Dizziness is a very unpleasant symptom that interferes not only with normal work and rest, but also with simply living. The state and sensations of a person at these moments are caused by disturbances that are caused by the receipt of sensory information (for example, vestibular or visual) and its processing. What happens in this case? It is difficult for a person to navigate in space; it seems to him that all the objects around him are in motion, and sometimes that he himself is rotating relative to stationary surfaces.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of this pathology. For example, vestibular vertigo (VV) can be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the apparatus of the same name located in the human ear. It is this analyzer that is responsible for precise movements, sense of space, vision and balance. And due to the fact that the vestibular apparatus (VA) is connected directly to the brain, dizziness can also occur against the background of pressure surges, anxiety and pain in the area of the heart muscle.
Why does a person feel dizzy?
What allows a person to be in a state of balance is the work of the brain (the cortex of which receives constant signals from the vestibular system), or, more precisely, the impulses emanating from it and reaching the eye and skeletal muscles. In the event of certain failures in the receipt of such signals, a person begins to feel the rotation of the surrounding space, the swaying of not only objects, but also his body.

Vestibular rehabilitation therapy
Fortunately, most of us go about our daily lives oblivious to the complexity of our body's systems that keep us upright and balanced.
But this only happens until, for some reason, our coordination and balance are disrupted, reminding us how vital simple everyday tasks are. Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT) consists of a set of exercises that encourage the brain and spinal cord to restore imbalances that occur due to diseases or abnormalities of the vestibular system or damage to the central nervous system.
This guide will help you understand:
- anatomy of the vestibular system
- why do we need ART?
- What disorders does ART usually treat?
Symptoms of vestibular vertigo
With vertigo, the patient complains that he is gradually “carried away” to the side, he cannot stand straight (with his eyes closed), the earth simply “goes away from under his feet,” and all surrounding objects rotate in space.
On a note! With any turn of the head, walking or standing up, the VH increases significantly.
In addition, other manifestations of pathology are observed:
- "Fog" in the head.
- Nystagmus. Sudden jerking eye movements make it difficult to concentrate. The patient can neither write nor read.
- The man loses his balance.
- A nauseating state, sometimes turning into vomiting.
- Sudden rush or flow of blood from the skin.
- Quite uncoordinated movements, manifested in an uncertain gait; inability to go up or down stairs, or to pick up any object. That is, fast and precise movements with vestibular dizziness (vertigo) are simply impossible. The patient always feels the fear of falling, so he tries to be on his feet less and spend more time in bed.
- Blood pressure may rise or fall.
- There is profuse sweating (that is, hyperhidrosis).
- There may be fainting. The patient, as a rule, feels the approach of a pre-fainting state (that is, the moment of loss of consciousness). This manifests itself in increased sweating, darkening of the eyes, nausea and a feeling of fear.
- The presence of general symptoms such as headache, changes in pulse and blood pressure, tinnitus and rapid breathing.

Important! If such manifestations are observed not against the background of vertigo, but on their own, then, most likely, this is a signal of the presence of a more serious pathology.
Characteristics of manifestations of dizziness and nausea

Phrases: “I feel dizzy”, “I feel sick”, “I feel weak and unwell” are heard quite often. The causes of such symptoms in women can be not only the joyful events of pregnancy, but also an imbalance in the body.
Dizziness is an uncomfortable condition caused by a false sensation of movement and rotation of objects around the body. It seems to the woman that the objects around her are rotating dynamically. The effect of ground vibration is also possible. Moreover, vision and sensation are preserved regardless of the focus of the gaze, and sometimes even with closed eyes. For each woman, the feeling of dizziness manifests itself purely individually, from lightheadedness and nausea to the effect of intoxication.
This symptomatology is mentioned by almost every patient. As medical experts have established, it can be a manifestation of more than 100 diseases, and can also be a consequence, addition of many pathological processes, or the result of excessive stress, poor nutrition and lack of rest.
Symptoms may be caused by:
- local reasons. For example, poisoning, infections, intoxication process;
- cerebral reasons. Due to the development of a lack of oxygen and necessary substances in the brain.
False dizziness
The symptom of dizziness in a woman can often be perceived incorrectly, since the view of this sensation is purely subjective.
The following symptoms are considered to be a feeling of dizziness:
- temporary loss of balance;
- loss of stability when walking;
- feeling of falling through while moving;
- nausea;
- fainting or pre-fainting;
- eclipse or darkening of the eyes.
These symptoms are not characteristic of dizziness, although they can lead to its manifestation. As medical research statistics show, 70% of women mistake the sensations of jolts, dips, ringing and emptiness in the head, instability when moving for dizziness. The effect of rotation of the body, environment, elements and objects is very rare.
Subsequent diagnostics reveal that such disorders in patients are caused by the following disorders and pathological processes:
- thyroid disorder, diabetes;
- dysfunction of the visual system;
- disease of the cardiovascular system;
- neurological pathology.
Accordingly, only 30% of patients have signs of vestibular disturbance in the form of dizziness combined with nausea, fever or cold sweat, vomiting and an actuating sensation of rotation.
Timely diagnostic methods and technology make it possible to identify the true causes of various symptoms and carry out the correct treatment.
Causes of weakness, nausea and dizziness in women
Severe dizziness and headaches among the fair sex are quite common symptoms. This problem significantly affects functioning, ability to work and personal life. There can be many reasons for dizziness in women. One of the reasons may be excessive sensitivity or emotionality.
Representatives of the fair sex of different age categories with a thin physique, as well as fans of dietary nutrition, are prone to dizziness and the development of weakness. Lack of proper and balanced nutrition leads to a lack of glucose in the blood. This process ensures a slim body shape, but depletes the body, including brain cells.
Dizziness can lead to malaise, weakness, nausea, vomiting, causing headaches. The causes of dizziness in women can be caused by the following factors and reasons:
- the period of pregnancy, which from the very beginning leads to profound changes in the body, its restructuring and, accordingly, the frequent appearance of dizziness. It is normal to experience dizziness and nausea in the first trimester, when a sharp hormonal surge occurs. Dizziness is considered normal throughout pregnancy in women suffering from low blood pressure. Constant dizziness can regularly provoke toxicosis - a process that is subject to regular monitoring;
- a reduced level of hemoglobin and iron in the blood also causes an unpleasant condition when dizziness, weakness and nausea occur. During pregnancy and the manifestation of corresponding symptoms, mandatory medical supervision is necessary;
- weak vestibular apparatus. This physiological feature of a woman’s body leads to the fact that she gets motion sickness when traveling in a car, plane, train, watercraft, and is unable to ride on swings and carousels;
- excessive emotions and stress. Women are prone to excessive emotions and stress in the process of making decisions and analyzing information. And also when participating in certain events, speaking in public and other individual events.
Important! Excitement and emotional arousal lead to poor circulation and improper supply of oxygen to the blood, which leads to oxygen starvation
Fatigue, unstable sleep, lack of rest, “chronic fatigue” syndrome, and the dynamic rhythm of life lead to exhaustion of the body. The result is a reboot of the neuropsychological system, as well as oxygen deficiency of cells, leading to dizziness.
Hypertension or hypotension, natural changes in atmospheric pressure lead to disturbances in brain function and dizziness. Women prone to hypersensitivity and dependence on natural changes (climatic, magnetic storms) may also experience symptoms of weakness, nausea, headache and dizziness.
Chronic diseases and symptoms of the acute phase of various diseases. Dysfunctions and pathologies of blood vessels, the spine, brain diseases, diabetes mellitus, and cancer lead to similar symptoms.
Menstruation and menopause are the cause of hormonal changes in the body. During menstruation, the amount of hormones in the blood increases, which leads to dizziness. A similar process occurs during menopause. Menstruation is accompanied by blood loss, hemoglobin levels are lost, which leads to oxygen starvation of the brain. Menopause is characterized by hormonal changes, so both processes can lead to malaise, nausea, weakness, headaches, dizziness, and emotional instability.
Regular dizziness in women is a very unpleasant and dangerous symptom. Delaying contact with a doctor or self-diagnosis with subsequent treatment leads to a worsening of the condition and neglect of the disease.
Weakness, characteristics and manifestation

Weakness is one of the most common symptoms, affecting both children and the elderly. The factors leading to this phenomenon can be very different, both physiological and psychological. However, manifestations and sensations are purely subjective and individual. It can manifest itself in a woman’s increased fatigue, dizziness, absent-mindedness, weakening of memory and attention, and lack of energy.
Causes of weakness in women include:
- overstrain – physical, emotional, psychological. Occurs as a result of lack of proper rest or emotional and psychological stress. Lack of proper rest and sleep, poor nutrition;
- chronic or acute diseases;
- infectious diseases - influenza, sore throat, ARVI.
Weakness leads to physical illness, disability, poor functioning and discomfort.
Process diagnostics
In order to diagnose the causes of dizziness, nausea and weakness, a woman should go to the hospital to see a therapist, who, based on the symptoms, will determine the circle of specialized specialists who should examine the patient:
- ophthalmologist, neurologist, oncologist;
- gynecologist, otolaryngologist, cardiologist, etc.
The examination is carried out using various laboratory and instrumental research methods:
- MRI, CT;
- X-ray, blood and urine tests;
- Audiography, Dopplerography, etc.
Important! A timely visit to a medical facility will allow a thorough diagnosis of the patient’s condition. The cause of the malaise will be determined, in the form of manifestations of dizziness, nausea and weakness, and a course of treatment measures adequate to the condition will be prescribed.

Women experience dizziness, nausea, vomiting, weakness and lethargy much more often than men. There are several reasons for this. Do you always need to see a doctor about this? If such symptoms are repeated frequently, this cannot be ignored and attributed to overwork and lack of sleep.
Classification of pathology
There are two types of dizziness:
- Vestibular. It is also called vertigo, true or systemic. This type of dizziness and the vestibular system are directly related. Disturbances in the functioning of the latter lead to vertigo.
- Not vestibular. Other names for this type are non-systemic or physiological. This type of dizziness includes fainting, presyncope, and imbalance, which are not of vestibular origin. They also include sensations of an incomprehensible nature, which are defined by such a word as “lightheadedness.”
Our approach to treatment (exercises on the stabiloplatform)

Stabilometry is a modern method that allows you to assess the state of a person’s balance in various diseases.
The patient is examined on a special platform that records minimal vibrations of the human body with subsequent computer processing. At the end of the study, a conclusion and recommendations for rehabilitation in the form of training are issued.
With the help of video games, a person, by moving fulcrum points, “guides” the actions of the character on the screen, thereby training his vestibular apparatus. Repeated repetition of such training increases the effectiveness of the therapy.

Treatment on a stabiloplatform with biofeedback is prescribed as part of complex therapy for diseases and pathological conditions such as:
- imbalance, loss of coordination;
- frequent dizziness and headaches;
- diseases of the vestibular apparatus;
- panic attacks accompanied by dizziness
- polyneuropathy;
- vascular diseases, conditions of impaired blood supply to the brain, incl. post-stroke
- various spinal injuries (vertebral displacement, curvature)
- flat feet
Treatment of neck diseases
Some patients who experience dizziness or balance problems also have orthopedic neck problems that cause or worsen their symptoms. In these cases, your physiotherapist at Healthy Sports can also provide hands-on treatment in combination with the other ART exercises described above.
Strategies for self-administration
Secondary damage due to vestibular problems can occur due to frequent falls. As part of your ART, your doctor will talk about simple strategies that can minimize the risk of secondary injuries. For example, you may be advised to use walking aids if you are tired or in a particularly busy environment, such as a grocery store.
Conclusion
ART can be extremely helpful in reducing or eliminating any vestibular symptoms and imbalances you may experience due to diseases or abnormalities of the inner ear or central nervous system. These exercises will lead to the best results if they are prescribed by one of our doctors at the Healthy Sports Medical and Health Complex.
You can undergo an examination at the Healthy Sports Medical and Health Complex, make an appointment by phone: 58-88-28
Pathology of a systemic nature
There are two types of true dizziness (vestibular disorders):
- Peripheral. Caused solely by pathology of the nerve or middle ear.
- Central. Vertigo is caused by problems with the functioning of the brain.
In addition, there are:
- Tactile (or tactile) vertigo, the main symptoms of which are sensations of swaying on the waves, unsteadiness of the ground, as well as rising and falling of the body.
- Proprioceptive. Symptoms: a feeling of slow movement of your body in space.
Possible causes of systemic vestibular vertigo:
- Vestibular neuronitis.
- Post-traumatic state after traumatic brain injury.
On a note! Post-traumatic dizziness may not be observed immediately, but some time after the injury (for example, after 5-6 days).
- Meniere's disease.
- Toxic lesion of VA. The cause of this pathology may be the use of aminoglycosides accumulated in the lymph of the vestibular analyzer.
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. It can occur when there is a sudden change in the position of the body or head (that is, when bending forward, backward, and so on). Dizziness does not last long - the duration is a few seconds or about 1 minute. It occurs more often in people whose age has exceeded 50. Moreover, it occurs more often in women than in men.
- Chronic pathologies of the inner and middle ear (for example, eustachitis, otitis media or otosclerosis).
- Vertebrobasilar insufficiency, caused by disruption of the brain due to reduced blood flow.
- Temporal lobe epilepsy. Symptoms of the pathology: nausea, increased sweating, pain in the temple area; as well as loss of consciousness and even memory. In addition, there may be a disorder of perception (that is, taste, smell, touch, etc.) and hallucinations.
On a note! Typically, temporal lobe epilepsy is diagnosed in childhood or adolescence.
- Neoplasms in the brain of a malignant nature. There is an increase in intracranial pressure and, as a result, compression of the brain nuclei. As a result, the person experiences severe headaches and dizziness. Vomiting is also observed.
- The causes of the development of vestibular vertigo can be diseases such as osteochondrosis and multiple sclerosis, as well as various neuroses.

Nausea, dizziness and weakness in diseases of the nervous system
Diseases of the endocrine system have a large list of symptoms. The pathological condition is often mistaken for ordinary fatigue. In addition to fatigue and drowsiness, diseases of the endocrine organs have the following symptoms:
- muscle weakness;
- weight gain or loss;
- disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- sweating;
- urination becomes frequent;
- thirst appears;
- memory deteriorates;
- there is a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract).
Endocrine diseases in women are disguised as other pathologies. Correct diagnosis can determine that the cause of drowsiness and weakness in a woman is endocrine changes.
Meniere's disease
This is a non-purulent disease of the inner ear. A characteristic sign of Meniere's disease is an increase in the volume of endolymph, and, as a result, an increase in pressure inside the labyrinth.
The pathology manifests itself in the form of attacks of dizziness, which can last several minutes, or maybe a whole day. In this case, there is loss of balance, autonomic disorders (they can persist for several days after the vertigo ends), noise in the ear, a feeling of increased pressure in the ear, vomiting and involuntary rhythmic eye movements (this symptom is called nystagmus).
On a note! As the pathology develops due to membrane rupture due to swelling of the labyrinth (that is, the inner ear), hearing loss occurs (usually on one side). Most often, complete hearing loss is not observed.
Signs of chronic fatigue
Chronic fatigue involves feeling sleepy and groggy for several months. The symptoms do not go away even with proper rest.
- constant feeling of weakness and fatigue;
- a woman gets tired quickly, even with minimal exertion;
- periodic pain in muscles and joints;
- lack of ability to analyze;
- poor concentration;
- there are feelings of anxiety and restlessness, especially at night;
- headaches may appear;
- a patient with chronic fatigue syndrome is characterized by irritability;
- frequent manifestations of chronic pathologies.
Chronic fatigue is manifested by non-specific symptoms that can be confused with symptoms of other diseases. For example, a patient may notice an enlargement of the lymph nodes, which occurs for no reason.
Constant drowsiness and weakness in women can be caused by the development of nervous exhaustion and depression. When the Nervous System is exhausted, the patient may experience the following:
- with minor loads, compressive pain in the head is observed;
- there are vision problems, skin manifestations, frequent allergic reactions and poor appetite;
- problems with intimate life. Dysfunction and loss of sexual desire;
- the patient has difficulty processing information and remembering it;
- blood pressure and heart rhythm are disturbed;
- the patient becomes cold for no reason and experiences anemia in the limbs;
- digestive disorders;
- nausea;
- insomnia;
- nightmares;
- disturbances in speech, coordination and memory appear;
- Sometimes there may be a drop in body temperature to 35 degrees.

During depression, the following symptoms join the signs of nervous exhaustion:
- a woman may be annoyed by the people around her and their actions;
- photophobia and irritability with loud sounds appear;
- lack of self-confidence appears;
- actions are difficult for the patient;
- rest improves well-being for a short time;
- in a state of rest a person cannot relax;
The causes of drowsiness and weakness in women can be varied. It is important to seek medical help in time.
Nausea, dizziness and weakness are often symptoms of diseases of the brain and peripheral nervous system.
The patient feels a loss of balance, and the object around them seems to begin to rotate around the patient or vice versa. If the activity of the nervous system is disrupted, these symptoms are also accompanied by increased sweating.
As a rule, symptoms of diseases of the nervous system occur very sharply and are clearly expressed. Such symptoms last from several minutes to several days. The patient may experience tinnitus, hearing loss, decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate, and vomiting.
Often, periodic peripheral dizziness, nausea and weakness are provoked by various lesions of the inner ear. These include:
- Deposition of calcium salts in the inner ear. This pathology has a benign course and manifests itself in certain head positions. In this case, symptoms can last from a few seconds to several minutes.
- Poor circulation in the inner ear.
- Increased pressure of the fluid that is in the inner ear. High endolymph pressure is the most common cause of Meniere's disease, which occurs with decreased hearing acuity and tinnitus on one or both sides.
- Infectious diseases in which the structures of the inner ear become inflamed.
- Toxic substances (including some medications).
- Diseases of the spine, for example, arthrosis of the cervical spine.
- Eye diseases.
As for dizziness of central origin, the causes can be diseases such as multiple sclerosis, cerebrovascular accident, brain tumors, trauma, syringomyelia, migraines, epilepsy and other brain diseases.
Dizziness Weakness Nausea Lethargy Headache
Vestibular neuronitis
The disease can occur suddenly (sometimes after suffering a viral or bacterial pathology, especially of the upper respiratory tract), last several minutes or several hours, up to several days. Patients suffer from vestibular neuronitis (or neuritis) quite hard and remain in bed for several days, as they are simply unable to get up and perform any actions. The pathology is accompanied by severe dizziness, vomiting, loss of balance, nystagmus, pronounced autonomic disorders, congestion in the ear, noise in it and sometimes a feeling of fear. The hearing is usually preserved.
On a note! Any change in body position and head movement contributes to increased manifestations of pathology. By the way, statistics say that in 50% of cases of vestibular neuritis, attacks of dizziness recur after several months or years.

Diagnosis of the cause of dizziness
A detailed history of your medical condition is the most important information your doctor needs to diagnose the cause of your vestibular disorder and then administer appropriate ART.
The doctor will ask you to describe your vestibular symptoms in detail. Any symptoms you experience above or others should be mentioned. Your doctor will want to know when the first episode of your symptoms occurred, how long they lasted, and whether they were related to any other events, such as a car accident, head injury, illness, or infection.
He will also want to know how often symptoms have recurred since the first episode and the general pattern of symptom frequency. Find out exactly what causes your symptoms, such as moving your head in a certain direction or getting out of bed. For dizziness, your doctor will ask about the nature of what you're feeling and whether you experience episodes of true dizziness where you have a spinning sensation.
The doctor will also want to know if there is anything that reduces or increases your symptoms, and if you are taking any medications, or if you have a family history of any inner ear disorders or central nervous system disorders.
He may ask you to rate the intensity of some of your symptoms on an objective scale. Finally, they will ask about all the daily activities that are related to your vestibular problem, such as walking, driving, working, and even household activities such as dressing, bathing, showering, and housekeeping.
He will also want to know if you have any falls.
The doctor will examine your eye movements by asking you to follow certain objects with your eyes or by asking you to move your head while keeping your attention on a specific target.
An examination of the joints and neck muscles is also carried out to determine the cervicogenic nature of dizziness.
Finally, your doctor may ask you to fill out a questionnaire to determine the intensity of your vestibular symptoms.
Depending on what the doctor finds during the initial examination, they may send you for a series of other tests to further determine the cause of your vestibular symptoms.
Vestibular rehabilitation
As stated above, ART can be used to treat various disorders that cause dizziness or balance problems. Almost any disorder that occurs due to vestibular dysfunction and does not receive sufficient compensation can be treated with ART. The effectiveness of ART depends on correct diagnosis of the cause of the imbalance, the skill/training of the therapist in developing and administering the treatment, and adherence to the prescribed exercise program.
As explained earlier, the purpose of ART exercises is to encourage the brain and spinal cord to compensate for any balance deficits that arise due to diseases or abnormalities of the inner ear or central nervous system. In other words, patients teach their vestibular system to do one of several things; adapt to the stimuli presented, substitute other sensory pathways, or become accustomed to changing vestibular signals sent to their brain so that they can manage their vestibular disorder and maintain normal functioning despite possible ongoing symptoms.
In some cases, ART can eliminate vestibular symptoms. Unfortunately, however, this is not always the case, so minimizing symptoms or the frequency of recurrence of symptoms is considered a successful outcome of ART.
Research in the field of ART shows that, in general, ART exercises are effective in reducing many symptoms of vestibular disorder and that these improvements can often persist for several months after therapy. However, the effectiveness of therapy often depends heavily on what exactly is causing the vestibular symptoms in the first place and the use of individualized exercises rather than a standard exercise protocol.
ART, however, is not always effective for all vestibular problems. There are even some vestibular problems where exercise is not considered appropriate, so proper diagnosis of the cause of the symptoms is important.
ART exercises
If your physiotherapist feels that ART is right for you after completing your assessment, they will prescribe a range of individual exercises for you to do regularly. These exercises will focus on your specific vestibular problem and associated symptoms.
Additionally, the exercises you are prescribed will focus on any day-to-day problems you are facing as a result of your symptoms. Some exercises will be done with your physical therapist on a stability platform, and others will be retrained so that you can do them on your own as part of a home exercise program.
Medications to treat your symptoms may be an addition to ART and should be discussed with your doctor.
Post-traumatic vertigo
As a result of traumatic brain injury, the bone membranes of the labyrinth, which are particularly thin, can be damaged. As a consequence, systemic vertigo occurs, accompanied by dizziness, sudden nystagmus, loss of balance and vomiting. Moreover, any sudden movement of the head leads to increased symptoms. The reasons for this condition may be:
- Disturbance in the functioning of one of the labyrinths.
- A longitudinal or transverse fracture of the temporal bone pyramid, which results in damage to the eardrum or hemorrhage in the middle ear.
Basic information about the vestibular system
The vestibular apparatus (equilibrium device) is a proprioceptive sensory organ that serves to perceive gravitational and inertial forces, or to position and accelerate the head. Generally speaking, one of the two parts of the inner ear is spoken of, although its function is different from that of the ear (hearing).
The vestibular system coordinates eye movements with head movements. It is also one of many components of the complex vestibular system, whose job is, among other things, to maintain the body's balance. Other senses used in the vestibular system are the proprioceptive and extraperceptive organs.
Dizziness of a non-systemic nature
Vestibular dizziness of a physiological nature can be caused by severe stress, motion sickness in transport, prolonged rotation, sudden climate change, overwork, malnutrition, loud sounds or unpleasant odors. The cause of the disease is a discrepancy in the activity of the vestibular analyzer at different levels of the nervous system.
On a note! If you suffer from dizziness and nausea during long trips by car (or on a bus), that is, you get motion sickness, then it makes sense to have a few mints or tablets of a drug such as Vestibo with you.
Diagnosis of disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular analyzer
First of all, in order to confirm the presence of vestibular vertigo, the neurologist must listen carefully to the patient, without prompting him with any terminology or offering him a choice. During the conversation, the specialist must understand whether we are talking about vertigo or another disease that also needs to be identified.
Next, the patient undergoes a neurological examination, and the doctor sends him for laboratory tests. This refers to a clinical blood test. If necessary, a neurologist can provide a referral for consultation with specialists such as a vestibulologist or otoneurologist. You may need an examination of the cervical spine, that is, MRI, radiography and CT. In some cases, to exclude diseases such as epilepsy or benign paroxysmal vertigo, an EEG of the brain is prescribed. In addition to all these diagnostic measures, studies of the vestibular analyzer can be carried out, namely stabilography, rotation tests and vestibulometry.
Causes of dizziness, nausea, vomiting and weakness in women
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Oxygen starvation of brain tissue.
- Orthostatic collapse.
- Hypoglycemia and anemia.
- Poisoning.
- Spinal damage.
- Stroke.
Such diseases are characterized by the sudden onset of all symptoms, dizziness, nausea, vomiting and weakness. At such moments, a woman experiences great anxiety, which can worsen her condition. Therefore, if dizziness and weakness occur, the first thing you need to do is pull yourself together.
Hormonal disbalance
There is a certain balance of hormones in the body. Its violation leads to serious consequences. If the required amount of these substances is not restored, significant disruptions in the functioning of all organs and systems may occur.
Similar article - Does the hepatitis B vaccine help?
It is impossible to establish the balance of hormones on your own ; it is necessary to undergo tests that will show the woman’s hormonal levels, and only after that the doctor will prescribe treatment. The course of taking medications can be very long, up to several years, and sometimes it only takes 2-3 weeks .
Causes:
- Diseases of a gynecological nature.
- Colds and viruses.
- Constant strong physical activity.
- Poor nutrition.
- Excess weight.
- Smoking , alcoholism.
- Postpartum hormonal imbalance and pregnancy.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- Climax.
- Puberty period
- Psychological reasons.
In addition to dizziness, nausea and vomiting, a woman may experience other symptoms that indicate hormonal imbalance . It is quite easy to suspect that you have a hormone imbalance, because such signs cannot be ignored.
Signs of hormonal imbalance:
- Sudden change of mood.
- Increasing body weight.
- Constant feeling of fatigue and insomnia.
- Dizziness , nausea and vomiting.
- Headache .
- Lack of sexual desire.
- The appearance of acne on the body and face.
Oxygen starvation of brain tissue
Oxygen starvation of the brain can occur for several reasons. The signs of this condition and their severity make it possible to understand how serious and severe the disease process is.
Causes:
- Poor blood circulation in the meninges.
- Shock states.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system.
- Chemical poisoning
- Lack of oxygen in the air.
To make a final diagnosis, the doctor needs to know all the signs of the disease, and in addition, a number of diagnostic procedures. This condition is very dangerous for a woman and requires immediate medical attention.
Signs:
- Dizziness , nausea and vomiting.
- Increased heart rate and breathing.
- Pale skin.
- Cold sweat on the face, arms and legs.
minor appear , but the more severe the disease develops, the more organs are affected, and vital processes are disrupted.
In the acute stage, the disease cannot be ignored. The woman is hospitalized and given the necessary treatment, and in addition to the general signs of the disease, very severe symptoms are added.
Orthostatic collapse
This disease is a jump in blood pressure, downward. This happens due to a sudden change in the woman’s position, when she quickly gets out of bed or, conversely, if the woman quickly lies down. Staying in one position for a long time can also cause an increase in symptoms of the disease.
Causes:
- Dehydration of the body.
- Side effects of some heart medications.
- Infectious intoxication
- consumption .
- Diabetes .
- Neurological diseases.
- A constant state of stress.
- Refusal to eat or not eating enough.
- Elderly age.
The disease is classified according to the duration of symptoms and is divided into several stages, mild, moderate and severe. Depending on the stage of the disease, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Most often, this disease affects young women trying to quickly lose weight. To quickly achieve the effect of losing weight, girls take diuretics and laxatives, which is fraught with pronounced signs of this disease.
Signs:
- Dizziness, nausea, vomiting.
- Fainting.
- Noise in ears.
- Hearing impairment.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Thirst.
- Weakness in the limbs.
Hypoglycemia and anemia
A decrease in blood sugar is called hypoglycemia. A decrease in hemoglobin levels is called anemia. These two diseases can manifest themselves in the same way. Both conditions are quite dangerous for a woman. A large number of representatives of the fairer sex suffer from anemia.
This is associated with monthly menstruation, especially if it is heavy. The symptoms of both diseases are similar: dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
Causes of glycemia:
- Diabetes.
- Dehydration.
- Wrong diet.
- Alcoholism.
- Constant overwork.
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Failure of the heart, liver and kidneys.
Causes of anemia:
- Prolonged menstruation and some gynecological diseases.
- Bleeding of any nature.
- Increased need for hemoglobin.
- Poor absorption of iron by the body.
To clarify an accurate diagnosis, a number of laboratory blood tests are required. Women, turning to a specialist, must describe their condition in detail. Treatment of these ailments can take several months , and in especially severe cases up to several years .
Poisoning
The signs of poisoning are familiar to everyone: dizziness, nausea and vomiting. The causes of this condition can be various foods or chemicals. It is quite possible to cure the disease yourself if it manifests itself in a mild form. Sometimes a woman needs hospitalization.
Spinal injuries
Every woman, when dizziness, nausea and vomiting occurs, will first of all think about the cause of this condition. If there have been recent injuries or damage to the spine, it becomes clear what influenced the presence of such unpleasant symptoms.
Spinal injuries can be very dangerous; if dizziness, nausea and vomiting occur, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Stroke
This disease is deadly. In the early stages, doctors can help a sick person recover as much as possible, so at the first signs of illness, it is better to immediately call an ambulance.
Causes:
- The occurrence of blood clots in small vessels.
- Rupture of the vessel wall and hemorrhage in the brain.
Women are susceptible to this disease at a later age than men, but these days, even young people are becoming victims of stroke. In order to protect yourself from such a terrible disease, you need to undergo medical examinations regularly and be less nervous.
Signs:
- Dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
- Depression and loss of consciousness.
- Headache.
- Increased breathing.
In addition to the main diseases, the symptoms of which may be dizziness, nausea and vomiting, there are more rare and deadly ailments. Only doctors are able to identify the true cause of such conditions, so medical examinations should not be neglected.
Treatment of dizziness
Treatment of vestibular vertigo should be aimed solely at relieving the patient of neurological disorders and very unpleasant sensations. For this purpose the following may be assigned:
- Medications from the histamine mimetic group, for example, Vestibo, which helps improve blood flow in the brain and properly stabilizes intralabyrinthine pressure. The product also helps to cope with gag reflexes and has a positive effect in terms of transmitting impulses along the nerves of the vestibular analyzer.
- Medicines of the benzodiazepine group, for example "Relanium", after the use of which all the symptoms characteristic of this pathology disappear.
Important! Remember: Relanium is highly addictive. Be careful and take it only as prescribed by your doctor (as, indeed, all other medications).
- Treatment of vestibular vertigo requires mandatory monitoring of blood pressure levels.
- Taking nootropics, antiplatelet agents, vasodilators and venotonics.
- If necessary, antiepileptic drugs.
- Antihistamine drugs (for example, Meclozine or Promethazine) have a good effect.
- To reduce feelings of fear and general anxiety, tranquilizers (for example, Lorazepam or Diazepam) are prescribed.
- Metoclopramide is a good way to relieve the exhausting nausea.
- How to treat vestibular vertigo in Meniere's disease? A good result is achieved by taking a drug such as Betagistin, which helps dilate the blood vessels of the inner ear and improves its microcirculation. If taking this medication (or any others in this group) does not give positive results and vertigo continues, then the option of surgical intervention cannot be ruled out. By the way, in the presence of Meniere's disease, patients are recommended to limit the consumption of coffee and salt, and also completely stop smoking.
Important! Betagistin is generally well tolerated. But remember: those who have diseases such as gastric ulcers, bronchial asthma or pheochromocytoma should treat it with caution. Under no circumstances should this drug be used by pregnant women.
- If necessary, antiviral drugs.
- If a patient has paroxysmal positional vertigo of a benign nature, experts consider the use of any drugs that have a depressing effect on the activity of the vestibular apparatus to be inappropriate. But taking drugs that irritate the VA can give good results in therapy.
- For pathologies in children, medications such as Betagistine or Cinnarizine may be prescribed.
- Don’t forget about non-drug treatment, which can help restore normal coordination of movements. Therapy is carried out in collaboration with a psychotherapist. Sometimes anticonvulsants and antidepressants are prescribed.
Important! Do not self-medicate. Only a doctor, after a thorough examination of the patient, can prescribe correct and adequate treatment.
Anatomy
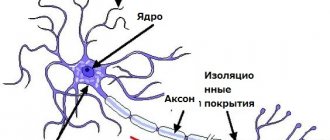
The anatomy and physiology underlying the human body's sense of balance is complex. Many systems are involved, including the brain, spinal cord, eyes, ears, and receptors in the skin, joints, and muscles. Impairment in any of these areas due to injury or illness can negatively impact your sense of balance.
The inner ear, also called the labyrinth, consists of the semicircular canals along with the saccule and the uterus. Collectively, this inner ear system is called the vestibular system or vestibular apparatus.
The inner ear also contains the cochlea, which is the main structure involved in hearing perception.
The three semicircular canals respond to rotational movements of the head. The canals are located at 90 degrees to each other and are filled with a fluid called endolymph. Hair cells are located at the base of each semicircular canal and project into the endolymph. The movement of the head causes movement of the endolymph in the channels, which in turn causes the hair follicles to move accordingly and emit impulses about balance that travel to the brain. Hair cells in the sac and utricle respond to linear acceleration of the head, such as when riding in an elevator or moving forward.
Sensory information from the inner ear is transmitted to the brain through the vestibular portion of the eighth cranial nerve, which is also called the vestibulocochlear nerve. The cochlear part of the nerve transmits hearing information. Certain areas of the brain, particularly the cerebellum and brain stem, as well as parts of the cerebral cortex, process sensory information coming from the inner ear. When both the right and left inner ears send the same information to the brain, the body is balanced. When the body or head moves, the sensory information from the ears is not identical, so the brain perceives the movement and the body adjusts accordingly.
The ears work closely with the eyes to maintain balance. The basis of this is
vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). This is an automatic function of the eyes that stabilizes images on the retina in response to head movements. This reflex causes the eyes to move in the opposite direction to the movement of the head so that the eyes remain stationary on the observed target. Thus, precise information from the vestibular system influences the sense of balance.
If one inner ear is affected by disease or injury, then sensory information sent to the brain will falsely indicate movement from that vestibular system. In this case, the eyes will adjust accordingly and move opposite to the perceived movement despite the fact that the head is actually stationary. The result is involuntary back and forth eye movements. This eye movement is called nystagmus and, if present, makes any healthcare professional suspect a vestibular problem.
There are two other reflexes, the vestibulocervical reflex and the vestibulospinal reflex, which also help the body maintain a sense of balance.
The vestibulocervical reflex works in conjunction with incoming vestibular information and the neck muscles to stabilize the head. And the job of the vestibulospinal reflex is to create compensatory movements of the body in response to vestibular input in order to maintain balance and avoid falling.
Disturbance along any part of the anatomical pathway described above can affect the perception of balance or equilibrium. A problem with the part of the inner ear or sensory information transmitted to the brain through the vestibulocochlear nerve is called peripheral vestibular disorder.
If a problem affecting balance is due to damage to a structure within the brain itself, which then affects the reception and integration of balance information, it is called a central vestibular disorder.
Traditional medicine in the fight against vertigo
In folk medicine, there are many recipes for how to cope with vestibular vertigo. Here are some of them:
- An excellent recipe that helps cleanse blood vessels and improve blood circulation in the brain. We put a handful of fresh pine needles in a thermos (by the way, you can even use twigs), pour boiling water (1 liter) into it, close it and leave it to steep overnight. In the morning, strain, add chopped lemon and leave for another 2-3 hours. The entire infusion must be drunk within 24 hours (the next day we prepare a new mixture). Moreover, you need to take the healing drink either 60 minutes before a meal, or 1 hour after a meal. The course of therapy is 10 days.
- Tea with mint leaves and chopped ginger root. Should be taken twice a day. The course of therapy is until the disease disappears. Prepare the tea as follows: pour mint leaves (10 g) and ginger root (20 g) with boiling water (200 ml), leave for 10 minutes and drink warm.
- Tincture from red clover inflorescences. Helps fight vestibular disorders (dizziness in particular). Pour clover flowers (40 g) with alcohol (you can also use vodka), leave for 7-8 days in a dark place. Take 1 teaspoon three times a day (after meals).
- A good result is obtained from seaweed, which should be consumed every day, 1 teaspoon.
- Decoction of meadow clover. Pour boiling water (1 glass) over the plant flowers (1 teaspoon), cover with a lid and simmer over low heat for 5 minutes. Then remove, cool, filter and drink a tablespoon 4 times a day.
- An infusion of dry leaves of the Siberian princeling plant. Dry raw materials (5-6 g) are poured with boiling water (1 glass), left for 60 minutes, filtered and taken warm, ½ glass 2-3 times a day.
- You can breathe in peppermint, rosemary or camphor oil for 5-7 minutes to reduce vertigo, and sometimes get rid of it altogether.
- Eat more foods containing phosphorus. These are walnuts, fish, eggs, cheese, cucumbers, peas or radishes.

Important! Traditional recipes can give positive results if the pathology is caused by functional disorders that appear rarely and do not last long. If the disease is organic in nature, then you should consult a doctor. Only he can conduct a competent diagnosis and determine the cause of the disease. Do not self-medicate. You may miss valuable time.
Exercises for vestibular disorders
Sometimes, with dizziness, gymnastics for the vestibular apparatus can give positive results in the fight against the disease:
- In the morning, immediately after sleep, we bend the body to the left, right, back and forward. We do about 14 approaches, alternately with eyes open and then with closed. In order for vestibular exercises for dizziness to produce tangible results, it must be done every 2-3 hours.
- We try to direct our gaze in different directions. Such actions help to concentrate visual attention and, to some extent, cope with nystagmus.
- Draw lines (for example, on the ground). They can be straight or curved. We try to walk along them, first with our eyes open, and then with our eyes closed. Such exercises for vestibular vertigo help to significantly reduce the manifestations of the disease.
- We take a tennis ball and throw it from hand to hand (with our eyes open). We do this for about 5 minutes. We repeat the exercise, but with our eyes closed.
On a note! Along with vestibular exercises for dizziness, you can massage a point located at a distance of 2/3 from the upper lip to the nose. You need to massage it with your thumb, pressing lightly. These steps will help alleviate your condition.
Diagnostics
Today there are many methods for diagnosing dizziness. To find out the exact cause of dizziness, a comprehensive examination is needed. Videonystagmography, videooculography and devices that examine the vestibular apparatus can most accurately determine why a woman is constantly experiencing dizziness.
If the culprit of this condition is the spine, then MRI and CT will reveal this very well. Some laboratory tests will show the cause of dizziness, if its root cause is viruses and infections.
If you are concerned about frequent attacks of nausea, weakness and dizziness, you should consult a doctor. In particular, it is necessary to obtain advice from an otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, neurologist and endocrinologist. During the initial examination, doctors will refer you for further diagnostic procedures.
Among the laboratory and instrumental diagnostic measures for nausea, dizziness and weakness, the following are most often carried out:
- Blood tests (general and biochemical blood tests).
- Determination of blood glucose levels (including determination of the dynamics of glucose utilization in the blood).
- Electrocardiographic examination of the heart.
- Audiography.
- Tomographic studies (CT, MRI).
- X-ray examination of the skull.
- Ultrasound Dopplerography – to study the condition of cerebral vessels.
As a rule, the above studies are enough to make a diagnosis. In some cases, other specific studies may be required to clarify the diagnosis.
Dizziness Nausea Diabetes mellitus Hypertension: types, causes, symptoms and treatment Hypertension Stroke Osteochondrosis
If fatigue is observed along with drowsiness, the doctor may prescribe examinations that study sleep phases. Polysomnography and multiple sleep latency tests are used. The procedures study the boiling rate and at what phase the interruption occurs.
Laboratory and instrumental methods are also used in diagnosis.
- Blood examination. Biological material is taken for biochemical and general analysis. Diagnosis sometimes requires an immunogram, which helps identify inflammation and tissue destruction.
- If symptoms indicate heart disease, a cardiogram is performed.
- Tomography of internal organs helps detect pathological processes.
- The activity of the brain and blood vessels of the head is checked using Electroencephalography.
It is important for each patient to undergo a complete examination to determine the cause of constant fatigue and drowsiness. This approach makes it possible to prescribe quality treatment.