Sometimes a retiree suffering from Alzheimer's experiences glimpses of consciousness. At such moments, he realizes the full scale of the disaster, and he may become hysterical because of what a burden he has become for his relatives. Relatives, firstly, do not need to delude themselves that this is a sign of recovery (Alzheimer, unfortunately, cannot be cured). Secondly, there is no need to tell the person about everything that he did and said - this will upset him even more. Thirdly, in this situation, you need to try to reassure the patient, explain that he is not to blame for the current situation and, of course, promise that everything will be fine, and together we will be able to overcome the disease (the patient does not need to know about the seriousness of the diagnosis).
Traditional recipes and diet will help against Alzheimer's
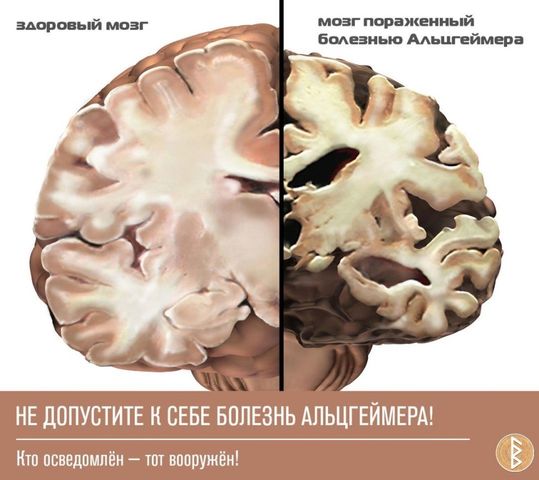
A fairly common progressive pathology of the brain, characterized by memory loss, difficulty in various activities, problems with speech, loss of orientation in space and time, personality changes, and mood instability, is called Alzheimer's disease. The disease is named after the German scientist who first described the disease and its symptoms.
According to statistics, older people are more susceptible to developing this disease. Unfortunately, the disease is incurable. However, there are many ways that will help not only slow down the progression of the disease, but also prevent its occurrence. Treatment of Alzheimer's disease with folk remedies is effective and will help minimize the manifestations of the disease.
Signs and symptoms of illness
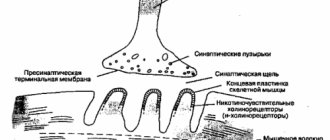
Sufferers of the disease often have a deficiency of acetylcholine, although it is unclear whether this is the cause of the disease or its result. However, therapy focuses on measures that either prevent the destruction of acetylcholine or enrich brain tissue with its precursor, choline. Hence the logical conclusion: any agents that increase the level of this neurotransmitter in the brain, including medicinal herbs and natural recipes, remain in our time the main salvation for those suffering from Alzheimer's dementia.
Other medications for the symptoms of the disease are also being tested. By tradition, they are all synthetic. And also according to tradition, pharmaceutical companies pretend that they do not notice promising natural alternatives, i.e. herbs containing substances that prevent acetylcholine from being destroyed. Fortunately, in addition to the tasteless moss, quite a few plants are, in principle, capable of preventing the manifestations of the disease and slowing down the development of this age-related dementia.

Unfortunately, many of us have seen this depressing disintegration of personality. With the disease, which is named after Alzheimer's, a person loses his mind. It starts with small lapses in memory and can progress to the point where he does not recognize people close to him in photographs. This is a cruel end, but treating Alzheimer's disease with folk remedies at home in the conditions familiar to you, with the right approach, can help. You will be surprised that it is quite possible to carry out therapy using alternative medicine compounds at home. In this article we will tell you how therapy is carried out outside of a hospital, and that you can try different recipes.
What provokes the development of the disease?
A story from life. Once, an elderly woman complained of memory deterioration, as well as problems with orientation in space and time. Moreover, the patient experienced the emergence of multiple speech disorders, as well as progressive loss of other skills. After some time, the woman became helpless. She developed more and more dementia. She stopped recognizing her family and friends. After five years she died.
This happened in 1906. At that time, doctors and medicine in general had fewer options compared to today. Alois Alzheimer, a scientist from Germany, while examining the brain of the deceased, identified a new nosological form characterized by changes in neurofibrils (the supporting and drainage system of neurons).

Today, knowing what pathology is and knowing how to treat Alzheimer's disease, doctors have the opportunity to prolong the lives of patients, as well as minimize the symptoms of the disorder, and even more: prevent its occurrence.
The exact cause of the development of pathology is not yet known to modern medicine. However, there are several factors that in one way or another can provoke the appearance of a brain disorder. So, the occurrence of Alzheimer's disease may be due to:
- genetic predisposition;
- the presence of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, in particular hypertension;
- lack of fatty acids in the diet;
- frequent stress;
- the presence of bad habits.
It has been proven that pathology is more common in older people, and the weaker half of society suffers more from it.
Folk remedies against Alzheimer's
Non-traditional methods of treatment in combination with therapy prescribed by a doctor can bring good results. It is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and take the medications prescribed by him. It is necessary to use formulations made from natural and herbal ingredients wisely. Remember, this is an adjuvant therapy, and if you completely replace drug therapy with drugs, this can lead to disastrous consequences.
The following herbal compositions are natural antidepressants. They will help improve cerebral circulation, improve condition, and minimize the manifestation of pathology.
1. Use of a healing decoction. Mix the fruits of Chinese lemongrass with ginseng rhizome in equal proportions. Brew the raw material in the amount of fifteen grams of boiled water - a liter. Place the container on the stove, wait until it boils, and then boil the mixture for a quarter of an hour. Drink ¼ glass of filtered drink several times a day.
2. Motherwort tincture against illness. This remedy helps normalize blood pressure and calm the nervous system with noticeable signs of excitability and aggression. Pour 20 grams of crushed dried rhizomes of the plant with medical alcohol - 500 ml. Place the tightly closed container in a cool place for two weeks. Take a spoonful of strained medicine diluted in 50 ml of water three times a day.
3. Ginkgo biloba in the treatment of the disease. Pour 50 grams of crushed dried leaves of the plant into a glass container. Fill the raw materials with vodka - half a liter. Close the container and refrigerate for half a month. Take ten drops of the medicine twice a day.
4. Use of dioscorea tincture. This medicine helps improve brain function. Pour 100 grams of finely chopped plant rhizomes with vodka - a liter. Leave the tightly closed container in a cool place for two weeks. It is recommended to take a spoonful of the composition three times a day.
5. Use of healing teas. There are many plants that have antidepressant effects and also help stimulate the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Steam 15 grams of crushed St. John's wort in five hundred milliliters of boiled water. Infuse the composition in a thermos for an hour. Drink ½ glass of filtered drink four times a day. Teas from heather, chicory, leuzea, and calamus are prepared in a similar way.
6. Strong tea against frustration. It is recommended to drink two cups of green or black tea every day, but only strong. Tea helps in activating the functioning of nerve cells. Green tea is a storehouse of antioxidants. If desired, you can add honey to the drink.
7. Treatment of Alzheimer's disease with honey. Many people know that honey improves memory and has anti-sclerotic properties. It is recommended to eat three spoons of the product every day.
Diet for Alzheimer's disease
It is clear to everyone that it is worth minimizing or, even better, eliminating the consumption of smoked, spicy, fried and fatty foods, sweets, and flour products. The diet should be balanced and fortified.
It is recommended to include in the diet:
- Blueberries. This berry has powerful antioxidant properties. Moreover, eating blueberries regularly will help slow down age-related changes in the brain.
- Citrus fruits. They are rich in ascorbic acid.
- Carrots are a storehouse of beta-carotene.
- Beets, peas, cereals, cabbage are rich in folic acid.
Disease prevention
In order to prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary:
- Healthy food;
- treat cardiovascular diseases;
- avoid stressful situations;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- walk more often in the fresh air;
- drink at least two liters of fluid every day.
It is known that the disease affects people with average and low levels of intelligence. To prevent its development, train your memory, read more, learn new things, learn foreign languages. Find something you like. It doesn’t matter what it will be: fishing, yoga, singing. The main thing is that your life will become rich and varied.
Giving up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol) is the key to longevity. Take vitamins. Don't forget to also monitor your sugar levels and blood pressure. Last but not least, get tested regularly for Alzheimer's disease. This will facilitate timely diagnosis.
Effective folk remedies
It is similar to cardiovascular diseases in one very important respect: it largely depends on lifestyle. Try taking Vit. E. Research shows that taking vitamin E for moderate Alzheimer's disease can eliminate the symptoms of the disease. It is recommended to take 400 to 800 IU (international units) of vitamin E per day. However, if you are considering taking more than 200 IU for a medical condition, check with your doctor first. In a study conducted using Vit. E, an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke was found.

In treating the disease, take this wonderful plant as your assistant. Ginkgo leaf extract for Alzheimer's improves memory mainly due to the fact that it has a beneficial effect on blood circulation, including cerebral circulation. The drug is presented in the form of a solution or tablets (also available under the name Memoplant) and can be taken at home in a usual dose of 120 - 240 mg (calculated as dry extract) per day. However, if you are prescribed monoamine oxidase inhibitors for a medical condition (depression or anxiety), then take ginkgo before taking it. Check with your doctor as these drugs may interact.
The best natural medicines
- Monarda (Monarda, different species). Monarda contains the compound carvacrol, which, according to Austrian scientists, inhibits the breakdown of acetylcholine. This plant also contains thymol with a similar beneficial property. Some monarda substances have been shown to be able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier (between the blood and brain tissue). The role of this barrier is to prevent anything extraneous from entering our nerve centers. However, it becomes an obstacle not only to harmful substances, but also to those that may be useful to a sick person. The ability of monarda's healing compounds to cross the blood-brain barrier means that the extract of this plant can be used as a topical folk remedy for Alzheimer's. If so, washing your hair with an herbal shampoo should be no less effective than taking tacrine hydrochloride orally. And at the same time, most likely, it will be safer for the liver and, certainly, will cost much less. You won’t be able to buy such a miraculous shampoo, but it’s not difficult to make it yourself. To make this formulation for Alzheimer's therapy, simply add a few droppers of Monarda tincture to what you like to wash your hair with.
- Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis). Judging by some data, damage to brain structures by aggressive free radicals plays an important role in the development of Alzheimer's disease. If so, rosemary in treating Alzheimer's should help. It contains a couple of dozen antioxidants - substances that neutralize the effects of free radicals. Among these protective compounds, rosmarinic acid is considered particularly powerful. In addition, half a dozen components were found in rosemary that seem to suppress the breakdown of acetylcholine. It is interesting, by the way, that for Alzheimer's disease, aromatherapists recommend rosemary oil (as well as lemon balm, fennel and sage).
Since ancient times, rosemary has been considered a herb for strengthening memory - among some peoples it even symbolized it. Folk remedies such as shampoo, tea from this plant and just a bunch of it in a hot bath protect against Alzheimer's dementia no worse than tacrine or hupercine. Add to this the safety and pleasure of using rosemary in any form. Even if you don’t gain intelligence as a result, there will certainly be no harm.
Among the acetylcholine-inhibiting compounds in this herb, at least some enter the bloodstream through the skin and are likely able to cross the blood-brain barrier. Therefore, regular use of rosemary shampoo is similar in effect to taking tacrine. This shampoo is sold ready-made, but this folk remedy for getting rid of Alzheimer’s is easy to make yourself: a few pipettes of the tincture with what you wash your hair with. American walnut (Bertholettia excelsa). As already mentioned, treatment for Alzheimer's disease consists not only of trying to preserve acetylcholine, but also of intensively supplying the brain with its precursor, choline. It is part of lecithin, and the latter, according to my data, is most abundant in American walnuts - up to 10% of dry weight. However, many other plants are also rich in it. The list is topped, in descending order of concentration of this substance, by dandelion flowers, poppy seeds, soybeans and mung beans.
Fenugreek leaves and shepherd's purse contain quite a lot of choline itself, which can help cope with the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Less of it is found in horehound (horsemint), ginseng, cowpea, peas, mung beans, luffa, lentils and angelica.
- Salvia officinalis (Salvia officinalis). Herbalist of the 17th century. John Gerard wrote that sage "helps the weak brain and memory, quickly healing them." British scientists have confirmed that sage substances inhibit enzymes that break down acetylcholine, i.e. help preserve this neurotransmitter, apparently essential for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease. Like rosemary, sage is rich in antioxidants. Just be careful when using this folk remedy for Alzheimer's: this herb contains a lot of thujone, a substance that in high doses can cause seizures.
- Stinging nettle (Urtica dioica). This herb contains a lot of the element boron, which can double the level of estrogen sex hormones circulating in the blood. And they, as studies show, improve short-term memory and improve mood in some patients with Alzheimer's disease.
- Willow (Salix, various species). Research shows a reduced prevalence of Alzheimer's dementia in those who take high-dose anti-inflammatory drugs for arthritis. If they really help prevent Alzheimer's disease, then willow bark, rich in salicylates similar to aspirin, should have similar properties. If you do not tolerate aspirin well, this treatment is most likely contraindicated for you.
- Asian centella (Centella asiatica). This Indian plant has been used for centuries to strengthen memory and intelligence. It is unlikely that such a reputation for this folk remedy against a serious illness – Alzheimer’s disease – arose out of nowhere.
Treatment of Alzheimer's disease with folk remedies

Folk remedies in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease are auxiliary methods that enhance the effect of medications and maintain a satisfactory physical and mental state of the patient. Folk remedies include not only taking medicinal herbal decoctions, but also consuming certain foods in combination with physical exercise and methods of activating the brain. Learn more about each of them.
Methods for treating Alzheimer's disease with folk remedies
Alzheimer's disease is a severe disease that affects the human body in old age. Scientists have not yet come to a clear conclusion: what are the reasons for the development of pathology. Currently, therapy for the disease makes it possible only to stop the destructive processes occurring in brain cells; it includes a course of medications and the use of traditional medicine. How to treat Alzheimer's disease at home, what folk remedies will help significantly improve the quality of life of an elderly person?
Healing herbal decoctions are auxiliary agents that can enhance the effect of medications prescribed for the disease. Physical exercises, proper diet and techniques that increase the activity of brain cells are methods to help the patient at home.
“Understand his feelings, but don’t offer to choose”

— What is the most difficult thing in a situation when your loved one gets Alzheimer's disease?
The hardest thing is to accept that your dad or mom is gradually turning into a complete stranger. Or the grandmother was the head of the family, everyone listened to her, and now her advice is no longer adequate.
Information is very important here, it is important to know how the disease manifests itself, and to understand that everything is her fault, and not a loved one.
In each case, the disease progresses individually, much depends on heredity, social status, and education.
According to statistics, the more knowledge and skills a person has, the slower Alzheimer's disease reaches basic functions.
But high intelligence and material well-being do not insure against the disease: Margaret Thatcher, Terry Pratchett, Ronald Reagan, Annie Girardot and other famous people suffered from it.
It is very important to see a doctor in time.
At no age, be it 90 or 120, should an elderly person show signs of dementia. This is a disease, not old age.
— How can relatives maintain their usual way of life, family traditions, and peace of mind?
— You cannot enter into an argument with an elderly person suffering from Alzheimer’s disease, or try to convince him otherwise. Even if he starts blaming: “You stole my money. You hid my passport." It is useless to shake your wallet or passport in front of his nose; he will not understand, because he is sure that it is missing.
But you can try to understand the feelings of an elderly person, take them seriously and offer help: “Yes, it’s very unpleasant when documents disappear. It's very sad when money is lost. Let's look for a passport together. Come on, let’s go to the bank together and see if the money is in the book.”

It happens that an elderly person gets up every morning and gets ready for work, even if he retired a long time ago. You can say: “Today is a day off.”
Or: “Come on, I’ll take you with you.” Usually, when you go out and circle around the house, a person with Alzheimer's disease forgets where he was going. But his desire was satisfied, and the anxiety - I need to go, but they don’t let me in - is no longer there.
It’s good if you manage to maintain a calm voice all the time and speak measuredly.
Do not offer a person with dementia a choice, do not ask: “What do you want to eat?”
Because he may not understand the choice, and this will make him feel bad: “How is it possible, I don’t understand what they are telling me.” He will start to get angry and refuse to eat at all. It’s better to say: “Let’s eat the cutlets that you love.”
Many people with dementia refuse to bathe or change clothes. It is not necessary to put the whole person into the bathtub. You can wash it in parts: today - your legs, tomorrow - your head.
My aunt agreed to shower if everyone lined up for the shower. Collectivism was important to her. Another woman obeyed when a relative put on a white robe and told her to wash herself. For her, any person in a white coat is a doctor whose recommendations must be followed.
Features of treatment at home
Features of the treatment of Alzheimer's disease include strict adherence to the daily routine. You should take prescribed medications every day, support your body with folk remedies, and engage in physical exercise and brain training.
Physical activity depends on the patient's age. The attending doctor prescribes a set of physical exercises for each age group.
An elderly person with this diagnosis should spend more time outdoors, and exercise can be replaced with a leisurely walk that lasts at least an hour.
To train your brain, you need to memorize small passages of poetry or prose every day, collect puzzles, and solve scanwords and crosswords.
Phytotherapy
Treatment and prevention of Alzheimer's with folk remedies includes taking decoctions of medicinal plants, which are natural antidepressants that increase blood flow and stimulate brain function.

Decoctions and infusions that are used for the disease:
- Infusion of lemongrass fruit and ginseng root.
Grind the dried ginseng root, crush the lemongrass fruits with the blunt side of a knife, take equal proportions of the raw materials, mix. Place a teaspoon of the mixture in a wide-necked thermos, pour one liter of boiling water, leave for a couple of hours. Take the infusion in small quantities several times a day. The infusion has a positive effect on the activity of brain cells.
- A decoction of motherwort.
Place a tablespoon of dried raw materials in a glass bowl, add two glasses of hot water, cook in a steam bath for 9-12 minutes, cool, strain, add another 2 glasses of boiled water. Drink half a glass of the decoction 2-3 times a day. The product will help normalize blood pressure, relieve aggression and increased excitability.
- Healing tea from St. John's wort and heather.
Add dried plant leaves to tea leaves and drink healing tea throughout the day. Plants are strong antidepressants.
- Infusion of ginkgo biloba leaves.
Medications
Although the drugs available today do not provide a cure, some can slow down the progression of the disease and prolong the active period of life. Therefore, medications should be used, of course, if the benefits of taking them outweigh the risk of side effects, and there are no contraindications to treatment . Several groups of drugs are used.
Replacement therapy
Allows you to overcome the deficiency of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the brain. The following drugs are prescribed:
- donepezil (Aricept);
- rivastigmine (Exelon);
- chalantamine (Reminyl);
- amiridine;
- tacrine.
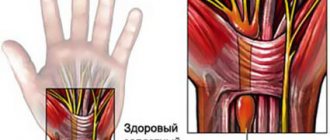
These medications are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine), cholinergic receptor agonists (substances that perform the function of acetylcholine when there is a deficiency of it) and acetylcholine precursors (which form the deficient neurotransmitter in the body). Thus, the deficiency of this neurotransmitter is eliminated and the symptoms of the disease are reduced. Does not affect the progression of pathology.
Medicines help slow the death of neurons, thereby eliminating the main symptoms of dementia
These drugs help improve memory and perform simple daily tasks. They do not affect mental disorders (depression, anxiety, aggressiveness, etc.).
The drug memantine (Axura, Ebixa) is also widely used Also refers to replacement therapy, but with a different mechanism of action. It also does not stop the progression of asthma, but improves the clinical picture for some time.
Symptomatic therapy
Prescribed depending on the symptoms present. For fear, anxiety, aggressiveness, sleep disturbances, and depression, various tranquilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants are prescribed, taking into account an individual approach to each patient.
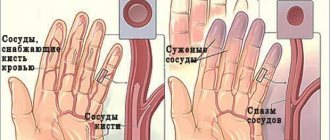
Neuroprotective therapy (Cerebrolysin, Sermion, Ginkgo biloba) can increase the viability, stability and plasticity of neuronal cells. Vasoactive drugs are also used to improve cerebral circulation, anti-inflammatory and hormonal agents.
Folk remedies to help cope with Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease is one of the most common forms of dementia, an incurable disease of the nervous system, which is accompanied by a gradual loss of cognitive abilities (memory, speech, logical thinking) and subsequent death. The risk of developing the disease increases significantly after 65 years of age, and the average life expectancy after diagnosis is 7–14 years.
The causes of the development of the disease have not been sufficiently studied to date; It is believed that the key factors are genetic predisposition, destructive changes in a large number of nerve cells, metal poisoning, trauma, and brain tumors. There is no effective cure for Alzheimer's disease.
Measures for the prevention and conservative treatment of the disease include maintaining an active lifestyle, intellectual exercises, and diets. Traditional medicine also offers a number of methods for preventing and combating diseases of the central nervous system.
Promising therapies
Considering that today there is not a single treatment method that would slow down or stop the progression of AD, it is absolutely understandable that the brightest minds in medicine are looking for the treasured cure. The following developments can be considered promising.
Alzheimer's vaccine
Unlike conventional vaccines, it is not aimed at preventing a disease, but at fighting an existing one. The vaccine, when introduced into the body, causes the human immune system to produce antibodies to beta-amyloid (the morphological substrate of AD). As a result, deposits of this pathological protein are reduced, and the disease slows down its development.

Professional care for patients can significantly improve their quality of life
MDA7 drug
The drug was developed to treat neuropathic pain, but was found in a study to slow the progression of Alzheimer's-type dementia. Its action is based on an anti-inflammatory effect in the central nervous system, which is associated with an effect on cannabinoid receptors in the brain.
Rosiglitazone
This is a medicine for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. It has been shown to improve memory and learning in animal studies, but these findings need to be confirmed in humans.
Insulin
Insulin demer is a modern recombinant insulin, which has recently been increasingly used for the control and treatment of diabetes mellitus. A recent study revealed its positive effect in patients with asthma. The drug was administered in the form of a nasal spray to facilitate penetration into the brain through the blood-brain barrier. After some time, the patients' cognitive abilities improved.
Recommended Diet

People over 65 years of age should pay special attention to the quality and variety of their diet. You can prevent many ailments by eating seafood more often, in particular fatty fish, without disdaining vegetables (tomatoes, onions, broccoli, garlic, spinach, carrots) and other plant products (kiwi, oranges, lemons, currants, melon) .
General principles of herbal therapy
As a rule, all methods that can maintain the functional state of the nervous system and stimulate its tone are relevant in the treatment of this disease. Thus, to combat the extinction of thought processes, herbs of the buttercup and barberry families are widely used; In the fight against dementia, hawthorn has proven itself to be excellent, especially in infusions . Immunomodulators will also be useful for Alzheimer's disease: for example, Eleutherococcus, Leuzea, arnica.
Herbal tonics to combat illness
It is not difficult to prepare an infusion based on hawthorn . Take the flowers of the plant and mix them with a glass of hot water. Let the product sit for half an hour and take it three times a day. Among other things, this infusion normalizes blood pressure.

Ginseng root is an excellent remedy for Alzheimer's disease.
An excellent remedy for Alzheimer's disease is ginseng . Take the root of the plant and mix it with lemongrass fruits in equal proportions. Pour about 10 g of this mixture into 1 liter. hot water and put on fire. After a quarter of an hour, the drug can be taken in small sips throughout the day.

Withania root is an excellent remedy for Alzheimer's disease
Or use withania root . Mix about 10 g of root with 300 ml. hot water and boil. After 10 minutes, you can drink the entire decoction, then repeat the procedure throughout the day.

Black and green tea helps with Alzheimer's disease
One of the most well-known remedies for this disease is simple black or green tea . It should be quite concentrated: 1 teaspoon of loose leaf tea per small cup. Drink this cup daily on an empty stomach.

Motherwort helps in the fight against dementia
Motherwort can also provide invaluable assistance in the fight against dementia . Use a tincture based on this plant for regular internal use.
Aralia and Echinacea are also good tonics.
Alzheimer's disease ranks among the diseases that impose the most significant burden on the public. Costs include dementia care, lost productivity, and direct medical expenses.
“Not out of anger, but out of pity”

— Loved ones caring for an elderly person with dementia may lose patience and be rude to the patient.
- We are all humans. You cannot remain in a blissful state all the time. You are a relative, you care. I yelled, lost my temper, and then it’s very hard to get over it. But you can do something nice for an elderly person.
It’s useless to reproach yourself; it’s better to think differently: “Yes, I’m to blame. But now I’ll bake pancakes with my mother and give her pleasure.”
If mom has Alzheimer's disease, she will forget the fact of the quarrel, but will feel unhappy without understanding why. Kind words can fix this.
Of course, in Russia it is difficult for the relatives of such patients for objective reasons. There are not enough qualified doctors and services to help with patient care. But the situation is gradually changing.
Experts from the Ministry of Health have developed an Anti-Dementia Action Plan, which has already begun to be implemented. (According to this plan, by 2025, every clinic should have a room for memory disorders, operating under compulsory medical insurance - editor's note.) A long-term care program has been launched in pilot regions.
We always tell our relatives: don’t carry this burden alone. Gather a family council, share responsibility and care. Consider accommodation options in a boarding house, if you have the financial opportunity.
— Relatives of such patients are often visited by thoughts like “he would rather die.” This is scary to read.
- Yes, on the forums many people write: “I wish he would die.” But when a loved one with dementia passes away, they still feel sad and sad, they write about it, and other people sympathize with them and support them.
Many relatives think this way because it hurts them to see how a loved one - mom or dad - suffers, and they cannot help. This is not out of anger, but out of pity and hopelessness. They perceive death as relief from suffering. Some then write: “Finally, my mommy is out of her misery.”
Getting rid of headaches and fainting
Often the course of this disease is accompanied by severe headaches in patients. In this case, Veronica officinalis, astragalus, and periwinkle will help alleviate discomfort . Mix the crushed ingredients in equal proportions and add hot water. Then let the product brew overnight and use three times a day.
Another drug will save you from losing consciousness. Mix oregano, purslane and lavender in equal proportions and prepare a decoction similar to the previous recipe.
Seizures and acid deficiency in the body: preventive measures
You can cope with cramps and muscular dystrophy in Alzheimer's disease with the help of Echinops (fruit), hemlock and cinquefoil . Prepare a decoction based on these plants and consume them in equal portions throughout the day.

Baths based on dry fern leaves are quite helpful for cramps and dystrophy.
Baths based on dry fern leaves also help a lot with cramps and dystrophy..

A medicine based on spruce branches replenishes acid deficiency
The onset of old age is also characterized by a deficiency of acids necessary for the body to maintain effective functioning. A drug based on spruce branches will help fill the gaps . Chop the branches and place them in a 3-liter jar, fill with the required amount of spring water. Then add a third of a glass of sugar and a teaspoon of sour cream. Leave the container in a dark place to infuse. The product will be ready in 3 weeks.
Alzheimer's disease, treatment with folk remedies

Alzheimer's disease is a neurodegenerative disease and the most common form of dementia. It appeared back in 1907, the first person to diagnose the disease was Alois Alzheimer, a famous German psychiatrist, after whom the disease was named.
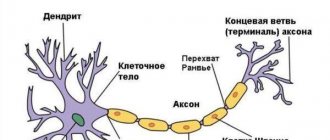
This disease occurs due to the death of brain neurons, which leads to so-called dementia.
A disease such as Alzheimer's disease manifests itself in old age after 65 years, but the first signs can begin to appear as early as forty. The largest risk area for morbidity is the female population.
To date, the disease is considered incurable; a drug has not yet been created that can cure the patient.
The average lifespan with Alzheimer's disease is about seven years.
Causes of the disease
There are a number of reasons that may lead to serious illness. Several hypotheses have been put forward, here are the most basic:
- Cholinergic hypothesis, which implies the occurrence due to a decrease in the synthesis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This was the earliest version of its occurrence; in the modern world it is already considered that this assumption is unlikely.
- The amyloid hypothesis, following this statement, assumed that it was deposits of beta-amyloid. The gene, which encodes a protein located on chromosome 21, forms beta-amyloid. Due to accumulation, ameloid plaques are formed, which contribute to the death of brain cells, but this hypothesis has a number of inconsistent conclusions.
- The Tau hypothesis states that the formation of neurofibrillary tangles occurs inside cells due to the “tangling of threads” of the tau protein.
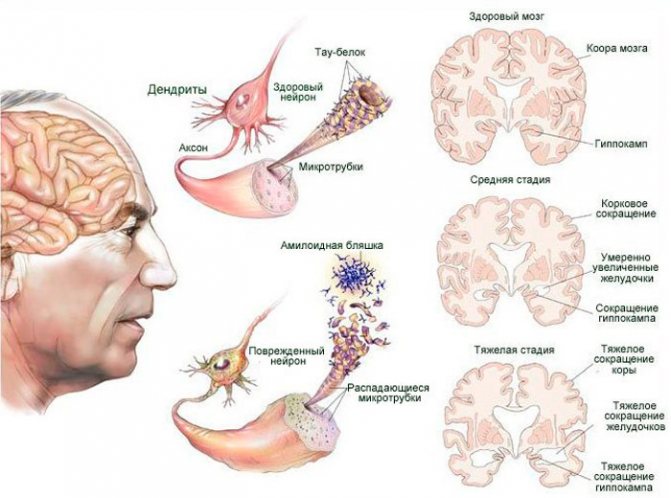
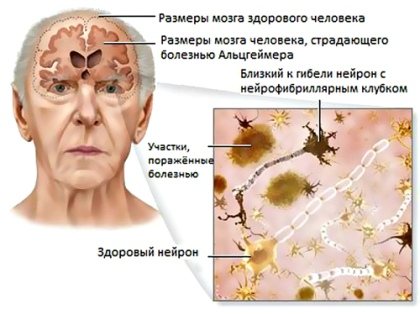
Causes of Alzheimer's disease
The progression of the disease is completely unknown
The cause is often a genetic predisposition. It happens that the disease becomes familial, and Alzheimer's disease is passed on from generation to generation.
Symptoms of the disease
This disease is recognized by the following symptoms:
- Memory impairment appears, which intensifies, short-term and complete memory loss occurs;
- Difficulties in arithmetic operations, counting money, calculating simple addition or other operations related to numbers;
- Problems with quickly making any decisions;
- Loss of ability to write and read;
- Manifestation of paranoia and depression;
- The occurrence of hallucinations;
- Loss of the ability to recognize family and friends;
- Problems with the toilet, often incontinence;
- Inability to self-care.

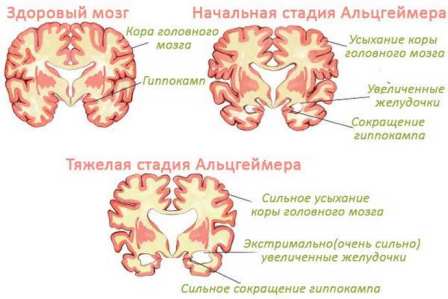
Symptoms of the stages of Alzheimer's disease
Diagnosis of the disease
If one of the symptoms listed above occurs, you should consult a doctor, these are neurologists and psychiatrists. Specialists study the history of the disease, anamnesis, and ask leading questions to find out the full picture of the disease.
This is all due to the fact that Alzheimer's disease manifests itself in everyone with its own characteristics. Specially designed computer tests are also used for diagnosis.
There are a number of additional methods that confirm the diagnosis.
- Computed tomography of the brain;
- Dopplerography;
- A puncture is taken from the human spinal cord (to determine protein levels);
- Generalized chemical blood test.
At the end of the research process, the doctor draws up a complete picture of the disease. After determining the stage of the existing disease, the necessary course of treatment is prescribed.
Choice of treatment method
There are a number of drugs that can significantly slow down the expansion of the disease, or alleviate the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Drug treatment can be divided into groups:
- Drugs whose action is aimed at improving memory and helping to improve the thinking process often use rivostigmine-containing medications.
- Drugs whose work is aimed at combating a psychological state, namely apathy, excessive anxiety, nervousness, depression.
All medications require strict prescription by the attending physician; self-medication can only make things much worse.
Folk remedies
In the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, you can additionally resort to traditional medicine, but you should consult a doctor so as not to cause harm. It is worth considering that the main thing is not to overdo it with folk remedies.

Such drugs have a direct enhancement of the effect of the medications taken and maintain the patient’s physical and psychological condition at a sufficient level.
Traditional treatments include not only herbal decoctions that promote treatment, but also a proper diet, physical exercise and methods that activate brain activity.
Herbal recipes, tinctures
In folk remedies for treating Alzheimer's disease, the following are often used:
- Soy lecithin, you need to take 2-3 g daily.
- An infusion of ginseng root, to prepare it you need to take 4-5 g of grated root, add five lemongrass berries, add one liter of water and boil for 15 minutes, drink cooled, like tea.
- You can make motherwort tincture at home yourself by infusing motherwort in vodka, or you can also buy it ready-made at pharmacies.
Diet
The patient should eat high-quality food, which is filled with vegetable fats; the diet must include fish, fruits, and vegetables. Tomatoes, onions, garlic, black currants, and oranges are considered some of the healthiest.

Healthy Diet
A very important point is the presence of antioxidants in foods, and these are: carrots, legumes, cabbage, dried fruits. To fully stimulate the nerves, it is recommended to drink strong teas.
Gymnastics
When you are sick, you need to do breathing exercises; yoga classes are perfect. If a person is already very elderly, then it is necessary to take daily walks in the fresh air, possibly with short breaks.
Mental stress
When diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease, it is necessary to strain your mental abilities, solve crosswords, read books, and learn works by heart.

These actions will contribute to mental stress.
Video: Alzheimer's disease
Conclusion
Alzheimer's disease and its treatment is a rather difficult moment, this disease is fatal, you should treat your nervous system with caution, and if symptoms occur, seek help from specialists as soon as possible.
Symptoms of Alzheimer's disease
Here is a list of the 10 most common symptoms of Alzheimer's disease:
- A memory disorder that interferes with everyday functions - forgetting important dates, first names, surnames, repeating the same questions, when the patient relies on close people in matters that he previously handled himself, etc.
- Impaired planning and solving problems related, for example, to maintaining a household budget, difficulty completing tasks according to instructions, etc.
- Difficulties in performing everyday tasks at home, at work, during leisure; problems performing activities that previously did not cause problems, such as driving a car, cooking, running a home, engaging in hobbies, etc.
- Disorders of orientation to place and time - patients may have difficulty distinguishing the time of day, year and awareness of the passage of time, they may forget where they are and how they got there.
- Visual disorders (visuospatial disorders) - there are problems with reading, judging distances, distinguishing colors, etc. When passing by a mirror, patients may feel that they see a stranger in it.
- Difficulty speaking and writing - problems participating in conversation, stopping in the middle of a dialogue, repeating the same questions, difficulty finding words, etc.
- Losing and hiding things in strange places, being unable to find them.
- Lack of ability to correctly assess a situation, manifested in gullibility (which can be exploited by third parties) or indifference to their own appearance and cleanliness.
- Avoidance of work, social contacts, hobbies.
- Mood disorders and personality changes—Patients may feel anxious, confused, fearful, or sad in places they previously felt comfortable. They may also become more suspicious.
If you experience at least 2 of the 10 symptoms described above, you should consult a psychiatrist or neurologist.
Initial phase of the disease
The onset of Alzheimer's disease is primarily a memory impairment. At an early stage, its loss may be perceived or recognized as simple forgetfulness. Gradually, the problem becomes a lack of control over the household budget or the ability to follow instructions, for example, at work or while driving a car.
Changes in the environment may cause confusion, and the patient becomes lost while walking or driving.
Development of Alzheimer's disease
Over time, the patient becomes unable to work, becomes easily lost and confused, and begins to require daily care. He may be distinguished by good behavior and manners, and carry on a superficial conversation, although he has problems with speech and the correct choice of words.
Decreased visuospatial abilities begin to interfere with dressing, eating, or solving simple puzzles. Patients may lose the ability to perform basic calculations or check the time.
In the later stages of the disease, people can still walk, but they usually wander aimlessly. Inevitably there is a loss of correct judgment, prudence and acceptance of new information.
A common problem is illusions. The patient begins to claim that he is being robbed, that his spouse is cheating on him, or that the people closest to him are not who they think they are.
Changes also affect mood. The daily rhythm of activity is easily disrupted. Night wandering often causes injury to patients and anxiety to household members. Some patients begin to move slowly, shuffling their legs, with obvious clumsiness in their movements.
Final stage of the disease
At the final stage of the disease, patients are bedridden, do not interact, and do not communicate physiological needs. They need help with all activities related to eating, clothing or toileting. The typical duration of the disease from the onset of symptoms is about 10 years.