What it is?
Dilatation of the cavity of the left ventricle occurs when it is impossible for blood to pass into it from the atrium. The most common cause of this condition is valve narrowing.
Against the background of mitral insufficiency, the atrium on the left experiences enormous stress, trying to push blood through the narrowed opening. Often, dilatation of the left ventricle of the heart occurs due to atrial fibrillation. This form of the disorder is characterized by prolonged atrial fibrillation.
The danger of the pathology is that its symptoms may not appear at all or may be similar to the human condition with heart failure. Sometimes it becomes an unexpected finding during a patient's cardiac ultrasound.
In medical practice there is such a thing as idiopathic dilatation. This pathological condition can occur with a completely healthy human heart and lungs. As a rule, in this case, cardiologists advise the patient to lead a correct lifestyle and completely eliminate alcohol. Such recommendations allow the patient to restore his health within 9-12 months. If the cause of the pathology does not lie in excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, then all that remains is to observe the size of the left atrium.
Possible complications and treatment
The expansion of the chambers of the heart leads to serious consequences: over time, dilatational hypertrophy occurs - stretching and thickening of the walls of the heart. The condition provokes the development of:
- chronic heart failure;
- chronic infectious heart diseases;
- mitral insufficiency;
- valve ring expansion;
- thrombosis, thromboembolism;
- atrial and ventricular fibrillation.
These complications affect the patient's quality of life and, in severe cases, lead to death. Therefore, treatment should be prescribed and monitored by a cardiologist.
The goal of therapy is to eliminate or correct the primary disease that led to the stretching of the chambers. Depending on the underlying pathology, the following may be prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- anti-ischemic drugs;
- antiarrhythmic drugs;
- cardiac glycosides;
- beta blockers;
- ACE inhibitors;
- antihypertensive drugs;
- antiplatelet agents;
- diuretics.
If drug therapy does not bring results, surgical methods are used, mainly the installation of a pacemaker. The device monitors heart contractions.
Supportive and preventive methods are an integral part of therapy, without which success is almost impossible. Improving blood circulation, strengthening the heart muscle, increasing immunity, easing the load on the heart improves the quality and prolongs life expectancy. To do this you need:
- create the right diet based on plant foods, lean meat, various types of fish, seafood, dairy products, nuts and grains;
- play sports or just move more, walk, do exercises;
- get rid of bad habits.
Reasons for development
Understanding what dilatation of the right ventricle of the heart is, it is necessary to initially determine the nature of its origin. When a patient has hypertrophied areas in the heart muscle, this entails thickening of the myocardial walls and an increase in the mass of the right heart. Such problems lead to volumetric and structural changes in parts of the myocardium, organ hypoxia, and increased pressure in the right atrium.
In infants, this pathology may be a consequence of congenital heart disease. Hypertrophy in infants occurs due to a defect in the ventricular septum, as a result of which blood does not enter the aorta, but is thrown into the right ventricle. This forces the baby's atrium to experience severe stress when pumping a large volume of blood.
Dilatation of the right ventricle in adults, in particular in professional athletes, is usually associated with cor pulmonale, namely with breathing problems. Against the background of a lack of air in the pulmonary arteries, blood pressure rises, and the right atrium increases in volume.
Dilatation can be caused by several reasons. Most often they are represented by changes in the myocardium and overloads that this department experiences as a result of narrowing of the mitral valve. Pathological conditions are usually caused by an inflammatory process in the heart - myocarditis. Often the cause of the pathology is ischemic disease and hypertension.
left ventricular dilatation
On September 7th we turned 1 month old!
Kitten already has his first documents: birth certificate, citizenship, registration, SNILS, Taxpayer Identification Number and, for now, a temporary medical insurance policy.
What we can do:
- confidently hold your head while lying on your tummy, raise your shoulders, pushing off with your arms,
- we push off with our legs, both lying on our tummy (toes) and lying on our back (heels),
- we try to crawl,
- we begin to turn over,
- let's go, my kitten
- distinguish mom from dad,
- we cry in different ways when we need something (to eat - la, if we don’t need it - nooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo----, and we’re twirling our heads, it hurts, etc.).
What worries us:
- eyes festered (washed with tea leaves, chamomile, smeared with tetracycline 1%),
- my tummy hurts, gasses (espumisan, hilak forte) torment me.
12-th of September
We went to the hospital to see the pediatrician. There is no doctor at our site; the appointment was conducted by the manager. They examined us from all sides, measured us, listened to us. The verdict is a healthy baby, developing according to his age. We weigh 4852 g (+1562 g), height 57.5 cm (+3.5 cm). She assigned us to health group II “A” (includes healthy babies, but either there is a family history, or the mother’s pregnancy and childbirth were accompanied by complications). She gave us coupons for an ultrasound scan. and ECHO-KG. On the same day we saw a surgeon and an ophthalmologist, and we were also vaccinated against hepatitis B (we have a schedule of 0-1-2-12). The ophthalmologist said that we are great, the fundus is good, the eyes are already clean, but it’s better to wash your face with chamomile. Attendance at appointment in 1 year. The surgeon is also doing well, he just advised me to trim the frenulum at the uvula while the children are still small. Turnout at 6 months
September 13
We went to pediatric dentistry for 50 years of the Komsomol. The bridle was cut. My Kitten was sleeping and didn't even wake up
September 17
We had an ultrasound scan.
We looked at the internal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys) and hip joints. Everything is normal, developed according to age, moderate intestinal flatulence. Neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) – hematoma (pseudocyst), moderate dilatation of the left lateral ventricle. This is what the opening of the amniotic sac resulted in
September 19
were on ECHO-KG.
Conclusion: Open oval window
(Occurs in 1 - 2% of people. Currently, in pediatric practice there is an overdiagnosis of the open foramen ovale. Blood shunting occurs from left to right, is inconsistent, the volume of the shunt is small. There is no pulmonary hypertension and dilatation of the right chambers. These patients require observation 1 once every 2-3 years).
False chord of the left ventricle
(Filamentous structure located in the cavity of the left or right ventricle. Located between the interventricular septum (IVS) and the wall of the heart, the head of the papillary muscle and the wall, etc. The base of the additional chord does not thicken in systole. The number of chords may be different . Occurs in 98% of cases. Minor anomaly of cardiac development).
With ultrasound data rm. I need to see a neurologist. I'll go next week.
But with ECHO-CG only at 2 months. (The ultrasound specialist said that it’s okay, these deviations do not affect the functioning of the heart).
September 25
We saw a neurologist.
According to neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain), done on September 17,
We have a hematoma (pseudocyst), moderate dilatation of the left lateral ventricle.
Diagnosis:
Mild hyp. pathologies, pseudocyst of the brain.
Recommended:
- mother's massage;
— Elkar 30% 5 drops. 2 r. per day (course 1 month)
In words she said that in general the child is good (ttt), he is developing well, correctly, according to his age. We stand on our legs correctly on the entire foot. Take Elnar, the pseudocyst should resolve and should not be there at the next appointment.
Turnout at 3 months with new ultrasound results.
We are 2 months old on October 7th!
Weighed in at home - 6100 g (+1248 g)
We'll go to the hospital on Thursday.
What we can do:
- confidently hold your head while lying on your tummy, raise your shoulders, pushing off with your arms,
— we push off with our legs, both lying on our tummy (toes) and lying on our back (heels), we try to crawl,
- roll over from tummy to side,
- we walk, we smile
- we distinguish mom from dad, visually focuses and keeps a moving and stopped object in the field of vision,
- turns the head to the source of the sound, searches for it with the eyes,
- we cry in different ways when we need something (to eat - la, if we don’t need it - nooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo----, and we’re twirling our heads, it hurts, etc.).
What worries us:
- my tummy hurts, gasses (espumisan, hilak forte, linex) torment me.
On the recommendation of doctors, we also take Elkar and Aquadetrim.
Scheduled examination by a pediatrician at 2 months.
Weight - 6130 g (+1278 g), height - 61 cm (+3.5 cm). I was vaccinated against hepatitis B. I was prescribed Aquatrim and Elcar and my mother's massage. At the 3 month appointment, take tests: blood, urine. See a neurologist.
On 10/31/2013 we took tests...
Somehow they collected the urine and started to gush out - all the time he strives to describe who is changing his diaper, but here they are, they waited and waited, almost missed it))) they collected just a little bit, I hope that it will be enough for analysis.
They donated blood in the hospital, while they were waiting in line, they began to be a little capricious, in the office they calmed down, when they pricked their finger they didn’t cry, but when they squeezed out the blood, they burst into tears... as soon as it was all over and the aunt let go of the finger, he immediately calmed down and didn’t leave the office again crying, dad met us there, quickly got dressed and went to visit grandma.
We weighed ourselves at home, we already weigh 7 kg.
Tomorrow we are going to the hospital for a scheduled appointment for 3 months, vaccinations will be given (diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, polio). Damn scary...
Symptoms
Sometimes patients are diagnosed with disturbances in the functioning of the left and right ventricles at the same time. This cardiac pathology is called chamber dilatation of the ventricles. Among its symptoms are:
- shortness of breath even with little physical exertion;
- the occurrence of pain that radiates to the left under the shoulder blade or to the chest area;
- fatigue, lethargy, low performance;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure.
Dilatation may be asymptomatic or accompanied by disorders characteristic of many other cardiovascular diseases. Often, patients complain of arrhythmia, in which the moderate heart rate increases. But drug treatment for increased heart rate in this case does not give any results. Therefore, it is important to correctly diagnose the disease, which will allow choosing the most optimal therapy for the patient.
How does dilatation manifest?
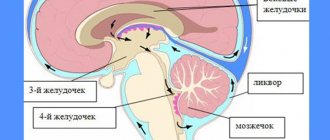
The only factor after which the expansion of the ventricles of the brain begins is an excessive amount of cerebrospinal fluid, which, as it were, stretches the cavities. This occurs due to the fact that for some reason the movement of this fluid in the body is disrupted.
In fact, dilatation is not a disease or pathology, it is a symptom of another disease. This situation often occurs in children born prematurely. If the baby was born at the right time, then dilatation of the lateral ventricles is not observed.
Dilatation of the cerebral ventricle is visualized
To determine whether there is excessive expansion of these organs, measurements are taken using different techniques. The main criterion is the depth of the ventricles, which should fluctuate around 1-4 millimeters. If this indicator is exceeded and the ventricle takes on an incorrectly rounded shape, the doctor will be able to diagnose dilatation. The doctor should also pay attention to the condition of the occipital horns, anterior horns and carry out appropriate studies to confirm the diagnosis.
Main signs of pathology
The normal diastolic volume of the right atrium at 18–25 years of age is about 105 cm3, the left atrium is 90–135 cm3. By the age of sixty it increases by 5–10 cm3. In women it is usually 3–6 cm3 more. When contracted, the cavities are reduced by almost half. Any volumes above the norm are defined as atrial dilatation.
The right atrium receives blood from the vena cava, coronary sinus of the heart and many small veins, and the left atrium receives blood from the lungs. There are no valves at the confluence of the pulmonary and vena cava. The reverse flow of blood is stopped due to the contraction of the ring-shaped muscle formations.
Overdistension of the chambers is caused by difficulty in the passage of blood flow through the atrioventricular openings located between the ventricles and atria. A mechanical obstacle can cause dilatation due to impaired functioning of the valve apparatus and endocardial diseases.
Myocyte cells are responsible for the ability to contract in the atria. The process of contractility is ensured by the mechanism of connection of actin and myosin fibers with the participation of electrolytes and energy production. Any heart disease associated with myocardial damage necessarily affects the supraventricular formations.
The disease at an early stage does not have its own symptoms. It can be diagnosed by undergoing a preventive examination by a cardiologist. At a late stage, the disease manifests itself with various signs that are similar to the symptoms of heart failure.
Dilatation of the left atrium, symptoms:
- Edema.
- High fatigue.
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
- Heartache.
- Extreme pallor of the skin.
- Dyspnea.
Moderate dilatation is observed in tall athletes, their body is constantly exposed to physical stress, so a slight expansion is considered quite normal.
Forecast
Dilatation of both atria requires treatment, as it is a pathological change. It is selected based on the cause of the disease. The generally accepted treatment regimen includes taking ACE inhibitors, antiplatelet agents, drugs to improve tissue metabolism and relieve symptoms that accompany coronary heart disease.
In case of heart failure, the use of glycosides is required. Particular attention is paid to normalizing heart rate. For this purpose, the patient may be prescribed beta blockers.
Since dilatation is difficult to detect due to the absence of symptoms, drug therapy is not always able to eliminate the changes that have occurred, which may be irreversible. In this case, surgery may be required.
If these transformations are left unattended, they can cause heart failure or life-threatening arrhythmias. At the same time, timely identified pathology and its adequate treatment are not the key to success, but will stabilize the patient’s condition and improve the quality of life.
By eliminating the cause that caused the problem, you can stop the progression of dilatation.
An integral part of therapy is prevention and regular examination by a cardiologist. Without these measures, a positive outcome is almost impossible.
To avoid serious heart health problems, you should:
- Maintain a healthy diet and eat healthy foods. The diet should be rich in plant products. It is recommended to eat lean meat, fish, seafood, grains and different types of nuts. It is advisable to exclude fried, fatty foods, as well as foods with a high salt content from the diet.
- Engage in light physical activity regularly. It is best to increase the duration of walks in the fresh air and do morning exercises.
- Eliminate all bad habits. It is very important to completely give up alcohol and cigarettes.
Following a diet, monitoring body weight, regularly visiting a doctor and following his recommendations - all this will help stop the pathological process and improve the quality of life with dilatation.
With moderate dilatation, people often do not suspect its existence and live a normal life, without taking medications or other methods of therapy. If the disease was detected at an early stage and treatment was carried out, which led to the patient’s recovery, the person’s life expectancy will not be reduced. Such cases, unfortunately, are rare; more often the situation develops differently.
It is often impossible to find out what factor provoked the development of dilatation, and over time, complications of the pathology that led to the expansion of the atrium cavity begin to arise. Such disturbances become a trigger, under the influence of which the atrium stretches more and more.
After failure of a major organ occurs, a person must take medications for life. It is rare to talk about favorable prognosis for this disease, despite all the actions of doctors.
- The five-year survival rate of people with dilatation is about 80% for patients with a disease characterized by the absence of symptoms or their minor manifestations.
- After the onset of dilated cardiomyopathy, life expectancy is significantly reduced, the percentage of surviving people is approximately 15-30%.
- If, under the influence of the disease, heart failure is diagnosed, then the person will cross the five-year survival line only in 50% of all cases.
- Thromboembolism leads to the death of the patient in 20% of situations.
You cannot despair and give up if such a diagnosis is made. There is always a chance of complete relief from any illness. Modern medicine does not stand still and new developments and drugs are constantly appearing to treat a large number of diseases.
Dilatation of the left atrium can be caused by a number of other diseases, which indicates the need for regular visits to medical institutions and diagnostic testing. When any disorder is identified at an early stage of development, it is much easier to deal with it.
Diagnosis of cardiac dilatation
Minor enlargements of the heart cavities do not lead to the patient’s characteristic complaints. Therefore, initial changes are often an incidental finding during routine preventive examinations.
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound examination of the heart. It allows you to evaluate the functioning of the organ in full: the size of the chambers, the condition of the vessels, valves.
Electrocardiography is used to exclude concomitant pathology of the cardiovascular system, type of rhythm and conduction disturbance.
Using chest x-ray, you can evaluate the size of the heart and its chambers and identify the presence of signs of pulmonary hypertension.
Stress tests provide valuable information about the functionality of the cardiovascular system.
Coronary angiography is prescribed to determine the tactics of surgical treatment.
Prevention
Congenital and acquired pathologies lead to dilatation. But prevention can be used to both avoid the disease and stop its development. To do this you need to follow the simplest rules:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol in excessive quantities;
- do not overeat;
- do not overwork and avoid nervous overload.
Prevention of the development of atrial dilatation consists of measures aimed at preventing the development of diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. These include:
- balanced diet;
- cessation of alcohol abuse and smoking;
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- regular moderate physical activity.
Clinical signs
Symptoms of dilatation do not appear with moderate dilatation. Retrospective analysis shows slight tachycardia during walking, agitation, or physical activity. Signs of dilatation are clinically manifested by general symptoms of heart failure.
The doctor should suspect atrial dilatation when registering arrhythmia and conducting a comprehensive examination. You need to pay attention to:
- shortness of breath of the patient when moving, talking;
- arrhythmia of heart contractions during auscultation;
- swelling on the feet and legs.
In their complaints, patients talk about:
- the appearance of unclear weakness, drowsiness;
- fatigue;
- reduced performance.