Headache is considered one of the most common symptoms on the globe, affecting millions of people every day. This prevalence is due to the fact that cephalalgia accompanies many different diseases of various origins. According to statistical studies, about 70% of the population experience headaches from time to time. Pain sensations can differ from each other, being localized in different parts of the head, manifesting themselves with different intensities and changing their character. Pressure in the temples and pain in the eyes is a common complaint when visiting a neurologist, based on a long list of provoking factors.
Pain in the temples can be caused by a number of reasons
Causes of pressing pain in the temple
There are many reasons for pain in the temple, and among them there are serious disorders:
- Pathology of the tone of cerebral arteries and veins.
- Vascular atherosclerosis.
- Diseases of the temporomandibular joint.
- Overstrain of the neck and head muscles.
- High blood pressure level.
- Migraine.
- Prolonged eye strain.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Infectious diseases.
- Increased level of intracranial pressure.
- Cluster headaches.
- Intoxication of the body.
- In women, puberty or menopause.
- Consumption of food containing large amounts of flavor enhancers.
The main predisposing factors for attacks when there is pain in the temples are disturbances in the vascular bed associated with changes in the normal regulation of the tone of the arteries and veins. In second place is damage to nerve trunks and sensory endings. Lifestyle increases the likelihood of developing pain syndrome - alcohol abuse, smoking, frequent overwork and stress lead to frequent attacks of pressing pain in the temples.
Pain in the temples due to impaired vascular tone
One of the causes of pain in the temples is a violation of the tone of the cerebral vessels
Under the influence of various factors, a violation of cerebral vascular tone can occur, which is manifested by narrowing or expansion of cerebral arteries and veins. Such changes entail a violation of adequate nutrition of any part of the brain, which, in turn, provokes the development of pain.
Pain with angiodystonia of the cerebral vessels is of a dull, pressing nature, pressing on the right or left temple, forehead, eyes. The head hurts at any time of the day or night, the attack is accompanied by additional symptoms: dizziness, memory deterioration, insomnia, and numbness in the fingers.
Cephalgia in atherosclerotic vascular lesions
Atherosclerosis is an insidious disease in which atherosclerotic plaques are deposited on the inner walls of blood vessels, gradually blocking the lumen and impeding the passage of blood through them. People who suffer from hypertension, kidney disease and are overweight are most prone to atherosclerosis.
Pressure and pain in the temples if the cerebral vessels are involved in the process. The pain is pressing or throbbing in nature, localized in the temples and can move to the forehead, back of the head and eyes. In addition to pain, patients with atherosclerosis complain of difficulty concentrating, decreased performance, dizziness, constant fatigue and irritability. These symptoms arise due to a lack of oxygen and nutrients as a result of difficulty in delivering blood through narrowed vessels.
Cholesterol plaque
Cephalgia and temporomandibular joint dysfunction
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is the most complex joint in the human body due to its structural features. The process of the temporal bone is part of the articulation, and the nerve trunks responsible for sensory and motor function pass through the temporal region to the joint, so many TMJ diseases manifest themselves in pain and pressure in the left or right temple, depending on the affected side.
Common pathologies of TMJ are arthritis, arthrosis and musculo-articular dysfunction. The headache can be pulsating and pressing in nature, in some cases, be quite intense, spreading along the lower jaw to the opposite side, radiating to the eye and forehead. Additionally, crunching and limited joint mobility may be observed.
Tension headache
As you know, the human skull is covered with a muscular layer called the scalp. With prolonged physical activity, a long stay of the head and body in one position, heavy strain on the eyes, as well as under the influence of stress and excessive experiences, the muscles of the head and neck become overstrained and sore. In this case, pain occurs that presses from all sides, including in both temples and eyes, compresses the head with an invisible hoop in the forehead area. Tense muscles interfere with the normal passage of blood through the compressed vessels, end products of metabolism accumulate in the muscles, so the headache can persist for quite a long time.
Cephalgia with hypertension
Headache associated with high blood pressure is more common in patients in the older age group. With increased pulse pressure, blood presses on the walls of blood vessels, which contain many pain receptors, causing a headache. When the pressure rises, the patient experiences pain in the temples and the back of the head, most often of a pressing or pulsating nature. In addition to pain, when blood pressure rises, you feel dizzy, spots appear before your eyes, nausea, vomiting, general weakness and shortness of breath are noted.
Migraine and cluster headaches
Migraine is characterized by intense headache, localized predominantly on one side. Unpleasant sensations can spread to the area of the upper jaw, back of the head, forehead and temples, manifested by pressing, pulsating, bursting pain, often causing additional pain in the eyes. Exposure to external stimuli (bright light, loud sounds) increases pain, and the attack is often complicated by nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and general weakness.
Cluster cephalgia is characterized by a series of attacks of intense pain several times a day. The attack begins with severe pain in the eye socket and ear, spreading to the forehead, temples and behind the eyes, and the headache is so severe that there is evidence of cases of suicide in order to stop the torment.
Treatment and diagnosis of pressing pain in the temples
To completely get rid of cephalgia, it is imperative to identify the cause of the attacks. To do this, the neurologist conducts a detailed survey of the patient, finds out the intensity of the pain, provoking factors, the duration of the attacks and the time of their occurrence. If necessary, the patient is sent for computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, angiography to assess the condition of the brain and its vessels. In some cases, a consultation with an ophthalmologist is required to diagnose the eye condition.
Inflammation of the temporal artery
Symptoms:
1. Severe, throbbing pain that appears suddenly and is localized mainly in the temples and back of the head.
2. Pain occurs when chewing, moving the jaw and head, for example, when combing; Along with general painful sensations, there is severe pain and pressure in the temples.
3. Redness, a clearly noticeable hard stripe on the temples in the ear area.
4. Pain in the eyes, double vision and blindness (sometimes temporary, sometimes long-term) in one or both eyes.
5. High fever, weight loss, and general weakness may appear.
6. Sometimes I feel dizzy.
Features of drug therapy
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0_FCumUiWJY
If a person constantly has pressure in the eye area, then certain measures should be taken. First you need to undergo an examination, including x-rays, tests, diagnostics of the vessels of the cervical spinal column and brain, CT or MRI. Only based on the results obtained, the doctor will be able to begin adequate therapy.
To treat the disease-causing syndrome, the following medications are often prescribed:
- analgesics or antispasmodics: “Spazmalgon”, “Analgin”;
- anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen;
- for cervical osteochondrosis, pulsation of the temples, vasodilating drugs are prescribed: the drug “Aminophylline”;
- muscle relaxants, if other means do not have the desired effect;
- to eliminate heaviness and tension in the temples, use Indomethacin;
- In the complex treatment of neurocircular dystonia, motherwort or pharmaceutical valerian extract is used. To enhance the therapeutic effect, drugs such as Elenium, Gidazepam, Picamilon are indicated.
Perhaps the doctor will recommend medications that regulate the functioning of blood vessels. If a patient is diagnosed with migraine, simple medications will not work. You will need triptans: “Imigran”, “Sumamigren”, “Tempalgin”. Self-medication in this case is not recommended.
Treatment of the disease syndrome should begin with these medications
Course of the disease
The inflammation affects one or more arteries in the temples, most often the main temporal artery. The reasons why the disease occurs are unknown, but the influence of heredity, viral origin or immune defects is indicated. Often the disease occurs together with polymyalgia rheumatica, a disease characterized by morning sickness and stiffness of muscles and joints.
Symptoms may appear suddenly or develop gradually. Sometimes a small part of the artery in the temples is affected, in other cases the aorta (the largest artery in the body that comes from the heart), heart and carotid arteries are affected. The pain is induced mainly by the illuminated vessel wall, but there is a gradual narrowing of the arteries of pain, ischemia and lack of oxygen.
Sometimes there is spontaneous improvement, but deterioration is also possible: due to the interruption of blood flow to the optic nerve, blindness can occur.
Main causes and diseases
There can be many reasons that can cause headaches and blocked ears. All of them are divided into physical, which do not require treatment, and pathological, for which treatment is necessary.
The first group includes:
- Getting water into your ears when swimming or showering.
- A sharp change in atmospheric pressure. The symptom is clearly manifested especially with a rapid decline in indicators.
- Hormonal disorders that can be caused by hormonal disorders during pregnancy or menopause.
- Stress, neuroses and depression.
Unpleasant signs that arise for these reasons do not require treatment, as they are a normal state of the body under certain circumstances.
Among the reasons that can provoke the appearance of ear congestion and headaches are the following:
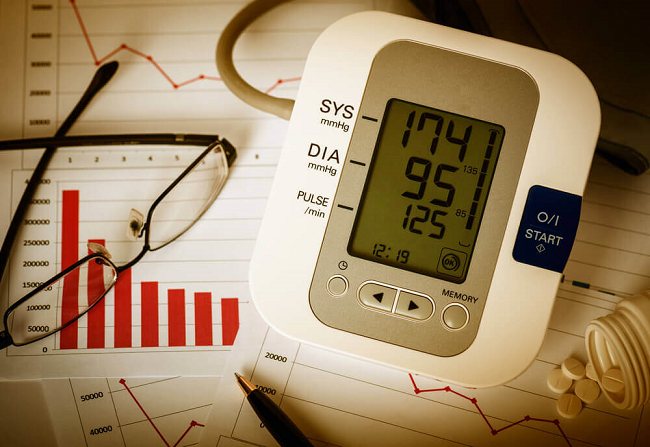
- High blood pressure. It is considered a rather dangerous condition, which is accompanied by the appearance of spots or black spots before the eyes, nausea, developing into vomiting. A throbbing pain is felt in the temples. Discomfort and a feeling of squeezing appear in the area of the heart muscle. When a set of symptoms occurs with a certain frequency, you should not delay visiting a specialist, as they indicate a pre-stroke condition. Also, overload in the form of high blood pressure causes thinning of the heart wall and increases the risk of developing heart failure.
- Osteochondrosis. Headache, blocked ears and other symptoms in the form of pain in the spine and limitations in physical activity can be caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. As a result, blood circulation is disrupted, as the vessels leading to the brain are compressed. The causes of the disease are a sedentary lifestyle and excessive physical activity.
- Viruses and colds. In addition to headaches and ear congestion, symptoms include sneezing, nasal congestion, pain in muscle tissue and joints, and fever. Treatment is comprehensive, and in severe cases the use of antibiotics is required.
- Acute sinusitis. Characterized by swelling and inflammation of the nasal mucosa. The cause of the disease is various types of bacteria. Breathing through the nose worsens, resulting in oxygen deficiency. This is what leads to blocked ears. Against the background of the inflammatory process in the nasal sinuses, a headache is also observed, which intensifies when turning the head. Lack of therapy increases the risk of purulent masses entering the body, which leads to infection. Among the consequences are swelling of the membranes of the brain, meningitis, and abscess.
- Inflammation in the middle ear. When an infection that has entered the nasal cavity penetrates the ear canal, the following diseases develop: mastoiditis, acute or chronic otitis media, labyrinthitis.
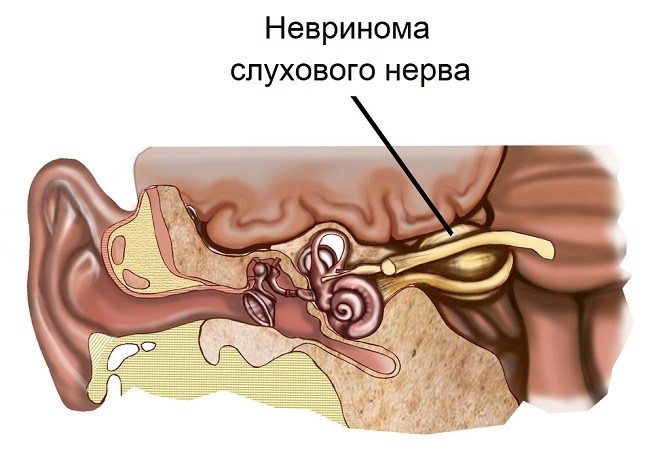
- Neuroma. This is a benign neoplasm that forms on the auditory nerve. It is detected mainly in women. In addition to headaches and ear congestion, symptoms such as dizziness and nausea are observed. In addition, there is a disruption in the performance of the masticatory muscles.
- Cork. Ear wax is not a rare disease. Earwax is a necessary element that protects the ear canal from infections and bacteria that can penetrate through the ear canal into the brain. But if there is an excessive amount of it, a plug is formed that reaches the eardrum. The result is not only a headache, but also ear congestion.
- Injuries. Most often, such symptoms are observed with traumatic brain injuries and ear damage, which can occur due to frostbite, burns with acid, alkali, foreign objects, or an unsuccessful fall.
All diseases pose a threat to health, and in some cases, life. If unpleasant symptoms appear regularly, it is important to immediately consult a doctor who will conduct a comprehensive examination, establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a course of therapy.
Treatment
The main treatment is corticosteroids. The doctor usually starts therapy with 40-60 mg daily dose of Prednisolone, which is divided into 2-4 doses. If the symptoms (severe headache, pressure in the temples) subside (usually within a few weeks), you can take the medicine only in the morning.
As the condition stabilizes, the dose is gradually reduced. The goal of therapy is to free the patient from taking corticosteroids so that the disease does not relapse.
Treatment usually lasts about 1-2 years, sometimes much longer. Prednisone and other corticosteroids cause a number of side effects, such as weight gain, bone loss, high blood pressure, bruising, cataracts, and mood swings.
Nature of spasms and additional symptoms
In the vast majority of cases, tension and pressing pain in the temples occurs due to impaired cerebral circulation.
That is, regardless of the disease that led to this condition, the pathogenetic mechanism of the development of the disease is the same in all cases - increased pressure of influx of blood on the cavernous sinuses with subsequent irritation of the receptors clearly leads to the occurrence of pain.
If you have a headache or pressure on your eyes, you should consult a therapist. There are many causes of the pathological condition, among them there are disorders that pose a serious danger to humans:
- Decreased tone of veins and brain vessels.
- Atherosclerosis of the arteries.
- Pathologies of the temporomandibular region.
- Tension pain.
- High blood pressure.
- Migraine attacks.
- Trauma to the skull and brain.
- Infectious pathologies can provoke pain in the temples.
- High intracranial pressure.
- Cluster spasms.
- Poisoning the body with harmful substances.
- Representatives of the fairer sex experience menopause and puberty.
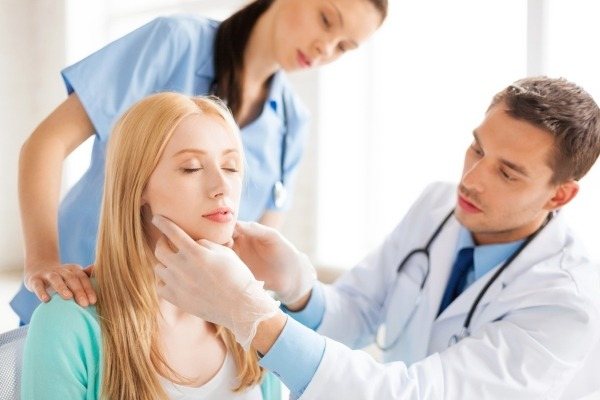
To establish the cause of the pathological condition, you should undergo a comprehensive diagnosis
In this condition, patients most often seek medical help. The rhythm of modern city life, working at a computer, and a sedentary lifestyle cause dizziness and tension pain.
Unpleasant discomfort develops in stages and intensifies with mental and emotional “stress.” Pressing pain takes over the temporal, occipital part, moves to the forehead - the head feels as if in a vice. A person experiences strange sensations when combing his hair or wearing a hat.
If there is constant pressure and pulsation in the temples, the causes of this pathology may be the following:
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position at the computer leads to overstrain of the neck muscles, disruption of blood flow as a result of insufficient oxygen supply to the brain, a person gets a headache;
- emotional chronic stress - it is precisely because of this that the left temple is most often compressed and pulsating.
Tension pain must be distinguished from the syndrome that develops with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. In the latter situation, spondylolisthesis and osteophytes compress the vessels responsible for the supply of oxygen to the brain. As a result of insufficient blood flow and irritation of nearby organs, the patient has a headache.
What to do if there is pressure on the eyes or forehead due to tension:
- work at a computer in a comfortable position and an anatomical chair;
- take a break for 5-10 minutes every hour;
- when the temples pulsate, a massage effect on the back and temporal region of the head is indicated;
- relaxing warm-up of the neck and shoulders;
- resting with a wet towel on the forehead, temples with the windows closed in silence;
- baths with essential lavender oil, a decoction of medicinal valerian.
You can eliminate the pain of tension and pulsation in the temples with the help of herbs that have sedative properties: lemon balm, motherwort. Daily walks in the fresh air will improve blood circulation in the brain; for cervical osteochondrosis, vasodilators (nicotinic acid, aminophylline) and physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended.

One way to eliminate tension pain
If there is pressure in the temples or a headache, for effective therapy it is necessary to establish the cause of the syndrome. In this case, not only the nature of the pathological condition matters, but also other signs.
Each disease has its own specific symptoms:
- With hypertension, the temples hurt very much. There are also other signs: dizziness, stuffy ears. Hypertension can cause a stroke, so the disease requires immediate treatment.
- Vascular atherosclerosis: the patient’s performance, level of memory, thinking decreases, anxiety increases, dizziness, and insomnia bother him.
- With a migraine, most often the left temple (right) throbs or compresses the entire head. Every movement can increase the intensity of the spasms. The patient may experience vomiting, nausea, and visual impairment.
- Severe poisoning causes not only a squeezing sensation in the temporal region, but also vomiting, nausea, and arterial hypertension.
- Pheochromocytoma is a disorder of kidney function. The temporal part is not easily compressed, but pulsates intensely and hurts. Other symptoms are also present: pale skin, excessive sweating, high blood pressure.
- Temporal arthritis is accompanied by spasms, intense pain in the joints, muscles, and visual impairment. The doctor may feel a lump in the area of the left or right temple. A neurosurgeon treats this pathology.
- Hypotension. The patient has severe pain in the temples and eyes, the syndrome has a negative effect on hearing, and the person may experience sound hallucinations.
- Neurocircular dystonia. In addition to pulsation in the temples, the patient develops “white spots” before the eyes, the limbs become cold, and there is pain in the heart area, which is almost impossible to neutralize with simple medications. The condition periodically worsens.
Often, various irritants become the source of painful discomfort in the head area. The following factors can provoke the development of unpleasant discomfort:
- Carbon monoxide toxicity. The main symptom of poisoning is bilateral spasms in the temporal region, dizziness, shortness of breath, nausea, and problems with fine motor skills. This condition poses a serious threat to the patient, and, therefore, he urgently needs the help of a qualified doctor.
- Hunger. If the patient has not eaten for more than a day, he has a severe headache, temples throb, dizziness and malaise appear. He may faint.
- Height. While staying on the mountain, over 4 km, a person begins to worry about high blood pressure and his temples hurt. Such a condition can pose a threat to him due to a constant lack of oxygen and the likelihood of increased intracranial pressure.
- Airplane. Most people suffer from intense spasms in the temple area during and after a flight. This “irritating” phenomenon occurs as a result of intracranial pressure. The discomfort disappears 2-3 hours after landing.
Pressure in the temples is very often observed when immersed in water to a significant depth. If the pathological condition occurs constantly and does not go away for a long time, you must seek medical help.
Prevention
Until now, preventive measures are unknown.
Attention!
With every unusual condition in which there is a headache, pressure on the temple/temples and visual disturbances occur, something needs to be done! That is why it is advisable to contact a specialist as soon as possible. In particular, with inflammation of the temporal artery, attention should be paid to ophthalmological symptoms. If you experience double or blurred vision, see your doctor immediately. Delay in treatment can lead to permanent blindness.
Lifestyle correction
In 90% of cases, pressure in the temples can be easily prevented if you follow a number of recommendations as a rule. This will prevent the appearance of unpleasant sensations, will have a general strengthening effect on the body, and will have a positive effect on the functioning of the brain.
Prevention of pressing sensations in the temples:
- quitting smoking, drinking alcohol, coffee, energy drinks;
- the use of relaxation techniques - yoga, meditation, breathing exercises, spa;
- alternating periods of work and rest - night sleep of 7-8 hours, refusal of daytime rest, elimination of physical and emotional overload;
- inclusion in a sports regime;
- reducing eye strain, performing exercises to relax the eye muscles while working.
Particular attention should be paid to following the rules of a healthy diet. By eliminating foods that are potentially dangerous due to chemical additives from your diet, you can not only get rid of chronic pressure in your temples, but also prevent the development of a number of chronic conditions.
If there is a lot of pressure on your temples, you should not endure the unpleasant sensations. The peculiarity of the symptom is that under the influence of negative emotions it will only intensify. It is better to use one of the available methods to combat pain or take a pill.
The main and most pressing causes of feeling pressure in the temporal region include:
1. Arterial hypertension is a disease characterized by chronically high blood pressure. People with primary arterial hypertension, in addition to its main symptoms, often suffer from constant headaches in the temporal region. To correct blood pressure levels, you need to follow a diet with a limited salt content, no more than 5 grams of a teaspoon per day, dosed physical activity, walking in the fresh air, adhering to the recommended therapy by your doctor, giving up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages . The danger of arterial hypertension is a hypertensive crisis. During a hypertensive crisis, the headache becomes diffuse and is accompanied by dizziness, tinnitus and other neurological symptoms.
2. High intracranial pressure can also cause constant headaches and a feeling of pressure in the temples. Increased intracranial pressure is caused by swelling or inflammation of the brain, hematoma in the cavity of the cranium, accumulation of blood in the vessels of the brain due to intoxication, hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, foreign bodies, various developmental anomalies, hydrocephalus, meningitis.
3. Stress can also cause headaches, but these headaches will be psychogenic in nature, the so-called tension pain. When a patient complains that something is pressing on the temple area, as if it is bursting from the inside. To eliminate this factor, rest is necessary; in some cases, sedatives and sedatives like valerian will be used to combat this disease. It is better to choose a remedy made from natural ingredients; herbal teas based on peppermint or other herbs can also help.
4. Long-term intoxication with alcohol, nicotine, salts of heavy metals, various vapors of toxic gases. To eliminate constant pain in the forehead and temples in this case, it will be enough to remove the irritating factor. Often the cause may be acute poisoning, for example, with methanol, which in turn can lead to loss of vision and other more serious consequences.
5. Head injuries can also give such symptoms. Traumatic brain injuries and bruises can vary in severity, ranging from mild to extremely severe. In such cases, when asked “Where does it hurt?”, a person will not be able to name a specific area of the head; most likely the pain will be diffuse. In such cases, it is necessary to do a computed tomography or MRI, or, in extreme cases, an x-ray. The most common cause of head injury is road traffic accidents, followed by fights while intoxicated.
6. Brain tumors also require immediate additional and instrumental examination. Headache in the frontal region and a feeling of pressure in the frontal region are some of the alarming symptoms of this pathology. A tumor can be either benign or malignant. A malignant tumor is prone to metastasis and the brain is one of the favorite places for metastases, such places also include the skeletal system and liver.
7. Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels due to the formation of plaques is fraught with stroke. Even if the notorious atherosclerotic plaque closes the lumen of the vessel by at least half, complaints of dizziness, tinnitus, headaches of varying duration and intensity in the frontal and temporal parts of the head appear, and to this is added excessive anxiety, decreased performance, sleep inversion, decreased memory and attention.
8. The hormonal cause of headaches occurs in women during menstruation or menopause. During such periods, a woman is susceptible to stress, her hormonal levels are unstable, not only her head hurts, her whole body can hurt, and other complaints may also come to the fore.
9. Climate and environment play an important role in human life. Excessive heat and cold have a detrimental effect on the human body; the blood vessels do not know how to react to temperature changes and, by narrowing, provoke a new attack of headache. You should treat your body more carefully and avoid such changes.
10. Unbalanced diet and fasting: some foods, especially those containing high cholesterol, can provoke headaches in the forehead and temples, especially if there is arterial hypertension and high blood cholesterol. Fasting is absolutely contraindicated for frequent, severe headaches, since the brain ceases to receive the required amount of nutrients necessary for its further productive work.
11. Hereditary factor. Genetic predisposition plays a crucial role in the development of any disease and headache is no exception in this case. If this is a common occurrence in a family, then avoiding this fate is much more difficult. The true etiological factor should be found and further treatment should be carried out according to it. Idiopathic headaches can also occur, but the likelihood and prevalence of this disease is very low, and the pain is localized in the frontal region or diffusely.
Pressing pain can hinder your actions
Tinnitus and temple headaches
There is pressure on the temples, a headache and noise in the ears – is there a connection?
Tinnitus (tinnitus) is often accompanied by a condition in which there is headache (particularly in the temples), since, as a rule, both problems have the same underlying cause - stress. However, when tinnitus is associated with a temporary headache that originates from the temporal bone, has quite complex anatomical structures and is located above the ear, thus directly related to hearing, the problem must be specifically addressed.
The head is heavy and presses: reasons, how to get rid of it
Heaviness in the head may indicate the development of the disease. Similar symptoms can appear as a result of overwork, poor diet (thirst, hunger), stress, or injury to the head.
If the symptoms are caused by a disease, a neurologist will help determine the exact cause.
More often, such a symptom occurs as a result of pathological processes that affect parts of the central nervous system, less often when the disease affects other organs and systems.
Characteristics of the condition
A heavy head is a condition that patients describe as a feeling of unclear, cloudy consciousness. The head feels as if it is made of cotton – a sensation similar to what occurs in an arm or leg when the limb is numb. Often the head feels as if it is leaden with a feeling of pressure from within. Symptoms are complemented by retardation of thinking and impaired orientation in space.
In this case, a feeling of heaviness in the eyes and head is accompanied by a deterioration in cognitive abilities. The person does not think well, his memory and mental activity deteriorate.
It is difficult for him to concentrate, concentrate on work, perceive and process new information.
Constant fatigue and a feeling of cloudiness in the head interfere with communication, performing household and job duties.
Causes
The causes of heaviness in the head are often associated with physical and mental fatigue. In this case, the discomfort goes away spontaneously after a long, complete rest.
Cloudiness in the head occurs due to an unhealthy lifestyle (abuse of alcohol, drugs, physical activity at night, irregular diet) or due to a pathological process.
Common causes of development:
- Lack of sleep, sleep disorder. Often, a feeling of vagueness inside the skull appears after prolonged sleep, which is usually associated with poor rest hygiene or venous stagnation. To prevent discomfort, it is necessary to ventilate the room before going to bed and choose comfortable bedding (pillow, mattress).
- Poor nutrition. A deficiency of important nutrients - vitamins, microelements, protein, healthy fat (olive oil, avocado, sea fish) leads to the feeling that the head is plagued. Disturbances can be triggered by the consumption of foods that cause an allergic reaction.
- Chronic stress. Regular exposure to stress has a negative impact on health, leading to the development of depression, insomnia and discomfort in the skull area.
- Taking pharmaceutical drugs and nutritional supplements. Some medications (anticonvulsants, painkillers, statins, antidepressants, sleeping pills and sedatives, acetylsalicylic acid) provoke the development of fuzzy head syndrome.
- Increased blood pressure levels. Any deviations in blood pressure values from the norm can provoke a feeling that there is cotton wool inside the skull.
- Meniere's disease, vestibular disorders. Pathologies of the vestibular system are one of the likely causes of the feeling of a cloudy head.
- Thyroid dysfunction. Excess and lack of hormones lead to an unpleasant feeling inside the skull.
- Concussion, brain contusion. Suffered TBIs cause a condition where the head is dizzy, there is pressure on the ears and there is a pressing pain in the area of the skull. Disturbances occur in the acute period and can be observed much later than the episode of TBI, transforming into post-traumatic syndrome.
The feeling of a heavy head can occur against the background of inflammatory processes occurring in the respiratory, visual and hearing organs. Pathologies of the heart and vascular system can provoke the appearance of symptoms. Damages to the joints and other structures of the musculoskeletal system are often accompanied by a condition where clouding occurs in the head.
Possible diseases
Discomfort in the head occurs due to metabolic disorders. For example, a lack of glucose, which is a nutrient for nerve tissue, leads to a feeling of foggy haze in the head.
Additional signs include irritability, increased sweating, weakness, rapid heartbeat, inability to concentrate, and confusion.
Associated symptoms will help make a differential diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Vegetovascular dystonia
A heavy head is a symptom that is often observed with VSD. Vegetative-vascular dystonia develops as a result of disruption of the regulatory functions of the central nervous system and is accompanied by a change in the tone of the vascular wall.
Associated symptoms: pain in the heart area, general weakness, increased fatigue, respiratory failure (rapid, shallow breathing, feeling of lack of air), cardiac arrhythmia (rapid heartbeat).
Symptoms may be observed: darkening of the eyes, feeling of chills or heat, tremors of the limbs.
Impaired blood circulation and liquor dynamics
Pathology caused by venous congestion in the skull area is manifested by heaviness in the head, dizziness, and weakness. Patients describe sensations as if they were pressing, bursting from the inside.
The condition is accompanied by a dull pain in the area of the skull.
In most cases, the pathological focus is limited to the occipital region, sometimes unpleasant sensations spread throughout all parts of the skull.
If the venous outflow is disrupted, the constant feeling of a heavy head, which hurts and is dizzy, intensifies if the patient remains in a horizontal position for a long time, for example, after a night's sleep.
With an increase in intracranial pressure, patients complain of a feeling of fullness, noise, ringing in the ears, sound signals supplied from the outside are perceived painfully, as are light stimuli.
Symptoms are common: meningeal syndrome, confusion, repeated bouts of vomiting.
Vertebrogenic pathologies and diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Osteochondrosis (destructive-dystrophic changes in bone tissue) and spondylosis (formation of pathological growths on bone tissue) of the cervical spine are manifested by pain.
Pain in the spine area increases after physical activity. Pathologies are characterized by the appearance of pain in the skull area, a feeling of compression, fullness, and heaviness in the head.
Associated symptoms: dizziness, muscle spasms, limited mobility of the spinal column, numbness and tingling in the extremities.
Fibromyalgia is a disease of unknown etiology, which is characterized by painful sensations in the skeletal muscles, most often in the occipital area, in the back, neck, shoulders, hips, and chest.
Associated symptoms: heavy, cloudy and not normal head, confusion, increased fatigue.
Patients complain of muscle stiffness in the morning, poor health, deterioration of cognitive abilities (confusion, inability to concentrate).
Neurotic disorders
The feeling of an empty head often occurs with neurasthenia, a progressive psychopathological disorder that develops against the background of chronic stress or during treatment of a somatic illness.
Often, such disorders are detected in patients prone to perfectionism.
The reasons for the feeling of a heavy head and the state when there is pressure in the skull from the inside, or you want to quickly think, but your thought processes are inhibited, are associated with asthenia of psychogenic origin.
Associated symptoms: heavy head, dizziness, general weakness, daytime drowsiness, night insomnia.
Symptoms are often observed: pain in the skeletal muscle area, feelings of depression and anxiety, increased sensitivity to light and sound stimuli, sleep disturbance.
Patients are unable to control their emotions and tend to quickly lose self-control. In the later stages of the course, lethargy, apathy, and loss of interest in the surrounding reality are observed.
Systemic diseases
Lupus erythematosus is a chronic inflammatory disease associated with autoimmune disorders. Symptoms depend on the location of the lesion. Damage to the joints is manifested by pain and deformation of bone structures. Damage to the skin is manifested by characteristic erythema (redness of the skin), alopecia (hair loss).
Damage to the respiratory system is accompanied by recurrent pleurisy. Neurological symptoms include a feeling of a cast-iron head, neuropathy, psychosis, convulsive syndrome, aseptic meningitis, cerebellar disorders (ataxia - impaired coordination when contracting a muscle group, motor coordination disorder).
Vestibular disorders
Constant dizziness and heaviness in the head are symptoms characteristic of diseases of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
Non-systemic forms of dizziness are accompanied by a feeling of imminent loss of consciousness, feelings of lightheadedness, fog and heaviness inside the skull.
Such symptoms are typical for diseases of the inner and middle ear, which develop under the influence of a variety of associated factors.
Systemic forms arise as a result of pathological processes affecting parts of the vestibular apparatus - structures located in the area of the inner ear, and parts of the brain responsible for the perception and processing of external information.
Associated symptoms depend on the type of pathology.
For example, with Meniere's disease, attacks of dizziness and a feeling of a cotton head are complemented by deterioration in hearing acuity, noise, ringing in the ears, and impaired motor coordination in the later stages (staggering, unsteadiness when walking).
In addition to the main symptoms, peripheral dizziness is usually manifested by autonomic disorders - rapid heartbeat, jumps in blood pressure, increased sweating, hyperemia (redness) of the skin. When parts of the brain responsible for processing information about the position of the body in space are damaged, signs are usually detected: imbalance, unsteadiness of gait, pain in the skull area, nausea, vomiting.
Diagnostics
Your doctor will explain why your head feels heavy and feels tense. A diagnostic examination is prescribed taking into account the dominant symptoms.
To identify structural changes in brain tissue, examination is carried out in the format of MRI, CT, and ultrasound. X-rays are often taken, due to the need to study the condition of the bone structures of the skull and spinal column.
The state of the circulatory system of the brain is determined using Dopplerography and angiography.
A blood test (general, biochemical) shows the functionality of the kidneys and liver, the concentration of glucose, cholesterol in the serum, the rate of coagulation and other characteristics of the blood.
The attending physician will tell you how to get rid of heaviness in the head, taking into account the results of a diagnostic examination and other factors (age and general health of the patient, the presence of concomitant pathologies).
Why does tinnitus occur with headaches in the temples, and what to do about it?
Factor #1 – stress
Stress is often responsible for conditions where there is ringing in the ears and headaches (mainly in the temporal region). The pain is not so severe as to prevent a person from doing something, but there is little pleasure in it.
High levels of ongoing stress and anxiety in people whose profession involves talking on the phone constantly puts them at risk, and they are the most vulnerable to developing tinnitus.
Medicines and sedatives can relieve symptoms, but on the other hand, they have many side effects.
Factor No. 2 – insomnia
Some case studies point to lack of sleep as a trigger for the development of tinnitus. Often, due to international business trips, people experience lack of sleep due to time zone changes; they are most at risk of becoming victims of this disease. Call center workers who frequently miss sleep due to shift work also often report conditions that include ringing in the ears, pressure in the temples and headaches.
True, in case of physical discomfort due to the above reasons, there is no need to do anything or take medications. Relief will come when a person rests for at least 7 hours.
Factor No. 3 – subarachnoid hemorrhage
We are talking about bleeding into the space between the brain, which can occur spontaneously due to a burst cerebral aneurysm or severe traumatic brain injury. However, such cases are rare, accounting for about 1 in 15,000 cases of tinnitus today.
Factor No. 4 – spinal tap
A lumbar puncture is a test in which cerebrospinal fluid is collected using a needle. After it, a severe headache may appear, lasting up to 12 hours after the procedure. The painful sensations are very intense, preventing the person from doing practically anything.
Pressing on the temples: causes of pressing pain (primary and secondary), how to treat
Headache (GB, cephalalgia), which presses on the temples, squeezes the entire head with an “iron hoop”, moves to the back of the head and to the eyes, probably visits almost all of us from time to time. According to statistics, every second inhabitant of the planet has ever had similar problems, even if he is considered relatively healthy.
Why do you feed pharmacies if hypertension is afraid of the usual like fire...
Tabakov has revealed a unique remedy against hypertension! To reduce blood pressure while preserving blood vessels, add to…
This pain is extremely unpleasant, intense, and does not go away on its own. Sometimes it puts so much pressure on you that you don’t feel like working, or having fun, or taking active rest at such moments. You need to take the pill immediately and lie quietly for a while to feel relief. But pills do not always help; there are types of cephalgia that can torment a person so much that he begins to think about suicide (cluster headaches).
However, what is the reason for these unpleasant phenomena? What to do, how to treat this? Is it possible to get rid of this headache once and for all?
She will unexpectedly appear when you least expect her...
Unfortunately, this is not about love or how “every evening will immediately become amazingly good.” Quite the contrary. A headache (temple, back of the head, eyes), accompanied in some situations by nausea, can turn into a big problem for a person, reducing his performance and quality of life, especially if he feels its presence constantly.
For the most part, the sensation of pressing pain in the temples occurs suddenly, without any warning, so it can come as a complete surprise to a person. For example, he went to bed quite healthy, and in the morning, when he could still soak up a warm bed for an hour or two before the alarm went off, he woke up from a pressing temporal pain. Often pain occurs not only in one area, sometimes something presses on the back of the head and temples, sometimes cephalgia is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms (pulsation in the temples, nausea, flashing spots before the eyes, intolerance to bright light or loud sounds, pressure on the eyes, etc.). d.).
The clinical picture and nature of the pain mainly depend on the causes that caused it, and it should be noted that there are many of them (some authors claim that there are more than fifty of them). We should probably agree with this statement, since cephalgia can be primary and secondary, and is often formed against the background of another pathology, which also has its own causes.
They cannot be predicted in advance
The cause of pressing pain in the temples can be a variety of life factors, sometimes beyond our control, therefore unpredictable and uncontrollable. And they do not always result from some serious pathology. For example:

- Changes in weather conditions: changes in atmospheric pressure, changes in weather conditions (suddenly a strong wind rose, which blows for a day, or two, or more, humidity and air temperature went up or down) - weather-dependent people feel all this very well. Many of them probably already have a history of such a symptom complex (it is not particularly considered a disease) such as vegetative-vascular dystonia. And throughout the entire period of turbulent natural phenomena, these people feel a headache, which puts pressure on the temples and eyes, discomfort may appear in the occipital region and other symptoms may develop (changes in blood pressure, nausea, noise effects);
- Great physical stress associated with heavy lifting or frequent head tilting will after some time result in pressing pain in the temples;
- Stressful situations and psycho-emotional stress can provoke pressure in the temporal parts and occipital region, create discomfort in the eyes, and also cause nausea and a gag reflex;
- Pressing pain in the temples can occur during periods of both short and long fasting;
- Gives similar symptoms and mental stress. Troubles, when an unknown force presses on the temples and eyes, often haunt students during exams, most of all those diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Similar phenomena occur from time to time in people whose profession is associated, for example, with a microscope or computer. Of course, this does not happen all the time, otherwise a person simply would not be able to work in this place, and the work regulations stipulate taking 15-minute breaks every hour. However, anything can happen (what if it’s an emergency?), and a person, with the goal of absolutely completing the task, is forced to ignore the instructions, and then after a few hours of intense activity he will probably feel his temples hurt and pressure on his eyes. The same type of pain is observed in jewelers, assemblers (on the assembly line), and drivers;
- Traveling in transport (engine noise, the sound of train wheels, stuffiness in the cabin of a car or carriage). Especially, people suffering from certain pathologies are sensitive to flights. Not only does the airliner itself rise to a high altitude, causing a change in blood pressure in such passengers, but passengers, while traveling, end up from one climate zone to another. As for water transport, everyone knows (some have experienced it, some have just heard) “seasickness”. True, here there is no pressure on the temples and nausea, but simply nausea, vomiting and dizziness. Headache from motion sickness is extremely rare;
- A long stay in a stuffy room, in the sun (relaxing on the beach, working in the field, which, in addition, is associated with frequent bowing of the head) can lead to the fact that in the evening a person will tell how his temples hurt and there is pressure on his eyes;
- Functional disorders of the endocrine system due to physiological conditions leading to hormonal changes (puberty, pregnancy, lactation, menopause) are transient conditions, so pressing pain in the temples and painful sensations in other localizations may disappear over time, which means the disease will also disappear;
- In some circumstances, it is difficult to draw the line between accident and pathology (we will classify it as unforeseen events), but various types of poisoning (food, alcohol, nicotine, medicinal, etc.) respond to pressing pain in the temples. The most common cause of such symptoms is intoxication with tobacco smoke and alcoholic beverages, especially low-quality ones (heavy smokers and people prone to alcohol abuse know how in the morning, after “too much”), there is pressure on the temples and nausea.
In other cases, the intervention of various diseases can be traced, sometimes quite serious, requiring long and persistent treatment, which, unfortunately, does not always lead to success.
Primary pathology: migraine and cluster headaches
The cause of hemicrania (migraine) is instability of the tone of blood vessels, but it does not cause a constant headache. Symptoms appear periodically and are often associated with the influence of provoking factors (stress, menstruation, exercise, weather changes, loud sounds, bright lights, smells). Pain in this pathology is focused in a specific part (in half of the head - one-sided), hence The name is hemicrania, that is, “half of the face.” The favorite place of migraine pain is the frontotemporal or orbital region, therefore, with a migraine, it often presses on the temples and makes you feel sick (nausea often ends with vomiting), the temples hurt and puts pressure on the eyes, and there is a lot of pressure in one temple - left or right, the other half, not affected by pain - rests.

Cluster (beam) cephalalgia is a whole “series” that can safely be called a “horror movie”. A series of paroxysms, which follow one after another and continue for several days, drive a person into a frenzy. This terrible “series” ends the same way it began – suddenly and without any prerequisites. Cluster pain, as with migraine, is one-sided. Acute pain pierces one temple, one eye, and it doesn’t matter - left or right, the pain is so strong that the other half does not feel well. Cluster pains are “wild”, extremely painful, 15-20 minutes of attack seem like an eternity... What if you imagine that an attack can last up to 3 hours? This also happens. Then you can go crazy and lose your life...
When the cause is another pathology
There are often cases when pressing pain in the temples (or pressing in one temple - left or right?), nausea, discomfort in the eyes indicate some specific diseases, especially if these symptoms are not an isolated episode, but are present constantly or come periodically, but often. Again, this can be a wide variety of pathologies, ranging from arterial hypertension to a brain tumor. Thus, we can identify the following reasons for the appearance of such conditions (for ease of reading, the reasons will be divided into groups).
Age, blood pressure, hormones
Age
Pressing pain in the temples can come as a result of age-related changes that affect the condition of the vascular walls. Typically, among older people, few people remain with “clean” blood vessels; to a greater or lesser extent, they are affected by atherosclerosis, which means that blood circulation in the brain becomes difficult, and pressing pain in the temples occurs. And not only. The back of the head and temples often hurt, the pain spreads to the eyes, forehead and other parts of the head.
Arterial hypertension (AH) and hypertensive crisis
Hypertension quite often causes discomfort in the occipital region (by the way, hypotension too, but the state of low blood pressure differs in the nature of the pain and other symptoms). Pressure on the back of the head and temples with a sharp increase in blood pressure, although outside of such excesses, hypertensive patients usually do not particularly complain of headaches.
The rapid rise in blood pressure during a hypertensive crisis creates the feeling that discomfort in the occipital region, to which the patient is already accustomed and does not consider pain, recedes into the background, but it is replaced by other symptoms: there is strong pressure on the back of the head, and the pain spreads to the temporal part of the head. Within a short time, as the crisis develops, the headache becomes simply unbearable, pressing on the temples and nauseating, breathing becomes impaired, the heartbeat quickens, the patient is in fear and anxiety for his life, it seems to him that he is leaving this world.
Intracranial hypertension
The following types of pain are typical for increased intracranial pressure:
- Presses on the back of the head and temples;
- Temples hurt and pressure on eyes;
- The pain with ICH is bursting, so it seems that the skull is under pressure from the inside.
Glaucoma
The temples hurt and put pressure on the eyes when intraocular pressure increases. Known since ancient times, glaucoma is currently still at the top of the ranking of ophthalmic diseases, which is facilitated by many unfavorable environmental factors and everyday life. The patient's complaints boil down to the following:
- Presses on temples and eyes;
- Fatigue is noted at sunset or earlier - when there is a load on the organ of vision;
- Episodes of blurred vision occur;
- There is a feeling of fullness in the eyes;
- Tearing (attacks);
- Frequently changing glasses (“I haven’t had time to use them, but now I have to go get new ones”).
In most cases, the patient first of all expresses such complaints about his eyes to the therapist, who will most likely have a reason to send the patient for a consultation with an ophthalmologist. By the way, with glaucoma it hurts on the corresponding side and presses in one temple - left or right.
Pathological hormonal imbalances
Cephalgia in diseases of the endocrine system is very often accompanied by fairly high blood pressure, nausea and vomiting. The primary cause may be various pathologies - pheochromocytoma, carcinoid syndrome, adrenal insufficiency, thyroid disease, etc.)
Impact of infection
Sinusitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis
Among infectious causes, an important place is occupied by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which very often act as a complication of the infectious process. A headache of this type occurs in pathologies related to such a branch of medicine as otorhinolaryngology. Surely, people suffering from chronic sinusitis and other ENT diseases localized in this area know how during exacerbations the temples hurt and there is pressure on the eyes.
Viruses
Viral infections that can be contracted after contact with infected people (usually during certain seasons, during epidemics). More often, a viral infection manifests itself against the background of hypothermia and a decrease in the body’s defenses. ARVI and influenza are considered typical representatives of mass viral infections - it is unlikely that anyone has never felt their symptoms at one time in their life, there is pressure on all parts of the head, there is fever, coughing, and sneezing, which makes the temples hurt even more and presses on the eyes.
Tinnitus, headache and temple pressure: secondary factors
Contrary to early claims that explained unpleasant episodes of tinnitus as “all due to stress,” it is now known that a family history or group of conditions known as temporomandibular disorders (TMDs) may be responsible for tinnitus.
It was also found that headaches and tinnitus are symptoms of the disorder, not the disorder itself. That is why treatment of these symptoms will be most effective if you begin therapy with the treatment of VNR.
In addition to the fact that the temporomandibular joint is located very close to the human ear, there are a group of mechanisms that cause the symptoms to appear. For example, the nerve muscles that are directly connected to the ear originate at the intersection of the nerves that serve the muscles of mastication. With this arrangement, it is easy to predict that a slight disorder could lead to changes in the muscles associated with the ear.
It has been observed that certain types of ototoxic drugs that contain antibiotics such as aminoglycosides, vancomycin and erythromycin, quinine, and chemotherapy may be responsible for tinnitus and cause unpleasant temple headaches in older age group. The toxins present in most of these medications cause irritation in the temporal part of the skull and thus stimulate pain and discomfort in this area.
Whiskey crushes and dizzy
This is one of the most common complaints encountered by a neurologist.
According to statistics, more than seventy-five percent of residents of developed countries experience dizziness and pain in their temples.
Moreover, the reasons for this phenomenon can be very different (sometimes combined), here are the most common of them:
- Changes in the tone of cerebral vessels;
- Migraine;
- Intracranial pressure;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- A woman's menstrual cycle;
Sometimes pain in the temples appears after eating certain foods. This is due to the fact that monosodium glutamate is added to some processed foods. According to experts, it is this supplement that can cause pain in the temples.
In addition, increased sweating, reflex tension of the facial and jaw muscles, as well as shortness of breath are added to this symptom. About half an hour after eating, a throbbing or squeezing dull pain forms in the temples, which only increases over time
.
In some cases, the pain radiates to the eye or ear
. Here are the most common foods that contain monosodium glutamate:
- Gravy and sauces;
- Spices and seasonings;
- Semi-finished products;
- Some crackers and potato chips;
- Meat-based products;
Also, some doctors claim that dizziness and pain in the temples can be a consequence of eating chocolate. It contains a huge number of different substances that can, in one way or another, influence the occurrence of migraines.
For example, the substance finylethylamine can constrict blood vessels, thus causing pain, and cocoa beans contained in chocolate can reduce glucose levels and provoke hypoglycemia. Caffeine may also contribute to headaches. Therefore, it is recommended to refrain from eating such food at least for a while to determine the cause of the pain.
Prevention of headaches
You should stick to your diet relatively and exclude some foods from your daily diet. These products include: smoked meats, nuts, red wine, cheese. These foods contain tyramine. And tyramine, in turn, provokes headaches. Also, because of phenylethylamine, chocolate and chocolate candies should be excluded. Foods with excessive amounts of spices, hot seasonings and sauces. Avoid aspartame, which is found in all products that contain sweetener.
You need to ventilate the room well or find time to walk in the fresh air. Sometimes some time in peace and quiet is enough for the headache to go away. Therefore, you should lie down and try to relax, tune in to positive emotions. Do a self-massage of the scalp and face. Prepare a soothing tea based on mint or chamomile, after which you can try to fall asleep. A good option, especially during the hot season, is a cold compress with lavender essential oils. The compress should be applied to the forehead, temples or the place where it hurts for 20-30 minutes. Also, during a headache attack, it is recommended to avoid: alcohol, smoking, and drinking several analgesic tablets, since an overdose of the drug can lead to more serious side effects.
The rhythm of modern life forces the body to adapt to various conditions, including those beyond its control. Often, people living in megacities experience various ailments or health-related problems from time to time.