and phrases, and follow simple instructions, including drawing geometric figures. Depending on the severity of the disorders, preclinical disorders, mild, moderate or severe dementia are diagnosed.
Alzheimer's treatment in Moscow is preceded by diagnosis of the stage of the disease. This helps to assess the patient’s rehabilitation capabilities, prescribe effective therapy and provide relatives with detailed information about the management plan and prognosis. Registration for a consultation is available any day of the week.
The table below shows the stages of the disorder.
| stage | Household features |
| 1 | The patient partially retains the ability to self-care; assistance is required in performing some tasks: shopping, cooking, paying bills. At this stage, he can still live separately. |
| 2 | The patient cannot live alone as he needs supervision. Help is required with dressing, hygiene procedures, cooking and heating food. Professional skills that have become automatic can be retained. |
| 3 | The patient completely loses self-care skills, cannot eat food on his own, and does not control physiological functions. Over time, he ceases to understand spoken speech and loses the ability to express himself independently. The severity of the condition leads to the fact that relatives either stay with him around the clock, or decide on the issue of a nurse, hospitalization in a hospital, or registration in a boarding home. |
The transition from stage to stage correlates with a drop in MMSE scores.
Symptoms
Alzheimer's disease is a disease of old age and old age. The first signs of this disease appear after 65-70 years. A key element in the development of Alzheimer's disease is a disorder in the metabolism of the amyloid precursor protein. If this protein is genetically defective or the enzyme systems that break it down are defective, fragments are deposited in the brain tissue. The result is damage and death of brain cells. Until a critical level of atrophy of some parts of the brain is reached, the disease proceeds latently. Further, disorders of higher brain functions become noticeable and gradually progress. Usually, memory for recent events is impaired early; relatives have to retell conversations and events that happened several days ago. In the early stages, difficulties in orientation in space and less organization when performing household and everyday tasks may appear.
Doctors distinguish a special condition - moderate cognitive impairment. Higher brain functions in this state are somewhat worse than the age norm, but do not reach the level of dementia, that is, the person does not have insoluble difficulties in everyday life and restrictions on activity. In this case, it is recommended to undergo neuropsychological testing to confirm or refute the fact of violations of higher brain functions, and then carry it out every year in order to notice possible deterioration in time. Since there are many causes for mild cognitive impairment and dementia, in addition to Alzheimer's disease, neurologists collect detailed information about the patient, prescribe an MRI of the brain, and study the level of thyroid hormones and vitamin B12 in the blood. Forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating, and feelings of brain fog often accompany depression and anxiety disorders, and are sometimes the only symptoms of these conditions noticeable to the patient. Therefore, neurologists often involve fellow psychiatrists for accurate diagnosis. This entire set of examinations can help detect reversible, treatable disorders.
Alzheimer's disease: treatment in a private psychiatric hospital
Help for patients with atrophic brain disease can be provided in a 24-hour hospital, day ward, clinic consultations and home care.
Alzheimer's treatment in Moscow in a hospital setting is recommended for the following categories of people:
- Patients with a newly diagnosed diagnosis and severe behavioral disorders. Hospitalization will allow you to complete the examination and select therapy for aggression and refusal to take medications.
- Patients who are already receiving medications, but have difficulties with tolerating therapy or a combination of different groups of drugs. In this case, experienced doctors will adjust the prescriptions.
- Patients of any stage of the disease with delusions, hallucinations, aggressive or self-aggressive behavior. The purpose of such hospitalization is to quickly stop the exacerbation and select medications for further use.
- Patients with severe dementia requiring only nursing care and medication. Such hospitalization is necessary in case of departure, illness or other family circumstances in which the caregiver will temporarily not perform his duties.
When choosing a clinic, relatives of a patient with asthma should know that only specialists with specialized education can provide quality care. Hospitalization of patients with dementia in nursing departments and public clinics formally saves money, but has its drawbacks:
- placement of patients 4-8 people in a ward;
- limited list of medications;
- insufficient number of personnel;
- lack of a permanent psychiatrist or psychologist on staff;
- lengthy paperwork.
- queue for places in the hospital.
These features of placement and treatment of Alzheimer's in a non-core or government institution worsen the health status of such patients. Thus, overcrowding of patients has a depressing effect, and the risk of hospital-acquired infections increases. The small number of places where complex patients can be admitted limits the possibility of comfortable single or double occupancy, and independent choice of doctor and room.
The lack of necessary medications leads to the fact that the patient’s relatives have to purchase them at a separate cost or be content with what is available. An insufficient number of staff is the reason that patients receive worse care and stay in bed. The likelihood of life-threatening somatic diseases increases. In the absence of a permanent doctor, visiting staff may miss the development of complications or side effects in a weakened patient.
Knowing and taking into account the specifics of the disease, relatives have the opportunity to choose and choose the optimal option for inpatient treatment. You can get information about the conditions for placing patients, the cost and procedure for hospitalization by calling the clinic at any time. Consultations are anonymous and non-binding.
New directions in the study and treatment of the disease
The latest news in science is a revision of the amyloid theory of Alzheimer's development. Every new drug for the disease in the 21st century has been aimed at destroying or reducing the number of “neurofibrillary” tangles or “plaques.” But out of 100 drugs, only 20 continue to be tested. Huge amounts of money from pharmaceutical companies were wasted. Now scientists are working on a new line of pathogenesis and therapy for the disease.
The second direction is the creation of a vaccine against the disease. The Alzheimer's vaccine was developed by creating antibodies to beta-amyloid. Its number has actually decreased. But serious complications arose. These are hemorrhagic strokes, deterioration of blood circulation in the brain. Due to this, new studies were stopped. A vaccine against tau protein is currently being tested. Her result is better than the previous one.
The third line is passive immunization. This is the creation of monoclonal antibodies that attack only the amyloid beta protein. Crenezumab was developed based on this theory. It was claimed as a remedy for early dementia and pre-dementia conditions. After all, modern medicines work for early symptoms. However, the drug did not justify itself. Testing was stopped at clinical phase 2.
New data has appeared from Janssen . She is developing a beta-secretase inhibitor drug. It is this enzyme that is involved in the formation of pathological protein. Clinical trials have already begun. The third phase will end in 2023. However, many scientists doubt that the drug will reach the market. Its side effects are already known.
Scientists have not found a rational “grain” in anti-amyloid drugs. This may require going back further in your research. After all, it turned out that the human brain remains an unsolved puzzle.
Brief overview of AD research centers
| Brain Initiative (funded by the US government) Aimed at studying memory and the hippocampus | Theoretical result possible in 2025 |
| Cambridge | Studying the work of sick and healthy neurons, searching for the causes of Alzheimer's |
| Pharmaceutical companies (Roche and Eli Lilly) | Testing monoclonal antibodies in young people susceptible to Alzheimer's |
| Dementia Research Foundation London | Developing immunity against dementia |
Alzheimer's disease - care in day hospital and outpatient settings
Most patients with dementia are seen by specialists and receive therapy without being admitted to a 24-hour ward. Competent organization of Alzheimer's treatment in Moscow is possible in conditions that are as close as possible to home.
The examination and stay in a day hospital are suitable for patients with early or middle stages of dementia. In this case, relatives can bring the patient to the department in the morning and pick him up a few hours later. During this time the patient:
- will undergo the necessary examinations;
- will receive medications;
- will be examined by a doctor;
- will work with a psychologist.
Outpatient treatment of dementia occurs in the format of visiting a clinic and caring for the patient at home. A combination of these types of services is possible: for example, a doctor visits the primary patient, conducts screening, prescribes examinations and subsequently sees him in the outpatient department. A combination of clinic visits and home assessments helps the patient receive care regardless of his physical or mental condition. If your health changes, the doctor will arrange for hospitalization at the hospital on the day of the examination or appearance for a consultation.
If there is a person in the family with a serious illness that changes personality and habits, his relatives also begin to need help. The practice of anonymously seeking psychological help is aimed at preserving resources for further coping with the disease. You can learn more about this option for caregivers when you talk to your healthcare provider, call, or visit the clinic.
Which method is more effective and safer?
It is important to understand that Alzheimer's is an irreversible process, so the answer to the question of whether it can be treated or not is clear. If symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to determine the presence of the disease. This will simply help slow down the progression of the pathology.
It is impossible to say which method is the most effective. This is a disease that requires only an integrated approach. It is impossible to cure only by taking medications, using traditional medicine or communicating with psychologists. It is necessary to combine all methods, which will significantly improve the patient’s condition.
Alzheimer's disease: principles of treatment
Drug therapy to support memory should be prescribed immediately after diagnosis. Unfortunately, there is no treatment for Alzheimer’s that can reduce the symptoms of the disease or “delay” the patient at the same level. Drug and non-drug therapy only help slow down the progression of the disease and adapt the patient.
Medicines for AD are aimed at preserving the functioning and interaction of brain cells. They are prescribed in maximum tolerated concentrations. The doctor selects the optimal dosage, constantly assessing the patient’s well-being.
Two groups of drugs are used to treat dementia:
- cholinergic drugs;
- glutamatergic.
Joint reception possible. For concomitant diseases, the doctor will select medications from other groups: antihypertensives, vitamins, antipsychotics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants.
Often, relatives of patients are faced with refusal of therapy. This problem is solved by patches containing the drug. Transdermal systems are glued to areas of the body that are inaccessible for self-removal (for example, the back). The clinic’s psychiatrist will give full recommendations on their use and warn you of what you should pay attention to.
Non-drug therapy is aimed at training and strengthening memory and socializing the patient. An experienced psychologist provides assistance in the clinic.
Antidepressants and neuroleptics
The drugs recommended as part of symptomatic treatment are also selected individually for each person. Such medications can minimize and sometimes completely eliminate conditions such as depression and psychotic disorders, which occur quite often in people diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease.
This includes antidepressants and antipsychotics. The former help improve a person’s psycho-emotional state; the drug of choice is Tianeptine. But tricyclic antidepressants are not recommended for use; in older people they can increase the symptoms of the underlying disease.
Neuroleptics that can be used are Sonapax, Aminazine, and Tizercin. They have a calming effect, relieve spasticity and normalize sleep. Although medications can be purchased without a prescription, you cannot treat them yourself. Each has its own contraindications and side effects and can increase the symptoms of senile dementia.
Prognosis for the disease
Timely examination in the presence of cognitive impairment, identification and treatment of Alzheimer’s in Moscow will allow the patient and his family to prepare for a change in condition and organize their future life.
The course of the disease looks like a steady decline in cognitive abilities and the appearance of behavioral disorders. The average life expectancy of patients after diagnosis is about 4-5 years, the time from the appearance of the first signs of the disease to death is about 10 years. Feel worse:
- elderly patients;
- male persons;
- patients with limited physical activity;
- patients with psychosis.
Psychiatrists note that in patients engaged in mental work, the progression of symptoms of the disorder after detection and initiation of treatment, dementia develops at a faster pace. This is explained by a later request for help due to long-term compensation of the condition due to high intelligence.
If at first patients only need occasional help, then the gradual deterioration of their condition forces relatives to devote all their time to caring for them. Fatigue and burnout develop. Sleep disturbances, psychosis and the inability to take care of yourself are debilitating. Hospitalization and treatment of Alzheimer's in a private psychiatric clinic solves the problem of examination, selection of therapy and care for such severe patients.
If necessary, relatives who are in a state of chronic stress will receive qualified help from a psychologist or psychotherapist. Medical center specialists provide free consultations on these issues. To do this, just call the clinic any day.
During the course of the disease, various difficulties may arise: organizing everyday life, the need to adapt housing to the needs of the patient, fear of the first episodes of aggression, epileptic seizures. In these difficult situations, prompt assistance and support from a specialist who is not only familiar with the patient and his environment, but also has sufficient experience in managing people with this disorder is important. Treatment in a private clinic provides the opportunity for long-term observation of one patient by one doctor who knows the entire history of the development of symptoms and is interested in his well-being.
Alzheimer's disease, although it is the fourth leading cause of death, does not “kill” the patient on its own. More often, death is caused by infections at the stage when the patient stops getting out of bed due to the severity of neurological and somatic disorders.
Competent and anonymous Alzheimer's treatment in Moscow begins with a free consultation with an expert from a private medical center.
Questions and answers
I'm going to have surgery. I have a dad with Alzheimer's disease, and there is no one else to care for him. Is it possible to hospitalize him in the hospital during my treatment?
Yes, in the hospital the patient will undergo another examination and, if necessary, a correction of the treatment regimen. For more information about treatment, call at a time convenient for you.
Is it possible to completely cure Alzheimer's disease if you start taking medications at the first sign of deterioration?
No, the disease causes irreversible changes in the structure of the brain: cells die and connections between them are disrupted. Timely initiation of therapy slows down the onset of deterioration. The incurability of asthma does not mean that a person can refuse therapy. The drugs help slow down the loss of self-care skills, distance dependence on strangers, and therefore preserve the dignity and quality of life of the patient.
Previously, my grandmother and I visited another specialist and were diagnosed with Alzheimer’s. The doctor prescribed the drug, my grandmother has been taking it for about a month, complaining of nausea, vomiting, and has lost weight. Can anything be done?
Not all medications are effective or safe. Perhaps in your case there is an individual intolerance. To change or adjust your Alzheimer's treatment regimen, make an appointment by phone.
Is it true that a patient with dementia should not be given antipsychotics - they are supposedly harmful?
Antipsychotics are drugs used to treat serious and dangerous symptoms such as behavioral disorders, delusions, and hallucinations. They are prescribed only if indicated. Patients with brain damage are more sensitive to such drugs; the selection of a dosage regimen is within the competence of the doctor. Self-medication is dangerous!
Alzheimer's drug groups
There is no effective therapy for senile dementia. However, some groups of drugs control the symptoms of dementia. In some cases, the patient can return to normal life. Psychiatrists and neurologists most often use the following groups of drugs:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors;
- NMDA receptor antagonists;
- Neuroleptics;
- Tranquilizers;
- Normotimics;
- Antidepressants.
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are used for many degenerative diseases. These substances prevent the destruction of the main neurotransmitter of the nervous system, acetylcholine. Thanks to it, the nerve impulse is carried out. With the start of treatment, patients’ memory is restored and cognitive activity increases. The most commonly used AChE inhibitors are rivastigmine, donezepil, and galantamine.
NMDA receptor antagonists normalize the patient’s mental activity. Patients are able to concentrate and maintain attention thanks to taking pills. Side effects include dizziness, weakness, and unsteadiness of gait. Symptoms can be corrected by reducing the dose. The only representative of this class of drugs is Memantine.
Additionally! The theory of gluten-free nutrition suggests that patients with developing dementia avoid foods containing gluten. However, gluten is beneficial for the body. Cereals contain large amounts of B vitamins.
Neuroleptics can calm a patient with Alzheimer's disease and eliminate aggression, delusions and hallucinations. Taking medications should be agreed with a psychiatrist. Many of the drugs are contraindicated in dementia. A significant limitation is the elderly age of the patients. Dose selection is important here. A representative of the class is chlorprothixene.
Traquilizers combat anxiety, fear, and panic attacks. These symptoms are common in people with dementia. These tablets are most often used for Alzheimer's disease: Diazepam, Phenibut, Phenazepam.
Normotimics are needed to normalize mood. They are used in people with mental disorders. People whose character has been altered by the disease are treated with these drugs. They remove aggression and quarrelsomeness. The drugs used are gabapentin and carbamazepine.
Fact! When examining a patient with dementia, vitamin B12 levels are checked. If it is severely reduced, a high dose of the drug returns the patient's cognitive abilities.