Table of contents
- In what cases is a CT scan prescribed, and in which MRI?
- Main indications for CT scanning
- When is the best time to do an MRI?
- Contraindications
- Advantages of each type of tomography
- Benefits of CT
- Benefits of MRI
- MRI of the brain or CT scan – which is better?
- What will be checked?
- When there are restrictions
- Technical specifications
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Computed tomography
is a type of analysis in which a layer-by-layer scan of the patient's organ is performed. A tomograph is used to carry it out. The principle of its action is the reflection of X-ray radiation from tissues and bones. The result of the study is presented in the form of a 3D image on the doctor’s monitor, and can also be recorded on disk.
The CT machine consists of a table and a circle with movable sensors, which, rotating during the examination, take pictures from different angles.
Since using this method the patient receives a certain (but not very large) dose of radiation, this test should not be performed frequently.
Magnetic resonance imaging
- This is an examination based on the effect of magnetic resonance and electromagnetic radiation, which is reflected differently from more or less dense tissues.
A tomograph is also used for it, but of a different, closed type. It is equipped with a retractable table on which the patient is placed, and a tube-shaped apparatus into which this table is pushed.
This is a fairly safe examination method, although there are a number of limitations in its use, mainly related to the presence of metal implants in the body.
Concept of MRI and CT
Answering the question: what are MRI and CT (kate), it should be noted that both of these methods are aimed at studying the internal organs of a person and have one goal - obtaining information about the state of health for making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment.
Magnetic resonance imaging is the process of examining an organ that is showing signs of disease by applying specialized equipment to the body using a magnetic field. It is an oval-shaped capsule, from which a place extends out into which a person is placed. His arms, legs and head are secured with straps to ensure immobility. After which, it is placed in a capsule, where the process of influencing the magnetic field on the body occurs. The frequencies provoke a response, as a result of which the information enters the computer in a three-dimensional image, where it is automatically decrypted.
X-ray computed tomography (XCT) has a different operating principle. A person lies down on a couch and an X-ray beam affects his body. Under its influence, the specialist manages to take pictures of the organs that are to be studied. They are formed from different points, different distances and at different angles. All pictures have the appearance of a three-dimensional image.
Important! When using this method, the doctor has the opportunity to examine a cross-sectional image of the organ, and with certain equipment settings, the image in this form can reach a thickness of up to 1 millimeter. This indicator allows you to more accurately examine the structural features and damage to the organ.
CT and MRI are aimed at diagnosing diseases; they have a relatively similar medical result - obtaining information about the condition of internal organs, the stage of development of the disease and the ability to make a correct diagnosis.
CT equipment has its own characteristics
When is the best time to do an MRI?
Such a study is prescribed in the following cases:
- Suspicion of a tumor
- Regular headaches, dizziness, fainting
- The patient suffered a stroke
- Lost hearing or vision
- Injuries, hematomas and swelling
- Memory loss, problems concentrating
- Inability to perform CT
MRI is also prescribed to check:
- Correct course of treatment
- State of the brain after detection of a malignant tumor
- Pre- and postoperative control
Children may be prescribed magnetic resonance imaging if:
- He had pathologies during intrauterine development
- He lags behind his peers in various indicators
- Suffering from convulsions, dizziness, loss of consciousness
- Stutters or has other speech problems
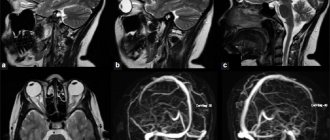
Can an MRI show a brain tumor?
Based on the results of magnetic resonance imaging, doctors can identify changes in tissue structure. Brain tumors on MRI are determined by direct and indirect signs. Doctors suspect a pathological formation based on the type and uniformity of changes in the MR signal:
- hypo- (weaker than surrounding areas) or hyperintense (response stronger than from normal areas);
- heteromodified (different characteristics are mixed);
- isointense (the tumor looks like other tissues, but differs from the normal architecture of the brain).
There are also indirect signs. The latter give reason to suspect a brain tumor against the background of an isointense tissue response or confirm its presence with an altered MR signal.
Multiple metastases in the brain substance on MRI without contrast
Secondary manifestations of pathology may be:
- lateral dislocation of the median structures;
- displacement of the vascular bundle;
- changes in the size and deformation of the ventricles;
- axial dislocation;
- occlusive hydrocephalus due to blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways;
- displacement or deformation of the basal cisterns;
- cerebral edema in the tumor area and around it (local, generalized, total, periventricular).
Pre- and post-contrast images of a malignant brain tumor
Using MRI for brain cancer, the localization of the tumor, the degree of its invasion into neighboring structures, features of the blood supply, stage of the disease and the presence of metastases are revealed. To obtain additional information, scanning is carried out in various sequences (T1, T2, FLAIR, diffusion-weighted, etc.), in native mode and after contrast.
Contraindications
Both studies are quite safe, but a number of restrictions on their use still exist. They must be kept in mind when deciding which analysis to perform: brain MRI or CT.
Computed tomography is not done in the following cases:
- When the patient is pregnant
- With a large weight (more than 130 kg) of the patient
Use it with caution for nursing mothers, and if the analysis has been carried out, then you should not breastfeed the baby for another day.
If the study is carried out with a contrast agent, then there are more contraindications:
- Allergy to iodine
- Diabetes
- Endocrine diseases
- Problems with the liver and kidneys
MRI should not be performed in patients who:
- There are metal prostheses made from materials that interact with a magnetic field
- Heart valves and pacemakers
- Metal clamps for vessels for aneurysm
- Hearing Aids
- Permanent dentures made of gold, steel and similar materials
The study is applicable with limitations when:
- Patient in the first trimester of pregnancy
- The patient suffers from a fear of enclosed spaces
- He has crowns and braces
Also, an obstacle to both studies may be the patient’s inability to lie still for the required time due to severe back pain.
If the patient knows about the presence of any limitation (pregnancy, previously diagnosed diabetes, metal implants, etc.), he must inform the doctor in advance.
Possible contraindications for one and the other method
Even if a CT scan in a particular case is more informative, the patient will be prescribed an MRI when he has absolute contraindications for a CT scan. These include:
- pregnancy;
- body weight exceeds 200 kg;
- intolerance to drugs containing iodine (with contrast-enhanced CT).
Computed tomography has relative contraindications. This means that the doctor, if available, will decide on the advisability of performing a CT scan in each specific case. Such contraindications include:
- childhood;
- lactation period (after the procedure, the woman will not be able to breastfeed for one day);
- renal failure;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- diabetes;
- multiple myeloma;
- diseases that prevent the patient from remaining still during diagnosis.
Absolute contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging are:
- body weight more than 120-140 kg;
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- gadolinium intolerance (in contrast studies).
Relative contraindications include the presence of metal structures in the mouth (if they are made of ferromagnetic metals), as well as severe renal failure (with contrast). In case of mental disorders and other diseases that prevent the patient from remaining motionless during the study, it is permissible to carry out the procedure with sedation or under anesthesia. Pregnancy, breastfeeding and childhood are not contraindications, since MRI of the brain is safe due to the absence of X-ray radiation.
Benefits of CT
Computed tomography is one of the most accurate ways to study disorders associated with the state of the brain. It is especially effective when it comes to identifying abnormalities caused by traumatic brain injury, as well as other problems with the bones and dense tissues of the skull.
This happens because X-rays are reflected in a special way from dense bone tissue. At the same time, the radiation dose that the patient receives is much lower compared to other x-ray studies. In this way, various diseases can be diagnosed without the use of invasive methods, which makes the procedure painless.
Using CT, you can diagnose a stroke, arterial disorders due to atherosclerosis, changes in the structure of the cerebral cortex and lesions of the facial bones. It allows us to examine such disorders in great detail and identify the causes of diseases.
The procedure takes no more than fifteen minutes. With this type of analysis, there is no risk of distortion of the result if the patient accidentally moves.
Patients suffering from claustrophobia can easily tolerate a CT scan because an open machine is used, in which only the head is immersed, and not the whole body.
It is important that the CT result can be seen immediately, although in some cases the image may not have enough contrast.
Comparison of the effectiveness of CT and MRI
If there are contraindications for CT scanning, then the study is performed with X-rays, ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. MRI is currently the most informative method for assessing the condition of the brain and blood vessels.
The diagnosis with this procedure is made thanks to a magnetic field that shows the state of the brain. This is the key difference between magnetic resonance imaging and CT scanning.
The main differences between MRI and computed tomography include:
- Diagnostic method. MRI uses a magnetic field, CT uses ionized radiation.
- Efficiency. Magnetic resonance imaging is more informative in comparison with CT (allows you to determine the boundaries, structure, structure and pathologies of the brain).
- Safety. CT scans expose patients to radiation, but MRIs do not. This difference makes MRI a safer method.
- Purpose. Computed tomography (and SCT) is more effectively used for diagnosing bone tissue, while MRI (and ultrasound) is used for diagnosing soft tissue.
- Contraindications. Magnetic tomography is not used in the presence of implanted pacemakers, tripods, or endoprostheses, while CT has no such contraindications. However, MRI is performed in the presence of melanomas, but CT is not.
- Duration of the examination. Diagnosis of the brain and blood vessels using MRI takes from 30-60 minutes, with CT – from a minute to half an hour.
Therefore, it is definitely impossible to determine which is better: MRI or CT. When choosing procedures, health status, expected diagnosis, area of study and other factors are taken into account.
Description of the brain MRI procedure (video)
Benefits of MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is no less accurate than CT, but its scope is somewhat different. It allows you to examine and diagnose diseases of the soft tissues of the brain and shows results in three planes:
- Axial (horizontal projection)
- Frontal (direct projection)
- Sagittal (lateral projection)
MRI allows you to very clearly see problems with soft tissues: benign and malignant (cancer) neoplasms (their shape, location and volume), dysfunction of the pituitary gland, nerve and muscle fibers. In this way, you can see and measure the volume of edema, tumors of the nervous system, and more. The bones will be displayed indirectly.
This test is safe, so it can be used to diagnose pregnant patients, but only in the second and third trimester. It is also allowed to be used for diagnosing children from the age of three. But it is necessary to explain to the child how the research will take place so that he is not afraid and tries not to move during the process.
MRI can be done several times over a short period of time.
The procedure lasts about half an hour. During this period, the patient is required to lie still. Otherwise, the image may be distorted and the result may not be reliable or accurate.
For patients with a fear of closed spaces, anesthesia can be used.
When there are restrictions
Magnetic resonance imaging can be done on pregnant women (excluding the first trimester) and children aged three years and older. Anesthesia can be used for a child, since he is not always able to remain motionless for a long period of time.
A CT scan for children and pregnant women is excluded, except in cases where the patient’s life depends on its implementation, and no other means can help, since during the procedure the patient receives a dose of X-ray radiation.
It can also be difficult for a patient with nervous disorders to remain motionless for the required period of time. In this situation, it is also possible to use anesthesia.
People who have metal objects in the body, as well as electronic pacemakers or heart valves, are contraindicated for MRI, since such things interact magnetically with the machine. Because of this, both distortion of the results and deterioration of the patient’s condition may occur. The exceptions are pins, crowns, removable braces and products made from non-inert materials (titanium and others). In this case, it is better for the patient to undergo a brain CT scan or similar analysis.
Harm from computed tomography
During computed tomography, the X-ray tube irradiates the entire surface of the patient's body, the radiation dose being 100-500 times higher than with a conventional X-ray examination. Therefore, there are some risks:
- Radiation exposure. The dose of radioactive radiation received during the examination is an order of magnitude higher than during a conventional x-ray examination. This slightly increases the likelihood of malignant tumors.
- The effect of a contrast agent on the body. Before the procedure begins, the patient is injected intravenously or given a special contrast agent to drink. In most cases, it does not harm the patient's health, but in rare cases, the contrast agent can cause nausea, vomiting or an allergic reaction manifested by skin rash, itching, and sometimes anaphylactic shock.
It is worth remembering that the health of people who are overweight, children and people under 25 years of age is most at risk. The tissues of these population groups are very sensitive to radio radiation, since the cells of a young body divide much faster
.
Technical specifications
MRI provides extremely clear images, excluding bones, in the form of projections from different angles; CT, on the other hand, has a less clear “picture,” but at the same time the structure of the bones is clearly visible in its results, and the image is presented on the monitor in the form of a 3D model.
Another important point is the amount of time you need to spend in the device. For CT it ranges from 5 to 15 minutes, for MRI – about half an hour. During this period, the patient should be as motionless as possible. But it is not so critical for the results of a CT scan if the patient moves a little. Such movement can introduce serious distortion into magnetic resonance imaging data.
A CT scan can help make an urgent diagnosis if a patient is seriously injured and has symptoms of a cerebral hemorrhage.
To choose the most effective examination method (brain MRI or CT), you need to pay attention to many factors. This can be done by a qualified doctor. The patient is obliged to provide all information that will help with this.
Benefits of CT Scan
Compared to conventional x-rays, computed tomography has several advantages:
- High-quality 3D images of organs, bones, joints and blood vessels.
- Detection of organ changes invisible during other examinations.
- High speed scanning.
- The minimum slice thickness is 0.5 mm.
- Elimination of overlapping of images of structures outside the examined area.
- The high-contrast resolution of the images allows you to see the smallest differences between tissues that differ in physical density by less than one percent.
- The doctor has the opportunity to examine the received images from a transverse, frontal or sagittal perspective.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- MEDSI clinics have the latest equipment, which allows you to get the most accurate results
- Radiologists, oncologists, surgeons and other professionals of the highest qualification categories take on the most complex and rare cases
- It’s easy to sign up for a consultation and find out more details - all you need is one phone call to 8 (495) 7-800-500
- MEDSI will help you choose the right examination (including brain MRI or CT), treatment and, if necessary, rehabilitation measures
Method capabilities
The capabilities of CT and MRI are somewhat different, and this is explained by the fact that the devices use different types of radiation. CT scans are most often prescribed in cases of:
- studying damage to bones and teeth;
- studying joint damage;
- diagnostics for injuries: “fresh” bleeding is clearly visible on CT;
- detection of spinal diseases, including hernias, osteoporosis, scoliosis and others;
- studying brain damage;
- examination of the chest organs (detection of tuberculosis, pneumonia and other diseases);
- examinations of the thyroid and parathyroid glands;
- examination of hollow organs (stomach, intestines, etc.);
- studying the condition of blood vessels, diagnosing aneurysms, atherosclerosis, etc.;
- examination of the genitourinary system.
A CT scan shows tumors, stones, and cysts. Thus, CT is an almost universal diagnostic method, allowing the doctor to see the most detailed picture of the body’s condition. To increase the information content of CT, it is performed using a contrast agent (in particular, when studying vessels and hollow organs).
MRI is usually prescribed to examine soft tissues, joints and blood vessels:
- examinations for suspected presence of a tumor in soft tissues;
- examination of intracranial nerves, structures of the brain and spinal cord;
- studying the membranes of the spinal cord and brain;
- examinations of patients with multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases, as well as those who have suffered a stroke;
- studies of ligaments and muscles;
- studying the condition of articular surfaces.