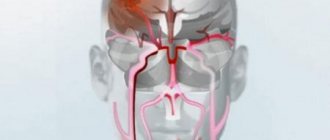
In the vast majority of cases, finding out how long people with cerebral palsy live is extremely difficult, because... This serious disease can occur with damage to different body systems. In some cases, with proper treatment, a person with cerebral palsy can live a long and completely fulfilling life, with almost no health problems. In severe situations, a child with such a developmental disorder may die within a few years. Cerebral palsy is a collective name for a number of movement disorder syndromes observed as a result of disorders of intrauterine development leading to damage to brain structures.
Signs of life expectancy with cerebral palsy
It is worth paying attention to such a problem as premature aging. This is a very pressing issue with this disease. It has been proven that by the age of 40, patients are susceptible to a decrease in life expectancy. The physical body wears out faster due to deformation of internal organs, joints and bones. Outwardly, people with cerebral palsy look much older than their legal age. If there has not been proper development and rehabilitation of the child since birth, then many systems, for example, the cardiovascular or respiratory systems, may remain underdeveloped. Thus, they work for wear, which also affects life expectancy.
Another sign that affects life with cerebral palsy is the type and course of the disease itself. With severe forms, constant epileptic seizures and with a recumbent course of this disease, the duration may be shorter than with moderate or milder forms.
Types of disease
Depending on the site of brain damage, there are five types of disease.
The most common form is spastic diplegia. This type develops due to damage to the part of the brain responsible for motor functions. This causes paresis in the lower girdle. It can be diagnosed both in the first days of life in case of a severe course, and by the year of life in a milder case. With proper care, rehabilitation and development of the child, life expectancy with this form can be equal to the life of a person without this disease.
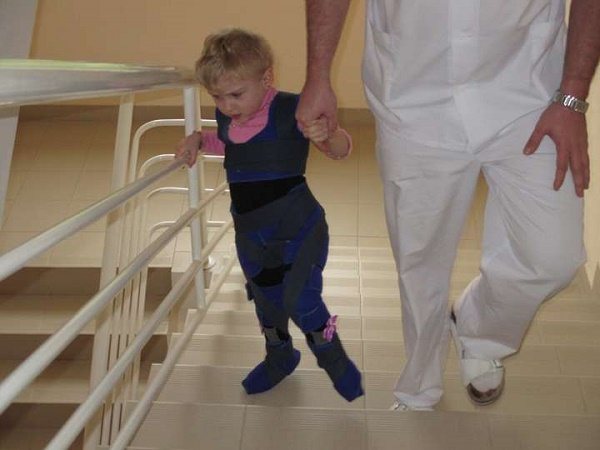
The next form is spastic tetraplegia. This form is characterized by deformations of the trunk and limbs; in half of the cases, patients suffer from epileptic seizures. Children with this diagnosis have strabismus and a disorder of the hearing system.
The third type is hemiplegia, characterized mainly by intellectual disorders, the shoulder girdle is more affected. As children develop, they can perform various movements, but very slowly.
The hyperkinetic form is caused by increased muscle tone, oculomotor disturbances, and hearing impairment.
Paralysis and paresis of the limbs and deformations of the torso are observed. At the same time, intellectual abilities are well developed. If a child is properly cared for, he is able to attend school and receive further education. Adapts quite well in society. The prognosis for life expectancy is quite favorable.
Cerebellar form - this type is characterized by low tone; patients often face difficulty in adopting a vertical position and problems with balance. Extension movements are also difficult and coordination of movement is quite impaired.
The secondary form of cerebral palsy is also quite common with this disease. An acquired type of paralysis can be caused not only by birth trauma, but as a result of a confluence of unfavorable factors during pregnancy. This may be poisoning with any toxic substances, the influence of unfavorable environmental conditions and bad habits (especially smoking during pregnancy).
how much cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy has claimed so many lives.
Material from the site Our Nerves Parents faced with such a serious diagnosis as cerebral palsy in their child ask the question: “How long do children with cerebral palsy live?” Just literally in the middle of the last century, patients with this disease did not live to adulthood.
Currently, a child with cerebral palsy, with comfortable living conditions, proper care, treatment and rehabilitation, lives to be 40 years old and even to retirement age. This depends on the stage of the disease and the treatment process.
If, during the disease, the activity of treatment aimed at combating brain disorders is reduced, this can significantly reduce the life expectancy of a child diagnosed with cerebral palsy, as with any other disease.
Children with cerebral palsy receive this diagnosis in 80% of cases at birth. The remaining percentage of patients develop the disease in early infancy due to infectious diseases or brain injuries. If you constantly work with such children, you can significantly develop their intelligence.
Therefore, the majority can study in specialized institutions, and then receive secondary or higher education and a profession. The child’s entire life depends entirely on the parents and constant rehabilitation.
Unfortunately, at the moment there are not a single case of complete recovery.
Signs of life expectancy with cerebral palsy
It is worth paying attention to such a problem as premature aging. This is a very pressing issue with this disease. It has been proven that by the age of 40, patients are susceptible to a decrease in life expectancy. The physical body wears out faster due to deformation of internal organs, joints and bones.
Outwardly, people with cerebral palsy look much older than their legal age. If there has not been proper development and rehabilitation of the child since birth, then many systems, for example, the cardiovascular or respiratory systems, may remain underdeveloped. Thus, they work for wear, which also affects life expectancy.
Another sign that affects life with cerebral palsy is the type and course of the disease itself. With severe forms, constant epileptic seizures and with a recumbent course of this disease, the duration may be shorter than with moderate or milder forms.
Depending on the site of brain damage, there are five types of disease.
The most common form is spastic diplegia. This type develops due to damage to the part of the brain responsible for motor functions. This causes paresis in the lower girdle.
It can be diagnosed both in the first days of life in case of a severe course, and by the year of life in a milder case.
With proper care, rehabilitation and development of the child, life expectancy with this form can be equal to the life of a person without this disease.
The next form is spastic tetraplegia. This form is characterized by deformations of the trunk and limbs; in half of the cases, patients suffer from epileptic seizures. Children with this diagnosis have strabismus and a disorder of the hearing system.
The third type is hemiplegia, characterized mainly by intellectual disorders, the shoulder girdle is more affected. As children develop, they can perform various movements, but very slowly.
Paralysis and paresis of the limbs and deformations of the torso are observed. At the same time, intellectual abilities are well developed. If a child is properly cared for, he is able to attend school and receive further education. Adapts quite well in society. The prognosis for life expectancy is quite favorable.
Cerebellar form - this type is characterized by low tone; patients often face difficulty in adopting a vertical position and problems with balance. Extension movements are also difficult and coordination of movement is quite impaired.
The secondary form of cerebral palsy is also quite common with this disease.
An acquired type of paralysis can be caused not only by birth trauma, but as a result of a confluence of unfavorable factors during pregnancy.
This may be poisoning with any toxic substances, the influence of unfavorable environmental conditions and bad habits (especially smoking during pregnancy).
No one can say how long a child with this disease will live. Doctors are people, and no one has the right to decide or diagnose life expectancy prognoses.
Of course, the predisposing factors for assessing the duration are the course of the disease, the form of cerebral palsy, and the child’s intellectual capabilities. Children with severe forms and complications, especially those with the respiratory system or epilepsy, are at greater risk.
But even the most severe forms of cerebral palsy are not hopeless with good care, parental care, proper treatment and constant rehabilitation. Children can live quite a long life and even adapt to society, even if only handicapped.
Medicine does not stand still; neurosurgery is constantly evolving, offering new approaches to the treatment of such severe chronic diseases. And in combination with traditional drug therapy, the chances of a long life are constantly increasing.
material from the website Nervzdorov
In the vast majority of cases, finding out how long people with cerebral palsy live is extremely difficult, because... This serious disease can occur with damage to different body systems.
In some cases, with proper treatment, a person with cerebral palsy can live a long and completely fulfilling life, with almost no health problems. In severe situations, a child with such a developmental disorder may die within a few years.
Cerebral palsy is a collective name for a number of movement disorder syndromes observed as a result of disorders of intrauterine development leading to damage to brain structures.
The main causes of cerebral palsy
A disease such as cerebral palsy has already been sufficiently well researched; currently, the study of the main causes and mechanisms of development of this disease continues. The main predisposing factor for the development of cerebral palsy is an intrauterine disorder that develops as a result of an unfavorable course of pregnancy.
The main factor contributing to the development of cerebral palsy is hypoxia. In the case of insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus, entire areas of the brain die off, which leads to the appearance of certain syndromes observed in cerebral palsy. Hypoxia and other unfavorable factors that can provoke the development of cerebral palsy can lead to:
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- toxicosis;
- nephropathy of pregnancy;
- premature placental abruption;
- infectious diseases;
- Rh conflict between mother and child;
- somatic diseases in the mother;
- injuries during pregnancy;
- birth injuries;
- protracted labor.
In newborns, further development of cerebral palsy can be provoked by hemolytic disease, toxic brain damage and asphyxia of various etiologies.
Morphological changes in brain tissue can be different, which explains the difference in manifestations and severity of symptoms in patients. Very often, newborns experience hemorrhages, the appearance of areas of scarring and degeneration of the cortical structure.
Mostly such lesions are observed in the anterior parts of the brain, but damage can spread to other areas. How many years a child with such brain damage will live largely depends on the extent and depth of the process.
Classification of types of cerebral palsy
Depending on the location of the damaged area of the brain, there are 5 main types of cerebral palsy. The most common form of cerebral palsy is spastic diplegia.
This type of disease accounts for approximately 80% of cases of cerebral palsy.
Spastic diplegia develops as a result of damage to the motor centers, which is accompanied by the appearance of paresis, mainly of the lower extremities.
The hemiparetic form of cerebral palsy develops as a result of damage to the motor centers in only one hemisphere of the brain. This disorder is accompanied by paresis of the arms and legs on one side of the body.
The hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy develops due to damage to subcortical structures. This form of cerebral palsy is quite rare. Clinically, it is manifested by involuntary movements, that is, hyperkinesis, which are especially clearly noticeable when the child is tired or excited.
The atonic-astatic form of cerebral palsy is diagnosed in approximately 10% of cases. It is characterized by the appearance of muscle atony and impaired coordination and statics.
The most severe form of cerebral palsy is double hemiplegia as a result of complete damage to both hemispheres of the brain.
This form is characterized by the development of muscle rigidity, as a result of which the child cannot not only walk and sit, but also hold his head up independently.
Among other things, mixed forms may occur, which are accompanied by manifestations of different typical types of this disease.
Symptoms of cerebral palsy
Considering that cerebral palsy can include para-hemi-tetra-monoparesis and paralysis, as well as disorders of muscle tone, vestibular apparatus, speech of varying degrees of intensity and hyperkinesia, it is almost impossible to predict life expectancy. In addition, in the vast majority of cases there is significant impairment of motor skills and psychological development.
Intellectual development disorders, mental disorders, hearing and vision impairments, and signs of epilepsy are not uncommon in children suffering from cerebral palsy. Different children, as a rule, have a different set of syndromes, so without a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition, it is difficult to answer how many years they live with cerebral palsy in a particular case and what are the possibilities for rehabilitation and improving the quality of life.
Most often, the diagnosis of cerebral palsy is made approximately 3-4 months after birth, when there is a significant lag in neuropsychic development from generally accepted norms. The most common sets of symptoms in children with cerebral palsy include:
- hearing problems;
- vision problems;
- speech motor impairment;
- periodic or constant muscle tone;
- violation of the musculoskeletal system.
Despite the fact that children with cerebral palsy often experience a decrease in intellectual capabilities and the ability to learn and acquire new skills, such disorders do not occur in all cases.
In mild cases of cerebral palsy, children adapt well, are capable of learning and can receive education in specialized schools or even study together with healthy peers, and in the future it is quite possible to enter higher educational institutions.
With proper adaptation, children who do not have problems with mental abilities can subsequently lead an almost full life, work and fully care for themselves. Life expectancy with mild cerebral palsy is quite high.
In severe cases of cerebral palsy, children experience not only significant physical abnormalities, but also mental ones, this leads to the fact that it is extremely difficult or impossible for the child to adapt to life; in addition, there is no opportunity to acquire new skills and knowledge, which limits intellectual growth in the future . Life with severe cerebral palsy is quite difficult, since the underlying disease is often accompanied by additional complications.
The lifespan of patients with cerebral palsy is shortened not only by systemic disorders in the body caused by the disease, but also by complications that may appear in the child as he grows up.
The most common complications of cerebral palsy that can seriously impair the quality and length of life include bladder dysfunction, hypertension, severe forms of scoliosis, difficulty swallowing, and bone fractures.
Basic approaches to the rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy
Identification of causes and factors, as well as consideration of the clinical picture, allows us to make a diagnosis such as cerebral palsy.
https://nervzdorov.ru/www..com/watch?v=v4YMcCFFLNI
To confirm the diagnosis, the following studies are often performed:
- MRI;
- ECG;
- EchoCG;
- psychological tests.
The length and quality of life of children with cerebral palsy depends on the comprehensiveness of the approach to treating this disease.
It should be noted that children suffering from cerebral palsy can achieve significant gains in terms of physical and mental development, but complete remission is not currently possible.
To improve the quality of life of patients with cerebral palsy, the coordinated work of treating neurologists, psychoneurologists, defectologists, psychologists, physical therapy instructors, massage therapists, speech therapists and another group of specialists is required, depending on the existing symptomatic manifestations.
Often, with proper and timely therapy and all necessary procedures to improve their general condition, patients with cerebral palsy live to be 30-40 years old, and sometimes to retirement age.
https://nervzdorov.ru/www..com/watch?v=NyTsn0S0XDs
However, it should be noted that cerebral palsy is a predisposing factor for the development of malignant tumors, infectious lesions, sepsis and other equally dangerous pathological conditions that can significantly shorten the patient’s life.
Source: https://xn--80adbclru1f.xn--p1ai/%D0%B4%D1%86%D0%BF-%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%8C% D0%BA%D0%BE/
Signs of life expectancy with cerebral palsy
It is worth paying attention to such a problem as premature aging. This is a very pressing issue with this disease. It has been proven that by the age of 40, patients are susceptible to a decrease in life potential. The physical body wears out faster due to deformation of internal organs, joints and bones. Outwardly, people with cerebral palsy look much older than their legal age. If there has not been proper development and rehabilitation of the child since birth, then many systems, for example, the cardiovascular or respiratory systems, may remain underdeveloped. Thus, they work for wear, which also affects life expectancy.
About life expectancy calculations
The life expectancy calculation is calculated from the average life expectancy in a given population of people with similar conditions. This estimate is based on historical and scientific data. This is not an exact lifespan. Any person can live much more, or less, than their expected life expectancy. It is necessary to understand this.
There are two main purposes for calculating the life expectancy of a person with cerebral palsy. First, answer the parent's question, “Is my child viable? And how long will he live? The parent wants to know the prospects for the child’s life and development, taking into account his state of health. How long will he live - days, weeks or years? Is he given a short life or a long, fulfilling life? Qualified doctors can usually answer these questions for parents.
Other purposes for calculating life expectancy are related to estimating future medical and rehabilitation costs. This may be related to obtaining compensation, or lifetime benefits due to medical negligence, or planning for expected expenses. A financial assessor analyzes many factors to obtain an estimate of life expectancy, which is then used to estimate the future financial costs associated with the child's treatment and rehabilitation. After all, this assessment is based on available scientific evidence and medical research.
Life expectancy is an indicator of mortality risk. This is the average number of years a person can live if mortality factors do not change. The mortality rate is decreasing due to the development of science and technology. Life expectancy is calculated based on several factors, but these factors can change over time, which may change the original calculation.
No person is guaranteed a standard path in life. Every person goes through major milestones in their life, but no one can say when, what and how will happen. Life expectancy cannot be predicted accurately, only estimated. These estimates are mainly used for rehabilitation planning and financial costs.
The main causes of cerebral palsy
A disease such as cerebral palsy has already been sufficiently well researched; currently, the study of the main causes and mechanisms of development of this disease continues. The main predisposing factor for the development of cerebral palsy is an intrauterine disorder that develops as a result of an unfavorable course of pregnancy.
The main factor contributing to the development of cerebral palsy is hypoxia. In the case of insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus, entire areas of the brain die off, which leads to the appearance of certain syndromes observed in cerebral palsy. Hypoxia and other unfavorable factors that can provoke the development of cerebral palsy can lead to:
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- toxicosis;
- nephropathy of pregnancy;
- premature placental abruption;
- infectious diseases;
- Rh conflict between mother and child;
- somatic diseases in the mother;
- injuries during pregnancy;
- birth injuries;
- protracted labor.
Classification of types of cerebral palsy
Depending on the location of the damaged area of the brain, there are 5 main types of cerebral palsy.
The most common form of cerebral palsy is spastic diplegia. This type of disease accounts for approximately 80% of cases of cerebral palsy. Spastic diplegia develops as a result of damage to the motor centers, which is accompanied by the appearance of paresis, mainly of the lower extremities. The hemiparetic form of cerebral palsy develops as a result of damage to the motor centers in only one hemisphere of the brain. This disorder is accompanied by paresis of the arms and legs on one side of the body.

In cerebral palsy (CP), prognosis and survival depend on the form of the disease and its severity. A child with a predominantly motor impairment may attend regular primary and secondary school as recommended by a pediatric neurologist. A prerequisite is an approach without barriers. Families raising a child with cerebral palsy have the right to social assistance. Children, adolescents and adults with this condition sometimes require (depending on the severity of the disability - self-care and mobility) the presence of a personal caregiver.
Cerebral paralysis
Cerebral palsy is an all-encompassing term for a group of chronic conditions characterized by disturbances in the central control of movement and poor posture of the body and limbs due to developmental disorders or damage to the brain. The disease manifests itself in the first few years of life.
Disease symptoms that affect the life expectancy of people with cerebral palsy include a wide range of impairments, often comorbid with other health problems and mental health problems. According to statistics, almost 50% of all children with pathology have epileptic seizures associated with impaired consciousness, body spasms, etc.

Children with moderate and severe cerebral palsy often lag behind in physical growth and development compared to their peers, and suffer from visual and hearing impairments. A large percentage of children have problems with spatial vision, which is necessary, for example, to judge distance.
Sometimes vision is lost forever, or the perception of touch or pain is impaired.
The next factor that influences how long children with cerebral palsy live is the form of the disease.
The most common form is spastic diplegia, affecting up to 85% of children diagnosed with cerebral palsy. Affected muscles tend to become tense and stiff. Patients experience reflexes that are absent in a healthy person. The degree of the spastic type of the disease is determined by the extent of the lesion (unilateral or bilateral).
When one side is affected, we are talking about the hemiparetic form. Usually the upper limbs are more affected than the lower limbs, so patients can walk, and their psychological development is usually normal.
If all limbs are affected, tetraparesis is diagnosed. Impairments in this type of disease can be moderate (patients can stand and walk) or severe (normal movement is impossible). Often severe disability is associated with delayed psychomotor development and intellectual disorders. Often there are other diseases associated with impaired brain activity (epilepsy, hydrocephalus, microcephaly, etc.).
The dyskinetic form occurs in approximately 15% of patients. Its main feature is the inability to purposefully move or achieve a target position. The muscles alternate between tension and relaxation, and involuntary movements occur. Patients are unable to control the body, which interferes with normal activities (sometimes it is difficult for a person to even eat). Often this type of lesion is associated with hearing impairment.
A rare form of the disease is the ataxic (cerebellar) type. The disease is characterized by imbalance and inability to make small movements of the limbs. Patients have problems with movement and walking; mental retardation is a major complication.

The fourth form is a combination of the previous types, most often spastic and dyskinetic.
Cerebral palsy is not an infectious or hereditary disease. It can be congenital - present already at the time of birth due to infection during pregnancy, Rh incompatibility, stroke, etc. These factors affect the baby in the womb. The next reason is the acquisition of the disease as a result of brain damage in the first few months or years of life. Brain damage can be caused by a brain infection, TBI at birth, a fall, or, unfortunately, child abuse.
The causes responsible for the development of cerebral palsy are divided into prenatal, perinatal and postnatal. Factors that cause the disease are also criteria that determine how many years people with cerebral palsy live.
How many years do children with cerebral palsy live, life expectancy with diagnosis – Neurology
In the vast majority of cases, finding out how long people with cerebral palsy live is extremely difficult, because... This serious disease can occur with damage to different body systems.
In some cases, with proper treatment, a person with cerebral palsy can live a long and completely fulfilling life, with almost no health problems. In severe situations, a child with such a developmental disorder may die within a few years.
Cerebral palsy is a collective name for a number of movement disorder syndromes observed as a result of disorders of intrauterine development leading to damage to brain structures.
Cerebral palsy statistics
Cerebral palsy statistics show a gradual increase in the number of sick people. According to WHO (World Health Organization), the number of children born with a diagnosis of cerebral palsy is 3-4 cases per 1000.
What kind of disease is this
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a disease of the central nervous system with concomitant disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Doctors believe that the disease is not hereditary, although such cases are known. Causes of cerebral palsy:
- fetal prematurity;
- infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy (mainly herpes);
- intrauterine oxygen starvation;
- fetal injuries during gestation;
- Rh conflict between the blood of mother and child;
- intoxication;
- alcohol abuse during pregnancy;
- use of stimulants during childbirth.
Cerebral palsy statistics note that there are 30% more boys with this diagnosis than girls. Newborn boys have larger heads, so the risk of birth trauma is much higher.
Endocrine diseases can also cause the development of cerebral palsy. A healthy lifestyle for the expectant mother significantly reduces the risk of the disease. Features of cerebral palsy:
- Changes in the structure of central nervous system tissues.
- Restriction in independent movement and self-care or their complete absence.
Signs of cerebral palsy:
- strabismus;
- convulsions;
- slow or too sudden movements;
- lack of reaction to noises and loud sounds.
With cerebral palsy, the symptoms may be different for each person. It depends on which parts of the brain are most affected and how quickly the disease progresses.
How long do children with cerebral palsy live? If we take the period of the middle of the last century, then only a few managed to survive to adulthood. Today there is no specific age limit. It is difficult to live with such a diagnosis, however, it is not a death sentence.
Disease rates by country
What are the statistics of cerebral palsy in the world? At the beginning of the last century, information about the disease was practically absent, and there were only a few facts identified. Since the beginning of the 60s, a significant increase in indicators began. The main reason is the intensive use of stimulants during childbirth.
With the advent of modern equipment and an improvement in the quality of medicine, the percentage of premature babies nursed (birth weight 500–1000 grams) has increased significantly. But the number of patients with cerebral palsy has also increased. Number of sick children by country:
| A country | Russia | Kazakhstan | Belarus | Ukraine | USA |
| Number of cases per 1000 births | 6–8 | 5–9 | 2–3 | 2–3 | 3–4 |
| Total number of people (2016) | 1.5 million | 14738 | 5000 | 20000 | 550000 |
Cerebral palsy statistics vary greatly across countries. The indicators directly depend on the quality of medical services and the lifestyle of the country’s population.
A significant increase in registered cases is observed not only in the Russian Federation. The statistics of patients with cerebral palsy in Kazakhstan also demonstrates high rates. Kazakhstan is significantly ahead of Belarus and Ukraine in terms of cerebral palsy. Every year, 1000–1500 children are born in the country with this diagnosis.
Treatment of cerebral palsy
Modern medicine divides cerebral palsy into several forms (cerebral palsy statistics as a percentage):
- Spastic tetraplegia – 2%.
- Spastic diplegia – 40%.
- Hemiplegic form – 32%.
- Dyskinetic form – 11%.
- Ataxic form – 15%.
Statistics of children with cerebral palsy show that it is impossible to completely cure the disease. Medicine can only alleviate the patient’s condition - minimize pain, gradually develop muscle tissue, and prevent the disease from progressing.
Treatment started in the first year of a child’s life brings more tangible results than at an older age, when the consequences of cerebral palsy begin to appear (scoliosis, joint dislocations, general deterioration). Rehabilitation of cerebral palsy is a long process aimed at eliminating disorders in the body:
- speech defect;
- mental development;
- changes in the musculoskeletal system.
All over the world, cerebral palsy rehabilitation centers are being opened for patients with central nervous system disorders. Several large government institutions are located in Moscow. There are also private clinics. However, the cost of services in such institutions is much higher.
Best methods:
- drug therapy (drugs that stimulate muscle tone);
- massage of affected areas;
- Exercise therapy (physical therapy).
Additional methods are various simulators and auxiliary devices (bicycles, walkers, stand-up machines), speech therapist sessions (for speech disorders), load-bearing and pneumatic suits.
In severe forms of the disease, doctors resort to surgery. For the most part, the direction is towards plastic surgery of muscles and tendons. The process restores structure and shape. In extreme cases, neurosurgical intervention is prescribed.
During the operation, the affected areas of the spinal cord are removed, and additional stimulation is performed. Most often, surgical intervention is performed for cerebral palsy in adults, when the disease is advanced and irreversible phenomena are observed.
As an additional treatment, animal-assisted therapy is used. The method is based on communication with animals. Horseback riding is often practiced.
The technique has a positive effect on the restoration of the musculoskeletal system. Communication with dolphins gives positive results in improving the psycho-emotional state of the patient.
Source: https://perinatal39.ru/infektsionnye-zabolevaniya/skolko-let-zhivut-deti-s-dtsp-prodolzhitelnost-zhizni-s-diagnozom.html
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the form and severity of the disease. A pediatrician or pediatric neurologist must warn parents of children with cerebral palsy about the right to financial support for caring for a chronically ill child and extension of maternity leave to 7 years.

Patients should be examined even in adulthood due to the vital need for rehabilitation and sanatorium treatment, frequent epileptic seizures and other complications requiring constant professional care.
Treatment
Unfortunately, the disease is completely incurable, but modern medicine can improve its course, consequently, the child’s state of life and the prognosis of cerebral palsy (how long people live with such a diagnosis).
There is no standard therapeutic procedure; each patient requires a specific approach. The goal of treatment is to alleviate the patient's movement disorders, develop his personality and skills, and aim to increase independence and quality of life.
The fundamental stone of treatment, through which the disease can be better predicted, is regular physical therapy, not only with a physical therapist, but also with the help of parents, according to a predetermined plan. Frequently used therapeutic methods are the Voight exercises or the Bobath concept, which increase the chances of maximum recovery.
The Voight Method, or reflexive locomotion, is based on the theory that a person's movement patterns are encoded in the brain, and applying pressure to specific places in specific positions activates them.

The Bobath method is based on a general approach to the child. In infants and bedridden patients, the carrying, lifting, turning, feeding method is mainly used. Thus, Bobath's concept uses the child's own actions. The therapy uses movements that occur in everyday life. Massages or exercises in the pool are carried out at the same time.
Hydrotherapy or hippotherapy also helps. With the right attitude towards a child, you can influence his condition from the first days.
The family of a person with cerebral palsy is an important part of the therapeutic process and is involved in the planning and implementation of treatment.
If cerebral palsy affects the facial muscles, treatment should begin with visits to a speech therapist. The help of a psychologist or special educator is also recommended.
If rehabilitation treatment does not help, muscle stiffness or weakness persists, orthopedic surgery must be performed to restore muscle balance.
To alleviate secondary diseases, drugs are used (against epilepsy or to relax muscle spasms), drugs that support brain metabolism.
The effects of muscle stiffness are relieved by antispasmodic medications such as botulinum toxin and muscle relaxants. Moderate to severe muscle imbalances are compensated by various orthoses, crutches and other compensatory devices.
Treatment for cerebral palsy takes a long time, sometimes lifelong.
How long do children with cerebral palsy live?
In cerebral palsy (CP), prognosis and survival depend on the form of the disease and its severity. A child with a predominantly motor impairment may attend regular primary and secondary school as recommended by a pediatric neurologist.
A prerequisite is an approach without barriers. Families raising a child with cerebral palsy have the right to social assistance.
Children, adolescents and adults with this condition sometimes require (depending on the severity of the disability - self-care and mobility) the presence of a personal caregiver.
Cerebral paralysis
Cerebral palsy is an all-encompassing term for a group of chronic conditions characterized by disturbances in the central control of movement and poor posture of the body and limbs due to developmental disorders or damage to the brain. The disease manifests itself in the first few years of life.
Disease symptoms that affect the life expectancy of people with cerebral palsy include a wide range of impairments, often comorbid with other health problems and mental health problems. According to statistics, almost 50% of all children with pathology have epileptic seizures associated with impaired consciousness, body spasms, etc.
Children with moderate and severe cerebral palsy often lag behind in physical growth and development compared to their peers, and suffer from visual and hearing impairments. A large percentage of children have problems with spatial vision, which is necessary, for example, to judge distance.
Sometimes vision is lost forever, or the perception of touch or pain is impaired.
The next factor that influences how long children with cerebral palsy live is the form of the disease.
The most common form is spastic diplegia, affecting up to 85% of children diagnosed with cerebral palsy. Affected muscles tend to become tense and stiff. Patients experience reflexes that are absent in a healthy person. The degree of the spastic type of the disease is determined by the extent of the lesion (unilateral or bilateral).
When one side is affected, we are talking about the hemiparetic form. Usually the upper limbs are more affected than the lower limbs, so patients can walk, and their psychological development is usually normal.
If all limbs are affected, tetraparesis is diagnosed. Impairments in this type of disease can be moderate (patients can stand and walk) or severe (normal movement is impossible).
Often severe disability is associated with delayed psychomotor development and intellectual disorders.
Often there are other diseases associated with impaired brain activity (epilepsy, hydrocephalus, microcephaly, etc.).
The dyskinetic form occurs in approximately 15% of patients. Its main feature is the inability to purposefully move or achieve a target position.
The muscles alternate between tension and relaxation, and involuntary movements occur. Patients are unable to control the body, which interferes with normal activities (sometimes it is difficult for a person to even eat).
Often this type of lesion is associated with hearing impairment.
A rare form of the disease is the ataxic (cerebellar) type. The disease is characterized by imbalance and inability to make small movements of the limbs. Patients have problems with movement and walking; mental retardation is a major complication.
The fourth form is a combination of the previous types, most often spastic and dyskinetic.
Cerebral palsy is not an infectious or hereditary disease. It can be congenital - present already at the time of birth due to infection during pregnancy, Rh incompatibility, stroke, etc. These factors affect the baby in the womb.
The next reason is the acquisition of the disease as a result of brain damage in the first few months or years of life.
Brain damage can be caused by a brain infection, TBI at birth, a fall, or, unfortunately, child abuse.
The causes responsible for the development of cerebral palsy are divided into prenatal, perinatal and postnatal. Factors that cause the disease are also criteria that determine how many years people with cerebral palsy live.
Prenatal causes (before birth):
- Infections of the expectant mother during pregnancy - toxoplasmosis, rubella, HIV, herpetic infections. These pathologies often lead to premature birth.
- Anomalies of brain development.
- Maternal thyroid disorders during pregnancy.
- Impaired development of the fetus in the uterus - especially in the case of maternal hypertension or malnutrition, with a lack of nutrients necessary for the developing child.
- Fetal intoxication - excessive alcohol consumption during pregnancy, drug use.
- Bleeding in the brain - This problem most often occurs in premature infants because their brains do not have sufficiently developed mechanisms to protect themselves during times of stress.
- Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage is the most common cause of cerebral palsy today. Hypoxic injury is a lack of oxygen in the uterus necessary for the fetus. The brain is the most sensitive to oxygen deficiency; This deficiency results in ischemia or irreparable damage.
Perinatal causes (during childbirth):
- prolonged labor;
- asphyxia of the newborn;
- inflammation of the membranes at the end of pregnancy.
Postnatal causes (postpartum period):
- congenital heart defects, the manifestation of which is insufficient blood supply to the brain;
- intoxication;
- cerebrovascular infections.
What is the life expectancy with cerebral palsy?
Most people diagnosed with cerebral palsy, with proper care, now live into middle age and old age. British statistics show that 86% of patients survive 50 years.
Although a person with this disease is limited in many ways, it is not a cause of death.
Care for adults with cerebral palsy in our country is inadequate, and many patients will not receive the care they need.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the form and severity of the disease. A pediatrician or pediatric neurologist must warn parents of children with cerebral palsy about the right to financial support for caring for a chronically ill child and extension of maternity leave to 7 years.
Patients should be examined even in adulthood due to the vital need for rehabilitation and sanatorium treatment, frequent epileptic seizures and other complications requiring constant professional care.
Treatment
Unfortunately, the disease is completely incurable, but modern medicine can improve its course, consequently, the child’s state of life and the prognosis of cerebral palsy (how long people live with such a diagnosis).
There is no standard therapeutic procedure; each patient requires a specific approach. The goal of treatment is to alleviate the patient's movement disorders, develop his personality and skills, and aim to increase independence and quality of life.
The fundamental stone of treatment, through which the disease can be better predicted, is regular physical therapy, not only with a physical therapist, but also with the help of parents, according to a predetermined plan. Frequently used therapeutic methods are the Voight exercises or the Bobath concept, which increase the chances of maximum recovery.
The Voight Method, or reflexive locomotion, is based on the theory that a person's movement patterns are encoded in the brain, and applying pressure to specific places in specific positions activates them.
The Bobath method is based on a general approach to the child. In infants and bedridden patients, the carrying, lifting, turning, feeding method is mainly used. Thus, Bobath's concept uses the child's own actions. The therapy uses movements that occur in everyday life. Massages or exercises in the pool are carried out at the same time.
Hydrotherapy or hippotherapy also helps. With the right attitude towards a child, you can influence his condition from the first days.
The family of a person with cerebral palsy is an important part of the therapeutic process and is involved in the planning and implementation of treatment.
If cerebral palsy affects the facial muscles, treatment should begin with visits to a speech therapist. The help of a psychologist or special educator is also recommended.
If rehabilitation treatment does not help, muscle stiffness or weakness persists, orthopedic surgery must be performed to restore muscle balance.
To alleviate secondary diseases, drugs are used (against epilepsy or to relax muscle spasms), drugs that support brain metabolism.
The effects of muscle stiffness are relieved by antispasmodic medications such as botulinum toxin and muscle relaxants. Moderate to severe muscle imbalances are compensated by various orthoses, crutches and other compensatory devices.
Treatment for cerebral palsy takes a long time, sometimes lifelong.
Home treatment
High-quality home care is the next factor that determines how many years children with cerebral palsy live. Support, patience, and the right approach to the child are crucial for a good prognosis.
Children with cerebral palsy should live in a family that provides them with the necessary care. Parents can use the services of the Center for Care for Children with Cerebral Palsy. It is important not only to educate the child, but also to develop his mental and social skills.
Source: https://vsepromozg.ru/teoriya/skolko-zhivut-deti-s-dtsp