General understanding of brain tumors
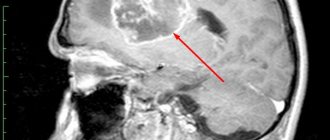
A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that form in or around the brain.
The neoplasm is capable of direct destruction of healthy brain tissue, and also causes inflammation and swelling of the nervous tissue and contributes to an increase in intracranial pressure. A brain tumor can be malignant or benign. A malignant neoplasm grows quickly and often damages healthy brain tissue by penetrating into them. Benign tumors are characterized by slow growth and less aggressive behavior.
Brain tumors are usually divided into two groups: primary and metastatic. Primary tumors originate from brain tissue. The formation of a metastatic focus is associated with the separation of malignant cells from tumors of another location and their penetration into the brain. For this reason, metastatic tumors are always malignant, while primary brain tumors can be either benign or malignant.
The classification of brain tumors takes into account the location of the lesion, the type of tissue included in its composition, the nature of the neoplasm (malignant or benign), etc. If the tumor is considered malignant, then a mandatory study of its cells under a microscope is carried out, which makes it possible to determine the severity of pathological changes. Based on the analysis, one can judge the degree of malignancy and stage of the tumor. The degree of malignancy and stage of the tumor depend on the growth rate of cancer cells, the volume of blood supply to the tumor, the presence of areas of necrosis (cell death), the degree of similarity of malignant cells to normal ones, as well as the extent of spread of pathologically altered cells to healthy tissue.
The exact cause of primary brain tumors remains unknown. Genetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of some tumors. In a very small number of patients, the development of brain tumors is associated with exposure to radiation, including for therapeutic purposes, in childhood.
Symptoms of brain tumors include headaches, nausea and vomiting, seizures, behavioral changes, memory loss, and hearing or vision problems.
Up
Treatment Options for Brain Tumors
There are many treatment options for brain tumors. The choice of the appropriate method depends on the type and size of the tumor, its growth rate and the general health of the patient.
In the treatment of brain tumors, surgical interventions, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted biological therapy and combined techniques are used. To rapidly reduce intracranial pressure, the first choice treatment is usually surgical resection of the tumor.
Radiation therapy
Over the past two decades, scientists have been able to develop new techniques for irradiating brain tumors while protecting surrounding healthy tissue. These include brachytherapy, intensity-modulated radiotherapy and radiosurgery.
Radiotherapy is used only for those tumors that are sensitive to it. This uses X-rays, gamma rays or proton beams, which are directed to the tumor from the outside, causing the death of cancer cells and reducing the volume of the tumor.
Radiation therapy usually takes several weeks. In case of multiple tumor foci, irradiation of the entire brain is possible.
New methods of radiotherapy include:
- RapidArc® technology, which involves the rotational movements of a linear accelerator and has all the benefits of intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT). The prevalence of this technology is still low.
- Intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT): is a modern method of high-precision radiation therapy using computerized linear accelerators, which provides targeted delivery of radiation to the tumor or any area within it. In this case, the beam of rays fully corresponds to the three-dimensional parameters of the tumor, as a result of which the entire radiation dose is entirely focused on the target, and the effect on healthy cells is minimized.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery is a high-precision method of radiotherapy, during which narrow beams of rays converge on the tumor at different angles. For this procedure, rigid fixing frames are used on the head. CT or MRI is used to determine the exact location of the tumor, and software helps the doctor adjust the radiation dose. Stereotactic radiotherapy is similar to radiosurgery, but involves fractionation of treatment, that is, dividing it into several sessions. This regimen is suitable for the treatment of tumors located inside or near vital structures of the brain, the exposure of which to high doses of radiation is extremely undesirable, and is also used for extensive tumors.
- Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (TCRT): combines the capabilities of traditional radiation therapy and the technology of changing the shape of the X-ray beam, which ensures its conformity (correspondence) to the parameters of the tumor. In this case, the neoplasm receives the maximum dose of radiation, while the surrounding healthy tissues are protected from it. When planning treatment, CT and/or MRI are used, since TCRT requires the most accurate consideration of the localization of the tumor and the anatomical formations around it.
- Brachytherapy (internal radiation therapy): temporary placement of radioactive materials into tumor tissue, causing the release of a high dose of radiation within the tumor.
For primary brain tumors, surgical treatment (resection of the lesion) is often prescribed. In this case, the entire tumor or part of it is removed without significant harm to surrounding tissues. If it is impossible to remove the tumor, surgery is used to reduce intracranial pressure or relieve symptoms (so-called palliative treatment).
For brain tumors, chemotherapy is also possible, which is considered the standard treatment for primary malignant tumors (often in combination with radiation therapy).
Chemotherapy drugs, which slow the growth of cancer cells or destroy them completely, are given before, during, or after surgery and/or radiation therapy to prevent tumor recurrence.
Chemotherapy drugs are given as tablets or injections, often in combination with radiation therapy. In addition, it is possible to use radiosensitizing drugs that increase the effectiveness of radiotherapy.
Up
Patient rehabilitation
Among the side effects observed immediately after a session of radiation therapy for a brain tumor using modern gentle methods, the most common is a transient feeling of fatigue. Sometimes slight hyperemia (redness) of the facial skin may occur, and in rare cases, easily removable swelling. The occurrence of burns and scars is extremely rare.
In the long term, hair loss may occur in a small area in the area where the rays are projected; over time, the hair will grow back. The nature and percentage of likelihood of long-term consequences depend on the location of the tumor.
Using modern technologies, radical treatment of brain cancer using radiosurgery or undergoing a course of radiation therapy after traditional surgery does not cause problems, and in the vast majority of cases does not require a stay in a medical institution during the rehabilitation period. Recovery takes from several days to several weeks.
In modern oncological practice, two main types of interventions are used to remove a tumor in the brain structure - craniotomy and radiation therapy. Each of these methods needs to be considered in detail.
In some cases, as a result of surgery, some consequences of surgery to remove a brain tumor may occur in the form of:
- deterioration of visual abilities;
- the occurrence of epilepsy;
- decreased brain function in some areas;
- infection of the operated area;
- the occurrence of memory and speech disorders;
- violations of the normal functionality of the vestibular apparatus;
- disorders of the digestive and urinary systems;
- paralysis
In order to recover quickly after surgery to remove a brain tumor and return to normal life, competent rehabilitation will be required.
The rehabilitation period begins immediately after surgery and can last an average of two to four months.
The rehabilitation period includes the following areas:
- taking medications whose action is aimed at preventing the recurrence of the tumor;
- a set of physiotherapeutic procedures to eliminate swelling, severe pain and numbness;
- massage sessions;
- taking neuroprotective medications that help restore all mental processes;
- a course of reflexology for the complete restoration of all reflex functions;
- classes with a professional speech therapist to restore all speech abilities;
- treatment in sanatorium-resort conditions.
It is very important to be constantly vigilant after treatment for a brain tumor in order to detect a possible relapse of the disease in time.
Recovery after major operations takes a long time. The patient will need a lot of effort and time to put his body in order. Rehabilitation after removal of a brain tumor will last more than one month. A new period of life will begin. The patient must completely abandon all bad habits, change their lifestyle, and practically learn to live again.
Postoperative treatment and a course of chemotherapy will force you to go through unpleasant moments: hair loss, brittle nails, cracked skin - just a small part of what awaits you after radiation courses. Unfortunately, such methods cannot be canceled: medicine has not yet come up with other ways to treat oncology.
The diet will accompany a person throughout his life. Smoked foods, salted foods, tea, coffee, spices, and meat are prohibited. Sun tanning is also prohibited. Overwork, stress, and anxiety can only renew the malignant process. The morale of the patient is very important. In such terrible moments, loved ones can turn away and leave the person alone with the illness, and this is the closest path to the end.
Brain tumor and how long do you live with it? It is impossible to completely defeat a fatal disease, especially if the disease is in the third or fourth stage. The patient can only win a couple of years in a difficult battle for life. The second stage will give more time, subject to careful treatment, compliance with all rules, routine, and medication. The first stage is curable. The patient can look forward to a long and happy life.
Oncology is rightfully considered the most serious disease. All efforts of doctors and scientists are aimed at studying cancer. Many people are working to create a unique cure against it. And yet the first step towards recovery must be taken by the patient himself.
All about brain glioma Survival for stage 4 brain cancer Symptoms of a brain tumor Types of benign brain tumors and treatment methods
Specialists are armed with the following types of surgical intervention:
- stereotactic method,
- removal of some cranial bones,
- craniotomy,
- endoscopic trepanation.
Surgical removal of a brain tumor can cause complications in some cases. Possible appearance:
- epileptic seizures,
- defective brain function in some areas of the body’s life,
- deterioration of vision and other functions.
This is especially true for operations performed using the trepanation method. A long recovery period will be required for the damaged connections between nerve fibers and blood vessels to begin to function properly.
Possible postoperative consequences:
- paralysis,
- disorders of digestion and urination,
- infection of the surgical site,
- dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus,
- speech and memory disorder.
After surgery, some brain functions may not be fully performed. In this case, a rehabilitation period will be required to restore brain function. This may include training and education.
After trephination, the first measures will be actions aimed at preventing bleeding and swelling of brain tissue.
The absence of postoperative complications does not always depend on the qualifications of the surgeon. Their occurrence is mainly determined by the location of the formation, whether it affects vital structures of the brain, the size of the tumor and the extent of the process. The more massive the surgical intervention, the more time is needed to restore the connection between nerve fibers and blood vessels.
After surgery to remove a brain tumor, the consequences can be very diverse. Possible disruption of the digestive and genitourinary systems, visual and hearing impairment, and speech impairment. In most cases, these are transient phenomena that are restored as brain function improves.
Correct management of the patient in the postoperative period is the main component of his successful recovery. Immediately after the operation, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit for round-the-clock monitoring by medical staff. If no complications arise during this period, then on the second day the patient is transferred to the neurosurgery department for further treatment and observation.
In some cases, radiation therapy is performed after removal of a brain tumor. This is an additional guarantee of the complete destruction of all cancer cells.
Caring for such a patient includes constant dressings and ensuring that the scalp always remains dry. Otherwise, the sutures may become infected. After 10–14 days, the suture staples are removed.
Rehabilitation after tumor removal is divided into primary and distant. In the first case, we are talking about the socialization of the patient and the restoration of lost skills. Often the patient has to learn to walk, use household objects, and speak again. This work is carried out by professional psychologists, speech therapists, and exercise therapy instructors.
Long-term rehabilitation is carried out throughout the patient's life. It is not recommended to fly by plane or climb mountains. Sudden changes in atmospheric pressure can have a detrimental effect on the blood vessels of the brain. Drinking alcohol is strictly prohibited. It can cause seizures and cerebral edema, a fatal postoperative complication.
The main question that concerns patients and their relatives is how long the patient can live after surgery to remove the brain and what will be the quality of his life. This assumption is difficult to make at the stage of primary diagnosis. Most often, the prognosis will be more favorable for those in whom the tumor was detected on time, at stages I – II of development.
The more extensive the process, the smaller the chances. After conducting research on how long patients live after brain surgery, it was found that visiting a doctor in the first 2 to 3 years (or earlier) after the appearance of a tumor guarantees a cure and life expectancy in more than 80% of cases. If a tumor is detected at a later date, the same ratio does not exceed 20%.
The duration and quality of brain surgery are influenced by the size of the tumor, the extent of the process, the nature of the tumor and metastasis. Only having data on all these issues in hand can a doctor talk about a possible prognosis for surgical intervention.
The cost of surgery to remove a tumor depends on the type of medical procedure performed, its volume and the clinic where the tumor will be excised.
So, for example, in Russian clinics the cost of a craniotomy ranges from $2,500; in a foreign hospital the price of the same operation is several tens of thousands of dollars.
The price of the endoscopic method, which is performed only in leading Western clinics, varies from $1,500 to $20,000. Only a doctor can tell the full cost of a particular intervention when he knows the exact data on the pathology and determines the type of intervention required.
Surgery to remove a brain tumor is often the only way to save a patient's life. But the further quality of life and its duration depends on the patient himself. Paying attention to your health, giving up bad habits, and following all doctor’s recommendations will allow you to lead a full life without any special restrictions.
What happens during radiation therapy?
Before starting radiation therapy, the patient is consulted by a radiation oncologist. During the consultation, the doctor evaluates the medical history and conducts an examination. In addition, consultations are carried out with other specialists who are part of the group of treating personnel.
Once the most suitable treatment method has been selected, the radiotherapy planning phase begins. At this stage, a radiation oncologist who specializes in radiation therapy for malignant tumors conducts treatment simulation. This uses standard radiography or CT, and in some cases MRI. The results of the examination are important for choosing the type and direction of the beam of rays.
It is important to remain still during simulated radiotherapy, although no radiation treatment is given during this period. A fixation mask is used to hold the patient's head in a certain position. As a rule, radiation therapy begins 1-2 days after drawing up a treatment plan.
During each radiation therapy session, the patient lies motionless on the treatment table while the radiologist or technician administers the treatment according to parameters prescribed by the oncologist. A radiotherapy session takes only a few minutes and is completely painless.
During stereotactic radiosurgery, a rigid head frame is used to immobilize the patient. In addition, during the procedure, regular scans (CT or MRI) are performed, which allows you to accurately monitor the position of the tumor and adjust the radiation dose if necessary.
Treatment planning and the first radiotherapy sessions take 1 or 2 hours. After this, each session lasts only a few minutes, and the patient's total stay in the radiology department does not exceed 30-45 minutes. As a rule, radiotherapy is carried out 1-2 times a day, 5 days a week, for 5-7 weeks.
Up
Treatment Options
Treatment is selected individually, depending not only on the stage of development of the disease and the location of the tumor, but also on the gender, age of the patient, as well as on the general state of health and the presence of concomitant diseases. Surgery (complete or partial removal of the tumor and endoscopy) is the most effective treatment option, but it is not always possible. Drug treatment includes chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The second is milder, therefore it is prescribed at earlier stages of the disease. There is also cryosurgery (during treatment, tumors are exposed to low temperatures) and stereoscopic surgery, during which irradiation is carried out with X-rays and gamma rays. Radiation therapy also involves exposing the patient to radiation, but in this case different types of rays are determined.
Possible side effects of radiation therapy
Side effects of radiation therapy for brain tumors usually appear 2 weeks after the start of treatment. Most patients experience baldness, the degree of which varies in each case. Typically, hair grows back after radiotherapy is completed.
The second most common side effect is irritation of the scalp and around the ears, which causes itching, dryness, redness and swelling. If these symptoms appear, it is important to contact your doctor as soon as possible, but do not try to treat them yourself.
Another possible side effect of radiation treatment is fatigue. The best way to combat it is to get enough rest, healthy eating and help from family and friends. Energy activity is usually restored 6 weeks after completion of treatment.
Radiation therapy for brain tumors is often accompanied by swelling of the nerve tissue, so it is important to immediately tell your doctor if you experience headaches or pressure. Medications are used to relieve swelling, prevent seizures and reduce pain.
More severe side effects occur when radiotherapy and chemotherapy are administered simultaneously. To overcome unpleasant symptoms, the doctor must prescribe appropriate treatment.
Other possible side effects of radiotherapy include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Hearing problems
- Memory or speech problems
- Headache
Up
Possible risks and complications of radiation therapy
Radiation is a powerful weapon against cancer cells, but in some cases it also damages healthy cells and brain tissue, which is called radiation necrosis. Necrosis, a late complication of high-dose radiation therapy, causes headaches, seizures, and, in extremely rare cases, death. Radiation necrosis takes from 6 months to several years to develop. However, in recent years, the risk of developing necrosis has decreased significantly, which is associated with the advent of modern methods of targeted radiation therapy and the introduction of powerful imaging methods, brain mapping and information technology.
Other complications of radiation therapy for brain tumors include:
- Tumor recurrence
- Neurological disorders
In children, radiation can damage the pituitary gland and other parts of the brain, which is manifested by slowed growth and disturbances in psychomotor and physical development. In addition, radiotherapy in childhood increases the risk of developing malignancies later in adult life. The goal of modern research in the field of oncology is to replace radiotherapy for childhood brain tumors with chemotherapy treatment.
Up
Classification
Brain tumors are of the following types:
- primary tumors are formations that initially develop directly from brain cells;
- secondary tumors - tissue degeneration resulting from metastasis from the primary site;
- benign: meningiomas, gliomas, hemangioblastomas, schwannomas;
- malignant;
- single;
- multiple.
Benign tumors develop from cells of the tissue in which they appear. As a rule, they do not grow into neighboring tissues (however, with a very slow-growing benign tumor this is possible), grow more slowly than malignant ones and do not metastasize.
Malignant tumors are formed from immature brain cells and from cells of other organs (and metastases) carried by the bloodstream. Such formations are characterized by rapid growth and germination into neighboring tissues with destruction of their structure, as well as metastasis.
- primary tumors are formations that initially develop directly from brain cells; secondary tumors - tissue degeneration resulting from metastasis from the primary site; benign: meningiomas, gliomas, hemangioblastomas, schwannomas; malignant; single; multiple.
Is any examination and treatment required after the end of radiotherapy?
For brain tumors, periodic examination by an oncologist is extremely important. In addition to a standard physical and neurological examination, your doctor may order MRI, MR spectroscopy, perfusion or diffusion MRI, CT scan, PET scan, blood tests, or endoscopic procedures.
Such observation helps the doctor:
- Look for any signs of tumor recurrence
- Monitor the state of the brain
- Detect and treat side effects of radiotherapy or chemotherapy
- Diagnose the appearance of other types of cancer at the earliest stages
In addition, oncologists recommend home care, physical therapy and rehabilitation measures aimed at restoring working capacity, adequate pain relief, and participation in support groups for patients with cancer.
Up
Free quota surgery: how to get it and what’s changing in 2020
Cancer treatment >> Types of cancer >> Modern methods of treating brain tumors have significantly increased the survival rate of patients with this disease.
Thus, for some types of tumors (ependymoma, oligodendroglioma), it was possible to achieve fairly high rates (up to 86%) of 5-year patient survival. However, such an aggressive type of brain cancer as glioblastoma is still considered an incurable disease - the 5-year survival rate for glioblastoma remains less than 15%.
Even after a full course of complex treatment for glioblastoma, the risk of relapse—resumption of the development of the tumor process—is extremely high.
Latest advances in the treatment of brain tumors
Advances in fractionated and stereotactic radiotherapy over the past decade offer hope to patients with brain tumors by increasing survival and quality of life. Clinical studies show the effectiveness of a range of procedures and medications. These include:
- Gene therapy: introducing genetic material into tumor cells to destroy them or slow their growth.
- Angiogenesis inhibitors: drugs that interfere with the growth of blood vessels inside the tumor, causing it to become starved of oxygen and lack nutrients. This type of treatment is called angiostatic.
- Immunotherapy is an experimental treatment that triggers an immune response against specific tumor antigens. Various immunotherapy drugs are currently being studied in controlled clinical trials.
- New classes of biological drugs for targeted therapy directed against various parts of the metabolism and signaling pathways of tumor cells.
- More efficient drug delivery methods, such as convection delivery, are being explored in clinical studies.
Up