.
No matter how much they say that smoking is harmful to health, millions of smokers obediently agree with this information and continue to reach for a life-saving cigarette. Being under frequent stress, people sincerely believe that smoking calms their nerves. But is this so, and why does a cigarette itself often become a cause of stress?
Smoking and stress are linked
How smoking affects the human nervous system
Smoking is believed to calm the nervous system. At the moment of a stress factor, the smoker unconsciously grabs a cigarette; this is a conditioned reflex, because the brain remembered the previously positive effect of nicotine that entered the lungs with smoke. 1-2 puffs are enough for temporary relaxation to set in; the smoker feels that the anxiety has gone away, he has begun to think more clearly. But after 1-1.5 hours the body will again require a “dose of nicotine”. Imaginary calm will be replaced by irritability and anxiety. The influence of nicotine on the human nervous system is fixed, the dependence is formed, now that the nerves are acting up, the person will smoke.

The essence of forming a bad habit and the difficulty of giving up cigarettes lies in hormones. The main ones are gonadotropic, produced by the hypothalamic-pituitary system. The scheme of action is simple; to put it simply, nicotine “plays” with hormone levels. As soon as its concentration drops critically, the hormonal levels stabilize. Regular shocks lead to the endocrine system breaking down; instead of saving you from stress, a cigarette becomes a source of emotional instability.
Possible complications
Patients who have nicotine addiction are predisposed to the development of neurasthenia, a dangerous pathology that falls under the category of neuroses. The clinical picture of neuralgic disease consists of the following symptoms:
- causeless irritability;
- excessive fatigue;
- chronic headache;
- absent-mindedness, which causes a decrease in the quality of both physical and mental activity;
- sudden change of mood;
- insomnia.
If a smoker ignores the symptoms of neurasthenia and continues to smoke, the risk of developing concomitant diseases – radiculitis and polyneuritis – increases. The autonomic mechanism is also at risk: the negative effects of nicotine precede a disorder of the respiratory and digestive functions, as well as disruption of the heart.
Pseudo-help of cigarettes for stress
The formation of the opinion that a cigarette helps to relax is facilitated by word of mouth, which claims that stress is actually leveled. By deceiving himself, the smoker unconsciously misleads other people, often non-smokers.
What's really happening. Initially, at the very first “test of the pen”, after inhaling smoke, a person begins to cough, choke, sneeze, and cry. This is how the body tries to get rid of tar, nicotine, and carcinogens, which are poison. The central nervous system sends a signal that smoking is unnatural and dangerous. If a person listens to his body, he will develop a persistent dislike for cigarettes, he will never smoke.
However, repeated smoking forms a habit on a physical and psychological level. Gradually, under the influence of nicotine, the functioning of neurotransmitters (acetylcholine) changes, the body switches to their external replacement.
From the moment of inhaling until nicotine penetrates the brain, 7 seconds pass. There it “deceives” the central nervous system and begins to act as a psychostimulant, imitating the effects of neurotransmitters. It is at this stage that a person feels that nicotine calms the nerves. Some narcologists believe that the toxic substance can act like ethyl, blocking the rapid breakdown of dopamine, the pleasure hormone.
The secret of constantly returning to a cigarette and the formation of addiction lies in the fact that the receptors of the nervous system lose sensitivity to nicotine and natural neurotransmitters. At the same time, the production of dopamine decreases, which is expressed in excessive irritability, neurosis, and weakness of the smoker.

A vicious circle is formed - a state of shock from a cigarette, which is expressed in discomfort, which the body tries to remove. The nervous system sends signals, the person grabs a cigarette (it used to help), trying to replenish the level of the joy hormone with a puff and stop withdrawal symptoms.
Addiction to smoking body
Daily smoking precedes the formation of cravings for the neurotoxin, as a result of which a person becomes dependent on nicotine both physically and psychologically. A smoker needs to regularly replenish the supply of a toxic substance: prolonged abstinence from smoking cigarettes causes the development of obsessive thoughts.
Doctors distinguish four main stages of addiction to a neurotoxin. The first stage, also called self-indulgence, is characterized by the absence of dependence: a person smokes no more than one cigarette per day.
The third stage is characterized by the development of full-fledged dependence on nicotinic acid, which develops not only on a psychological, but also on a physical level: on average, a person smokes 15 cigarettes per day.
The final stage is observed in heavy smokers who experience severe discomfort during long-term abstinence from smoking: the norm for them is to smoke more than 20 cigarettes per day.
Is smoking dangerous for the smoker's psyche?
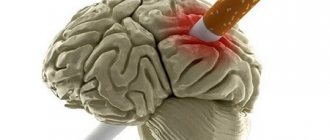
When nicotine, carcinogens, and combustion products enter the body, they first act on the lungs, then on the central nervous system. Particularly affected are the areas responsible for communication with acetylcholine receptors; they are responsible for the functioning of the human body. Under the influence of tobacco, muscle activity and intellectual functions suffer, and peripheral nerves are damaged.
Anxiety
Smoking and panic attacks and increased levels of anxiety are interconnected. Cigarettes definitely have a negative impact on the functioning of the ANS (autonomic nervous system).
Nicotine affects the brain:
- Direct toxic effect.
- Indirect action.
When poison is absorbed into the blood, a negative reaction is formed that changes the contractility of blood vessels and the functioning of the cardiovascular system as a whole. When smoking, blood vessels spasm (they narrow), the brain is poorly supplied with oxygen and glucose, and the functioning of the central nervous system becomes worse.
Depression
When a person quits smoking or experiences “nicotine hunger,” he becomes nervous. This is expressed in a negative effect on the nervous system in the form of symptoms:
- Depression.
- Severe irritability.
- Increased nervousness.
- Aggression, anger, reaching the point of passion, when the smoker’s brain “fogs.”
The absence of cigarette “doping” literally shuts down the nervous system. The smoker stops reacting adequately to what is happening around him and cannot concentrate on a specific action. Mental functions are leveled, as is the ability to perform physical work. In fact, nicotine hunger turns a person into a vegetable; only a new portion of puffs helps to get out of this state.
Mechanism of action of nicotine
Most smokers tend to believe that smoking has a beneficial effect on brain function, acceleration of mental activity, concentration, and that without a cigarette they are generally unable to concentrate. Perhaps some habit or self-hypnosis is at work here, but indeed, a few puffs can give a feeling of renewed mental abilities. However, this is associated only with the appearance of short-term excitement, which appears under the influence of small doses of nicotine. But then everything happens exactly the opposite: nerve cells begin to be inhibited by nicotine, tar and other components of the tobacco product and tobacco poisoning occurs with all the above symptoms.
How can you protect the nervous system of a smoker?
Restoring the nervous system after quitting smoking is a long, labor-intensive process. You will need to completely reconsider your diet, physical activity, social circle and occupation.
To do this you need:
- Quit smoking.
- Avoid being near smokers (passive smoking is more harmful).
- Do not communicate with smokers; often a person grabs a cigarette not because he wants to, but “for the company.”
- Constantly be busy physically and intellectually. It has been proven that due to idleness or when doing an unloved job, a smoker more often takes smoke breaks to “kill time.”
It is impossible to protect the nervous system from the effects of nicotine when smoking; the poison and combustion products still enter the central nervous system; it is impossible to create barriers to their penetration into cells. This means that an effective way to protect yourself is to completely give up cigarettes.
Breathing while smoking
There is an interesting, from a psychological point of view, explanation for why smoking relieves stress. A study was conducted that showed that even a few minutes before relief, a person calms down just by touching a cigarette.
Even inveterate neurotics peacefully close their eyes, feeling the smell of smoke, although just a minute ago they were ready to rush in rage at those around them.
Scientists associate this change in behavior and calmness with measured breathing, during which the smoker inhales nicotine. It is the ability to breathe rhythmically that relieves tension. Severe stress and smoking become interconnected, and the person seems to “exhale” the problem out of himself along with the smoke.
Why do you get nervous when you give up cigarettes?
“I quit smoking and became nervous” - almost 99% of smokers assess their condition without cigarettes in this way. The reason for this is:
- Withdrawal syndrome. Although nicotine has a weaker effect on the nervous system than drugs or alcohol, it changes gas exchange in the blood and can cause “withdrawal.”
- Psychological discomfort. Habitual rituals collapse, a person is forced to leave his “comfort zone,” which irritates him. An empty space is formed, which was previously occupied by smoking cigarettes; now you need to strain and find something to do.
- Physical discomfort. In the first days of quitting, in addition to withdrawal, the smoker is tormented by a cough, which also causes nervous instability.
- Fear of failure. Addicts implicitly expect that they will start smoking again. This “what if”, the expectation of the inevitable, leads the nervous system into a state of overexcitation.
Lack of nicotine is the main cause of “nerves”. Other smokers can cause dissatisfaction; a person is forced to fight with himself, and not stop communicating with friends, relatives, and colleagues.
Effect of tobacco on the respiratory system
Cigarette smoke contains more than four thousand toxic components, which, when they enter the lungs, settle there forever, or are carried by blood throughout the body. Arsenic, contained in cigarette smoke, is a poison on the basis of which chemical warfare agents were created, which were actively used for gas attacks during the First World War.
Benzene contained in cigarette smoke actively promotes the development of cancerous tumors. Statistics show that smoking is the cause of lung cancer in more than 90% of cases. Microparticles of polonium, which are contained in cigarette smoke, are radioactive and, settling in the lungs, will irradiate the body for the rest of their lives, also contributing to the development of cancerous tumors.
How does nicotine affect the body?
Acting as a stimulant, nicotine has a negative effect on the human body:
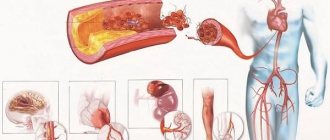
- promotes the development of vascular atherosclerosis, and this leads to strokes and heart disease;
- promotes the formation of blood clots;
- has a carcinogenic effect (promotes the development of cancer);
- causes cell mutations that increase in subsequent generations.
A novice smoker, as a rule, experiences nausea and sometimes vomiting when trying to smoke - these are the body’s protective reactions to poisoning.
- excitability increases,
- reaction time decreases,
- the feeling of anxiety disappears,
- short-term memory improves,
- attention improves,
- appetite decreases,
- general relaxation sets in.
Symptoms
- The feeling of hunger disappears, and therefore a person is quite capable of losing weight from his addiction.
- The whole body relaxes.
- The person becomes calm and can easily endure stressful situations.
- There is nervous excitement, which can manifest itself in a thirst for activity.
However, you should not deceive yourself, since all these processes are temporary. But they are the ones who can identify a novice smoker who does not yet smell of cigarette smoke.
Over time, the situation worsens - the slightest stress can increase the number of cigarettes smoked daily, and the smoker will need more cigarettes to calm down.
The effect of tobacco on the reproductive system
Toxic substances contained in cigarette smoke are distributed throughout the body and, among other things, attack the human reproductive system. The situation is especially dire in the case of the female body. All female reproductive cells are formed from birth and in the first three years of life. And this supply is no longer updated or replenished.
However, with male reproductive cells the situation is also bad. Despite the fact that they are created and renewed during life, if the body is, in principle, poisoned with toxins due to smoking, then healthy cells cannot appear in the poisoned body. And for a smoker to conceive a healthy offspring, it will take years to restore and cleanse the body, and even in this case, there is still a possibility that the child will be born sick.
Even the notorious Adolf Hitler understood the harmfulness of smoking and its impact on the gene pool of the nation, so in the Third Reich there was a fierce fight against smoking, but the most interesting thing is that the tobacco factories of the Third Reich were working at full capacity, selling their products... to the conquered territories, mainly Slavs.
And the war against our people did not end, it simply moved to another plane - it became invisible. Hitler's behests are successfully carried out by tobacco corporations, 97% of which are foreign, that is, 97% of the profits from the destruction of Russians go to foreign companies. And can those who every day by purchasing a new pack sponsor the destruction of their people talk about patriotism and love for the Motherland? Each smoker not only kills himself, he kills on average 10-15 people around him and sponsors the genocide of his people every day.
The occurrence of acute nicotine intoxication
Therefore, it is necessary to know the characteristic signs of such poisoning:
- nausea and vomiting;
- salivation;
- rapid pulse and high blood pressure (at the beginning of smoking);
- weak pulse and low blood pressure (30 minutes after smoking);
- confusion;
- general weakness;
- decreased vitality;
- stomach ache.
Help with such poisoning:
- access to fresh air,
- Irrigation of facial skin with cold water,
- protection of the respiratory tract from vomit.
If convulsions occur, before the ambulance arrives, ensure airway patency and prevent tongue biting.
The emergence of a smoking habit is very often combined with other equally dangerous addictions - alcohol or drug use.
Considering everything said above, the conclusion suggests itself: bad habits are a serious threat to the health of not only an individual person, but also society as a whole.
The fact is that the nervous system is the most complex and at the same time the most fragile in our body. In many aspects it has not yet been fully studied, but we can say with certainty that nerve cells are very delicate and sensitive, and it itself is the main one in our body. Why? Because it is she who is responsible for our thinking, conscious and unconscious actions, and it is under her control that absolutely all processes take place in our body. And since nicotine is a powerful neurotoxin, it becomes clear that it is the nervous system that must first suffer from smoking in general and the effects of nicotine in particular. But how negative is this influence?
What is nicotine
When a person smokes, nicotine enters his body along with tobacco smoke. It is a very potent neurotoxin. Its key property is the ability to easily penetrate any protective physiological barriers. Nicotine has the ability to be absorbed into all biological fluids, including blood fluid.
- Stopping breathing.
- Slowing heart rate.
- Death.
Smoking and the nervous system are interconnected. A large number of smokers smoke a pack of cigarettes per day. A person who smokes does not die because nicotine does not penetrate in full immediately, but gradually, over a certain period of time.
Features of nicotine and alcohol
The work of the nervous system is based on the transmission of impulses from the brain to a specific organ. A substance produced in the human body, acetylcholine, is responsible for this process. Under its influence, the functioning of various organs changes:
- heart rate decreases;
- pressure decreases;
- peristalsis of the digestive organs increases;
- the muscles of the bronchi, bladder, uterus, etc. contract.
In addition, acetylcholine is involved in the transmission of impulses between different parts of the brain. Its small concentration facilitates the transmission process, and an increased volume can have an inhibitory effect. Disruption of acetylcholine metabolism provokes hallucinations and dangerous mental pathologies.
Early smoking can negatively affect children's psyche. In adolescents, the normal development process of the body is disrupted and the following symptoms appear:
- weakness;
- increased fatigue;
- absent-mindedness;
- memory impairment;
- decreased intelligence.
All this negatively affects the child’s psychological state, provokes a lag in academic performance and physical development, and causes a feeling of alienation from the team. As a result, the teenager feels lonely.
The earlier a child starts smoking, the higher the risk of switching to other drugs - marijuana, etc. Teenagers are more susceptible to the influence of advertising in which a cigarette is an invariable attribute of a beautiful life.
Smoking is no less dangerous for older people. At this age, the risk of developing atherosclerosis increases, which leads to rupture of blood vessels and hemorrhage due to loss of their elasticity.
This disorder is typical for older people and often causes paralysis and even death of the patient. The negative consequences of addiction also include epileptic seizures. They are caused by degeneration of nerve fibers due to heavy smoking.
Smoking is considered a bad habit that negatively affects most organs. Addiction to nicotine leads to disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, which are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. To cope with the problem, you need to completely give up cigarettes.
Stories from our readers

Saved the family from a terrible curse. My Seryozha hasn’t drunk for a year now. We struggled with his addiction for a long time and unsuccessfully tried a lot of remedies over these long 7 years when he started drinking. But we made it through, and thanks to everyone.
Nicotine, alcohol, pain instead of joy...
The destructive effects of alcohol are known to everyone, as is nicotine. However, all the same, even knowing what a detrimental effect they have on the heart, liver, and reproductive health, few people are afraid of the consequences. People continue to drink alcohol and smoke cigarettes, often doing it at the same time, without thinking at all, or, conversely, trying not to think about the harm they cause to all their internal organs and systems.
Nicotine and alcohol have a huge impact on the body as a whole, and their compatibility can cause irreparable damage to health. That is why it is necessary to constantly remind about the terrible consequences that the use of these substances can bring, and to tell children and schoolchildren about the dangers of smoking and alcohol.
After all, a child’s growing body is most susceptible to such harmful effects, and the pathological changes that occur to it against the background of addiction to bad habits are irreversible. But unsubstantiated statements no longer frighten anyone; everyone has long been accustomed to operating with specific facts. Let's try to figure out what processes occur in the body under the influence of nicotine and alcohol, and what result their combined use can ultimately lead to.
Alcohol and nicotine are potent psychoactive substances that significantly affect the central nervous system. Psychoactive substances are substances that can alter a person's mental state, leading to various positive or negative health effects.
Those that, due to their influence on higher mental processes, are used in medicine to treat various mental diseases are called psychotropic substances. And those that are addictive and prohibited by law are called drugs. These substances, in addition to nicotine and alcohol, include the familiar caffeine, as well as some medicines and narcotic substances: cocaine, LSD, marijuana and others.
Alcohol and nicotine, although they are psychoactive substances, are not yet classified as drugs, although they cause very strong mental and physical dependence.

From a scientific point of view, nicotine is very highly toxic and is a dangerous poison that affects the central nervous system. However, when consumed in small doses, such as through smoking, it can act as a psychostimulant. It promotes a massive release of adrenaline and glucose, thereby causing excitement.
This effect can manifest itself in a person either as relaxation and calmness, or as revival with moderate euphoria. Smoking nicotine-containing substances often provokes the development of cardiovascular diseases, severe intoxication and lung cancer. In addition, nicotine has a pathological effect on the fetus.
According to the classification of psychoactive substances, nicotine belongs to the tertiary group at the intersection of stimulants and depressants. Alcohol in this classification is in the basic group and is classified as a depressant. Depressants are psychoactive substances that have a depressing effect on the central nervous system and significantly suppress all aspects of its activity.
The importance of the central nervous system for the human body
The central nervous system (CNS) is the basis for the normal functioning of the human body. It is she who ensures the interconnection of all organs and systems, as well as interaction with the environment. It is thanks to the central nervous system that a person is able to perceive external and internal stimuli through the organs of touch, smell, vision, etc.
It is the nervous system that provides an adequate response to these stimuli. It can be expressed in the form of speech, motor activity or secretory secretions (sweat, urine, saliva, gastric juice). In addition, control over the internal integrity of the body and supervision of the passage of life processes both at the intracellular level and at the level of organs and systems is carried out by the central nervous system.
Of course, there is no need to diminish the influence on the integrity and coherence of the work of the human body from its other components. But you need to know that without a nervous system, not a single organism on Earth can exist. This is the main connecting link for all human organs and systems.
Effect of tobacco on the digestive system
The teeth are the first to suffer from smoking. Exposure to high temperature cigarette smoke (60–80 degrees) leads to the destruction of tooth enamel, the formation of cracks and, as a result, pain, reactions to cold and hot, and subsequently to complete tooth destruction. Also, under the influence of cigarette smoke, the production of saliva increases, which leads to irritation of the gums, their weakening and tooth loss.
Regular smoking during the day leads to chronic lack of appetite, as nicotine slows down the functioning of the stomach. Nicotine also increases stomach acidity, which subsequently leads to ulcers and gastritis. WHO statistics are disappointing - among smokers the number of deaths from gastrointestinal cancer is four times higher than among non-smokers. Also, according to WHO, 69% of cases of stomach and intestinal ulcers are associated with smoking.
Description and characteristics of the problem
But how does smoking affect the brain? How does nicotine addiction develop? Ten seconds after the first puff, nicotine enters the brain, influencing nerve receptors, including acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that transmits impulses to muscles and internal organs. Nicotine has the same effect, but is not controlled by the brain.
- Serotonin or the “joy hormone” is involved in a person’s emotional stability.
- Dopamine has a similar effect to serotonin.
- Norepinephrine has a stimulating effect on the body. A person who smokes often believes that cigarettes help improve performance.
- MMC.
- Glumate, which promotes a surge of positive emotions when smoking a cigarette.
A person's condition after smoking may vary. But the effect of nicotine, which seems to relieve stress, is actually illusory. The effect of nicotine on the brain is negative, as it stimulates the activity of the central nervous system, promoting an artificial increase in the level of dopamine and serotonin, which creates a feeling of joy and satisfaction. This is how nicotine addiction develops.
Over time, a person is forced to smoke more cigarettes per day, as the level of nicotine in the body begins to gradually decrease.
Nicotine addiction develops for the following reasons:
- Genetic predisposition,
- Age.
Possible consequences of exposure
Under severe emotional stress or in stressful situations, many people with an addiction experience a strong desire to smoke. This is associated with psychological dependence on cigarettes. During breaks, a person’s health worsens.
The abnormal effect of a toxic substance on nerve impulses is due to the fact that it becomes part of the mechanism of their transmission. The human body contains many nerve endings that are sensitive to the toxin.
If nicotine stops entering the body, withdrawal occurs. In such a situation, the nervous system also suffers. When quitting smoking, the following symptoms are often present:
- Emotional fluctuations arise. The person may feel nervous, become more anxious and irritable, and have difficulty concentrating.
- There are problems with attention. It is difficult for a person to sit in one place.
- Severe sweating appears and frequent hot flashes occur. Chills are also often present.
- Blood pressure decreases and heart rate slows down. Headaches and tachycardia often occur.
Important! In some situations, nicotine intoxication occurs. It occurs if a person smokes 5 cigarettes in a row. In this case, there are symptoms of nervous system pathologies such as eyelid twitching, convulsive syndrome, and dilated pupils.
In difficult situations of nicotine intoxication, consciousness suffers, and a person develops delirium. In the absence of timely medical assistance, there is a risk of death.
Statistical data
General statistics of medical research:
- the most smokers are people from 25 to 45 years old;
- every 4th death aged 35-65 years is somehow related to smoking;
- 80-88% of those who die from lung cancer are smokers.
- women start smoking at an earlier age than men;
- over the last decade of the last century, there were more heavy smokers (those who smoke more than 20 cigarettes a day) among women (their number increased from 13 to 23%);
- mortality from lung cancer among women exceeded mortality from breast cancer;
- the weight of newborn children of smokers is on average 200 g less than that of newborns of non-smoking mothers;
- the number of stillbirths and deaths among newborns and neonatal children of smoking mothers increased by 33%.
- although the sale of cigarettes to children is prohibited, more than 6 million teenagers under the age of 13 smoke;
- 80-90% of smokers started smoking before the age of 21;
- Every day, approximately 3,000 schoolchildren try smoking for the first time;
- Teenagers smoke approximately 1.1 billion packs of cigarettes per year.
- 20% of cases of cataracts are due to smoking;
- diseases associated with the blood supply to the brain, under the age of 65 among smokers are 24% among men and 6% among women;
- Every year, up to 250 thousand cases of lower respiratory tract infections (bronchitis, pneumonia) are observed in newborns and small children under 1.5 years old - from families of smokers;
- up to 500 thousand cases of asthma in children were more severe due to passive smoking;
- Babies born to women who smoke have an increased risk of developing sudden neonatal death syndrome.