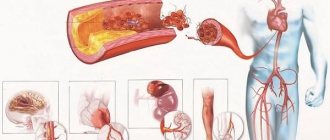
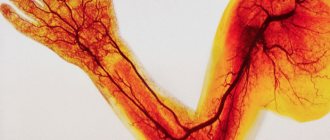
One of the main causes of vascular diseases, including the brain and heart, is cigarette smoking. Their effect on the body is realized through rapid changes in the composition of the blood, which carries nicotine and other toxic substances absorbed from the mucous membrane of the mouth and respiratory tract. Of all the organs of the human body, the brain suffers the most from tobacco toxins, since it is the brain that receives the largest dose of neurotoxic poison. What is the effect of smoking on the brain and cerebral vessels and what causes the appearance of nicotine addiction - read the article.
About the effect of smoking on the human brain
According to research, about a quarter of all energy received by a person goes to maintaining brain function. Regular smoking leads to the fact that the brain requires much more energy . The brain is not able to accumulate nutrients; it processes them instantly.
The initial impact is almost invisible. The fact is that, being under the influence of pesticides, the human body automatically launches recovery processes. But over time, the body copes with this function worse , and the smoker runs the risk of feeling all the consequences of his addiction.
If you consume more than 1 pack of cigarettes daily, the negative effects increase and the risk of developing dangerous diseases increases sharply.
In addition, toxins entering the smoker’s body neutralize the immune properties of the brain. Immune cells, recognizing compounds that are atypical for the body, destroy the resulting infections. However, nicotine suppresses these protective functions.
Meet Alena. And she hasn't smoked for over a year! Alena quit smoking four times, but without success. Then she bought Monastery tea and never returned to the bad habit.
Does smoking affect intelligence and memory?
The greatest brain damage was detected in the frontal areas. A smoker has difficulty performing simple daily tasks such as going to the store, driving, etc. Over time, the damage becomes more and more, which begins to affect the intellect . Smoking affects the metabolism of the cerebellum and midbrain. The smoker loses his balance and has problems with coordination.
The photo below shows the brain of a healthy person and the brain of a smoker (the damage to the frontal zone is clearly visible).
As a result, after regular smoking a person may face the following consequences:
- An increase in nicotine intake into the body leads to disruption of brain activity, and as a result, to a decrease in the level of intellectual abilities.
- Over time, memory deteriorates noticeably, and it is difficult for a smoker to concentrate on certain processes or tasks.
- The smoker spends more time on completing assigned tasks. Analysts estimate he will spend 20% more time.
How do cigarettes affect the blood vessels of the brain?
In most cases, smoking constricts blood vessels in the brain, which increases blood pressure . Headaches in smokers are common.
Sometimes a smoker's body reacts to an addiction by dilating blood vessels and lowering blood pressure . This is manifested by symptoms such as weakness, dizziness, and attacks of nausea.
The walls of healthy vessels (endodelia) narrow and expand, depending on the blood flow. But nicotine disrupts the elasticity of blood vessels, which causes them to spasm. Therefore, over time, scars and plaques form on the walls.
The tar and toxic substances contained in cigarettes thicken the blood. Blood flows slowly through damaged vessels of increased viscosity. Slow blood flow means oxygen starvation for the brain and death of nerve cells.
Local blood flow decreases with regular smoking, which leads to problems with venous outflow. As a result, atherosclerosis and stroke develop .
Can't quit smoking? Make a decision, order one of these smoking cessation products:
- Tibetan collection
- Tabamex drops
- Monastic tea
You've been addicted enough already! Quit without pain, weight gain or irritability.
Vascular effects
Nicotine is easily absorbed from the mucous membranes, which are exposed to cigarette smoke, which, in addition to this neurotoxin, contains more than 3,000 compounds. The effect of smoking on the blood vessels of the brain due to nicotine alone is expressed in the following:
- Blood clotting increases and its viscosity increases.
- The aggregation of blood cells, including red blood cells, increases.
- Blood pressure increases.
- Cholesterol metabolism is disrupted.
The effect of cigarettes is that local cerebral blood flow decreases when smoking tobacco, venous outflow becomes more difficult, the lumen of blood vessels narrows, and the blood supply to the brain as a whole worsens. As a result of increased blood viscosity, conditions appear for the development of atherosclerotic changes in cerebral vessels. And atherosclerotic changes are known to contribute to the development of conditions such as vascular dementia and ischemic stroke. You can learn more about dementia here: https://stop-dementia.ru/
How does nicotine work and why is it addictive?
A cigarette smoked can give a person different effects.
Some people use cigarettes as a means to combat nervous tension, while others use them as a stimulant. Nicotine is of natural origin and belongs to the group of alkaloids. Once in the brain, the substance begins to come into close contact with acetylcholines (mediators of nervous excitation). They are produced by the brain independently, and the amount of mediators is strictly controlled. Nicotine cannot be controlled, therefore, when it enters the brain, it provokes the following phenomena:
- The release of a large amount of energy, as a result of which increased activity of the smoker is observed. This is due to the fact that nicotine accelerates the release of neurotransmitters from neurons and increases the activity of cholinergic cells.
- Nicotine causes the brain to release large amounts of joy hormones and enhances the synthesis of glutamate. It is thanks to the latter hormone that a feeling of joy appears, which can form the preconditions for the emergence of addiction.
- The gradual deposition of nicotine on neurons dulls the feeling of euphoria, which is why the user experiences an irresistible desire to smoke again. This is how complete dependence on cigarettes manifests itself.
Many smokers perceive the effects of nicotine as a way to relieve stress and get rid of tension. However, this effect is illusory . Nicotine stimulates the central nervous system, artificially increasing serotonin levels, which contributes to the development of tobacco addiction.
If a person does not receive the required dose of nicotine, serotonin in the central nervous system tends to a minimum, which causes irritation and an irresistible desire to smoke. The body experiences serious stress, which increases if abstinence from smoking is prolonged.
Over time, smoking affects the character and psychological factors of the smoker's behavior. High excitability and nervous tension appear. Subsequently, these circumstances become catalysts for the development of nervous diseases.
Mechanisms of addictive behavior
Nicotine begins to act on neurons within 7 seconds after the first inhalation of tobacco smoke. It affects the brain in its various parts, since it is an analogue of the natural transmitter of nerve impulses - acetylcholine (ACh). Nicotine activates ACh receptors instead of acetylcholine and competes for binding sites with them, since it has a longer interaction with ACh receptors than their natural activator. This leads to the appearance of new ACh receptors, which then also interact with nicotine.
Stimulation of ACh receptors in the brain activates the release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate, dopamine, serotonin, β-endorphin, norepinephrine, γ-aminobutyric acid, etc. The influence of the main mediators on the human brain and its emotional state during smoking is presented in the table:
| Mediator | Effect |
| Glutamate | Involved in memory mechanisms and the formation of a memorable trace. |
| Dopamine | Provides a feeling of pleasure, but the supply of dopamine may be depleted when smoking. This leads to a feeling of fatigue and depression. |
| Serotonin | Improves mood and creates emotional stability. |
| β-endorphin | May create a feeling of euphoria. Has an analgesic effect. |
| Norepinephrine | Stimulates the body, sharpens attention, increases concentration. |
| γ-aminobutyric acid | Has a relaxing effect. |
Nicotine addiction and mental illness
Numerous studies by scientists show that the receptors that are most susceptible to nicotine are directly involved in the pathogenesis of mental illnesses . Statistics show that the majority of citizens with mental disabilities are active smokers.
If a psychological problem arises, a person’s chance of starting to smoke increases, and the development of dependence on nicotine increases significantly. According to experts, the relationship between smoking and the psyche is explained by several postulates:
- Smoking provokes affective and neurosis-like disorders.
- Nicotine cravings and mental illness have similar causes and predispositions.
- The onset of the disease occurs under stress, so with a high degree of probability the user may take up a cigarette. For a certain period of time, nicotine will help artificially increase dopamine levels, which will help hide the manifestations of mental disorders. However, it will not be possible to completely stop the disease.
The effect of nicotine on the nervous system
The neurotoxic poison that is released when a cigarette smolderes is similar in structure to acetylcholine. This substance helps transmit impulses from the brain to other organs. After the first puff, nicotine reaches the receptors in 3-5 minutes. It dilates blood vessels, and as a result, blood flow improves, heartbeat increases and a person feels cheerfulness, excitement, and a surge of energy. A smoked cigarette stimulates neurons and speeds up the movement of impulses.
When the effect of the substance weakens, the blood vessels contract from the lack of doping, a spasm occurs, the state of health worsens, and performance decreases. A smoker may feel overworked and experience sudden and frequent mood swings. The brain requires a new dose of stimulant. This is how addiction or tobacco dependence develops.
- How to fry zucchini in a frying pan - step-by-step cooking recipes with photos
- How to get brown color when mixing paints
- Frozen strawberry pie
Will the brain recover after quitting smoking?
Once a smoker gives up the habit, his body will gradually begin to recover from the damage caused. Studies show that within 3 weeks the elasticity of the blood vessels in the brain fully returns, which ensures normalization of blood circulation. Over time, the brain cells return to normal.
The key condition for recovery processes is complete cessation of smoking , ignoring other smokers and minimizing the risk of encountering cigarette smoke in the form of a “passive” smoker.
A former smoker should be examined to determine what damage has been done to the brain. The specialist will help him speed up the recovery of the body as a whole and give practical recommendations on how to do this with maximum efficiency.
Physical activity and proper nutrition are important. Increasing the amount of nutrients entering the body will give an additional incentive to all organs to begin recovery at an accelerated pace.
Renewal of cells of the nervous system with a complete cessation of smoking will occur in approximately 30-35 days . Over the designated period, the user will normalize his condition, irritability and nicotine withdrawal will go away.