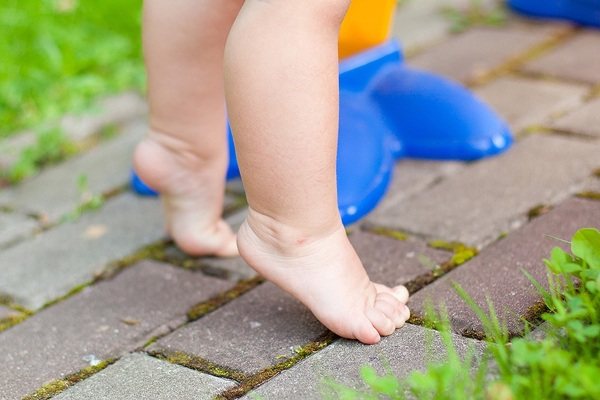
Pyramidal syndrome or pyramidal insufficiency syndrome is also called ballerina tiptoe syndrome or equinus foot placement.
This violation may be the result of a whole range of factors. In the vast majority of cases, it is accompanied by muscular dystrophy of varying degrees, associated with hypertonicity of the lower leg and foot.
Damage to the pyramidal tract with bilateral muscular dystonia is usually diagnosed in newborns or children in the first year of life, less often it appears in children two to three years old.
Kinds
Pyramidal insufficiency in children of all age groups is classified into 2 main types. This is a congenital type of disease, as well as an acquired pathology of the medulla oblongata.
Congenital
This type of pyramidal insufficiency is distinguished by the fact that dysfunction of the central nervous system does not yet occur at the stage of intrauterine development of the child, when the process of formation of tissues of the medulla oblongata occurs.
This type of syndrome can occur under the influence of a large number of factors related to the lifestyle of a pregnant woman, poor heredity or the negative impact of infectious microorganisms.
Congenital pyramidal insufficiency is difficult to treat, since in most cases the child has abnormalities in the development of the central nervous system, the correction of which is impossible. In this case, techniques are used that improve the function of the muscles of the lower extremities, and measures are also taken to prevent further progression of the disease.
Acquired
The acquired type of pyramidal insufficiency syndrome is characterized by the fact that initially the child is born completely healthy. Further development of the neurological syndrome is associated with long-term or short-term exposure to negative factors that caused the destruction of a certain number of medulla oblongata cells.
This type of pathology can be eliminated by treating the underlying disease, which disrupts the functions of the central nervous system and also prevents the full functioning of the muscles of the lower extremities. Symptoms of acquired pyramidal insufficiency appear immediately after a decrease in the performance of medulla oblongata cells.
How are children with this diagnosis treated?
Basically, for children diagnosed with pyramidal insufficiency, the doctor prescribes different procedures. You may also need orthopedic means, with the help of which parts of the body are given a physiological position, and balneotherapy (health baths).
To reduce muscle tone and strengthen muscles, doctors recommend acupressure and relaxation massage, a course of which is taken every 6 months.
Every day, parents should do special health-improving and preventive exercises with their child.
If necessary, doctors can prescribe vitamins, vasoactive agents (for microcirculation) and drugs that improve the process of metabolic breakdown.
Surgeries are resorted to only when the doctor has diagnosed:
- brain or spinal cord injuries/tumors
; - acute cerebrovascular accidents
that cannot be cured by chemical, physical and biological means (for example, thrombosis or intracerebral hematoma).
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms of pyramidal insufficiency in children are diagnosed by a neurologist based on the results of an initial examination of the child, as well as hardware examination of individual areas of the brain. The table below describes the main signs of this disease, which occur in 95% of patients with a similar diagnosis.
| Symptoms of pyramidal insufficiency | Features of clinical manifestations of the disease |
| Careful and unsteady walking on toes without using heel support | This symptom appears all the time, since the child is not able to stand on the entire area of the foot due to hypertonicity of the calf muscles. As the child's body matures, developmental disorders of the lower extremities become more pronounced. Signs of curvature of the bone tissues of the foot may appear, which in turn will require the use of special orthopedic shoes. |
| Weakened grasp reflex | In this case, the sick child cannot hold light toys, a spoon and other objects that are not heavy for his age. Such symptoms indicate that organic damage to the cells of the medulla oblongata disrupted the functioning of not only the muscles of the lower extremities, but also spread to other elements of the musculoskeletal system. |
| Tremor of individual parts of the body | The appearance of signs of tremor occurs at any stage of the physical development of the child’s body. The affected area includes the muscle tissue of the lower extremities, arms and facial disc in the area of the chin. At the stage of the initial examination of a sick child, tremor of the toes and hands, and abnormal mobility of the muscles of the lower part of the face are detected. The appearance of this symptom indicates a severe form of pyramidal insufficiency syndrome with damage to a large number of medulla oblongata cells. |
| Throwing back the head | A child suffering from congenital or acquired pyramidal insufficiency is unable to hold his head up independently. This sign is detected by the patient’s parents or pediatrician as early as 1 year of the baby’s life. The appearance of such symptoms is the first signal about the need for a comprehensive examination of the child’s central and peripheral nervous system. |
| Rolling up socks |
|
Quite often, making this diagnosis is complicated by the vagueness of the clinical manifestations of the syndrome.
Especially if the child is under 9 months of age. Once the baby reaches the age of 1 year, the symptoms of the disease are expressed more clearly, since the pediatrician or pediatric neurologist is able to identify a greater number of pathologies in the development of the muscles, nervous system and musculoskeletal system of the patient.
Pyramidal insufficiency in adults and children: is the diagnosis valid?
Sometimes neurologists make diagnoses whose names need to be explained in detail due to their pronounced specificity.
One of these complex terms is pyramidal syndrome, or pyramidal insufficiency.
What it is? Usually the doctor at the appointment does not have the opportunity to explain all the details, so we will talk about this disorder ourselves, about its causes, symptoms and signs, as well as about the treatment of the disease.
But the first thing that needs to be recalled is how such a term as “pyramids” appeared in neurology. Let's talk about this in more detail.
Where did the pyramids come from?
In fact, in the human brain there are not only the pyramids themselves, but also pyramidal pathways and the intersection of these pathways of the same name.
The most important, basic and most important is the pyramidal path system . This is the name of the descending nerve bundles that go from the neurons of the cerebral cortex down to the muscles that perform voluntary, that is, conscious movements.
In addition to voluntary, somatic movements, the influence of these neurons is such that a reflex arises that controls muscle tone.
All other tendon reflexes are closed at the level of the corresponding segments of the spinal cord and do not involve the reflex system of the pyramidal tract, that is, they are underlying.
However, when this pathway is damaged, they change, since the inhibitory influence of the upper sections disappears (with paralysis) or weakens (with paresis, or partial paralysis).
Some of the fibers in the brain switch to the second neurons of the cranial nerves, and the vast majority of them go down to the bodies of neurons, which are motor and lie in the anterior horns of the spinal cord along its entire length. The real anatomical name for this tract is the corticospinal tract, or corticospinal tract.
This is a thick bundle of white matter (axons - long processes of nerve cells) that originates in the motor cortex, namely in the precentral gyrus.
Since the “hole” in the skull, or foramen occipitale magnum (foramen magnum), is not intended for “slipping dumplings through”, but for connecting the brain and spinal cord in a narrow volume of space, the pyramidal tracts thicken at the level of the cerebral peduncles. When passing to the medulla oblongata, they form true lateral ridges on both sides of the medulla oblongata, very similar to two inverted pyramids. This is where the name of the tract, the intersection, and the diagnosis came from.
In the lower part of the medulla oblongata, a critical event occurs that must be taken into account when diagnosing and treating pyramidal insufficiency in adults and infants, namely: about 80 - 90% of all fibers on each side pass to the opposite side. Therefore, most fibers from the right hemisphere after decussation become left-sided, i.e. go from the left. This phenomenon is called pyramidal decussation. As a result, the cortex “supplies” both fibers from its side and the opposite side to the muscle.
If there is a break or disorder in the activity of the corticospinal bundle at any level - from the cortex to the spinal cord, then pyramidal insufficiency syndrome develops. However, the name “pyramidal insufficiency syndrome” or “pyramidal insufficiency” is incorrect from an anatomical point of view.
Clinical meaning of the syndrome
The practical meaning of all of the above is that the patient develops various disorders in the sphere of voluntary movements: from mild muscle weakness to complete paralysis.
Is this a disease? Of course not. This is simply a syndrome (that is, a set of signs or symptoms), and pyramidal insufficiency can occur in children and adults for a variety of reasons: from trauma and tumor to neuroinfection and simple immaturity of these pathways, which often happens in newborns.
What symptoms and disorders occur in this case?
Causes
Symptoms of pyramidal insufficiency in children appear in the first 1-3 years after birth.
The following causes of this disease are identified:
- congenital anomalies of the development of the central and peripheral nervous system of a child, when pathological changes in the structure of the tissues of the medulla oblongata occur at the stage of intrauterine formation;
- birth injuries of the skull bones, which led to partial dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- infectious diseases, the causative agents of which led to the destruction of the pyramidal cells of the medulla oblongata (the impact of this causative factor is possible at the stage of intrauterine development of the child, or infection with pathogenic microorganisms occurred after birth);
- complications that arose during the active phase of labor;
- intrauterine hypoxia of the child’s brain tissue;
- consequences of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- disruption of the process of outflow or production of cerebrospinal fluid of the ventricles of the brain, cerebrospinal fluid;
- intracranial hematomas;
- extraneous neoplasms in the tissues of the medulla oblongata, which are benign or oncological in nature;
- acute inflammatory process affecting the meninges (meningitis, as well as encephalitis);
A stiff neck is a symptom of meningitis. - hydrocephalus of the brain;
- genetic predisposition to the occurrence of this disease, if the child’s blood relatives have similar symptoms of pyramidal insufficiency syndrome;
- the negative impact of alcoholic beverages, drugs and tobacco products, which had on the child’s central nervous system during the period of intrauterine development (for example, if a pregnant woman had addictions);
- various types of traumatic brain injuries, regardless of the nature of their origin.
The cause of pyramidal insufficiency syndrome is determined by a neurologist during a diagnostic examination of the child. Eliminating the main factors that provoke dysfunction of the muscles of the lower extremities allows you to speed up the process of restoring full function of the patient’s legs, and also minimizes the risk of disease progression.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of pyramidal insufficiency in children are characterized by gait disturbances and increased or decreased muscle tone. To make this diagnosis, a neurologist performs an external examination of the patient, assesses the degree of reflex activity of the leg tissues, and the general sensitivity of the peripheral nerves.
Then the doctor prescribes instrumental research methods that can be used to detect pathological changes in the structure of the pyramidal cells of the medulla oblongata.
CT scan
Computed tomography is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing brain tissue, which reflects its functional state. This type of study makes it possible to see the presence of foci of organic damage to individual areas of the central nervous system responsible for the reflex activity of the muscles of the lower extremities and other parts of the body.

The examination is carried out using special medical equipment in the form of a computed tomograph. This is a completely safe diagnostic method, the average cost of which is 3,500 rubles.
Encephalogram
An encephalogram of the brain is carried out to assess the bioelectrical activity of the tissues of this organ.
This method of diagnosing children with pyramidal insufficiency allows us to determine the following types of pathological conditions of the central nervous system:
- the scale of the inflammatory process;
- irreversible changes in the blood vessels that supply brain tissue;
- extraneous neoplasms of malignant and oncological etiology;
- severity of consequences after previously experienced traumatic brain injury, surgery or stroke.
An encephalogram is carried out in an inpatient neurological department of a hospital or in a special diagnostic center, which has all the necessary material and technical resources. The average cost of this diagnostic method is 2500 rubles.
Biochemical and microbiological blood test
This type of laboratory test is prescribed for children with symptoms of pyramidal insufficiency in order to exclude the factor of infectious origin of this disease. Venous blood in an amount of 5-10 ml is used as a biological material for the study.
Biochemical and microbiological examination of blood reflects its cellular composition, as well as the possible presence of bacterial, viral and fungal microorganisms, the pathogenic activity of which can cause organic damage to the tissues of the medulla oblongata.
At the same time, the state of the child’s immune system is assessed. The price of this type of research ranges from 700 to 1350 rubles.
Spinal cord puncture
A spinal cord puncture is prescribed only in extreme cases, when, in addition to the main symptoms of pyramidal insufficiency, the child exhibits elevated body temperature, sluggish reflex reactions, general malaise, as well as convulsive twitching of muscle tissue throughout the body.
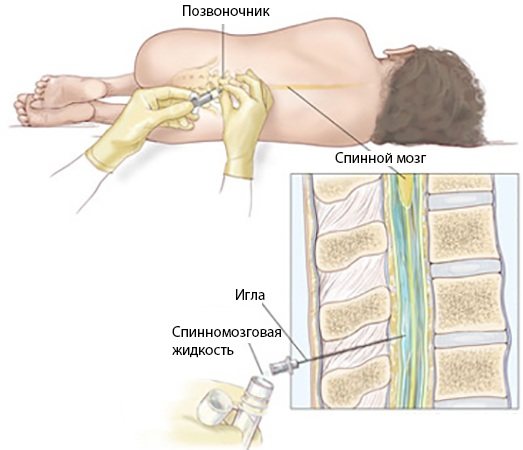
The presence of such signs indicates organic tissue damage to the medulla oblongata caused by meningococcal infection. Spinal cord puncture is performed under sterile operating room conditions.
The collection of biological material is performed by a surgeon of appropriate qualifications. Cerebrospinal fluid samples are sent to a microbiology laboratory to be tested for the possible presence of infectious or viral agents. The average cost of this type of diagnostics is 5,500 rubles.
Establishing diagnosis
Methods for diagnosing pyramidal insufficiency:
- (if there are cramps/spasms or the doctor suspects it);
- (used as an additional research method);
- (the neuromuscular system is checked by recording muscle potentials);
- (helps detect tumor processes);
- (reveals hidden convulsions that occur during sleep).
In addition to the above methods, tests will be required to confirm the syndrome.
Treatment methods
Symptoms of pyramidal insufficiency in children appear as the child grows older. Treatment of this pathology depends on the causes that provoked dysfunctional disorders in the tissues of the brain and muscles of the lower extremities.
To treat this disease, medications, surgery, and physical therapy methods can be used.
Surgery
This method of treating pyramidal insufficiency is used if the dysfunction of certain areas of the brain is associated with the presence of extraneous tumors.
Surgery is used to remove a tumor that disrupts the functioning of the central nervous system. Surgical treatment takes place in a sterile operating room under general anesthesia. The use of this method of therapy is possible only in the absence of medical contraindications.
Massage
Therapeutic massage is indicated for children with signs of pyramidal insufficiency to improve trophism of the muscles of the lower extremities, prevent their atrophy, and improve local blood circulation. This method of physical therapy must be carried out by a qualified massage therapist.
The main goal of treatment is tactile influence on muscle tissue that is in a state of hypertonicity or has signs of too little activity. To obtain a sustainable therapeutic effect, the child should attend 2-3 sessions of therapeutic massage per week.
Exercise therapy
The physical therapy method is used to create additional stress on the foot and muscles of the lower extremities that are not involved in the process of walking. This method of therapy is indicated for children over 2 years of age. Together with a rehabilitation doctor, the child performs leg bending and extension exercises, squats, exercises on a special exercise bike, and swims in the pool.
Exercise therapy allows you to increase the activity of muscles that have signs of dysfunctional disorders, prevents their atrophy, and also prevents further progression of the disease.
Wearing orthopedic shoes
This type of treatment is aimed at giving the child an anatomically correct foot shape. The selection of orthopedic shoe models is carried out jointly with an orthopedic doctor. The duration of wearing medical devices depends on the condition of the child’s ankle joint, as well as the severity of the symptoms of pyramidal insufficiency.
As the patient ages and grows, it is necessary to replace corrective shoes and purchase special insoles. The absence of well-organized orthopedic treatment will lead to curvature of the foot and deformation changes in the ankle joint.
Taking Nootropil
Nootropil is a drug that belongs to the category of nootropic drugs. This medication improves the functions of the central nervous system, cerebral circulation, and the conductivity of neural impulses. Nootropil contains the active substance piracetam 200 mg per 1 ml of drinking solution for oral administration.
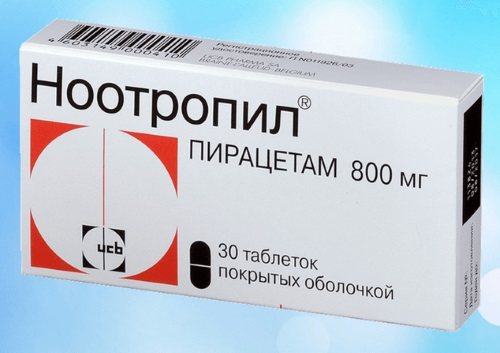
The liquid form of this drug is approved for use in the treatment of children over 1 year of age. The dosage and timing of treatment are determined by a neurologist or pediatrician who is registered with the sick child. The average cost of a medicine is 185 rubles.
Treatment with Encephabol
Encephabol is a drinking suspension that contains the active substance pyritinol dihydrochloride. This drug is a universal remedy that is used to treat most psychoneurological pathologies in children of all age groups.
Encephabol is indicated for use in children over 3 days of age. The dosage regimen is from 0.5 to 2 tsp. drinking suspension 1 to 3 times a day. The final dose is determined by the attending physician based on the child's exact age, weight, and severity of pyramidal insufficiency. The average cost of the drug Encephabol is 870 rubles. for 200 ml of drinking suspension.
Cerebrolysin
Cerebrolysin is an effective drug that is used to improve and restore impaired central nervous system functions. The active substance of this medication is a complex of peptide compounds obtained by extracting pig brain tissue. 1 ml of Cerebrolysin injection solution contains 215.2 mg of the main component.
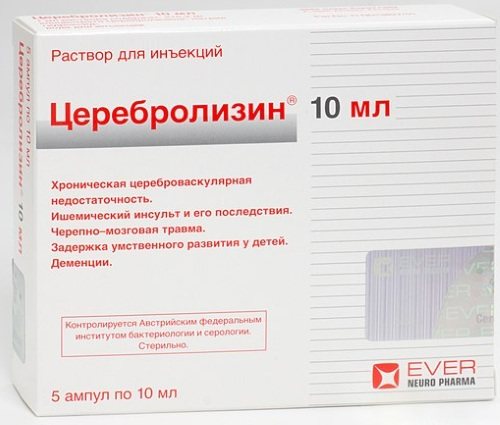
This medication is intended for intramuscular and intravenous administration. For children, the Cerebrolysin dosage regimen is 0.1-0.2 ml per 1 kg of child’s body weight. The average duration of the therapeutic course is from 10 to 20 days. The cost of this drug is within 940 rubles. for 5 ampoules with a capacity of 5 ml.
Possible consequences and complications
Lack of timely and adequate treatment of pyramidal insufficiency syndrome in children of all age groups can lead to the development of the following negative consequences and complications:
- deformation of the bone tissue of the foot;
- severe cramps of the lower extremities;
- paralysis of the muscle tissue of the legs;
- progressive tremor of the upper extremities, as well as other parts of the body;
- the appearance of accompanying neuroses;
- epileptic seizures in case of further progression of the pathological process in the brain tissue;
- poor posture caused by incorrect positioning of the legs;
- decreased quality of life in adulthood;
- severe clubfoot;
- a significant decrease in performance due to partial dysfunction of the musculoskeletal material;
- disability caused by paralysis of the lower limbs.
Pyramidal insufficiency in children is a syndrome of dysfunction of certain areas of the medulla oblongata, which were destroyed by the negative impact of external and internal factors.
This disease is characterized by increased or decreased tone of the muscle tissue of the lower extremities. In severe pathologies of the central nervous system, additional symptoms are noted in the form of tremor of the hands, chin, and delayed mental and physical development.
Treatment of the disease is aimed at eliminating the main cause that caused disturbances in brain function, as well as stimulating the leg muscles to work more actively. In the absence of adequate therapy, pyramidal insufficiency can progress, and the child’s health condition will only worsen.
Clinical picture and diagnostic methods
To identify pyramidal syndrome in adults, a simple examination by a neurologist is not enough. The patient must undergo a series of modern diagnostic procedures. To obtain comprehensive information about the patient’s health status, the neurologist will need the results of the following examinations:
- magnetic resonance imaging (prescribed in the presence of seizures or suspected epilepsy);
- computed tomography of the brain;
- electroencephalography , which helps to trace hidden seizures (in most cases they occur during sleep and therefore cannot be detected during an examination by a neurologist);
- electromyography , which allows you to determine the electrical potential of muscles;
- Ultrasound of the brain (if tumor formations are suspected).
Article on the topic: Proper nutrition for hemorrhoids - a detailed menu for every day, dietary features
Pyramidal insufficiency in adulthood also manifests itself in more noticeable symptoms that can be detected during a medical examination:
- hypertension;
- increased tone of the muscles of the arms and legs;
- convulsions;
- complete or partial paralysis of different parts of the body;
- violations of reflex activity, in particular, a decrease in its speed;
- in some cases, especially if the damage has occurred to the hypothalamic-pituitary system, sexual dysfunction and increased body weight may be observed.











