What it is
Exploding head syndrome is a rare sleep disorder in which a person experiences a loud noise in the ears while resting at night or when trying to sleep.
This pathology was first described by a specialist in the 19th century. Only in 2005 it was officially included in the list of diseases associated with sleep disorder.
There are many reasons for the development of the symptom; careful diagnosis is necessary for proper treatment.
Pain like lightning
Flashes of pain in the head not only bring severe suffering during their occurrence, but also burden the “painless period” with a depressing premonition of the development of serious complications.
Whether it is attacks of headaches or acute pain that arose suddenly against the background of a satisfactory general condition, you should not hesitate: you need to visit a neurologist.
Let's look at some pathological conditions as possible causes of severe, intense headaches.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is an outpouring of blood under the arachnoid membrane of the brain; most often it occurs when a blood vessel aneurysm ruptures, which is a kind of “pouch-like” protrusion of the vessel wall.
This abnormal structure of the vascular wall can be congenital or acquired as a result of diseases (atherosclerosis, hypertension, autoimmune vasculitis, tobacco smoking, etc.).
d), the existence of an aneurysm does not manifest itself at all in a person’s daily life, but in the presence of factors aggravating the general level of health (including psychological ones), its integrity is threatened.
With subarachnoid hemorrhage, a person experiences a strong “blow” to the head, followed by a sensation of a burning headache, “a spill of hot liquid in the head.”
Patients describe this condition as “boiling water pouring on the head”, “the head is on fire”. In the first seconds, this pain can be local: in the fronto-orbital, parieto-temporal regions, in the back of the head.
Pain in the occipital-cervical region then turns into a hot wave descending along the spine.
Further, the pain becomes diffuse - repeated vomiting, neurological disorders, and symptoms of irritation of the membranes of the brain occur. Particularly severe pain occurs with hemorrhage from the vessels at the base of the brain, due to blockage of the outflow of venous blood and a rapid increase in intracranial pressure.
In addition, a frequent complication of subarachnoid hemorrhage is spasm of the arteries of the skull, causing a severe squeezing, squeezing headache.
Hemorrhage into the cerebellum
The cerebellum is a part of the brain responsible for balance, body position in space and the tone of our muscles.
Hemorrhage in the cerebellum is characterized by a bursting headache of high intensity (a person can scream from such pain), accompanied by dizziness, imbalance and orientation in space, nausea and vomiting, speech impairment, weakness - decreased muscle tone, rapid repeated eye movements in a certain direction ( nystagmus).
Cluster headache
Harris' periodic migraine neuralgia (often called cluster pain) is characterized by attacks of unbearably severe headaches.
The vast majority (about 90 percent) of those suffering from it are men under the age of forty. Cluster headaches occur suddenly, acutely, without any (recognizable) cause, often a series of attacks that begin at night.
By nature, it is burning, cutting, bursting, and is localized in the periorbital region, behind the eye, spreading to the face, temple, often the entire half of the head and neck.
A person has a persistent feeling of the eye “bulging” out of the orbit, often experiencing lacrimation, congestion and discharge from the nose. The face on the painful side turns red.
Intense pain brings great suffering, as a result of which the person groans, rushes around the room, is extremely irritable and does not accept help from loved ones. The attack usually lasts up to half an hour and occurs several times a day.
Cluster headache attacks are characterized by seasonal frequency: in 65 percent of patients, in autumn and spring.
(!) During such periods of exacerbation, an attack is easily provoked by drinking alcohol (due to its dilating effect on the peripheral vessels of the body).
Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania
An acute headache such as chronic paroxysmal hemicrania has a picture similar in many respects to the disease described above. The number of her attacks can reach 13-16 per day. But this variant of chronic paroxysmal cephalalgia is characteristic mainly of women (83-85 percent). The predominance of paroxysms at night and seasonal frequency are not typical.
Its peculiarity is its high sensitivity to treatment with indomethacin, a drug belonging to the group of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Often, only this therapeutic effect makes it possible to distinguish CPH from Harris migraine neuralgia.
Pathology of the autonomic nerve ganglia in the cranial cavity
In everyday life, we are accustomed to calling headaches pain in the area of the cerebral part of the skull, meanwhile, pain in the face (and this is most often neuralgia of the branches of the cranial nerves) also refers to headaches.
Neuralgia is distinguished by its paroxysmal nature: “flashes of pain” that occur on the face or neck follow one another, radiating (spreading) to more or less closely located segments of the head and body.
These cephalgia have a burning, piercing, sharp character, “like an electric current”; a person realizes that there are zones, so-called. “trigger”, irritation of which causes an attack.
The peripheral variant of neuralgia is described above.
If the pathological process (often an infectious-toxic lesion, inflammation of the meninges, a tumor process (!)) affects deeper structures - the autonomic nerve ganglia, then the pain arises already “inside the skull”, and often radiates to the temporo-parietal, frontal orbital or parotid area, which often “distracts” from the true source of pain and complicates diagnosis.
Cervicogenic neuralgia of the occipital nerve
We will touch upon this type of neuralgia separately, because in the vast majority of cases it is caused by pathology of the osseous-ligamentous apparatus of the spinal column.
Lack of control of posture when walking and sitting, head and spine injuries, disorders of mineral (in particular calcium-phosphorus) metabolism in the body are the most common causes of instability of the cervical spine or persistent organic formations due to the destruction of bone and cartilaginous structures. Thus, conditions are created for irritation of the sympathetic plexus, vertebral arteries and veins, and occipital nerves, which can cause various types of headaches.
Tilt of the head/turn in the direction opposite to the pathological focus causes the so-called. lumbago - a sharp pain in the neck or back of the head, often radiating to the temple and periorbital region.
In this case, there is no need to remain indifferent to your feelings; visit a neurologist, because short-term pain can transform into chronic pain due to constant irritation of the occipital nerve.
Source: https://eslibolitgolova.ru/vidi/bol-pronzayushhaya-molniej.htm
Causes
There are a number of factors, the manifestation of which contributes to the development of attacks with disturbed sleep.
Experts highlight the main ones:
- constant anxiety, chronic stress;
- epileptic activity is observed in the temporal part of the brain;
- discontinuation of medications after prolonged use, these can be benzodiazepines, antidepressants;
- pathological structural transformations in the part of the brain responsible for the perception of noise or in the middle ear;
- mental pathologies;
- night sleep disorder that bothers a person for a long time;
- drug and alcohol abuse.
Each individual case is subject to careful study by a specialist. A full examination of the patient is indicated, and if necessary, additional examination methods are prescribed.
Prevention
All health problems are much easier to prevent than to treat later.
Measures to prevent pain on the scalp and hair roots are quite simple and do not require any financial costs:
- you should not often experiment with new hair care products;
- it is necessary to keep your hair clean;
- for combing, it is preferable to use wooden combs or high-quality massage brushes;
- no need to wear tight hats;
- the hairstyle should not pull the hair too much;
- periodically it is worth carrying out hair treatment and restoration procedures;
- It is advisable to devote 5 to 10 minutes every evening for a head massage;
- work problems should be left at work, not taken home;
- it is necessary to engage in physical education (fitness, yoga, swimming, walking);
- try to adhere to a proper diet;
- give up bad habits: smoking and alcohol.
1. Lead a healthy lifestyle (stop smoking and drinking alcohol).
2. Engage in sports or physical activity.
3. Walk more in the fresh air.
4. Avoid stress and nervous tension.
5. Eat right.
6. Have good sleep.
7. Regularly undergo examinations for diseases of the brain and spine.
8. Do exercises while staying in one position for a long time.
9. Drink more fluids.
10. Stop drinking coffee.
11. Take vitamins.
Symptoms
During deep sleep, before waking up or just before falling asleep, a person hears all kinds of noise in his ears, loud and unbearable sounds. As a rule, there are no painful sensations at high audible intensity.

Waking up from such noise, a person may fall into a state of “sleep paralysis”, followed by increased fear and anxiety.
Main symptoms.
- Immediately after waking up, panic attacks make themselves felt.
- The presence of sounds comparable to knocking, ringing, or explosion.
- An additional phenomenon with the described syndrome is in the form of bright flashes in the eyes.
- Cramps affecting individual muscles or entire groups of them.
Symptoms of the pathology make themselves felt sporadically or appear regularly and over a long period of time.
The described state disappears after a few seconds. With multiple repetitions of attacks, the quality of night sleep deteriorates, which negatively affects overall well-being.
The frequency of seizures varies; they can occur once a month or repeat every night.
How to act correctly
Urgent contact with doctors is vital if the headache is very severe after hitting your head; in cases where the condition is accompanied by nose or ear bleeding, convulsions, attacks of nausea or vomiting, loss of consciousness, speech, memory, reflexes, and temperature fluctuations.
If you have a headache after a blow, what should you do?
It is necessary to remember the algorithm of actions, since under these circumstances urgent measures are often required when there is neither the opportunity nor the time for consultations and doubts:
- If a person falls after hitting him, he can damage not only the skull, but also other parts of the body. They need to be checked for damage or fractures.
- If there is a suspicion of spinal disorders and skull fractures, the person’s body must be immobilized so that the damage does not worsen.
- It is advisable to fix the position so that the skull and chest are slightly elevated.
- Wounds are treated with ordinary peroxide, but if a bone fracture is suspected under the skin, under no circumstances should pressure be applied to its surface.
- If you have a headache and feel nauseous, you need to constantly monitor the patient and not let him throw his head back, especially if convulsions also appear. In this state, a person is helpless and can choke on vomit or his own tongue.
- There may be bleeding in the area of the head where the injury occurred. To stop it, ice is applied to the skin.
Diagnostic measures
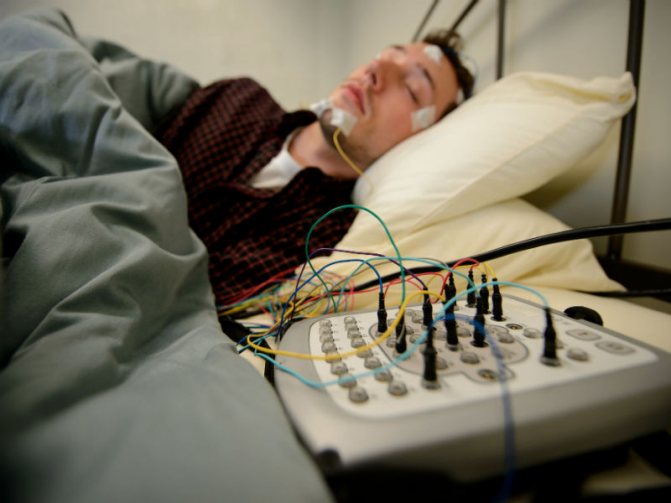

The condition of an exploding head is determined by a somnologist or neurologist. These specialists understand the intricacies of problems associated with sleep disorders. Initially, a consultation is held with the patient, during which the doctor analyzes all his complaints and unusual conditions.
A survey regarding regular night sleep will be important.
In advanced cases, polysomnography is prescribed. During the procedure, activity in the brain is studied, and heart rate and breathing parameters are taken throughout the night.
During the examination, disorders are identified in certain areas of the central nervous system.
If there are organic pathologies of the central nervous system, the diagnosis is determined using a technique called neuroimaging.
This procedure includes Doppler ultrasound, magnetic resonance therapy, and examination of the arteries in the brain using ultrasound.
Possible diagnoses
If someone complains: “I knocked myself, hit my head, now it hurts, but I don’t want to go to the doctor,” you need to convince the victim of the need to see a doctor.
Only an immediate visit to a medical facility can protect a person from developing cerebral edema, impaired cerebral blood supply, vascular destruction, loss of sensitivity and memory.
You should immediately contact your pediatrician if your child has a headache.
Headache after a blow may be a sign of the following diagnoses:
- Concussion.
- Aneurysms of blood vessels (stretching of their walls).
- Vascular malformations (pathological displacement of blood vessels).
- Internal hematomas.
- Ruptures of the eardrum.
- Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull and increased intracranial pressure.
- Brain swelling.
- Pneumocephalus (entry of atmospheric air into the skull).
- Vertebral displacement.
Principles of treatment
There is no established effective treatment regimen for the syndrome. In practice, neurologists often prescribe appropriate groups of medications to patients.
- Sleeping pills based on herbal ingredients.
- Antioxidants in the form of Tocopherol, Dihydroquercetin.
- Medicines that help normalize important metabolic processes at the neuronal level and improve blood circulation in the brain. This could be Cerebrolysin, Actovegin.
- Antidepressants of the tricyclic group, for example, Amitriptyline.
Due to the impossibility of long-term and careful monitoring of the patient, the effectiveness of the designated course of treatment is often in doubt.
The fact is that attacks of the syndrome, when a sharp sound explodes in the head, occur spontaneously, they are unpredictable. It is quite difficult to associate the absence of unpleasant outbreaks of noise with the use of medications prescribed by a doctor.
A positive result is achieved as a result of undergoing psychotherapy, since the often described syndrome is a consequence of chronic depression and stress.
Problems in a person’s professional field and personal relationships should not be discounted.
Why does my scalp hurt when touched?
Basically, there are 3 types of factors that provoke pain and ailments.
These include:
- Psychological or emotional;
- Cosmetological or household;
- Physiological.
Experts agree that an unstable emotional background is considered the main cause of unpleasant sensations.
To accurately determine the type of factor that caused the illness, you need to understand what applies to each of them.
If the personality is characterized by impulsiveness and instability, then there are much more complaints about pain in the head. This is associated with frequent stress, anxiety, sudden mood swings and prolonged mental tension.
Due to stress, a person notices increased hair loss. It is accompanied by soreness of the scalp when touched, which is localized either in a specific area or over the entire surface.
If the skin seems to pull when you touch it or when combing it, then this may be due to wearing an uncomfortable/tight headdress or too tight hairstyle. The use of hair care products needs to be given more attention; poor quality or the use of an expired product negatively affects the hair.
Symptoms include:
- Skin rash;
- Itching, irritation;
- Dandruff, flaking;
- Hair loss;
- Dullness and split ends.
Frequently washing your hair and using hot water is bad for the skin.
Any cosmetic products, regardless of price and quality, can cause an allergic reaction, which provokes skin algia.
This category includes the presence of bad habits, proper nutrition, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Headache is caused by vitamin deficiency, weak immune system and other reasons.
Individual characteristics and hereditary predisposition affect the likelihood of pain.