Cephalgic syndrome or, in other words, headache is a special pathological condition, which, despite its simplicity, can significantly reduce the comfort of a person’s life, and also serve as a clear symptom of more serious diseases. Correct diagnosis and timely treatment of cephalalgia, especially in children, is a rather difficult task, but absolutely necessary. Recently, in our society, due to numerous lifestyle disorders, cephalgic syndrome is actively gaining momentum and occurs quite often. Therefore, it is worth paying special attention to the standard rules that serve as the key to good good health.
Types of cephalgic syndrome
Cephalgia is mainly observed in people who suffer from chronic fatigue. But we should not discount more serious diseases, the symptoms of which are headaches. Currently, cephalalgia syndrome has a specific classification.
The division into groups is made based on the location of the pain and the causes contributing to it.
Thus, headaches can be of the following types:
- Vascular headache. Occurs when blood vessels overflow or are overstretched. Pain sensations can be rhythmic or pulsating.
- Cephalgia of muscle tension. Basically, this is a monotonous pain sensation in which there are sensations of squeezing, tightening or squeezing.
- Liquorodynamic headache. It is observed with increased intracranial pressure. At the same time, bursting pain is felt.
- Infectious-toxic pain. The cause of this type of syndrome is mainly a decrease in immunity and the introduction of harmful microorganisms into the human body.
- Neuralgic headache. It is expressed in the form of short-term attacks, which are preceded by some events: washing, swallowing, shaving and others.
Cephalgia mainly develops due to circulatory disorders in the brain tissue. Painful sensations occur when the lumen of the vessel expands, followed by a change in blood pressure. Also, spasm can cause discomfort.
Classification
Based on the nature of the etiological picture, the following forms of this syndrome are distinguished:
- vasomotor cephalgia or tension cephalgia - occurs due to muscle strain, accompanied by aching pain in the back of the head;
- vascular cephalgia - formed when blood vessels overflow, which leads to their increased tension;
- infectious-toxic – formed as a consequence of a decrease in the immune system, which leads to a deterioration in general well-being;
- liquorodynamic – present when intracranial pressure increases;
- post-traumatic cephalgia - occurs as a result of a head blow, concussion and other type of head injury;
- coital cephalgia - occurs after sexual intercourse;
- histamine cephalgia or Horton's syndrome - occurs during allergic reactions;
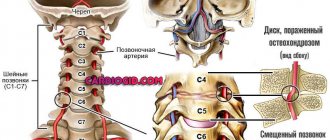
- vertebrogenic headache – caused by pathological processes in the cervical spine;
- Abuse cephalgia - a headache of this nature occurs against the background of prolonged or uncontrolled use of medications.
Trigeminal autonomic cephalgia, which combines the symptoms of neuralgia and is often positioned as chronic, is considered separately.
Based on the nature of the manifestation of the syndrome, the following types are distinguished:
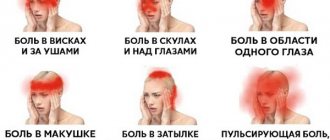
- cluster cephalgia – pain in the eye area, which can radiate to the temporal region;
- migraine cephalgia - unbearable pain, which is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, photophobia;
- short-term unilateral headache;
- pain in the frontotemporal region;
- pain in temples;
- in the back of the head;
- of a total nature.
Often, the nature of the manifestation of pain suggests the cause of their occurrence, but this can only be accurately diagnosed through an instrumental examination. Laboratory diagnostics in this case is often of an auxiliary nature.
Etiology of the origin of pain syndrome
The brain and surrounding tissues react quite sensitively to many changes occurring in the human body. Many people wonder why this particular area is so sensitive.
This is due to the presence of a large number of pain receptors in this area of the body. It is inside the skull that the dura mater and its minuses, meningeal arteries, large arterial vessels, cervical spinal roots and intracranial nerves are located.
In addition, external receptors are also responsible for the perception of pain: arteries, aponeuroses, middle ear, tendons, skin, etc.
Headache can occur as a result of any pathology that actively affects the receptors and mechanisms that trigger the development of the disease. Most often, pain in the head is the only sign of a disease; in more rare cases, it occurs with other symptoms.
That is why it is very important to determine what kind of pain a person has: throbbing, squeezing, squeezing, sharp, dull or bursting.
Causes of cephalgic syndrome
Taking into account that cephalalgia of the brain is a secondary syndrome that is quite common, it is impossible to determine the causes independently. In this case, it is imperative to consult a specialist in order to stop the development of the disease causing headaches as early as possible.
Today, there are many known diseases that are accompanied by pain in the brain.
Among such pathologies are infectious, oncological, bad habits, failure of the daily routine, inflammatory diseases and biochemical metabolic disorders. In children, the main reason is the incorrect daily routine.
Since there are many causes, diagnosing the disease is very difficult. Therefore, it is often impossible to say why a headache occurs.
Sometimes cephalalgia can be caused by several pathologies at once. The lifeline in this matter is related symptoms, which often appear a little later.
Basically, pain is caused by several factors:
- leading an unhealthy lifestyle;
- hereditary factor;
- neuralgic and vascular diseases.
According to the latest research data, we can conclude that the hereditary factor plays a very important role in the occurrence of pain in the brain. This is especially reflected in the state of a child’s fragile body.
Often, the reasons for the development of cephalgic syndrome are:
- bad habits;
- passive lifestyle;
- circadian rhythm disorder;
- starvation;
- lack of fresh air;
- long periods of time in front of the computer.
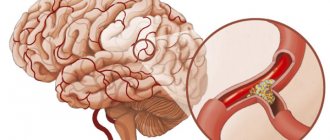
In addition, vascular dysfunction may contribute to the occurrence of headaches. In some cases, this pathology can cause a stroke.
It is important to remember that cephalgia is a sign of the development of quite dangerous disorders that can be fatal.
Reasons provoking the crisis
- People with VSD are susceptible to seasonal changes. If a healthy person notices autumn because it has become cool, and the leaves have turned yellow and begun to fall (the change of season does not affect their well-being), then a person with VSD will experience an autumn exacerbation caused by a change in landscape and mood.
Exacerbations may also include:
- summer;
- spring;
- winter.
- A crisis can be triggered by a change in the usual way of life: a sharp change in daily routine, climate or time zone. And this happens when you are called up for military service.
- Exacerbation of sluggish chronic diseases.
- Unusual physical activity will contribute to the onset of a crisis. And her army guarantees.
- A crisis cannot be avoided due to psycho-emotional overload. In the military community, recruits are susceptible to it. Hazing alone is worth it.
Cephalgic syndrome (Cephalgia)
Cephalgic syndrome or, in other words, headache is a special pathological condition, which, despite its simplicity, can significantly reduce the comfort of a person’s life, and also serve as a clear symptom of more serious diseases. Correct diagnosis and timely treatment of cephalalgia, especially in children, is a rather difficult task, but absolutely necessary. Recently, in our society, due to numerous lifestyle disorders, cephalgic syndrome is actively gaining momentum and occurs quite often. Therefore, it is worth paying special attention to the standard rules that serve as the key to good good health.
VSD and the army
There is an old joke that any problem can be solved in three ways - right, wrong and like in the army. Therefore, any military doctor will answer the question “Do they take guys with vegetative-vascular dystonia into the army?” without a moment’s hesitation and answer in the affirmative. Because I am sure that vegetative-vascular dystonia is a whim of spoiled mummy’s boys, and the army is the best place to get rid of the whim. In addition, there is a plan for conscription.
Therefore, they are recruited into the army even in cases where VSD is supplemented by diseases such as compensated hydrocephalus, cephalgic syndrome (frequent headaches caused by vasospasm), etc. Such cases have been recorded in practice.
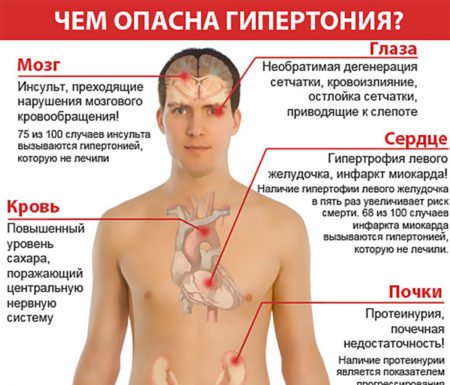
Consequences of hypertension
How headaches of different etiologies manifest themselves
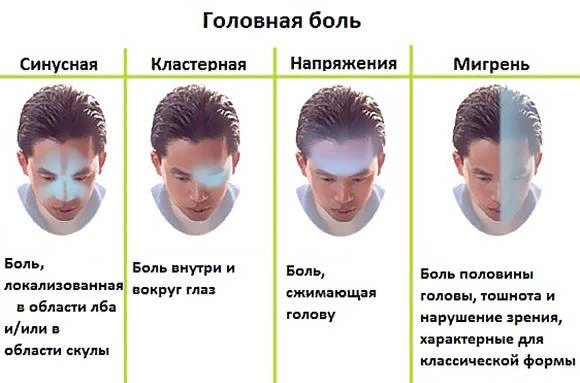
Very often a person complains of a headache that occurs immediately after opening his eyes. In this case, other symptoms are observed that confirm the fact of vascular headache:
- vasodilation and redness of capillaries;
- redness of the throat and nasal congestion;
- swelling and heaviness of the lower eyelids;
- changes in blood pressure;
- cerebral vascular edema;
- arterial spasm.
Muscle tension headaches may include the following symptoms:
- feeling of pressure or squeezing of the head;
- irritation from bright light or loud music is less common;
- weakness or moderate headache.
Signs of the liquorodynamic type of cephalgia are:
- severe arching pain that intensifies during movement, subject to increased intracranial pressure;
- often throbbing pain due to low intracranial pressure.
Infectious-toxic headache often manifests itself along with other symptoms:
- vomit;
- weakness;
- sharp, and then continuous headache (gradually fades and resumes again);
- pain in the muscles;
- irritation from loud music and bright lights;
- feverish condition.
With neuralgic headaches the following are observed:
- short-term pain sensations, following one after another with short breaks;
- pain sensations are cutting, burning and piercing in nature;
- any movements of the head provoke a headache (swallowing, chewing, touching, etc.).
Diagnostics and first aid
The diagnosis of cephalalgia is based on the analysis of the patient’s complaints. As already mentioned, headache is a symptom of a developing disease, so before treatment, a specialist identifies ongoing pathologies.
As a result of diagnostics, which involves laboratory tests and examination, the causes are identified and methods for eliminating them are selected. The most common disease that causes headaches is pathology of the cervical spine.
To reduce the risk of developing other diseases, a specialist must examine the neck and head for injuries. Internal organs are examined to prevent the development of acute processes.
First aid for a headache is provided only when its type is identified.
Thus, if pain is the result of stress or fatigue, then it is necessary to eliminate the factors influencing the causes. Often this is a bright light. And, of course, do not forget about healthy sleep, which often relieves cephalalgia syndrome.
Also a good remedy is a contrast shower and massage of the neck-collar area.
If it is not possible to take water procedures, you can wash your face, alternating warm water with cold.
The drug should be taken as a last resort, when the headache is truly unbearable. No-shpa, Combispasm, Spasmalgon and others are great for this.
If the headache does not go away within 12 hours and the symptoms worsen, you should seek help from a specialist. Nausea and photophobia may occur.
Principles of proper nutrition for osteochondrosis
Here are the principles that it is advisable to follow so that osteochondrosis and pain do not progress:
- Meals should be small, frequent, and the portion should be small.
- Food should not be high in calories, because weight gain increases the load on the joints.
- It is necessary to limit table salt, parsley and spinach. Spinach contains calcium oxalate crystals, which can deposit in joints.
- Eating aspic, jellies, mousses, and jellied fish can help restore joint tissue no worse than expensive imported drugs.
- Increasing the consumption of clean water prevents dehydration and fragility of the intervertebral discs.
There is no “special”, let alone expensive, diet for osteochondrosis.
How to get rid of pain
The main method of treating cephalalgia is taking analgesics and hormonal drugs. Often, you can eliminate pain yourself with the help of cold wet compresses, brewed herbs and hot foot baths. Such methods help with circulatory disorders.
If the cause of the headache is vegetative-vascular dystonia, the use of sedatives and stimulants is common. Additionally, physical therapy, replenishing the body with vitamins and baths are recommended.
If you experience a muscle headache, which is quite common with sinusitis, neurosis, osteochondrosis and other diseases, you will need medication, massage, manual therapy and gymnastics. The use of diuretics is encouraged.
The symptoms of neuralgic headache are eliminated by analgesics, but there are cases when they remain inactive. If this happens, you should resort to sedatives: physiotherapy and novocaine blockade.
If cephalgia is caused by long-term use of medications, you should stop the course of treatment or replace the provoking drug with another. Basically, such measures help get rid of headaches.
In children, treatment is carried out according to several principles: treatment during the interictal period and its relief. At the same time, all factors that can provoke cephalalgia are removed from the child’s environment. In this case, it is mandatory to use all preventive measures.
If a child experiences attacks of pain quite often, drug treatment will be required. Experts recommend taking painkillers only when there is an increased level of discomfort.
Treatment of a child begins with the choice of drugs, and in fact there are not as many of them as for the recovery of the older generation. Therefore, during the treatment period, analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and combination drugs containing caffeine are used.
If headache attacks are moderate or intense, it is recommended to take Paracetamol no more than 15 mg/kg. Phenacetin, Ibuprofen and Naproxen are also effective.
Symptoms
The disease has sufficiently accurately described symptoms to distinguish it from other headaches:
- The type of pain is paroxysmal, throbbing, of moderate or severe intensity, unilateral (bilateral migraine exists, but is a very rare disease), covering the temple, forehead or eye areas. When there is physical activity, noise, bright light, or tilting the head, the pain becomes more intense.
- The duration of the attack is from 4 hours to 3 days.
- Frequency – from several times a month to several times a year. The diagnosis of migraine is made when there are five similar attacks.
- Associated conditions are nausea and vomiting, which do not bring relief.
- The presence of identified factors provoking an attack.
- The condition after the attack is physical exhaustion, weakness, apathy.
All migraine attacks are divided into two large groups: general migraine and classic migraine.
General migraine
It is observed in 70% of people suffering from this type of headache. The attack occurs suddenly and has classic symptoms. This type of migraine is also called migraine without aura.
Classic migraine
Another name for the disease is migraine with aura. Aura is a specific condition that occurs in a person before a migraine attack and is its precursor. The duration of the aura manifestation takes from 5 to 60 minutes and can have the following types:
- visual aura - manifests itself in the appearance in the field of vision of one eye of bright flashes, lightning, snakes, glare, objects can change their shape;
- unilateral numbness of the limbs;
- hemiplegic aura - right or left limbs stop moving.
Migraine with aura has several varieties:
- basilar form - tinnitus and dizziness occur, sometimes fainting occurs, problems begin to appear in the external and internal areas of the visual field;
- vegetative form – panic attacks, fear, trembling, weakness appear, breathing and heart rate increase;
- migraine with aura without pain is a special type of migraine, characteristic of older people, in which after all the manifestations of the aura there is no pain, but slight dizziness is possible.
In terms of time, the aura can be prolonged, if it lasts more than an hour, have an acute onset, when all its manifestations take about 4-5 minutes, or normal.
It is very important that all manifestations of the aura completely disappear when the headache attacks end, that is, this phenomenon is reversible.
Preventive actions
The state of a person’s health directly depends on the lifestyle he leads. That is why, in order to minimize attacks of pain, you should adhere to certain rules:
- you need to make sports a part of your life and be in the fresh air as much as possible;
- rest and relax more;
- avoid stressful and conflict situations;
- always watch your posture;
- do not disturb sleep patterns (duration 6-8 hours);
- use an orthopedic pillow and mattress;
- be sure to adhere to proper nutrition;
- to refuse from bad habits.