Psychomotor agitation is a pathological condition that manifests itself in increased mental and motor activity of varying degrees of severity. This syndrome is expressed by anxiety, anger, confusion, aggressiveness or, conversely, excessive fun and other inappropriate behavior.
Psychomotor agitation can last from a few minutes to a whole week. It all depends on the clinical manifestations of the underlying disease, since usually this syndrome is a symptom of other, more complex psychopathic syndromes. But, whatever the underlying disease, the symptoms of excitement are basically the same:
- unexpected exacerbation of the disease;
- inadequacy manifested in movements;
- change in the emotional state of the patient;
- aggression aimed at both defense and attack (may have suicidal overtones).
Such patients pose a danger not only to others due to aggressive behavior, but also to themselves, therefore the manifestations of symptoms of psychomotor agitation require urgent emergency care.
Causes of the disorder
Psychomotor agitation syndrome in its classical form does not manifest itself in psychopathologically examined, healthy individuals. The factor in its appearance is a special mental readiness for mental agitation.
Almost any psychiatric pathology can cause psychomotor agitation with different underlying causes. Major psychiatric disorders are common causes. It is very often formed during moments of hallucinatory experiences and delusional formation. This condition is very typical in schizophrenia and similar pathologies. A subtype of schizophrenia affects psychomotor agitation, it can be different: paranoid, catatonic or hebephrenic. Any of these are symptomatic of schizophrenia.
Often, such a psychomotor state can also form during neurotic conditions; the development of excitement directly correlates with the level of anxiety and the neurotic component. In reactive stress conditions, after experiencing something seriously traumatic, it can form. Formation is often triggered by injury, some terrible event or accident.
Psychomotor agitation syndrome can occur due to certain somatic pathologies. This is a very common companion to myocardial infarction. This disorder is likely to form during prolonged infectious diseases, the most dangerous for this is their acute period. Intoxication pathologies lead to pronounced psychomotor agitation; pathologies involving the nervous system are the most predictive of this.
It can also form during traumatic brain injury. Moreover, at any stage of progression of TBI, everything depends on the correctness of relief. And even after a long time, such a person is much more irritable than her healthy peers.
In addition, epileptic states are also characterized by psychomotor agitation, especially delirious epileptic stupefaction and a state of twilight clouding of the psyche. Various automatisms and some auras in epilepsy can also be accompanied by psychomotor agitation.
A state of psychomotor agitation can form during intoxication due to drug addiction or alcohol abuse. Often this condition also forms during the period of abstinence, and becomes especially pronounced at the time of delirium tremens, that is, alcoholic delirium. In general, among states of clouding of consciousness, delirium is the most dangerous in terms of manifestations of psychomotor agitation. Delirium of this etiology can last quite a long time, which further increases the risk of psychomotor agitation.
Hysterical neuroses are often manifested by such excitement. Chronic delirium that turns into a disorder can also be the root cause. Psychomotor agitation may occur in individuals with mania, especially in severe manic states. In general, with the appearance of various types of depressive states, psychomotor agitation in a state of agitation is also possible.
The syndrome of psychomotor agitation is also characteristic of borderline states, in particular in a state of mental imbalance. It often occurs with a type of personality disorder, especially in hot-tempered personality types.
Causes
Psychomotor agitation can be caused for various reasons depending on the patient's case. The main reasons include:
- Reaction to stress. In extreme situations (for example, after life-threatening situations), mentally healthy people may experience reactive psychosis, which is expressed in motor restlessness of varying degrees of intensity and can abruptly give way to stupor.
- Exacerbation of infectious diseases with intoxication of the central nervous system.
- Various types of brain damage.
- Epilepsy. Occurs during twilight disorder of consciousness and is characterized by suddenness, aggressiveness and destructiveness. Such patients are extremely dangerous to others, and therefore require emergency assistance at the first manifestation of symptoms.
- Intoxication, acute or chronic (for example, alcohol).
- Delirium or confusion with the occurrence of hallucinations, imaginative delusions and feelings of fear.
- Brain damage in comatose states.
- Hysteria, which occurs as a reaction to a certain irritating factor. It manifests itself in aggressiveness and anger towards specific individuals against whom the patient holds a grudge. Such patients often try to attract attention to themselves by their behavior, screams and evoke sympathy from others.
- Mental illnesses: depressive psychosis, mania, schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Whatever the cause of psychomotor agitation, the patient needs emergency help at the first symptoms.
Symptoms and signs of psychomotor agitation
This condition has fairly classic symptoms, but it depends on the pathology that provoked it. Classically, this condition is perceived as aggressive and uncontrollable. But often psychomotor agitation is a state of activity without interspersed irritability and aggressiveness. Naturally, this is a very serious condition, which is easily detected symptomatically and can be diagnosed and treated.
Depending on the root cause, this condition may have different components, so-called side symptoms. Algorithms of psychomotor states are always characterized by the severity of the course, that is, its development is sudden and rapidly progressing. Although it is also possible that symptoms reach a certain level and remain stable.
Psychomotor agitation syndrome may be accompanied by hallucinations. Usually these are frightening hallucinations from which the patient runs away or attacks. In addition, there may be visceral hallucinations and paresthesias, in which the individual experiences unpleasant, painful, frightening states that allegedly occur to his body internally or externally.
The state of psychomotor agitation can manifest itself as delusions, which have paranoid tendencies, and also delusions of jealousy. With psychomotor agitation, consciousness is often impaired, which has even more life-threatening consequences.
The main sign of psychomotor agitation is classically considered to be increased mental activity, with the rate of speech progressively increasing. Sometimes this speed can increase to a state of racing ideas, when the patient finds it difficult to maintain the structure of thought. Such symptoms are most characteristic of mania and manifest themselves under the influence of bipolar disorder. In addition, there is always motor excitement with high activity in terms of activity and a low level of fatigue, often in combination with insomnia and high appetite.
But it is not often that there is such acceleration of mental and active processes with a large number of ideas. In many conditions with psychomotor agitation, mental stupor and primitivism are observed. In epilepsy with personality changes, twilight states very often manifest themselves as delirium with terrifying scenes of disasters and trials. For the individual this is very frightening, and he tries to protect himself from it. A very frightening psychomotor agitation in an alcoholic with delirium, which develops due to withdrawal syndrome, he experiences greater aggressiveness and expressive vegetative symptoms.
Very often, in addition to mental speed and aggressiveness, fragmentation can be observed. This is most typical for schizophrenic psychomotor agitation. Hebephrenic is usually characterized by the presence of foolishness, and catatonic is characterized by active negativism with an aggressive expression of one’s disagreement, which, moreover, can be replaced by psychomotor stupor.
Algorithms of psychomotor agitation are usually characterized by a lack of critical assessment of their condition. At the same time, there is absolutely no critical assessment, and the individual does not quite adequately assess the situation and the circumstances occurring around him.

Symptoms of nervous excitement
Symptoms of nervous excitement are disturbances in the movements of the eyeballs, asymmetry of the facial muscles, poor orientation in time and space, awkwardness and lack of composure. In addition, headaches and a slight delay in intellectual development are noted. Insomnia is a hallmark of increased nervous excitability. Insomnia is determined by a person’s condition if he cannot fall asleep for three to four hours, he tosses around in bed, trying to find a comfortable body position. A person may also wake up in the middle of the night and lie there until the morning with his eyes open. In some cases, insomnia is considered as a symptom of some somatic pathology.
Types of psychomotor agitation
The algorithms for this mental disorder have very classic symptoms, but they are slightly different, which is most influenced by the cause. Each psychopathology with such a manifestation has characteristic symptom complexes, on which psychomotor agitation is superimposed. For the most part, this symptomatology is very characteristic and differs depending on the species.
⇒ Schizophrenic agitation has three characteristic, most common types, although there are more types of schizophrenic disorders.
⇒ Catatonic psychomotor agitation is characteristic of the form of schizophrenia of the same name and manifests itself as expressive aggressiveness with active attempts to resist others and complete failure to comply with any orders. It is impossible to be calm with such individuals, since they can be very dangerous.
⇒ Hebephrenic also occurs in the form of schizophrenia of the same name. The main advantage of its manifestation is the increased foolish mood that prevails most of the time. In this case, there may also be aggressive inclusions.
⇒ Paranoid psychomotor agitation is characteristic of Kandinsky syndrome. It is pathognomonic in paranoid schizophrenia and is characterized by an affect of fear, a high level of anxiety, various kinds of automatisms, and paranoid ideas.
⇒ Hallucinatory psychomotor agitation is characterized by complete self-absorption and complete living of one’s hallucinatory experiences. Often patients perform all the actions that their hallucinations tell them to do. If this is delusional excitement, then it depends on ideas. Sometimes they try to escape from their pursuers, sometimes they actively prove their greatness, and can often be aggressive and behave unnecessarily threatening. Algorithms of psychomotor agitation are also formed during a manic state. When elation becomes apparent with varying cravings for activity and often excessive temperament.
⇒ The state of psychomotor agitation can have completely separate causes and types. Anxious psychomotor agitation may occur, which is manifested by a high degree of anxiety and severe exhaustion, as well as changes in social interaction. At the same time, there may be a desire to move around, and speech is limited to short, quick phrases. If such arousal is in the structure of melancholic raptus, then the individual can harm himself, perform self-harm.
⇒ Dysphoric agitation is a pathology that, in addition to a feeling of psychomotor agitation, is accompanied by a mood of melancholy anger. Dysphoric agitation is the most common companion to epilepsy and is even considered the equivalent of an epileptic seizure. In addition, it sometimes occurs with organic lesions. With epilepsy and/or pathologies with brain damage, there may be epileptiform agitation, with severe disorientation.
⇒ Psychogenic arousal has stress factors that are formed in certain situations that are possible in our fickle world.
⇒ Eretic psychomotor agitation is formed in mental retardation, as uncontrolled excitation caused by a disorder of brain activity.

Causes of nervous excitement
Nervous agitation usually develops if a person is subject to frequent stress, lack of sleep, irritation, nervousness, or suffers from a mental illness. All this can be expressed in frequent conflict situations with other people. Sometimes the cause of the development of increased nervous excitability is not emotional and mental factors, but anxious and suspicious character traits. However, often the first and second reasons are present in combination. A vicious circle develops: lack of sleep – irritation – nervous stress – insomnia.
Cupping and treatment options
This mental disorder is not a safe manifestation of psychiatric symptoms in any case. It necessarily poses a danger either for the individual with psychomotor agitation and/or for the environment. It is a very debilitating phenomenon because it has high and inadequate neurotransmitter activity. This phenomenon is stopped in stationary conditions due to the danger of its manifestations for the environment.
Depending on the root cause that caused psychomotor agitation, the accompanying symptoms and approaches to relief vary. Vivid aggressive symptoms with tendencies towards self-harm or external aggression towards the environment most actively require relief. Sometimes there is even a need to record such patients in an examination ward in acute psychiatric wards.
Sometimes, before treating such agitated patients, it is necessary to first catch and detain them. This is not always an easy task, especially when the patient is carrying dangerous items. This requires qualified assistance from trained personnel. In psychiatry there are a large number of ways to catch such patients. But if such an incident with a violent individual occurred outside the walls of a psychiatric hospital, then the most correct and deliberate step would be to call the police, since a doctor should never risk his life so recklessly.
In the relief of psychomotor agitation, it makes sense to talk about the drugs that are used, depending on the underlying pathology that provoked it. For schizophrenia, antipsychotics are used: Rispolept, Soleron, Quetiapine, Solex, Rispaxol. In addition, it is necessary to use correctors to prevent stiffness: Cyclodol, Calcium gluconate. Supportive psychotherapeutic groups can also be used.
In bipolar disorder, excitation can manifest itself in both phases, which greatly influences the selection of the drug. Thymostabilizers are used stably: Valprocom, Depakin, Litosan, lithium carbonate, Lamotrigine.
For depression, it is necessary to use antidepressants: Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Amitriptyline, Miaser, Imipramine.
Antipsychotics are also used for mania: Ziprasidone, Aripiprazole, Sertindole, Olanzapine, Zyprexa.
For epilepsy, it is necessary to use antiepileptic drugs, and on a regular basis; they also have normotimic properties: Valprocom, Carbamazepine, Depakine.
In case of psychotrauma, the effects of tranquilizing therapy are sufficient: Gidazepam, Phenazepam, Lorazepam, Midazepam, Nozepam. In addition, mandatory psychotherapy is subsequently indicated to help overcome this condition and prevent consequences and neurotic pathologies.
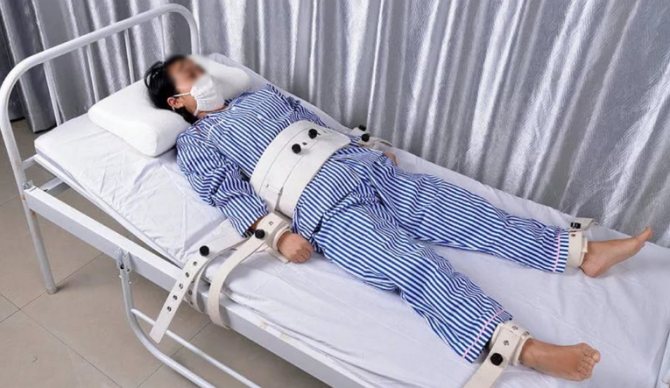
Treatment of nervous excitement
The most important way to deal with nervous agitation or causeless anxiety is to find and treat the cause. Without treatment, this nervous agitation leads to an increased risk of suicide. The following measures will help reduce anxiety:
- Calm environment
- Sufficient lighting
- Medicines such as benzodiazepines and, in some cases, antipsychotics
- Full, quality sleep
- Exercise stress
- A change in familiarity or surroundings, such as a short vacation
- Hobbies and interests
Don't focus too much on your anxiety if possible. This usually makes the problem worse. If your loved one is at risk of harming themselves or others due to nervousness or anxiety, and there are no other less restrictive ways to control their behavior, use only firm boundaries.