- Photo-Video
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Work with us
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
Dizziness – apparent rotation of objects inside the head or surrounding objects around one’s own body and a feeling of loss of balance.
Dizziness in children is a separate issue; it is very difficult to identify. The fact is that children cannot always describe this symptom. Until a child learns to speak, recognize his feelings and describe them in words, adults do not take his complaints seriously.
Features of the cervical spine
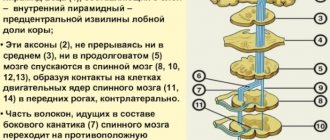
The cervical spine is formed by 7 vertebrae, the upper of which is adjacent to the bones of the skull and is called the atlas. This is the only vertebra that does not have a cartilaginous layer (intervertebral disc) with the next one - the axis. It is also distinguished from all others by its unusual shape.
In general, the cervical spine is more complex than the thoracic or lumbar spine, and at the same time much more vulnerable. Its vertebrae are the smallest, and their structural features ensure high mobility of the neck.
It is thanks to this that a person can change the position of the head in many directions with a fairly large amplitude. But the structural features of the cervical spine also provide a fairly high risk of developing changes in it, which can also occur in children, causing headaches and attacks of dizziness. This:
- Weakness of the neck muscles, as a result of which the spine does not receive proper support, and increased loads, for example, prolonged sitting with a bowed head or prolonged maintenance of another forced position, leads to rapid wear of the intervertebral discs and the development of osteochondrosis.
- The passage of large blood vessels called vertebral arteries through natural openings in the vertebrae of the cervical region. They are responsible for the blood supply to the brain. Therefore, when diseases of the cervical spine occur or there are congenital developmental anomalies, they can become bent or pinched, which leads to a decrease in the amount of blood entering the brain.
- There is a high risk of injury to the nerve roots that extend from the spinal cord in pairs at the level of each vertebra, if even minor deformities occur, including a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs.
Medicines and drugs that cause dizziness
All side effects from taking certain medications are indicated in the instructions. Particularly pronounced side effects associated with vertigo are observed with the following drugs:
- allergy medications (especially Diphenhydramine, which is now used extremely rarely and only by prescription);
- potent tranquilizers and sedatives;
- some antibiotics.
When smoking, a feeling of dizziness is caused by nicotine, a substance that dilates blood vessels in the brain.
Causes of headaches and dizziness in children
Thus, the mechanism behind the development of headaches and dizziness most often lies in:
- impaired blood circulation in the vertebral arteries - vertebral artery syndrome;
- pathological changes in the cervical vertebrae - osteochondrosis, spondylolisthesis, congenital anomalies of the spinal canal;
- posture disorders.
Often, in even young children, the cause of headaches and dizziness is vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD), i.e. dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system is observed. It most often develops if close relatives of the child also have such disorders, but VSD can be acquired during life, and at any age.
In all cases, the cause of the frequent occurrence of headaches and dizziness in children is either a violation of blood flow and the resulting hypoxia of the brain, or irritation of the nerves extending from the spinal cord by one or another anatomical structure.
However, all neck diseases are characterized by a protracted course and the development of persistent functional impairments, which, if left untreated, can not only negatively affect the child’s well-being and ability to learn, but can even lead to disability. Therefore, if a child of any age experiences frequent headaches or dizziness, it is necessary to immediately contact a neurologist. A comprehensive examination and prescription of treatment appropriate to the situation will help solve the problem and avoid the development of complications.
Vertebral artery syndrome in children
Vertebral artery syndrome is a consequence of circulatory problems in one of these two large vessels. It is characterized by a long-term headache that originates in the back of the head and spreads to the temples and forehead. Sometimes spasms of one or both vertebral arteries at once reach such strength that the child may lose consciousness.
The reasons for the development of the disease are quite diverse. They may consist of natural narrowness and tortuosity of the vertebral arteries, traumatic injury, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and spondylolisthesis. With vertebral artery syndrome acquired during life, they can be pinched as a result of compression by edematous tissues and spasmodic muscles, which is not uncommon for the inflammatory process that develops in osteochondrosis. Also, the reason for the decrease in the lumen of blood vessels may lie in irritation of the nerves that regulate their function.
Against the background of circulatory disorders in the so-called vertebrobasilar system, which is part of the circulatory system of the head, the posterior parts of the brain, responsible for the coordination of movements, suffer from a blood deficiency. As a result, this leads not only to attacks of dizziness and headaches in children, but also to:
- tinnitus;
- blurred vision, blurred or double vision;
- surges in blood pressure;
- nausea;
- increased fatigue;
- irritability, the emergence of unreasonable fears;
- feeling of numbness or tingling in the hands.
A distinctive feature of vertebral artery syndrome is the sudden onset of symptoms or their intensification when moving the head.
Vertebral artery syndrome can occur in different forms, the difference between which lies in which of the symptoms of the disease predominates over the others. If a child is more worried about headaches and dizziness, then he most likely may have vestibulo-atactic syndrome or Barre-Lieu syndrome.
The pathology cannot be ignored, since oxygen starvation of the brain can lead to irreversible consequences. In addition, with severe compression of the vertebral arteries, there is a risk of ischemic attacks and stroke. Such a dangerous condition can be differentiated by the occurrence of:
- motor and sensory disorders;
- speech impairment and difficulty swallowing;
- partial or complete sudden loss of vision;
- nausea, vomiting;
- severe dizziness;
- violations of motor coordination.
In such situations, you should immediately call an ambulance for the child.
Osteochondrosis in children
Today, cervical osteochondrosis is increasingly diagnosed in adolescents. This is facilitated by a sedentary lifestyle and addiction to gadgets. The disease is characterized by a decrease in height and wear of the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine, which leads to the convergence of the vertebral bodies and compression of the spinal roots. This is accompanied by pain in the neck and head, and can also cause dizziness. Moreover, the intensity and localization of pain directly depends on the nerve root at the level of which vertebra is pinched:
- the first pair, located immediately under the base of the skull above the 1st cervical vertebra C1, provoke pain in the occipital region;
- C1—C2 – pain in the occipital-parietal region, sleep disturbances;
- C2-C3 – pain in the neck, possible speech impairment due to numbness of the tongue;
- C3-C4 – pain in the area of the collarbone, shoulder girdle, spasms of the muscles of the head and neck, which leads to a diffuse headache;
- C5-C7 – pain in the neck, shoulder blades and arms.
The pain can be localized only on one side, which is caused by pinching of only one of the pair of spinal roots.
In addition, pinched nerve roots can provoke the development of other diseases that at first glance are not related to the spine. In fact, compression of nerves can cause disruption of the organs they innervate. Therefore, in such cases, children may be diagnosed with:
- diseases of the inner ear and hearing impairment;
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils (adenoids);
- frequent tonsillitis, laryngitis;
- thyroid diseases.
These diseases are usually diagnosed without difficulty, and treatment is prescribed as a result. But it is not always sufficiently effective and often allows only temporary remission, since the main cause - pathology of the cervical spine - persists. In such situations, after a few years, the child, who by that time will have become an adult, will face a protrusion or a full-fledged herniation of the intervertebral disc.
Progressive changes in the intervertebral discs can cause the development of vertebral artery syndrome and VSD. Thus, many diseases of the cervical spine are interconnected.
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is the displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other in the anteroposterior direction. As a result, the intervertebral discs are damaged and spinal roots may be pinched. The consequence is again a headache, as well as disturbances typical of damage to a particular root.
In children, the disease can be a consequence of receiving blows to the neck or birth injuries. This is often complicated by weakness of the neck muscles, which over time leads to progression of the pathology and worsening of the condition.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis accounts for about 30% of all spinal diseases in children. This term refers to the curvature of the spinal column in the lateral plane. The pathology is most typical for schoolchildren, but can also be congenital or develop in preschool age.
Although most often the deformity initially forms in the lumbar spine, over time it can lead to curvature of the entire spine, including the neck. This occurs due to the inclusion of compensatory mechanisms. As the body tries to correct the incorrect position of the spine and maintain the ability to maintain balance, the upper sections bend in the opposite direction, which leads to headaches.
The main causes of scoliosis are:
- incorrect posture when writing or working at a computer;
- uneven distribution of the load on the back when wearing a backpack;
- heavy sports activities started unreasonably early;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- spinal injuries;
- unbalanced diet;
- being overweight.
Most often, scoliosis occurs during periods of active growth of the child, i.e. at 4-6 years and 10-14 years. Therefore, at this time you need to be especially attentive to the spine and monitor your posture.
Parents themselves can notice the curvature of the ridge. In young children, the examination is carried out while lying on their stomach, and in schoolchildren, the examination is carried out while bending forward on straight legs. With scoliosis, differences in the position of the shoulder blades and shoulders, pelvic distortion, asymmetrical arrangement of the gluteal folds, and waist triangles will be noticeable. Children with this spinal pathology tend to slouch and walk with their heads down. However, in the initial stages of pathology development, it can be extremely difficult to notice deviations without instrumental diagnostic methods, and even impossible for an untrained person.
Vegetovascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not an independent disease, but is a consequence of existing pathological changes, which can be caused by a variety of factors. Even young children can suffer from VSD due to the peculiarities of their constitution. However, more often the pathology is diagnosed after 10 years, since at this time hormonal changes in the body begin to occur. In such situations, the autonomic nervous system may not have time to grow with the child, which will result in vegetative-vascular dystonia and the appearance of:
- headaches;
- irritability;
- memory impairment, concentration;
- weaknesses.
In addition to hormonal fluctuations, the cause of the development of VSD in children can be:
- excessive physical activity that depletes the body;
- smoking, drug use;
- transmission of acute infectious diseases;
- neurological disorders;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus and other endocrine disorders;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- severe psycho-emotional exhaustion, stress, depression.
Great importance when calculating the probability of developing vegetative-vascular dystonia is given to heredity.
Attacks usually occur suddenly after physical exertion or stress. They last on average about 20-30 minutes and may be accompanied by:
- headaches of varying strength, including migraines;
- dizziness;
- sweating;
- tachycardia;
- weakness;
- tinnitus;
- darkening of the eyes with the possibility of losing consciousness;
- anxiety, fear.
VSD can occur in different ways, on the basis of which 4 types are distinguished: hypotonic, hypertensive, cardiac, mixed.
Classification of dizziness
Dizziness, as one of the manifestations of vestibular pathology, can have physiological and pathological causes. Pathological include problems associated with the development of infectious diseases or somatic pathology, volumetric processes of the skull.
Physiological dizziness can be caused by oxygen deficiency or low partial pressure during prolonged stay in a stuffy closed room, with frequent and deep breathing due to hyperventilation syndrome, which is typical for screams and hysterics, with sudden rotational or linear accelerations. Physiological adaptation dizziness is typical for children due to sudden changes in body position in space. Manifestations appear and disappear on their own within a few seconds or minutes; they do not bother children much and do not require intervention.
By origin, dizziness can be central or peripheral in nature.
For central lesions, damage is typical in the area of the vestibular structures of the brain (nucleus) or some of its other parts as a result of hemorrhages, tumors or ischemic lesions. They disrupt the conduction of impulses from the brain to the body and back. Such sensations of rotation can be either periodic or constant.
With peripheral lesions, problems in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus itself are possible; such pathologies require certain diagnostic and treatment methods.
Important
Benign positional vertigo is typical of old age, when degenerative processes predominate in the brain, but is possible at an early age as a variant of immaturity of brain and vestibular structures. They usually occur with sudden movements and turns of the head, last a few seconds and do not cause severe discomfort to the child, but can cause falls and injuries.
The presence of positional benign vertigo (BPG) in childhood can be aggravated by concomitant pathologies - helminthic infestations, the presence of diabetes mellitus or frequent hypoglycemia, long periods of fasting, infectious pathologies, ranging from influenza and ARVI to childhood infections, as well as brain damage - meningitis or encephalitis, muscular torticollis, neuroses.
In adolescence, PDH can form due to sudden hormonal changes that provoke the phenomena of vegetative-vascular dystonia. As the disease progresses, headaches may occur, and PDH can be an analogue of migraine. Hypotonia, gait disturbances, and instability will also be typical for PDH.
In teenage girls, PDH can provoke heavy, painful menstruation, as well as hormonal disorders. In young men, this can be a sign of bad habits, poisoning with heavy metal salts, head and inner ear injuries.
Some of the causes of PDH may be stressful situations or severe neuroses, panic attacks or depressive disorders.
When to make an immediate appointment with a doctor
It is necessary to get an appointment with a neurologist as soon as possible if your child has:
- frequently recurring attacks of headache and/or dizziness;
- dizziness lasting more than 20 minutes or loss of consciousness;
- blurred vision;
- involuntary rapid eye movements during an attack;
- tinnitus.
Consultation with a specialist is mandatory if parents or other close relatives suffer from migraines, VSD or vertebral artery syndrome.
But due to his age, the child cannot always complain about his health or describe the nature of the symptoms that bother him. The hardest thing to understand is what worries a child under 3 years old. In such situations, you should make an appointment with a doctor if:
- the occurrence of changes in behavior, increased fatigue, loss of interest in outdoor games;
- frequent anxiety, crying;
- drowsiness, reluctance of the child to wake up.
You can suspect the presence of dizziness by the fact that the child begins to fall more often. Although falls are not uncommon for young children, nevertheless, if the baby suddenly falls out of the blue, involuntarily tries to hold on to a wall or a suitable object, you should ask him to try to walk in a straight line. If the child succeeds in this with difficulty or does not succeed at all, consultation with a neurologist is mandatory.
When a headache occurs, young children may clutch their head and scream or cry. With prolonged attacks, this may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, weakness and pale skin.
Forecast
As a rule, PDHs are favorable pathologies; they go away on their own, even without treatment, in most children as all brain structures and parts of the vestibular apparatus mature.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician, medical columnist
3, total, today
( 75 votes, average: 4.40 out of 5)
Trigeminal neuralgia - symptoms, treatment
Alzheimer's disease: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Related Posts
First aid for an attack
It is prohibited to give your child any medications on your own without a doctor’s prescription. If parents notice signs of headache or dizziness, they should reassure the child and stay close to him. To alleviate the condition, you should:
- provide bed rest and eliminate all irritants: bright light, TV, gadgets, loud music;
- Give water to drink if you experience nausea; cold water will help reduce its intensity;
- provide fresh air access to the room;
If attacks of dizziness bother your child at night, he should leave a night light on. When he wakes up feeling unwell, fixing your gaze on him will help prevent the condition from getting worse.
If the attack recurs, you must make an appointment with a doctor for examination and treatment.
What makes you feel dizzy?
Dizziness cannot be ignored. Even in an isolated case, it is recommended to establish the exact cause in order to protect yourself.
There are a number of physiological reasons associated with the transitional age of adolescents or with the characteristics of the human body.
- Production of adrenaline in the body. During an exam or any other exciting situation, a hormone called adrenaline is released into the human blood. It actively constricts blood vessels and prevents the flow of oxygen to the brain, which causes dizziness.
- Motion sickness. In this situation, dizziness is due to the fact that the brain does not correlate the readings of the vestibular apparatus and the surrounding environment. In adolescents, the blood vessels located in the brain are developing, so their function may not be accurate. As a rule, this occurs during a long trip by transport or on a watercraft.
- Fasting/dehydration. Diets are common among teenage girls, but due to active growth, the body needs an increased amount of nutrients. Due to starvation or dehydration, they are not absorbed into the body, causing dizziness.
- Excessive physical activity. During training, the body spends more useful elements to maintain its general condition. If there is more energy expended than consumed, the teenager may become dizzy.
Up to 14 years old
At the age of 14-15 years, vegetative-vascular dystonia develops. It occurs against the background of functional changes characteristic of every child. With proper treatment, the disease goes away and no longer bothers you in adulthood.
At 15-17 years old
At this age, adolescents develop secondary sexual characteristics, which is caused by hormonal changes. Teenagers are actively growing and gaining weight. Together, these factors can lead to dizziness.
Diagnosis of the causes of headaches and dizziness
To diagnose the causes of headaches and attacks of dizziness in children, the neurologist examines the patient, and also carefully interviews the patient himself, and, if necessary, his parents. During the examination, the doctor performs a series of neurological tests, the results of which will help assess the extent of the neurological deficit. These data may not be sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, all patients are prescribed an examination that may include:
- X-ray or CT scan of the spine;
- MRI of the spine;
- Ultrasound of neck vessels with Doppler sonography;
- UAC;
- blood chemistry.
The most technically difficult and expensive procedure is MRI, since for 20 minutes you need to lie absolutely motionless in a closed chamber of the device. Therefore, in young patients, the study is usually carried out in a state of medicated sleep.
Based on the results of the examination, the neurologist can already understand exactly what caused the child’s headaches and dizziness and prescribe the most appropriate therapy for a particular situation.
Diagnostics
First of all, it is necessary to contact the pediatrician and present to him all the existing complaints that have been identified in the child. The diagnosis of DPG is made by excluding all possible more serious causes of dizziness . For this purpose, a consultation with an ENT doctor, as well as a neurologist, is scheduled. Doctors will rule out intestinal and respiratory infections, damage to the ENT organs, in particular the middle and inner ear (chronic otitis). It is equally important to exclude the presence of parasites, vegetative-vascular dystonia, previously undetected head trauma or space-occupying formations of the skull. Infectious brain lesions and poisoning are also excluded.
The pediatrician will prescribe blood and urine tests to rule out anemia, kidney and heart damage, as well as additional health problems - diabetes and hypoglycemia.
X-rays of the skull or CT scan, MRI of the head and neck, as well as additional studies to exclude unusual forms of epilepsy with dizziness will be indicated.
Treatment of headaches and dizziness in children
For each child, treatment tactics are selected strictly individually, but it is always comprehensive. In this case, the doctor takes into account not only the nature of the detected pathological changes, but also the age of the child, existing concomitant diseases and other factors. Therefore, even with the same diagnosis, two different children may need different treatment.
So, the main components of therapy are usually:
- drug treatment;
- manual therapy;
- exercise therapy;
- physiotherapy.
The neurologist may also recommend reviewing the child’s work and rest schedule, taking measures to increase physical activity, increasing the number and duration of walks in the fresh air, normalizing nutrition, purchasing an orthopedic mattress and pillow, etc.
Small children can only be bathed in water whose temperature is not higher than 37°C. Hotter water can cause blood vessels to dilate, which can cause another attack of dizziness.
Drug treatment
The goal of drug treatment is to improve the child’s well-being, relieve the inflammatory process, normalize blood circulation and improve the quality of transmission of nerve impulses. Therefore, for any diagnosis it includes:
- NSAIDs;
- vitamins;
- drugs that improve blood flow.
Additionally, treatment can be supplemented with other drugs that will help eliminate existing disorders, for example, muscle relaxants, cardiac drugs, chondroprotectors, antidepressants, adrenergic blockers, etc.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy is considered one of the most effective and safe methods of treating spinal pathologies in children, but only when performed correctly. Inept actions or incorrectly chosen force of influence can cause significant harm to the child and provoke the development of complications. Therefore, when choosing a specialist, you should be very careful and not trust the health of children to non-professionals with insufficient experience.
Manual therapy of the cervical spine requires particularly high qualifications of the doctor and caution during its implementation.
The essence of the method is a targeted impact on the spine with your hands using methods of mobilization, manipulation, rhythmic mobilization, post-isometric relaxation, etc. This allows you to:
- return the vertebrae to the correct position;
- relieve pressure on the nerves;
- align the spine;
- reduce pressure on the vertebral arteries.
Also during the session, the chiropractor also works on soft tissues, as in a therapeutic massage. This helps improve blood circulation, activate metabolic processes and eliminate muscle spasms, which significantly improves overall well-being. But still, the main goal of manual therapy is direct work with the spine. Moreover, the method has virtually no contraindications, is characterized by the absence of side effects, which no other drug can boast of, and also provides a positive effect on the entire body.
Due to competent study of the entire spine and especially the problem area, it is possible to:
- eliminate the cause of headaches, dizziness and other symptoms, and therefore them;
- increase overall performance;
- strengthen the immune system and adaptive capabilities of the body;
- eliminate the risk of developing diseases of internal organs innervated by the compressed nerve;
- increase neck mobility, eliminate functional blocks;
- improve posture.
Manual therapy can be performed even on infants and children with serious pathologies.
For each patient, the number of sessions and types of manual influence are selected individually. On average, about 10 procedures are required, although a noticeable improvement in well-being can be noticed after the first one. But it is important not to give up treatment after receiving the first results. They must be secured, otherwise the achieved effect will be lost.
Exercise therapy
Physical therapy is one of the simplest, most accessible and effective methods of treating spinal diseases. For each child, the lesson program, as well as exercises, are selected separately, taking into account the diagnosis and general level of physical development. You should not try to find and start performing any exercise therapy complex on your own, since some types of movements or an incorrectly selected load can do a disservice.
Exercise therapy classes begin to be carried out outside the acute period of the disease. Initially, it is recommended to study in special groups or individually, but in any case under the supervision of a specialist. He will help a child of any age master the correct technique for performing each exercise and select the optimal load.
After the program has been finalized and the child follows it flawlessly, it is allowed to continue classes at home. But the effect of physical therapy will only be with daily exercise. It is important to avoid haste, sudden movements, and overexertion. And if pain appears or the condition worsens, you should immediately stop exercising and consult your doctor.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods are used outside the acute period of the disease. They help potentiate the effect of other areas of treatment, improve vascular tone, activate blood circulation and metabolic processes, and also have a beneficial effect on the state of the nervous system. Therefore, for pathologies of the cervical spine, courses are often prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- UHF;
- diadynamic therapy;
- laser therapy.
Thus, there are many reasons for the development of headaches and dizziness in children, among which there are also quite dangerous diseases that can lead to irreversible consequences. Therefore, if attacks occur regularly, you should consult a neurologist. Only a doctor will be able to correctly assess the child’s condition and explain the origin of headaches and dizziness, and, if necessary, develop the most appropriate treatment tactics for the detected disease. In the vast majority of cases, when pathologies of the cervical spine are diagnosed in children in the early stages, it is possible to completely eliminate them and return the little patient to health, cheerfulness and the ability to conquer new heights.
Doctors' answers
Hello, Victoria Viktorovna Semenova
Vomiting and dizziness can occur with increased intracranial pressure, intestinal infection, food poisoning, inflammation of the pancreas, biliary system. There is currently a gastroenteritis clinic. Considering that the child’s temperature rose to 38, and the next day the temperature returned to normal, it is more likely that foodborne toxic infection is occurring.
Dizziness and weakness are a consequence of intoxication of the body. At this point, you need to take your child to an infectious disease specialist for examination and a thorough history taking. It is also necessary to take a general and biochemical blood test, a general urine test, and a stool test for the intestinal group. FGDS and ultrasound of the abdominal organs may be required to exclude pancreatitis and biliary tract pathology.
During vomiting, the body loses fluid, so it is necessary to ensure an adequate drinking regimen: drinking frequently in small sips. Rehydration is best done with saline solutions (Regidron). If at the time of examination the doctor diagnoses signs of dehydration, intravenous fluids may be required.
Now look at the general condition of the child. If it worsens, you should seek medical help. If the condition is stable, then the child can be observed for up to 3 days. If nothing changes, you will need to see a doctor in person for examination and examination. Considering the symptoms, one can suspect a disorder based on psycho-emotional factors.
The child may be under a lot of stress, for example there is a problem at school. Therefore, for now, provide the child with emotional peace, tell her that she may not go to school tomorrow, and monitor her well-being today and tomorrow. Along the way, carefully try to find out how things were at school and whether there was a head injury.
Hello, Victoria Viktorovna! I am preparing an answer to your question, please wait a little.
There are many causes of vomiting and dizziness - these are various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, acute intestinal infections (toxic infections), brain injuries (concussion), any diseases of an inflammatory and non-inflammatory nature, accompanied by intoxication syndrome.
Considering the increase in temperature to 38 degrees, pain in the stomach, vomiting, I am inclined to believe that in this case it is associated with food toxic infection (gastroenteritis). However, this is only my guess and there may be another reliable reason - I cannot say for sure, because I have no opportunity to examine the child or collect an anamnesis, and I also do not know whether there are any abnormalities in laboratory tests.
In this case, I recommend going to the clinic and getting tested - UBC, TAM, sugar, bilirubin, AST, ALT, amylase, stool for intestinal group, FGDS, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Or you can call the pediatrician home - if the girl is not able to visit the clinic. A child should not be sent to school in this condition.
The pediatrician will issue a certificate stating that the child was sick (only if you apply today, the certificate will be issued from today). In diet - try to exclude fried, spicy, smoked, spicy foods, chocolate, soda. It is preferable to steam food. Don't force feed her - she doesn't want to, so don't eat, but she definitely needs to drink water.
Make sure the girl drinks at least 1.5 liters of liquid. If the condition worsens - more frequent vomiting, increased abdominal pain - you need to call an ambulance. I also recommend starting to take enterosorbents (Polysorb, Enterosorb, activated carbon). Dosage - taking into account weight, dosages are described in the instructions. Activated carbon is calculated as 1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight, 3 times a day.
Consultation is available 24 hours a day
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eimuMpRBudQ
We need to know your opinion. Leave a review about our service
Most people have experienced dizziness at least once. In adolescents, this phenomenon is observed more often than in adults, since many processes associated with growing up occur in their bodies.
Physical, mental and emotional jumps can affect the general condition of a teenager, causing dizziness. The article describes a common problem among teenagers - dizziness. The causes of dizziness in girls and boys and measures to help are also described in detail.
Associated symptoms
Dizziness is not an independent symptom, much less a separate disease; it is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- Cold extremities.
- Increased sweating in the arms, legs or throughout the body (breaks into a sweat).
- Feeling of panic, lack of oxygen: difficulty breathing.
- Lips, face go numb, weakness, lightheadedness.
- Nausea, possible vomiting.
- Accelerated pulse, high or vice versa, low blood pressure.
- There is noise in the ears, stuffy ears.
- It gets dark in the eyes.
- The eyes twitch involuntarily.
The appearance of symptoms and their intensification contributes to:
- Sudden change in body position.
- Movements associated with rotating the head, bending and lifting the body. Symptoms may appear when throwing the head back or vice versa, when lowering down, when turning in bed from side to side.
- Fixation of gaze on moving objects.
- Riding in transport.