A stroke is a difficult experience both for the person who survived the stroke and for his family. And even when the worst seems to be over, a person involuntarily thinks about the duration of his own life and looks for the answer to the question: how many years do they live after a stroke? After all, there is an opinion that even minor brain damage, such as a microstroke, shortens the patient’s life expectancy by years and nothing can be done about it. However, awareness of the reasons that provoked a stroke and adherence to the rules of a healthy lifestyle appropriate to the current situation are key points in increasing life expectancy.
Types of strokes
Not so long ago, cerebral circulatory disorders were considered a problem of adulthood. This is not surprising, because the factors that provoke it (hypertension, atherosclerosis) manifest themselves mainly after 45-50 years. But now stroke has become significantly “younger” and vascular problems are developing at an earlier age. This complicates diagnosis, since specialists often mistake NS lesions for symptoms of a psychogenic disorder.
Stroke that affects people can be of two types:
- hemorrhagic;
- ischemic.
Each of them has its own distinctive features and characteristics. According to statistics, people aged 25 to 45 years are often diagnosed with hemorrhagic stroke, but after 45 years, about 80% of cases are ischemic strokes.
Ischemic stroke and its consequences
This type of stroke occurs against the background of the development of thrombosis and blockage of blood vessels, when brain cells begin to starve and die. After an attack, the victim gradually loses both mental and physical abilities. A few hours after the stroke, the signs of a stroke may disappear, which misleads the patient and he does not go to the hospital. This is a fatal mistake, since the process of neuronal destruction is already in full swing. And if you do not start treatment, then an acute phase begins, during which the following is noted:
- paralysis;
- speech problems;
- urological dysfunction;
- psychological disorders;
- partial loss of memory and vision;
- numbness of the limbs, loss of sensitivity;
- impaired coordination of movements and fine motor skills.
Ischemic stroke
The consequences can have varying degrees of severity, and in case of serious disorders, the patient may need at least 6 months for rehabilitation and recovery. Often, ischemic stroke in all age categories is provoked by the following diseases:
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- rheumatism of the heart;
- neck vascular injuries;
- cardiogenic embolism;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives (for women).
Hemorrhagic stroke and its consequences
Hemorrhagic lesions are characterized by more significant consequences and a crisis course, with an immediate transition to an acute form. Such a stroke is provoked by ruptures of blood vessels, aneurysms, lacunae or tumors in the brain. In case of hemorrhagic stroke, delay in providing medical care can cause disability, coma and even death, since in this case there is deep damage to the cerebral cortex.
Hemorrhagic stroke
The consequence of a stroke of this type is paralysis, loss of vision and the ability to speak, motor skills disorders, mental and mental disorders, cerebral edema, infarction and tissue necrosis. Often, even after successful rehabilitation, previous functions are only partially restored, and older people very rarely survive an attack. The provoking factors of hemorrhagic stroke, as a rule, are:
- hypertension;
- systemic blood diseases;
- aneurysms and other pathologies of cerebral vessels.
However, there are several other factors that can cause any type of stroke. These include infectious diseases (meningitis, tuberculosis, encephalitis), clotting problems, benign or malignant tumors, as well as the presence of bad habits (nicotine and alcohol addiction, overeating, physical inactivity).
How long can a person live if he refuses food and water?
Many people ask the question when the problem described above arises: how long can a bedridden patient live if he does not drink or eat? Any qualified medical professional will tell you that this depends to a very large extent on the specific disease of the immobilized person, what physical form he is in, how long he has been lying down, how old he is and other nuances.
Although, in any development of events, it is clear that such a phenomenon shortens the period of life by several times, because without a natural source of energy, that is, food, the existence of an organism in this world will quickly cease. Daily bread and water are extremely important for both any healthy person and a bedridden disabled person , and without them, death will inevitably occur in a short time.
Research by scientists convincingly proves that after two weeks of such a strict “fast” as a complete hunger strike, a mechanism of self-destruction is triggered in the body. If you do not eat or drink, death will occur in 8-10 days. If you only ate to drink, you can last about sixty days.
And this is all if the body is strong enough. What if an ordinary decrepit grandmother is bedridden, and at the same time she also stops eating? Of course, then the process of weakening and destruction will proceed by leaps and bounds.
How many years do people live after a stroke?
Statistics answer the question of how many years people live after a stroke. As a rule, life expectancy is about 10 years, but in severe cases, death can occur immediately after the attack. Observations of specialists showed:
- some patients (30-35%) die in the first month after the attack;
- After the first year, only half of stroke victims are alive.
In addition, how long people live after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke also depends on the number of attacks.
But what is the overall picture and how long will a person live after a repeated major, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke?
In such circumstances, only 5-15% survive the first year after an attack, and over the next 5 years - about 42% of men and 25% of women. There are many reasons for such sad statistics, but the main thing is that the factors that led to the blow do not disappear anywhere. That is, a predisposition to blood clots, vascular damage due to atherosclerosis, hypertension and heart problems still remain in the body.
Factors influencing life expectancy after stroke
The duration of life after an impact directly depends on such factors.
- The severity of the attack and the extent of damage to brain tissue. Sometimes the severity of the blow is excessive, which leads to death or a global reduction in the life expectancy of the victim.
- Consequences of vascular damage. A person with extensive paralysis is doomed to a lying position, which without proper care is fraught with bedsores and pneumonia.
- Immobility after an impact provokes the formation of blood clots in the lower extremities. Such blood clots, when they break off, often enter the lungs and provoke thromboembolism, which often leads to death.
- Ensuring the safety of a stroke victim. It is necessary to exclude falls caused by dizziness and weakness in the legs, since any fractures, especially the femoral neck, are quite difficult to treat in elderly patients.
- Age. This is an equally important factor, since young people are more likely to survive.
- General health.
Features of the rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation after a stroke
After a vascular lesion of the brain, rehabilitation measures are mandatory, regardless of the severity of the lesions caused by the stroke. The entire recovery period can be divided into two stages: the first days after the attack within the walls of a medical institution and the rehabilitation period in special centers and at home.
Recovery stage in the first month after the attack
As a rule, doctors insist that the victim stay in a specialized department for 2 to 4 weeks. At this point, specialists of various profiles can reduce the entire therapeutic process to a specific system and further recovery. Disturbances in the blood supply to the brain lead to the formation of a focus of dead cells, and nearby cells often exhibit rather weak activity. To restore their normal activity, timely medical care is required.
It is better to remain under the supervision of specialists for some time after a stroke
First, patients are placed in the correct and comfortable position for them, and only then they begin physical therapy. Thanks to regular exercise and medication, brain cells begin to function more actively, which stimulates the restoration of damaged areas of the organ. But positive changes can only be achieved with a daily increase in loads. In the first 14 days, the victim is prescribed only a light massage with stroking and rubbing and procedures using electrical muscle stimulation. If the patient tolerated this stage well, then they begin to restore speech function.
Rehabilitation after discharge
Sometimes all the problems that arise can be eliminated in 2-4 weeks in the hospital, but if this does not happen, then the recovery stage is delayed. It is important for the victim to continue to systematically increase the load over the next two months.
The program of the therapeutic and gymnastic complex, carried out at home, is previously agreed upon with the local doctor. The neurologist develops an adaptation map, based on which all exercises and procedures must be performed. It should be noted that for older people (over the age of 70), a stroke is too severe a trauma, rehabilitation after which is almost impossible.
Source: NervovNet.com
Diagnostics
To diagnose inflammation, you need to listen for wheezing in the lungs using a phonendoscope. Particular attention is paid to the lower back. In addition to wheezing, crepitus can be heard. To confirm the suspected diagnosis, the patient is prescribed an x-ray at a point where there is a special apparatus designed for bedridden patients.
If necessary, transportation to the procedure site is carried out using paid services that have equipment for hospitalization of patients with impaired motor function.
Severe cases lead to direct admission to the hospital, where a full examination, including x-rays, will be carried out.
A comprehensive examination consists of the following studies:
- blood chemistry;
- general urinalysis (UCA);
- general blood test;
- electrocardiography;
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the heart.
To prescribe pharmaceuticals intended to get rid of the pathogen, it is necessary to take a sputum test. It is collected in two containers and sent to the clinical and bacteriological laboratory, one copy each. Studying the material helps to find the cause of the disease, the beginning of the development of tuberculosis or oncological processes.
Caring for a bedridden patient after a stroke
Immobility after a stroke is a consequence of severe disturbances in movements, their coordination, the possibility of purposeful actions, and decreased consciousness. This condition is accompanied by special requirements for maintaining vital functions.
Nutrition
Difficulty in feeding a patient after an acute cerebrovascular accident is associated with many negative factors:
- difficulty swallowing and chewing food;
- frequent choking;
- violation of taste determination;
- decreased sensitivity of the oral cavity;
- apathy, depression with loss of appetite.
In order to maximally provide the patient’s body with vitamins and microelements that contribute to recovery, it is necessary to prepare easily digestible dishes that do not require effort when taking them. For this, vegetable and fruit purees, mousses, first courses and porridges with a puree consistency, minced meat and fish, cottage cheese, and fermented milk drinks are recommended .
The main condition is that the food should be exclusively fresh, preference should be given to natural products, without preservatives or dyes.

Portions should be small, no more than 200 g at a time, the frequency of their intake is 6 - 7 times a day . Slow feeding is recommended and can take about 30 - 40 minutes. It is forbidden to rush the patient, as this poses a risk of food entering the respiratory tract. The position can be semi-sitting with pillows or on the healthy side.
For semi-liquid food, it is convenient to use cocktail straws (bent) or children's sippy cups, cups with a spout, as for drinking mineral water.
If the patient is able to eat from a spoon, then it is optimal to take a dessert spoon and fill it not completely, while making sure that there are no previous portions in the mouth. You should always feed from the healthy side. Water should not be taken with food, it overloads the stomach and can cause a gag reflex. Therefore, they usually suggest drinking half an hour before a meal or an hour after. The same applies to sweet drinks, desserts, and fruit juices.
Bathing
Every day the patient's body should be wiped with a sponge or terry cloth soaked in warm water. It is important that this happens consistently, especially in cool weather, to prevent hypothermia.
Therefore, for example, first the surface of the leg is treated, it is completely dried, and then they move on to the second. To protect the sheets from getting wet, when swimming, you need to put a medical oilcloth and a towel or diaper on it.
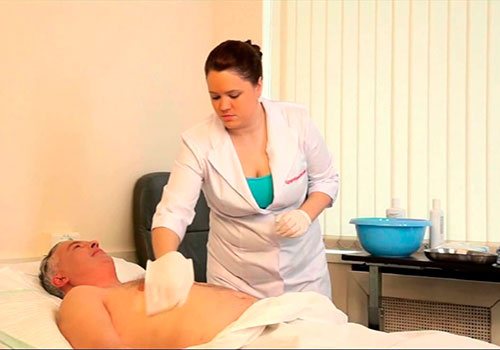
Every day the patient's body should be wiped with a sponge or terry cloth soaked in warm water.
A vessel is used for washing. Be sure to wash the genitals with soap for intimate hygiene, dry thoroughly, ventilate, and powder with talcum powder. If there are signs of redness or irritation of the mucous membranes and skin of the perineum, then after washing off the soap, use a weak (barely pink) solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin (one tablet per 300 ml of water).
Organization of the place
A bedridden patient can spend more than one month in bed, and sometimes even a year. It must be taken into account that the nervous system in such patients is damaged, the emotional background is disturbed, and intolerance to temperature changes, bright light and loud sounds is noted. However, their complete absence is also undesirable. The room must be kept clean and ventilated at least 4-5 times a day for 10-15 minutes.
Next to the bed there is a table for care items and medicines. Within the patient's reach, it is imperative to place everything he may need - water, napkins, a telephone or bell, an electric bell in order to call the caregiver for help.

Bed for bedridden patients with sides and mattress
It is optimal to place a special mattress on the bed to prevent bedsores. It has a structure in the form of cells; the compressor attached to it alternately fills them with air. This changing pressure on the skin helps to activate blood circulation and gives a slight massage effect.
Toilet
Even when using diapers, leakage cannot be ruled out, so it is often necessary to additionally place diapers on a waterproof basis or oilcloth under the sheets. You should carefully monitor the cleanliness and dryness of bed linen and clothing, change them regularly, and prevent the patient from lying on folds of fabric or scars.
Organizing a toilet is often a complex process. If the victim cannot sit up, but feels the urge to empty the bladder or bowel, then use a bedpan. Such patients wear adult diapers at night or in case of involuntary discharge of urine and feces. They cannot be allowed to be on the body all the time.
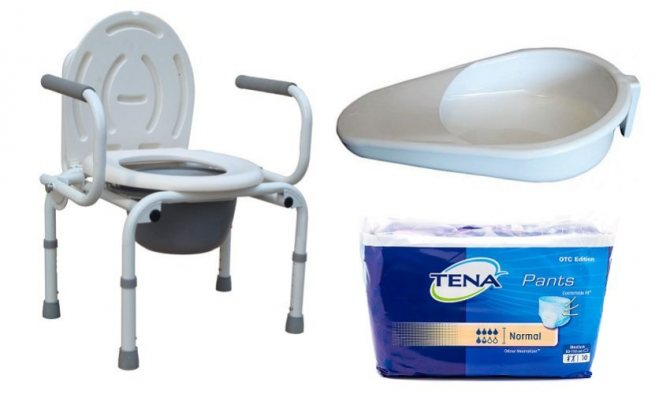
Tools for organizing a toilet for a bedridden patient
After the change and hygiene of the genital organs, the patient should simply be put on a diaper for half an hour. If more active movements are possible, then a toilet seat (a special bucket with a seat or a chair with a cut-out hole) is installed next to the bed.
Rehabilitation of a bedridden patient
To properly organize the recovery period, strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations is required. To make this task easier for relatives, you need to follow a clear daily routine. It is best to schedule all necessary hygiene procedures, taking medications, feeding, massage, and physical education classes by the hour.
Treatment
During the rehabilitation period, the mandatory intake of medications from the group of neuroprotectors, antiplatelet agents, hypocholesterolemic drugs, antihypertensive and diuretic drugs continues. Doses and frequency of use are prescribed by a doctor, and the person caring for a post-stroke patient must observe the time and sequence of their use.
It is also necessary to measure blood pressure at least 2 - 3 times a day and record the results. If unusual reactions occur, call a doctor immediately.
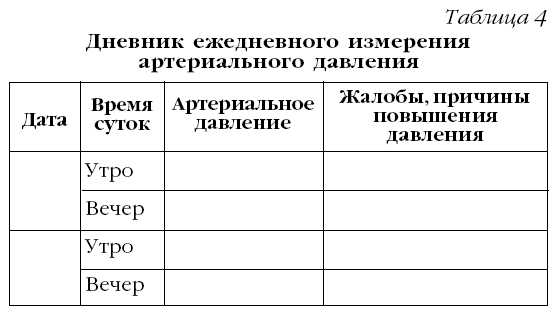
Sample of pressure recording and recording
Exercises
Massage and physical therapy are a necessary part of rehabilitation. They begin in the first week of a stroke and are usually carried out for a long period of time, taking 7-10 day breaks in agreement with the doctor. The duration of the session ranges from 10 (initially) to 30 minutes or more, depending on the patient’s adaptation.
The development of the limbs occurs after they are warmed by massage or thermal procedures (paraffin, ozokerite applications). Be sure to include movements for healthy and paralyzed limbs in the training.
Watch the video about physical therapy for bedridden patients:
Complications and methods of dealing with them
When you stay in a supine position for a long time, blood circulation and the functioning of almost all internal organs are disrupted, and the ability of the body's immune defense is significantly reduced. Because of this, complications can arise, sometimes leading to irreparable consequences.
Low pressure
The causes of hypotension may be drug therapy in an incorrectly selected dose, redistribution of blood in a constant horizontal position, or weakness of the heart muscle. Manifestations of this condition are pale skin, dizziness, tinnitus, chilliness, drowsiness, headaches, and severe weakness.
Medicines to increase blood pressure are used in the post-stroke period for emergency treatment - in a collaptoid or shock state (Dobutamine, Mezaton).
If hypotension is mild, general tonics are recommended:
- an infusion of rose hips, St. John's wort and immortelle flowers, taken in equal parts (a tablespoon of the mixture per glass of boiling water, brew overnight in a thermos, take 50 ml half an hour before meals);
- green tea;
- honey with pollen;
- juice from carrots and celery.
Watch the video about recipes for increasing and decreasing blood pressure:
Constipation
Intestinal dysfunction is associated both with neurological disorders and with forced physical inactivity and pureed food. To prevent constipation, you need to review your diet to include:
- juices from vegetables (carrots, beets, pumpkin), fruits (apricots, plums);
- vegetable oil (in the morning on an empty stomach, take a tablespoon with half a glass of cool water);
- decoction of prunes, dried apricots and figs;
- homemade fermented milk drinks using starter cultures;
- additive for porridge, kefir - a teaspoon of ground bran, pre-steamed with boiling water, be sure to drink at least 1.5 liters of water;
- ground dry seaweed (kelp) - use instead of salt;
- infusion of flaxseed (a tablespoon per glass of boiling water), strain after 20 minutes, drink twice.

If these preventive measures are insufficiently effective, laxatives help achieve regular bowel movements. In consultation with your doctor, use:
- laxative tea;
- Guttalax, Regulax, Picolax drops;
- Senadexin tablets;
- Duphalac syrup;
- therapeutic enemas Norgalax, Microlax, Normacol, Enema;
- laxative suppositories – Bisacodyl, Glycerin.
If there has been no bowel movement for more than 3 days, a cleansing enema is indicated.
Pneumonia
Acute pneumonia in the post-stroke period is the cause of death in approximately 20% of cases. In a bedridden patient, its main cause is the entry of water and food into the respiratory tract.
Severe pneumonia increases cerebral edema and leads to worsening neurological abnormalities. Manifestations may include: difficulty breathing, cough, chest pain, increased body temperature. It should be taken into account that in elderly and weakened patients, pneumonia can occur without fever. Treatment requires antibiotic therapy. It is possible to prevent the development of this complication by:
- regular breathing exercises;
- turning over in bed on your side every 2 hours;
- use of vibration (anti-bedsore mattresses);
- tapping the chest in a position on the healthy side.
Watch the video about preventing pneumonia in bedridden patients:
Bedsores
They arise due to excess pressure of the body weight on areas of contact with the bed. They may fester with the development of sepsis. When a bedsore forms, the skin turns pale, then turns red and becomes dead. To prevent the occurrence you need:
- from the first days of staying in bed, examine the patient’s sacrum, shoulder blades and heels, wipe them with camphor alcohol;
- change body position;
- avoid sweating or diaper rash;
- regularly replace wet clothes and sheets, use absorbent diapers under the buttocks and perineum;
- purchase an anti-decubitus mattress or rubber circle;
- Wash the patient daily and dry the skin completely;
- carry out massage and therapeutic exercises.
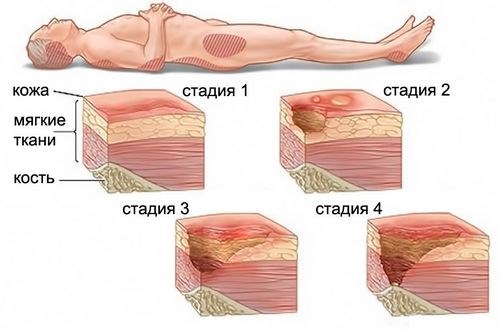
To heal the skin defect, ointments are used: Actovegin, Solcoseryl, Oflocain, Methyluracil, Panthenol, Argosulfan.
How long do bedridden patients live after a stroke?
Life expectancy is determined by the type of stroke (with ischemic stroke the prognosis is better), its extent, the severity of impairment of consciousness, the age characteristics of the body and the presence of concomitant diseases. If at the beginning of the disease deaths are more often associated with cerebral edema, then after the first month their causes become: pneumonia, blockage of the pulmonary artery, acute cardiac failure.
Bedridden patients after a stroke are completely dependent on the help of people caring for them. It is important to provide comfortable conditions in the room, organize proper nutrition, take medications by the hour, daily massage and therapeutic exercises. From the first days of illness, it is necessary to take measures to prevent bedsores, pneumonia, and work impairment intestines.
Source: CardioBook.ru
Consequences of poor nutrition
- The first consequence of not eating is extreme weight loss.
- A person confined to bed freezes, quickly gets tired from any movements, the functioning of the pancreas is disrupted, and blood sugar rises.
- Exhaustion causes bedsores to appear faster because the bones put a lot of pressure on the skin.
- Metabolism is inhibited, which is also very harmful to the functioning of the body.
And in conclusion, we want to conclude - if a person does not eat or drink for two days, be sure to call a doctor at home so that he can examine him and determine the cause of this phenomenon. After all, a hunger strike can only be a symptom, and the cause must be urgently eliminated before the bedridden patient loses his life. After all, each of us needs to drink and eat well, and this is beyond doubt.
Ischemic stroke and what are its consequences
The development of ischemic stroke is associated with thrombosis and blockage of the lumen of blood vessels, as a result of which cellular structures begin to become oxygen starved and slowly die. A patient with such pathological changes gradually loses a number of physical and intellectual skills.
Clinical signs of pathology may disappear within a few hours, and therefore the patient does not even visit a medical facility, and this is the main mistake, since the neurons are already dying, and the process will not stop on its own.
The result of lack of therapy can be:
- Partial loss of the ability to speak or see.
- Feeling of numbness in the upper extremities, loss of sensitivity in them.
- Paralysis.
- Partial memory loss.
- Impaired coordination of movements and fine motor skills.
- Urological pathologies.
- Mental disorders.
It is noteworthy that if a person has a left-sided ischemic stroke, in addition to death, there is a risk of developing such severe consequences as:
- Coma.
- Epilepsy.
- Paralysis.
Interesting! The chances of survival in patients with ischemic stroke are quite high compared to those who are faced with a hemorrhagic form of the pathology. However, they must follow all the doctor’s instructions during the rehabilitation course.
Changing sleep and wake patterns
Discussing the early signs of approaching death, doctors agree that the patient has less and less time to stay awake. In the 2 or 3 months before a person dies, they may spend less time without sleep. Due to lack of wakefulness, the metabolism in their body becomes weaker.
Therefore, without metabolic energy, a person sleeps much more. He is more often immersed in superficial sleep and seems to be dozing. This saves precious energy and reduces pain. The latter fades into the background, becoming, as it were, background. Of course, the emotional side suffers greatly. The paucity of expression of one’s feelings, the self-isolation of the desire to remain silent more than to speak leave an imprint on relationships with others.
The desire to ask and answer any questions, to be interested in everyday life and the people around you disappears. As a result, in advanced cases, patients become apathetic and detached. They sleep almost 20 hours a day unless there is acute pain or serious irritating factors. Unfortunately, such an imbalance threatens stagnant processes, mental problems and accelerates death.
Hemorrhagic stroke
The occurrence of hemorrhagic stroke is associated with more severe consequences and a crisis nature of the course, turning into an acute phase. All this is associated with rupture of vessel walls, aneurysms, lacunae or brain tumors.
In such a situation, the slightest delay in providing professional medical care will cause further disability, coma or death due to deep damage to brain tissue.
Consequences at 60 years of age, as well as at other ages, associated with hemorrhagic stroke may include:
- Paralysis.
- Blindness.
- Loss of ability to speak.
- Motor skills disorders.
- Pathologies of intellectual activity.
- Deviations in the psycho-emotional state.
- Necrotic tissue changes, infarction or cerebral edema.
Important! In most cases, even after rehabilitation measures, patients only partially regain physical skills, and older people most often do not survive.
Swelling
Edema appears on the lower extremities
Very reliable signs of death are swelling and spots on the legs and arms. We are talking about malfunctions in the kidneys and circulatory system. In the first case of oncology, the kidneys do not have time to cope with toxins and they poison the body. Swelling occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues, but the reasons for this can be different.
The blood flow becomes chaotic, and in the veins, especially the subcutaneous ones, the pressure increases so much that the walls of the vessel cannot stand it and begin to expand, like a balloon. In this case, metabolic processes are disrupted, blood is redistributed unevenly in the vessels, forming areas with spots.[1] It is not for nothing that they say that if such marks appear, then we are talking about complete dysfunction of the limbs.
Statistics about life after a stroke
Statistics provide the following basic data:
- For strokes under 45 years of age, the mortality rate does not exceed 25%.
- When an attack occurs after 50 years, the death rate reaches 40%
At the same time, it also follows from the data that the most severe consequences are observed in the fairer sex, but the very fact of stroke development is more common in men.
As for the elderly category of citizens whose age exceeds 70 years, death is the result of a stroke in almost 80%. And it makes no sense to talk about the complete recovery of the survivors.
In Russia, mortality from ischemic stroke occurs in 67.8% of cases, and from hemorrhagic stroke - 11.5%. In turn, undifferentiated stroke accounts for 17.4%, and subarachnoid hemorrhage – 3.3%.
Things are different with what the statistics are after a mini-stroke. In this situation, death is so unlikely that it is not even included in the average data.
The survival of patients who are at risk due to any aggravating condition, for example:
- Hypertonic disease.
- Atherosclerotic lesion of the vascular bed.
- Pathological damage to cerebral vessels.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol, smoking and abuse of caffeine-containing drinks.
- High physical and emotional stress.
- The period of bearing a child.
- History of traumatic brain injury of any kind.
- Senile period of life.
To increase their life expectancy, these people need to visit health care facilities more often for diagnostic testing and treatment when needed.
As for how many strokes a person can experience, even statistics do not give a clear answer. There were cases when the patient had 3-4 or more attacks. And each time the consequences of this condition become more severe.
What affects life expectancy after an attack?
Prognosis for the future life of patients after an attack depends on several aspects:
- Type of pathology.
- Degree of damage to brain tissue.
- Localization of affected areas.
- Age and gender.
- Duration of the immobilized state.
- Presence of concomitant pathologies.
Size of the pathological focus
The length of time a person can live depends on the extent of necrosis of brain tissue. So, if the damage was extensive, then the cells will not be able to fully recover even a year after the stroke. And since at this time the functioning of the body will be defective, the functioning of the organ systems will be disrupted more quickly, and this will create an increased risk of a new stroke, which shortens the remaining life expectancy.
Consequences of pathology
The average life expectancy of patients who develop serious pathologies such as paralysis, numbness or mental disorders after a stroke is significantly reduced due to the inability of such patients to lead full life activities. Thus, paralysis can become a predisposing factor for the formation of bedsores and blood poisoning, and mental disorders can become a predisposing factor for neurological diseases, which brings the patient’s death closer.
Age
It is much more difficult for older people and newborns to suffer a stroke. This is due to the fact that their cells do not have the ability to quickly renew themselves, and in the future they can develop:
- Inflammation of the cerebral cortex.
- Pathological lesions of the vascular bed.
- Bleeding in the brain.
- Heart attack.
In such patients, even if they survive the attack, with the slightest excitement or increase in blood pressure, a new attack starts, and they will not be able to live long.
Duration of immobility
A bedridden patient after a stroke rarely has sufficient motivation to actively participate in rehabilitation, which is especially pronounced in cases of paralysis or paresis. In this regard, he does not complete the entire course prescribed by the doctor, and his muscles continue to lose tone, the blood supply to the body deteriorates, thrombosis and necrosis develop, and blood poisoning occurs.
Because of this, inflammatory processes often develop, and the patient becomes especially sensitive to infections. As a result, a paralyzed patient lives much shorter and has a higher risk of having another stroke.
How do patients with different types of cancer die?
| Type of oncology | Men | Women |
| Lungs' cancer | 26,9% | 7,2% |
| Esophageal carcinoma | 8,6% | 11% |
| Breast cancer | —— | 18% |
| Brain cancer | 7% | 4,8% |
| Liver cancer | 22,5% | 12,8% |
Doctors always tell relatives how cancer patients die and what exactly happens in their body, depending on the location of the pathological focus.
Brain cancer
It has been established that brain tumors are the most aggressive and fast-growing of all cancers. The peculiarity of such malignant neoplasms is that they do not metastasize and the pathological process occurs only in the brain. Patients with this disease can fade away in just a few months, or even weeks.
Let's take a closer look at how a person with brain cancer dies. The painfulness of the symptoms increases as the tumor grows, it grows in the brain tissue and the general condition of the human body. The very first sign is headache and dizziness. Often patients do not turn to specialists, but drown out the symptoms with analgesics.
Death occurs due to cerebral edema, as well as when the systems that are responsible for the vital functions of the body (heartbeat, breathing) stop working. Before death, patients with brain cancer experience clouding of consciousness, delirium, hallucinations, and coma. Often the patient dies without regaining consciousness.
Lungs' cancer
The main symptom of lung cancer is respiratory failure. Those suffering from stage 4 lung cancer are on mechanical ventilation (artificial lung ventilation) because they simply cannot breathe on their own. Due to the breakdown of lung tissue and the accumulation of fluid in them (pleurisy), the body does not receive the normal amount of oxygen and other necessary substances.
Thus, carbon dioxide accumulates in the body, and all tissues of the body are in oxygen deficiency. Metabolic processes in cells are disrupted, and some chemical processes are completely impossible. In such patients in the terminal stage of cancer, cyanosis (blueness) of the hands and feet is observed. This is what lung cancer patients die from.
Mammary cancer

The peculiarity of metastasis of this type of tumor is its penetration into bone tissue. Much less commonly, breast cancer affects the brain and lung tissue. Due to the aggressiveness of treatment and a severe decrease in immunity, what causes such cancer patients to die is any infectious complications (even a common cold can be fatal).
When diagnosing stage 4 breast cancer, only symptomatic therapy is prescribed. It includes strong analgesics, since bone metastases cause severe pain and suffering for the patient. Women often ask whether it hurts to die from this type of cancer. Doctors warn and discuss pain therapy in advance, since in the final stages of cancer the symptoms are extremely painful.
Liver cancer
Some of the main causes of liver cancer are cirrhosis and hepatitis caused by a virus. In the last stage of liver cancer, patients experience the following symptomatic picture:
- frequent nosebleeds;
- large hematomas at injection sites;
- slow blood clotting: any abrasions or cuts continue to bleed for a long time.
In addition to hemolytic symptoms, the patient experiences nausea, general weakness and fatigue, as well as significant pain localized in the liver. Death from liver cancer is very painful, but at the same time the disease progresses quite quickly, which reduces the time of suffering.
Esophageal carcinoma
This is one of the most dangerous types of cancer of organs, since when a tumor grows in the esophagus, the risk of its penetration into nearby organs is extremely high. In medical practice, giant tumors of the esophagus are often encountered, which, when growing, form a single malignant system.
Patients with terminal cancer experience severe discomfort because, due to the location of the tumor, they cannot receive food normally. To feed them, a nasogastric tube, gastrastomy, and parenteral nutrition are used. In this case, the patient suffers from severe pain, dyspeptic disorders and severe exhaustion.
Prognosis for people over 80 years of age
Relatively speaking, 80 years for a person becomes the threshold during which survival rate after a stroke sharply decreases. In people aged 90 years, the death rate after a stroke reaches 70%, and half of this number of people first end up in a coma or develop cerebral edema.
In this age period, pathology often develops again, due to insufficiently high-quality preliminary therapy. But even if the patient is saved, he completely loses physical and intellectual skills, and his subsequent life is no more than a few years. This is due to the fact that such patients especially often suffer from infectious and inflammatory diseases and have a weakened immune system.
In many ways, how long people live after a particular stroke attack is directly influenced by the person himself, his motivation and the people around him. If you follow all the recommendations given by a specialist and with the support of loved ones, rehabilitation after an attack is quite possible, and life can be significantly extended.
How to live after a stroke part 1 Life after a stroke? Let's escape from a stroke! After a stroke, you can learn to live again
Source: KardioBit.ru
Treatment
Relief from symptoms of the disease in bedridden patients is problematic due to the impact of the disease on other organ systems. In addition, the disease, when the activity of the immune system decreases, can quickly turn from unilateral to bilateral. For such cases, in addition to treatment aimed at eliminating the pathogen, pharmacological agents are used to get rid of multiple secondary pathologies.
Detailed article about the treatment of elderly and bedridden patients.
Life expectancy forecast
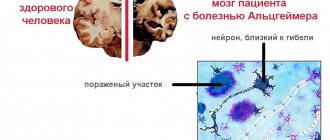
The so-called “senile insanity” develops in most cases in older people against the background of brain damage.
According to German researchers, the risk of developing the disease in 80-year-olds is 25%, and in 90-year-olds – 50%.
The active progression of dementia leads to the disintegration of mental activity. The patient ceases to be a full-fledged member of society and becomes completely dependent on the help of other people, so his relatives often wonder how many years a person with this diagnosis will live.
How long do people live with dementia? On average, people with dementia can live 5-10 years, sometimes more.
However, modern doctors do not give a definite answer, since everything is individual and influenced by many factors.
The life expectancy of an elderly person will depend on the moment at which the symptoms of the disease were discovered.
In addition, you need to take into account the general health of the patient who has been diagnosed. Against the background of various diseases, dementia can occur in completely different ways.
Impact of comorbidities
How long do people live with dementia? When predicting how long a person with a similar nervous system disorder will live, it is worth paying attention to the origin of the diagnosis. Thus, about 5% of all cases of the disease are reversible.
When dementia is caused by a tumor or infection, after getting rid of it, life expectancy can increase significantly.
In addition, mental disorders are sometimes caused by a lack of folic acid or vitamin D. By taking these substances, the patient can get rid of the symptoms of a frightening disease.
After a stroke
After a stroke, 10-30% of patients begin to develop signs of dementia:
- problems with memory, speech, reading and counting,
- slow movement, sudden changes in direction while walking,
- instability of emotional state, depression.
The mortality rate after a stroke in patients with dementia is three times higher than in patients who simply had a stroke.
However, timely use of medications and prevention of recurrent strokes can extend the life of an elderly person with symptoms of this disorder to 5-10 years or more.
Bedridden patients
While ambulatory patients with “senile dementia” can harm themselves by forgetting to turn off the gas or getting lost on the street, bedridden patients are at lower risk and can live 10 and sometimes 15 years.
Competent care and willingness to quickly come to the aid of an old man will significantly improve the quality and duration of his existence.
To prolong the life of a bedridden patient with dementia, it is very important to properly maintain personal hygiene: wash your hands, body, brush your teeth, genitals after going to the toilet, etc.
In order to pay sufficient attention to an elderly person, his relatives often use the services of a nurse with a special education. In addition, there are boarding houses that are ready to accept people with this diagnosis.
For Alzheimer's disease
In 70% of recorded cases, Alzheimer's disease leads to the development of senile dementia. As the disease progresses, it manifests itself as a decrease in the number of interests, slower thinking and motor reactions, increased irritability, and passivity.
Over time, hallucinations and paranoid ideas are added. In some cases, epileptic seizures occur.
Unfortunately, irreversible changes in the brain are accompanied by a persistent decline in previously acquired skills of independent existence.
The life expectancy for Alzheimer's disease complicated by dementia is 5-7 years. In severe forms (pronounced apathy, loss of speech skills, difficulties with movement), patients can live 1-3 years.
How long do people live with Alzheimer's disease? Find out from the video:
Vascular form of dementia
The occurrence of vascular dementia in old age can occur against the background of circulatory disorders (atherosclerosis, arrhythmia, pathology of the heart valves, hypertension, etc.).
Brain cells that lack nutrients and oxygen die off. Patients are subject to constant depression and absent-mindedness, increased fatigue, irritability, and sleep disturbances.
The life expectancy forecast for severe vascular dementia is on average 4-5 years, for a mild stage and slow development - from 10 to 15 years.
In approximately 15% of cases, complete recovery is possible.
Death is most often caused by a heart attack or stroke, so to prolong life it is worth paying more attention to the prevention of these ailments.
In people at a young age
Unfortunately, not only old people, but also young people at an early age - 28-40 years old - face a disease such as dementia. A mental disorder can develop due to an unhealthy lifestyle.
Modern youth are often susceptible to destructive behavior, which includes various bad habits and addictions. As a result of smoking, gambling, alcohol or drug use, brain activity slows down.
If the first symptoms of the disease are detected, there is a chance to prevent the progression of dementia and completely cure the patient. However, most often it is only possible to slow down severe mental changes and prolong the years lived by constantly taking medications.
The average lifespan with moderate development of mental decline and the use of symptomatic therapy will be 10-20, in some cases 25 years.
In severe cases, as well as with a genetic predisposition, the disease develops more rapidly and can lead to death in just 5-8 years.
Reduced need for food
Deterioration of appetite and sensitivity are signs of imminent death
When a cancer patient is at home, all her loved ones note the signs of death. She gradually refuses food. First, the dose decreases from a plate to a quarter of a saucer, and then the swallowing reflex gradually disappears. There is a need for nutrition through a syringe or tube. In half of the cases, a system with glucose and vitamin therapy is connected.
But the effectiveness of such support is very low. The body tries to use up its own fat reserves and minimize waste. This worsens the patient’s general condition, causing drowsiness and difficulty breathing. Impaired urination and problems with natural needs. It is believed that problems with going to the toilet are also signs of approaching death.
No matter how funny it may seem, in reality there is a completely logical chain in this. If defecation is not carried out once every two days or with the regularity to which a person is accustomed, then feces accumulate in the intestines. Even stones can form. As a result, toxins are absorbed from them, which seriously poison the body and reduce its performance.
It's about the same story with urination. It's harder for the kidneys to work. They allow less and less fluid to pass through and eventually the urine comes out saturated. Due to the high concentration of acids, even blood in the urine may be observed. For relief, a catheter can be installed, but this is not a panacea against the general background of unpleasant consequences for a bedridden patient.
How to increase the period
To maintain mental health and increase your life expectancy with dementia, you need to walk and exercise a lot, as well as regularly train your brain with intellectual exercises.
In addition, a balanced diet will help in the fight against dementia.
Patients are advised to follow a proper balanced diet, including foods rich in vitamins and natural antioxidants.
If the onset of dementia is diagnosed at a young age and at an early stage, doctors have a chance to cure the patient, while in old age the process is irreversible.
Unfortunately, there is no effective way to get rid of dementia that occurs against the background of various diseases.
However, with the help of a timely response to the emerging symptoms of the disease and well-chosen drug therapy, it is possible to slow down the rapid development of a mental disorder, extending a person’s life to 10 and sometimes 20 years.
Source: nerv.guru