point, writes March 3, 2020, 14:00 Irkutsk
Gender: Male Required: neurologist, vertebroneurologist
Hello, my name is Egor, age 28 years old, for almost half a year I have been tormented by Tick in my right ear, as if the eardrum was vibrating (the frequency does not coincide with the pulse), I noticed that this appears from noise, for example from the sound of water, or the kettle is boiling and etc. From the otolaryngologist's point of view, everything is perfect, from the examinations I did an MRI not so long ago, I am attaching a scan of the report; I consulted with several neurologists about the MRI and they said that there is nothing wrong. complained about Tik, this one is being ignored, not given any importance, but I’m already so sick of it, + the other day the session starts and all thoughts are only about this because it’s in the way. I must say that I have VSD, + I have had several concussions in my life. I don’t drink, I don’t smoke, I lead an active lifestyle. Here is a link to view a larger photo:
https://www.fotolink.su/v.php?id=253b12c2d8d8892baada4a6180cf22fe Thank you very much in advance for your answer, best regards!
Do you feel a contraction of the soft palate, an increase in tic in the ears while eating or talking? What preceded the onset of your painful condition?
No, I don’t feel it, it seems like nothing preceded it, I just noticed it sometime and that’s it, it continues, there seem to be no injuries. A tic in only one right ear, intensifies and generally appears from noise, as I wrote water for example or a kettle, etc. Recently it has become stronger, but I should notice and I have become more nervous, maybe this is connected with this. The neurologist prescribed Tanakan, I’ve been drinking it for a month now, so far there’s no benefit, but it shouldn’t be because it’s too early.
and as a psychologist, I understand that neurosis begins from this, but so far I’m coping, but with difficulty.
and I also thought that it would be correct to mention that the ear began to ache from time to time, the ear canal itself, it was a bit painful to press the earlobe, move the jaw, moreover, it would ache for about 20 minutes and go away, the nature of the pain is similar to inflammation, but it would not go away so quickly of course.
Egor, I don’t know whether this is still relevant for you or not, but maybe someone with the same problem will come across it in a search engine and will not repeat our mistakes with an incredible number of examinations, medications, and most importantly, a damaged psyche. None of the doctors will say anything and they won’t find anything on you, you’ll walk around with this knock, telling you how disgusting it is to live with it, and they’ll smile back at you and prescribe tranquilizers, because by the time you’ve seen all the doctors, or better yet, not If it happens, your nerves will be on edge and you will have to somehow relax them. The knocking will go away (you just don’t know when, it’s different for everyone) but until it goes away and you will constantly think about it and be afraid of “what’s next?? What’s so scary about this beginning?”, you will earn yourself real problems with both blood pressure and blood vessels due to constant physical stress, and many other things can happen just because you will be nervous because of a nervous tic in your ear.
Best wishes))
In the sense that I’m fine with blood vessels and blood pressure (otherwise you’re going to screw up their connection with tic)), but due to unnecessary worries, some people may not feel very good. I developed heart problems for myself: I constantly had a rapid pulse, even at night (because I couldn’t sleep - I was afraid of everything), and I also became too fanatical about sports, as a result - extrasystoles appeared! Moreover, at first I thought that it was a nervous tic in the chest and it was even pleasant, especially compared with what was in the ears, this one in the chest seemed so harmless) then another tic in the ear turned me into a terrible hypochondriac, now against the background of any nonsense such horrors begin get into your head. So don’t start it, stop thinking about this tic now - it will definitely pass.
Purchase effective medications to treat this disease
Causes of pulsation in the ear
If there is a pulsation in the ear, then this process was clearly preceded by certain disturbances in the functioning of the body. This symptom is a consequence of many changes, ranging from disorders of the central nervous system to serious pathologies.
Let's figure out where the throbbing pain in the ear comes from.
Overwork
If there is a pounding in the ear like a pulse, then this condition can be the cause of constant stress and fatigue.

When there are no signs of diseases that can provoke such a symptom, then, in most cases, it pulsates in the ear due to banal overwork.
Advice! If your ear throbs but doesn’t hurt, what should you do? In this case, you still need to see a specialist. Perhaps the reason for this manifestation may be hidden much deeper than it actually seems. After all, sometimes the essence of the problem that provoked the pulsation requires urgent medical intervention!
Pulsation against a background of fatigue leads to sleep disturbance, and if this continues systematically, disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system may develop.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Pulsation in the ear may be a consequence of the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system. A noise in the left ear that coincides with a heartbeat almost always indicates that the patient has diseases of the vascular system.
In most cases, pulsation is observed immediately after physical activity. Moreover, the symptom of pulsation, accompanied by slight dizziness, can be observed even after climbing stairs.
Pulsation in the ear: possible causes, normality and pathology, how to treat
The ear is an organ of hearing that performs very important functions in the human body. It provides the perception of sounds and their conduction, as well as orientation in space. Ripple or noise in the ear are symptoms of pathological changes in the auditory analyzer, the causes of which must be urgently determined in order to begin treatment in a timely manner. When there is a constant pulsation in the ear, a person becomes irritated and nervous, sleeps and eats poorly, and becomes depressed. These signs ultimately lead to even greater health problems: hearing impairment, mental disorders.
It can pulsate in both ears simultaneously or separately in each. The pulsation in the ear can be ringing, reminiscent of clicking, or dull, almost imperceptible. It is often accompanied by a feeling of congestion. In healthy people, the cause of painless pulsation in the ears, which occurs periodically, is stressful and conflict situations, physical and psycho-emotional stress, fluctuations in pressure and body temperature. In such cases, pulsating tinnitus is not a pathology and does not require special treatment. If it is heard constantly and is accompanied by pain, incoordination of movements, and the appearance of “spots before the eyes,” you should immediately visit a doctor. Such pulsation is a manifestation of a disease, the cause of which must be determined and eliminated.
The causes of pulsation in the ear are very diverse. These include:

- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the auditory analyzer,
- Closed and open head injuries,
- Vascular diseases - atherosclerosis, hypertension, various vascular malformations,
- Stress,
- Neoplasms of the head and neck,
- Wax plugs in the ears,
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics, especially ototoxic ones,
- Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,
- Hormonal surge during pregnancy, menopause,
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine,
- Daily use of headphones
- Pressure surges during air travel, diving, mountain climbing,
- The natural process of aging of the body.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
Persons suffering from cardiac pathology quite often experience tinnitus, reminiscent of a heartbeat. The pulsation is especially acute when the patient climbs stairs or bends forward. He feels pressure in his head, lack of air, and noise in both ears.
- With hypertension , vascular tone is disrupted, capillaries become overfilled with blood, and systemic blood flow becomes difficult. The sound of blood “friction” through the vessels is perceived by a person as a pulsating noise. “It’s as if the heart is pulsating in the ears” - this is how patients characterize this phenomenon. If a hypertensive crisis develops, the flow of blood into the vessels of the inner ear becomes uneven. This stimulates the nerve endings, which also results in pulsation in the ears.
- Atherosclerotic processes lead to loss of elasticity of the vascular wall, which ceases to contract in the same rhythm as the heart. Such pathological pulsation becomes audible. If the ear is pressed against the pillow, it becomes especially noticeable. Patients with atherosclerosis complain of regular dizziness, noise and pulsation in the head, easy fatigue, poor memory, and hypertension.
- Violation of the structure and functioning of large arteries and veins , their narrowing or stratification changes the speed and direction of blood flow, which hits the walls of blood vessels. Patients claim that their ear throbs, but it does not hurt. Small aneurysms manifest themselves as pulsations in the head. The larger the size of the protrusion, the more pronounced these unpleasant sensations are.
Diagnostics
The main method for recognizing neuralgia of the auditory canal is audiometry. During the procedure, the specialist tests the patient's hearing to detect sounds of different frequencies. If a person does not perceive high-frequency impulses, then he is diagnosed with cochlear neuritis. Bone conduction of noise and sensitivity to vibration are assessed using a tuning fork.
To determine the cause of the pathology, an ultrasound of the cervical spine, an ECG, and blood and urine are examined for general indicators. Discharge from the ear is examined for microflora to identify the type of causative agent of the disease. Based on the study, a suitable antimicrobial drug is selected.
Diseases of the ENT organs
Pulsation in the ear can occur with diseases of the ENT organs:
- Any part of the ear can become inflamed, as well as the Eustachian tube connecting it to the nasopharynx. Pathological changes in the auditory analyzer distort sound waves and reduce their perception. With otitis, the outflow of serous-purulent exudate is disrupted, an “echo effect” is created, internal noise increases, and blood pulsates. The patient has throbbing in the left ear due to left-sided inflammation of the auditory analyzer. If otosclerosis develops, in which the mobility of the auditory ossicles in the middle ear is impaired, then patients experience decreased hearing, dizziness and tinnitus.
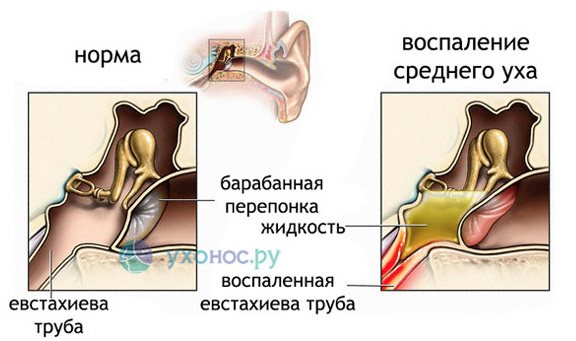
- Labyrinthitis is an inflammation of the inner ear caused by the penetration of infection from chronic foci in the body. The main manifestations of labyrinthitis are vestibular disorders. In patients, coordination of movements is impaired, everything floats before the eyes, ataxia, nystagmus, and autonomic disorders occur: pallor, hyperhidrosis and dizziness. Irritation and death of sound receptors leads to pulsation in the ears, reversible hearing loss and even deafness.
- Hypersecretion of earwax often results in the formation of cerumen plugs, which must be removed promptly. Earwax blocks the ear canals, which causes hearing loss, inflammation and the appearance of pathological pulsation.
Ear compresses
In addition to drug treatment, patients are advised to use warm ear compresses based on alcohol or camphor oil. To prepare them you will need:
- Compress with camphor oil - cut a hole in the center of the gauze napkin into which the ear could fit. Next, soak a napkin with camphor oil, wring it out and apply it to the sore ear, threading it through the hole. Finally, apply cotton wool and secure the compress with a bandage. The compress is replaced every hour (but can be left overnight).
- Alcohol compress - 20-25% alcohol is diluted with water (1:1) and a gauze cloth is moistened in it, then the compress is applied to the ear in the same way as described above and kept for 30-40 minutes.
a hole is made in the gauze for the ear
Before applying an alcohol compress, the skin around the ear is first lubricated with a thick cream (so as not to cause a burn). If the patient's body temperature is higher than normal, then any warming compresses are contraindicated .
Traumatic injuries
Brain injuries are a dangerous condition that threatens human health and life. With TBI, the blood supply to the auditory organ is disrupted, swelling and other signs of inflammation occur. This leads to dysfunction of auditory cells, disruption of sound transmission and sound perception. The throbbing and pressing headache intensifies when the victim begins to move his head.
If there is a fall or blow to the head, it is necessary to conduct a tomographic examination to rule out a concussion. This is extremely important for patients who experience increased pulsation and loudness of noise, drumming, dyspeptic symptoms, and dizziness. TBI has a severe course and serious consequences. After discharge, patients continue to complain of dizziness, pulsation in the head, and headache for a long time.
The eardrum twitches
- Signs
- How to get rid
- Folk remedies
Whistling in the ears is a fairly common symptom, which often means that something is wrong with a person’s ears.
However, this does not always mean the presence of pathology, and may only be the result of a long stay in a noisy room. To understand the cause of this phenomenon, you must definitely consult a doctor, and in this case it will be an ENT specialist, who will determine exactly what caused this symptom and how exactly to overcome it.
Most often this occurs in the following cases:
Our readers successfully use SustaLife to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
- Long-term exposure to incredibly loud noise, for example, if a person is in a discotheque, in a noisy room, or where a siren is wailing.
- Blockage of the ear canal with wax or other foreign objects, for example, a piece of cotton wool. Sounds pass through such an obstacle with great difficulty and the person begins to complain about clicks, ticking, whistling and other unpleasant phenomena.
- Whistling in the ears and head can cause diseases of the ear canal, especially if it is associated with inflammation of the eardrum or its damage, as well as suppuration. Other symptoms are pain and a feeling of overflowing fluid, as well as congestion.
- Atherosclerosis, otosclerosis and other vascular diseases will certainly lead to hearing impairment.
- High blood pressure is another common cause of this condition. In this case, such a manifestation usually occurs on one side.
- Tumor of the brain, especially in the temporal part.
- Cold.
- Allergy.
Even if a whistling sound in the ear appears occasionally and lasts only a few minutes, but this symptom has a certain periodicity, you should definitely consult a doctor.
The reasons, as it turns out, can be a variety of conditions. But the doctor may ask for a more detailed description of the problem. Therefore, it must be said that even after a person gets into a quiet room, the symptoms do not disappear. Moreover, it all starts with barely noticeable manifestations, but gradually the noise becomes louder.
Another important symptom is partial or even complete hearing loss. But this does not always happen. Usually in such cases, the answer to the question of why there is whistling in the ears may turn out to be the following: the eardrum is damaged.
Other manifestations that may accompany whistling in the left or right ear include discomfort, pain, sensation of a foreign body in the ear canal, swelling, inflammation, discharge, which can be liquid or purulent.
With further development of symptoms, dizziness, spatial disorientation, fainting, insomnia, and vision problems may appear. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor, as serious vascular or brain diseases may be suspected, which will require immediate surgical intervention.
How to get rid
Treatment depends entirely on the causes that caused the pathology.
It is impossible to determine this on your own; you must definitely seek advice from an ENT doctor. After this, the doctor will order certain tests and, based on their results, prescribe treatment for whistling in the ear. If the cause is an infectious disease, then you must take a full course of antibiotics. You should only take medications that are prescribed by a specialist, because some of them are highly toxic, which will negatively affect your hearing in the future.
If there are any indications for surgery, then conservative therapy will not help. If a tumor is diagnosed, it must be removed.
Most often, the same symptoms appear when small objects or even insects get into the ear canal. You cannot remove all this yourself, as you can easily damage the eardrum and remain deaf.
If the cause of this symptom is cerumen plug, then treatment consists of rinsing the ear canal. The procedure is simple, painless and absolutely safe.
If a patient has high blood pressure, then with the selection of the right medications and taking them regularly, this manifestation disappears quite quickly.
Whistling in the ears may also be associated with age. In this case, the doctor may recommend taking vitamins, doing health-improving exercises, taking restoratives and eating right. If there is significant hearing loss, it is recommended to wear a hearing aid.
If this symptom appears from cervical osteochondrosis, medications that will improve blood circulation and also prevent the development of exacerbations will help.
Anti-inflammatory drops for lumbago
For lumbago, you can numb the ear with anti-inflammatory drops:
- Otipax - the drug has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, eliminating symptoms, but not eliminating the cause of the disorder. Directions for use: 3-4 drops into the external auditory canal 2-3 times a day. Course of treatment: 10 days. Price: 290 rubles (15 ml).
- Otinum is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with antimicrobial and antifungal effects. Directions for use: 3 drops into the ear canal 3-4 times a day. Course of therapy: no more than 10 days. Price: 220 rubles (10 ml).
- Polydexa - the drug has an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect, is used for external otitis and in case of damage to the eardrum. Directions for use: 1-5 drops into the ear canal of each ear (2-3 times a day). Duration of therapy: 6-10 days. Price: 250 rubles (10.5 ml).
An ENT specialist will help you choose an individual dosage and course of treatment.