Speaking about a lacunar cyst of the brain, what it is can be defined as a pathological formation that has the shape of a cavity. There is a liquid formation inside it. This anomaly appears in the brain; in very rare cases, its development can begin in the cerebellum. According to statistics, about 4% of the population on our planet suffers from this pathology. It occurs predominantly in men. When such a cyst appears, patients will require urgent medical attention due to the very serious consequences that the disease has. Most of them are irreversible.
Lacunar cyst of the brain: what is it?
A lacuna is a small (from several to tens of mm in size) inclusion of cerebrospinal fluid. The walls of the capsule are represented by fibrous tissue. A chamber of fluid forms in different places in the brain:
- frontal;
- temporal;
- occipital
The lacuna is formed as a response of the body to an inflammatory or necrotic process in the brain. If some of the gray matter neurons die, the space with the dead particles is immediately surrounded by fibrous tissue. The communication between dead tissue and healthy tissue stops. This protection mechanism is designed to protect the brain from general inflammation, necrosis and other harmful processes. Dead cells can begin to spread disease-causing organisms, which will have a negative impact on human health.
What then is the danger of a cyst if it prevents the spread of necrosis and inflammation? The problem with chambers containing cerebrospinal fluid is that they can grow to large sizes and put pressure on healthy areas of tissue. This leads to disturbances in vision, psyche, coordination, memory and many other symptoms. The brain is the main control center of the body, therefore, with the slightest negative impact on its parts, the condition of the nervous system deteriorates significantly.
Pressure from the lacuna is not the only harmful effect. The aqueous inclusion may begin to spread the accumulated cerebrospinal fluid if the integrity of the fibrous walls is compromised. This process is also fraught with deterioration of brain function and various unpleasant syndromes. But the most dangerous consequence of the spread of cyst contents is the formation of malignant tumors.
Since a cyst poses a danger to humans, when it is detected, the camera is removed. More information about symptoms, treatment methods, cysts and possible complications is described below.
Symptoms of the disease

The fact that patients develop a lacunar cyst of the head is not always realized during their lifetime. The neoplasm does not give any signs of itself. It is possible to detect a cyst only in 25% of cases. When the tumor reaches large volumes, patients experience central nervous system disorder in several manifestations: the functioning of some organs is significantly weakened. Vision is greatly affected by this disorder.
A lacunar cyst of the brain is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Convulsive syndrome.
- Hallucinations.
- There is a noise in my ears.
- Sensitivity problems arise.
- Sleep gets worse.
- There is a throbbing sensation in the skull.
- Problems with coordination of movements.
When significant anomalies are achieved, limbs become paralyzed and visual function deteriorates. The skull is compressed. If a cyst appears in or near the cerebellum, the work of the vestibular apparatus becomes difficult, the gait changes, and balance is lost.
If such symptoms occur, a large, painful tumor develops. For these purposes, it is necessary to provide people with urgent medical care, which leads to the death of people.
This section is responsible for the contraction of muscle tissue, so when a cyst forms in this place, motor function is impaired. This is often characterized by involuntary contraction of muscle tissue on the face, convulsions and epileptic seizures appear. The clinical picture develops quickly; there are no prerequisites for the development of epilepsy.
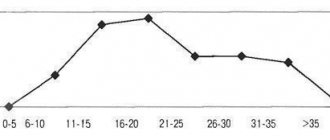
Incidence of the disease depending on gender and age
Men are more susceptible to cerebral lacunar cyst. They especially often suffer from it in old age, starting from 40-50 years. The people most susceptible to the disease are patients suffering from stroke attacks.
Lacunar cyst is considered a postnatal disease. Capsules rarely appear during embryo formation.
Important. More often they are acquired in nature, appearing as a result of injuries and illnesses.
Classification and localization
Lacunar cyst is classified into the following types:
- Porencephalic. A congenital form that can occur as a result of impaired development of the embryo in the womb.
- Postnatal. An acquired form that occurs during necrotic processes.
The localization of the cyst may be as follows:
- cerebellum;
- pons;
- subcortical centers;
- visual hillocks of the thalamus.
The congenital form of cystic formation in the brain occurs less frequently than the acquired form. Depending on the location, there are different cases - their ratio is approximately equal.
Types of brain cysts
Most lacunar cysts of the brain are postnatal, that is, acquired after birth. However, there is a separate category of lacunae - porencephalic cyst of the brain. It deserves attention because it differs from a regular cyst in symptoms and development.
Porencephalic cyst of the brain: what is it?
This type of cyst mainly forms in a child in the womb. Very rarely, a medical error (pressure on the head) can lead to the appearance of fluid chambers.
A porencephalic cyst appears as large areas of fluid in the brain. The percentage of neuronal damage in this type of disease is much higher than with the appearance of small lacunae and adults. Uncontrolled development of a porencephalic cyst can lead to serious disturbances in the development of the child.
Important. If this deviation is detected, the newborn remains in the hospital and undergoes a series of operations aimed at stopping the process of formation of lacunae. Treatment is considered urgent.
Pathogenesis
Normal circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is an established system. It includes several stages:
- Formation of fluid in the brain.
- Its movement along the ventricles.
- Entry into the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord and brain.
- Reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the blood.
When a cyst forms in the brain, fluid enters there during its circulation. However, due to the dense shell of the formation, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from it is difficult. So, liquid gradually accumulates in the empty cavity.
Reasons for the appearance of the camera
A capsule with fluid in the brain is formed against the background of trauma and inflammatory processes. The rarest reason for the appearance of vacuoles is a genetic predisposition. Patients often think that if they developed a cyst in infancy, this indicates the genetic nature of the disease. In fact, many children get cysts in the womb not as a result of faulty genes, but as a consequence of developmental disorders. The following problems during pregnancy can lead to the development of brain chambers:
- inflammatory processes;
- infections;
- threats of miscarriages;
- injuries to the abdominal area;
- malnutrition of the fetus through the placenta;
- smoking, taking drugs and alcohol, medications prohibited during pregnancy.
Cysts in newborns are detected at an early age and quickly removed. It is more difficult to get rid of a lacuna acquired in adulthood. Adult patients are less likely to undergo examinations and rarely suffer from symptoms of lacuna development.
Reasons for the appearance of cysts in the postnatal period:
- inflammatory processes of the brain;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- oxygen starvation of the brain;
- stroke;
- clinical death;
- alcohol abuse.
Any process that stimulates the death of neurons can lead to the formation of a chamber. It could be any bad habits.
Existing types
So what is it - a lacunar cyst in the brain and in what form does it manifest itself? Lacunar cysts in modern neurology are classified as congenital and acquired. Congenital forms are considered the primary form of the disease, acquired forms are considered secondary.
A congenital lacunar cyst can form in the mother's womb if the expectant mother allows herself to smoke, take alcohol and take psychotropic drugs. They are undoubtedly pathological factors for the formation of the fetus in the womb. As a result of their influence, the normal activity of a woman’s body is disrupted, on which the development of the fetus entirely depends. Bad habits of the mother can lead to gene mutation, malnutrition of the fetus, and deterioration of its blood supply. The cause of primary lacunar formation in a baby may be a disease suffered by the mother that affects the structure of the nerve fibers and tissues of the fetus.
This happens due to a violation of the development of the unborn child or a pathology of the development of the central nervous system. The formation of a cystic cavity occurs at any stage of embryonic development, but doctors suggest that most often this happens in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Symptoms of the disease
The severity of symptoms, as well as their nature, depends on where the formation is localized. It is important to take into account that until the moment of active development the lacuna does not manifest itself in any way. The first signs of a progressive problem appear when the formation reaches a large size.
General signs of a tumor in the brain:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- increased fatigue;
- behavioral disorders;
- sudden mood swings;
- problems with motor movements, fine motor skills of the hands or mouth;
- loss of some skills (reading, speaking, etc.).

Important. In its acute manifestation, the lacuna can cause frequent hemorrhages both inside the brain and from the nose - this is associated with increased blood pressure. If a patient delays seeing a doctor, he may develop hand tremors, blindness and other neurological disorders.
Symptoms depending on the location of the cyst:
- Frontal part. This section is responsible for muscle contractions, so when a cyst forms in this location, disturbances in the functioning of muscle tissue may occur. This is often expressed in involuntary contraction of the muscles of the mouth and face, in convulsions and attacks of epilepsy. The difference between epileptic seizures caused by lacunae and standard ones is that the clinical picture develops quickly, despite the fact that there were no previous prerequisites for the development of epilepsy.
- Occipital region. If this part of the brain is damaged, vision is impaired. A person may lose vision partially or completely. With neurological blindness, vision is usually lost abruptly, without visible injury or cause. Before the onset of complete blindness (which is not necessary in the case of a cyst), the patient may experience temporary loss of vision, suffer from “night blindness,” causeless “floaters,” etc. violations.
- Basal ganglia. One of the most serious lesions, as pressure on this department leads to a lack of coordination. This mainly concerns coordination of a complex type: motor activity, in which it is necessary to bend and take complex poses. When the ganglia are damaged, both general coordination of the limbs and fine motor skills of the hands are affected. Tremors of the hands may develop.
- Temple area. Violations of this area lead to mental disorders and hallucinations of a mixed type. The patient may suffer from hallucinations that are either tasteful, visual, or auditory, or may experience one of these types.
- Crown area. At the same time, writing and speech skills (oral, using gestures and any other), and coordination of limbs may be lost. If it is severe, the patient may stop perceiving the speech of others, as the speech processing areas will be affected.
The larger the cyst, the more pronounced and systematic the symptoms a person experiences. Since the listed signs of lacunar chamber formation are very serious, you need to consult a doctor at the first suspicion to prevent complications.
Important. If counseling and therapy do not occur on time, irreversible brain changes will occur.
Signs
Symptoms directly depend on which part of the brain the tumor is located in and how large it is. Pain begins to bother you if the tumor is growing or has already grown to an impressive size. The functioning of certain organs may also be disrupted.
Can appear:
- headache;
- problems with the musculoskeletal system;
- epileptic seizures;
- paralysis;
- lack of coordination;
- swallowing disorder;
- paralysis;
- breathing disorder.
Such a cyst is removed only as a last resort, when there are clear indications and the symptoms are life-threatening and disrupt the most important functions of the body. If the cavity grows rapidly, emotional and mental disorders, convulsions, and seizures appear; these are also clear indications for surgical intervention.
Methods for diagnosing cerebral cysts
Patients rarely go to the doctor with suspicion of having a cyst. Since the signs of the disease are very non-specific, the average person cannot distinguish it from deterioration of vision, problems of the nervous system, or the consequences of injury. Therefore, the problem is usually detected during general regular examinations (dispensary examination or medical examination before taking up a certain position). During a clinical examination, a cyst can be detected by a therapist based on the symptoms described, or by an X-ray or MRI, CT specialist.
During diagnosis, it is necessary to differentiate the cyst from diseases with similar symptoms. You can confuse the symptoms of a lacuna with the following ailments:
- gradual loss of vision;
- senile changes in the nervous system;
- dementia;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- mental disorders;
- malignant tumors in the brain;
- inflammatory processes (meningitis, etc.);
- concussions;
- etc.
The list of diseases whose symptoms are similar to those of a brain cyst is huge. Therefore, if you suspect the presence of a chamber with liquid, a serious examination is immediately prescribed - computed tomography, MRI or X-ray.
X-ray examination can detect uncharacteristic areas of gray matter. The lacunae in the image will look like contrasting areas that stand out sharply against the background of other, uniformly colored parts of the brain. The problem with such research is that the size of the capsule may not exceed 1-2 mm, so it is very difficult to see. If the formation is small, you will need more accurate examples of devices - MRI or CT.
Computed tomography is not recommended for children, older people, patients in a state of decompensation, or people sensitive to ionizing radiation. This procedure, like x-rays, is carried out on the basis of a small radiation background. If contact with ionizing radiation is undesirable, an MRI procedure is performed based on the action of magnetic waves.
How to live
If there are no symptoms of the anomaly, it does not grow, you can calmly live with it. Such patients only need to undergo regular MRI scans to monitor whether it has begun to enlarge. Such benign anomalies rarely develop. To help the patient, the doctor may prescribe restorative conservative treatment. There are medications that improve blood circulation and oxygen supply to tissues.
It is important for patients with cysts to be monitored and undergo regular examinations.
With a small size of the progressive tumor, the quality and life expectancy of the patient does not change in any way. The harmless course is due to the fact that the small diameter of the cyst does not affect the brain and does not disrupt its functioning.
The only thing that changes when diagnosing a benign tumor is a stable examination and monitoring of the dynamics of pathology on computed tomography every six months.
Possible complications
The list of complications that can arise as a result of untimely or incorrect treatment of a cerebral lacuna is very long. The main danger of a cyst is that it can lead to irreversible changes (at extreme stages of development). It is necessary to eliminate the problem by removing it as early as possible, when the damage from the formation is not yet so great.
Main complications:
- Inflammatory process of the brain. It can develop either as a result of an incorrect removal procedure or during the natural development of the capsule.
- Cancer tumor. The cyst has a carcinogenic effect on neighboring tissues: it constantly deprives oxygen, nutrients, and releases toxic secretions. With continued exposure, it can lead to the development of cancer.
- Loss of vision. This is a temporary condition that goes away after the capsule pressing on the optic region is removed. However, if the integrity of the visual department was damaged during the operation, blindness may remain forever.
- Loss of coordination. This includes both problems performing physical activities and the inability to perform fine motor tasks correctly. This condition is also usually temporary.
- Memory losses. As a residual phenomenon, the patient can be haunted even after removal of the cyst, but each time it becomes less pronounced.
- Epilepsy. This syndrome can be especially severe when trying to treat epilepsy with medications that do not help in the case of exposure to the cyst. After prolonged pressure from the capsule, the disease may persist for some time even if the chamber is removed.
Set of measures
If the lacunar cyst is a small cyst and the patient is not bothered by the clinical manifestations of brain dysfunction, then treatment, as a rule, is not prescribed, but it is recommended to carry out regular monitoring of the growth of the formation.
There is an opinion that asymptomatic cysts should not be considered diseases, but rather anomalies. Other experts, on the contrary, are convinced that even small formations accelerate the onset of senile dementia and contribute to the development of neurological diseases.
It is necessary to treat the pathologies that caused the cyst. For this, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and antihypertensive drugs can be used, depending on the etiology of the disease.
In cases where formations arise as a result of hemorrhage in the brain or symptoms develop that reduce the patient’s quality of life, surgical intervention is indicated. Today this is the only way to get rid of lacunar cysts.
Methods used to remove formation:
- Bypass surgery - the patient is given a drainage tube through which the fluid filling the cavity drains out. The walls of the cyst fall and grow together. The disadvantage of this method is the high risk of infection when using the shunt for a long time.
- Endoscopy – removal of a cyst through a puncture in the skull using an endoscope equipped with a video camera. The safest and non-traumatic method. However, there are contraindications for its use.
- Craniotomy is a highly effective operation that allows you to remove cysts of any location, but with a high risk of brain damage.
At the moment, shunting and trepanation are used extremely rarely.
Consequences.
If therapy is not carried out normally, negative consequences appear in the form of problems with coordination of movements, hearing and vision disorders, inflammation, and death.
In babies, hydrocephalus may occur, where cerebrospinal fluid collects in the ventricles, causing the brain to shrink. If the disorder is correctly diagnosed and treated, it will be possible to get rid of the signs of the disease and prevent the appearance of new cysts. For preventive purposes, it is necessary to undergo preventive procedures less than every 2 years.
If a lacunar cyst of the head is not identified in a timely manner, the patient does not receive proper treatment, which leads to disastrous results. Postischemic lacunar cyst is fraught with the following disorders: problems with coordination of movements, difficulties with auditory and visual analyzers, hydrocephalus, death, encephalitis.
The consequences and prognosis are unfavorable if rapid growth of the lacunar cyst is observed. Complications can vary in severity: from hearing loss, vision loss, to inflammatory lesions in the brain and death. In other cases, the presence of a cyst does not pose a threat.
Many people need a clear understanding of why a brain cyst is dangerous. A brief explanation is as follows: it is dangerous because it can begin to grow at any moment, disrupting the functioning of neighboring parts of the brain, causing tissue ischemia and the spread of foci of necrosis. As a result, if it is not detected in time and therapy is not started, the consequences of a brain cyst in an adult can be as follows:
- mental disorders;
- epilepsy;
- paralysis;
- blindness, deafness, speech and motor function disorders;
- dementia and personality disorder;
- death.
Prevention
There are no specially developed tips on how to avoid this disease. You need to carefully monitor your health. This is especially true for athletes 20-40 years old who are at risk.
How to treat intercostal neurosis?
Find out how to remove salts from your joints.