Every person has encountered bumps on their forehead. The most common is a bump on the forehead caused by a blow. Distinctive signs are a purple, bluish tint, as well as pain at the site of the lesion. We will tell you in this article how to get rid of a bump on your forehead after a blow.
A bump on a child's forehead from a blow is not uncommon. You should consult a doctor if your child has:
- Nausea, vomiting;
- The child cannot turn his head;
- Cries, has become lethargic;
- The pupils have enlarged.
Such signals may indicate the likelihood of a concussion. In most cases, a lump on a child’s forehead after a blow does not require medical intervention.
A natural remedy is “Aibolit”, made on the basis of beeswax. Should be applied morning and evening. Make an iodine network on the affected area.
Lump on forehead from impact: first aid
It is important to provide first aid if a bump appears on the forehead from a blow. Follow the steps below correctly and in a timely manner, this will help remove the bump on your forehead in 1 day.
- Inspect the site of damage, notice a wound or abrasion, treat it with a disinfectant (Hydrogen Peroxide, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin);
- Apply a cold compress to the impact site: a metal object (spoon, coin), a bottle of water, a cloth soaked in cold water, ice wrapped in gauze. You need to hold it for 10-15 minutes to quickly get rid of the bump caused by the blow.
Treatment of a bump on the forehead from a blow
A lump on the forehead can be quickly treated Traumeel S is a homeopathic medicine. Apply 2 times a day. Act immediately to get rid of forehead bump in 1 hour. Only a small bruise will remain. Also use Troxevasin or Lyoton ointment.
A proven medicine is heparin ointment and bodyaga, the latter can be used to make lotions. Heparin ointment relieves the effects of hemorrhage well.
A large bump on the forehead from a blow goes away overnight if you make an iodine mesh. Draw a "lattice" pattern until the bump disappears, repeating as the previous one is absorbed.
This is how a hard lump on the forehead after a blow is treated. A soft lump on the forehead requires special treatment; in most cases it is an abscess. Consult a doctor to prescribe vitamins and restorative medications; in some cases, surgical intervention is required.
How to remove a bump on the forehead using folk remedies
Make a compress from raw potatoes, grate them on a fine grater and wrap them in cloth. Repeat in the morning and evening for 20-30 minutes.
A proven method is to soak flannel in a three percent salt solution. Place the fabric in a bag and leave it in the refrigerator for 5-6 hours. Then soak the bag in water and apply a compress to the site of the impact. Change pieces of fabric every 3-4 minutes. The duration of the procedure is 10-60 minutes.
Cabbage and plantain leaves help well. Simply apply to the cone, after finely chopping or beating with a hammer, and leave for 5-10 minutes. Grind the cabbage leaf in a meat grinder, boil in milk, wrap in a napkin, apply 2 times a day for an hour. This helps to resolve the hematoma and relieve swelling. Remember, traditional methods always help to get rid of a bump on the forehead.
11.09.2017
A hematoma on the forehead is a lump that forms due to injury, rupture of blood vessels due to the accumulation of blood in the resulting space. Sometimes a doctor's help is not required, the bumps go away on their own, and sometimes medical intervention is required.
Hematoma on the forehead: drugs and treatment methods
- July 26, 2018
- Orthopedics and traumatology
- Evdokimova Irina
A hematoma on the forehead (bruise) is an accumulation of blood under the skin at the site of a bruise or blow, which occurs due to damage to small vessels. Very often, after an injury, not only hemorrhage appears, but also swelling, which in everyday life is called a lump.
The frontal bone is covered with a small amount of soft tissue, and the site of hemorrhage begins to bulge. Traces of bruises on the face are always visible to others, in addition, bruises are quite painful. Therefore, a person wants to get rid of bumps and bruises on the forehead as soon as possible.
There are many medicinal and traditional methods of treating such bruises.
First aid for hematomas
Immediately after a forehead bruise, measures must be taken to ensure that the hematoma does not increase in size. To do this, you need to apply cold to the site of impact as soon as possible. The blood vessels will narrow and the bruise will not spread further. This can be done in the following ways:
- Wrap a piece of ice in a piece of cloth or towel and apply it to the sore spot. This should be done in the first few minutes after the injury. Sometimes an ice compress can help completely prevent a hematoma on the forehead.
- If you don’t have ice on hand, you can soak a towel in cold water and apply it to the bruised area. Frozen food wrapped in a piece of cloth can also be used as a cold compress.
- You can apply any cold object to your forehead, for example, a coin or a spoon. But this method is less effective than exposure to ice.
Cold compresses should be applied for at least 30 minutes. If the injury occurs close to the eyes, you need to take short breaks every 10-15 minutes.
This area of the face is delicate and prolonged exposure to cold is not advisable. You can use lead lotion. To do this, you need to moisten a piece of newspaper in cold water and apply it to your forehead.
Pharmacies also sell special lead water for lotions.
These methods are effective only in the first minutes after a bruise. They help prevent the appearance of a large hematoma on the forehead. What to do if a bruise has already formed and is rapidly growing in size? In such cases, cold compresses will no longer help; other treatment methods must be used.
Heparin-based ointments
Heparin is an anticoagulant substance. It prevents blood from clotting, and as a result, the clots inside the hematoma dissolve. Heparin ointment contains an anesthetic that helps relieve pain. Drugs in this group include:
- "Heparin-acrigel".
- "Lavenum."
- "Trombless gel".
- "Lyoton-gel".
Heparin ointment is applied to the sore spot 3 times a day. After use, slight redness on the skin may occur. But there is no need to be afraid.
This is the result of the influence of ointment components that have a vasodilating effect. The course of treatment takes from 3 to 20 days, its duration depends on the size of the hematoma on the forehead.
You just need to remember that if there are not only bruises on the skin, but also open wounds, then such remedies are contraindicated.
Ointments with dexpanthenol
Dexpanthenol is a substance that, when absorbed into the blood, is converted into vitamin B. Preparations based on it promote the healing of damaged blood vessels at the site of injury. Such ointments will help you quickly cope with even a large hematoma on the forehead, as they act directly on the circulatory system.
To treat forehead bruises, the following drugs with dexpanthenol are used:
- “Troxevasin Neo”;
- “Dolobene”;
- “Venolife gel”;
- “Hepatrombin.”
Ointments are used 2-3 times a day. They should not be used for wounds, abrasions or scratches on the damaged area.
Herbal ointments
Among herbal ointments, preparations based on comfrey herb are used to treat bruises on the forehead after a blow. This healing plant contains substances that stimulate cell division and help damaged tissues recover. You can use ointments with arnica; they also promote rapid healing of bruises.
To treat forehead bruises, herbal ointments are used such as:
- "Arnica-GF";
- "Arnigel";
- "Vitateka";
- “Larklarkspur balm with comfrey and bee venom”;
- "Dr. Theiss Comfrey Gel."
The ointments are applied to the sore spot and left overnight. The duration of treatment depends on the extent of the damage.
Badyagi-based products
Badyaga is a freshwater sponge. When dried, it is used to prepare ointments for hematomas. Badyagi powder has a local irritant effect and promotes the resorption of hematomas. The following types of ointments are produced:
- “Badyaga 911”;
- “Badyaga forte.”
There is also badyagi powder in pharmacies; it is applied to the site of the bruise for 15-20 minutes and then washed off. But these products cannot be used if there are wounds and abrasions on the skin. Allergy sufferers should also avoid using drugs based on badyagi.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies help to quickly remove a hematoma on the forehead. Of course, you won’t be able to get rid of a bruise in one day, because it takes time to restore damaged tissue. But marks from a small bruise can be removed in a short period of time if you regularly apply compresses using home remedies:
- Compress with honey. This product improves blood supply to the damaged area, and the hematoma resolves faster. Add crushed wormwood herb to honey and make a compress with the mixture on the bruised area.
- Cabbage compress. This vegetable helps resolve bruises. Take a whole cabbage leaf and beat it with a hammer. Then apply it to the sore spot. You can squeeze the juice out of the cabbage, moisten gauze with it and put it on the bruise.
- Potato compress. The potatoes are grated to a pulp, the mixture is applied to gauze and applied to the hematoma.
- Aloe. The leaf of the plant is cut in half and the pulp is applied to the damaged area.
If the hematoma is small, then the effect of using folk remedies can occur within 3-4 days. For large bruises, the course of treatment will take 7-10 days. Compresses should be done 5-6 times a day; it is useful to combine different means.
What is contraindicated to do for hematomas?
Sometimes a person, trying to get rid of bruises as quickly as possible, makes mistakes. As a result, the hematoma not only does not disappear, but also becomes larger. If there is a bruise on the forehead, the following actions are contraindicated:
- use warming ointments (“Finalgon”, “Apizartron”);
- apply warm compresses to the injury site;
- bandage the affected area tightly;
- take medications that thin the blood (acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol).
Ointments that are intended to treat bruises on the body should not be applied to the forehead area. This may cause allergies on the face.
When is medical help needed?
How to treat a hematoma on the forehead if it does not disappear for a long time? In this case, you need to contact a traumatologist or surgeon. Old bruises can become infected and then fester. The doctor will puncture the hematoma, place a drainage and prescribe antibiotics.
You should immediately contact a medical facility if the hematoma is accompanied by the following phenomena:
- After a bruise, a person experiences headache and dizziness.
- The victim complains of nausea and vomits periodically.
- Hematoma occurs not only on the forehead, but also around the eyes (in the form of “glasses”).
Such symptoms may be signs of a concussion and sometimes serious traumatic brain injury. In these cases, emergency medical attention is required.
Hematomas on the forehead are not always harmless. After all, the damage occurs in an area close to the brain. It is not always possible for a person to independently assess the danger of injury. Therefore, in case of forehead bruises, it is imperative to pay attention to the person’s general well-being and, if there is the slightest doubt, call a doctor.
Source: https://SamMedic.ru/332832a-gematoma-na-lbu-preparatyi-i-metodyi-lecheniya
Types of hematoma
To begin, determine the extent of the injury:
- Lungs. They form in the forehead area, but can also appear on other parts of the face. The cause is minor mechanical damage. They are easy to treat, they do not cause complications, and are not dangerous to humans.
- Average. They form a few hours after an impact or fall. The pain is severe and the injured area swells. It is recommended to treat this formation with medications and folk remedies, but consult a doctor.
- Heavy. Their formation occurs after two hours, then the pain intensifies. Medical attention is required, sometimes surgery.
Causes of bumps on forehead
Bruises on the forehead are caused by hitting a hard surface. Active people and athletes face this. It's easy to get a bump on your forehead if you slip at the gym and hit your forehead on a concrete wall. On the street during icy conditions, people fall and do not have time to put out their arms, hitting their heads.
You can fall and hit your face on the ground. A bruise occurs when one person hits another with a hard object, rock, bat, or objects in a fight.
The force of the impact will be strong and the consequences will be serious.
Such formations are also present in children. In childhood, the reasons are as follows:
- active games;
- ice skating, roller skating, cycling;
- combat training;
- performing lifts in ballroom dancing.
Children are at high risk of injury, have unstable bodies, and sensitive skin. A baby who is unable to roll over may roll off the sofa and hit himself.
Despite the fact that the frontal bone is strong, after an injury you need to pay attention to the formation. If the injury is serious, you need to go to the doctor and have your head checked for a concussion.
The child hit the back of his head, what to do?
06.07.2017
Hello, dear parents. We have already discussed the topic of head impacts during falls, for example, what to do if a child hits his ear, or a child hits his nose when falling. Today we will talk about what to do if a child falls and hits the back of his head.
In this article, you will learn what such a fall can lead to, what consequences can occur if you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, and what symptoms indicate the seriousness of the toddler’s condition.
You will also learn how to provide first aid and what to do to try to prevent possible bruises on the back of the head.
Alarming symptoms
It is possible that a blow to the back of the head will pass with virtually no characteristic symptoms appearing. Or maybe the bruise will just hurt. But parents should know that if any signs and characteristics appear in the behavior and well-being of the baby, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, and sometimes call an ambulance immediately.
- The baby's limbs were numb.
- In the eyes of the little one, everything splits into two.
- Nausea occurs, which may be accompanied by severe vomiting.
- Detection of differences in pupil sizes, short-term eye twitching.
- The skin became pale. A blue tint may appear.
- The child cries a lot, do not calm down for more than 15 minutes.
- Convulsive attacks appeared.
- There was a nosebleed and hemorrhage in the eyes.
- Changes in coordination of movements, imbalance.
- Clear discharge appears from the ears, mouth or nose.
- It is difficult for the child to turn his head to the side.
- Speech retardation.
- The child hit the back of his head, the lump grew very large - be sure to see a doctor.
Possible results of the impact
Parents should know what injuries, other than a minor bruise, their child may suffer as a result of a blow to the back of the head:
- Brain contusion. This can happen if the child hits the back of his head on the floor. Since small children have not yet fully formed and strong enough skeletal system, and in particular the bones of the skull, a brain contusion may occur after a fall. If the form of such an injury is mild, the doctor will prescribe medication; in the case of severe injury, surgery.
- Concussion. Occurs quite often with blows to the back of the head. As a rule, treatment takes place without complications, with the help of medications.
- Fracture. Often accompanied by discharge from the child’s ears or nose. They can be presented as clear liquid or blood. Treatment is conservative.
- Traumatic brain injury. Can be closed or open. The treatment process is the longest. Symptoms of this pathology are severe drowsiness, fainting, vomiting, and convulsions.
One day my son fell on the street and hit the back of his head. At the same time, there was even an abrasion with slight bleeding, which was successfully stopped. Everything worked out without drug treatment.
Once, when my friend and her daughter were returning home from kindergarten (in winter), they slipped, fell and hit the back of their heads. Everything turned out okay for the mother, but the girl was diagnosed with a concussion and appropriate treatment was prescribed.
There was also a case with a neighbor boy. He was visiting his grandmother and one day she washed the floor in the hallway and told him not to leave the room until it was dry. But then the cat Vaska jumped out from under the sofa and ran into the corridor. Sashenka, who had been trying to get the cat for a long time, ran after him, forgetting about his grandmother’s warning.
He slipped, fell and hit the back of his head hard. At that moment a big lump jumped out, he cried for about five minutes without stopping, either from pain, or from resentment that Vaska managed to escape again. Mom took Sasha to an appointment at the clinic, where, on the doctor’s recommendation, they underwent x-rays. Fortunately, everything worked out fine.
They were prescribed medications to resolve the lump.
The child hit the back of his head, consequences
It is important to know that as a result of the blow, the child may develop certain consequences. Depending on how serious the injury was or the delay with which the parents went to the hospital (that is, assistance was not provided in a timely manner), the following consequences may be distinguished:
- The child has problems perceiving the environment. What is typical: if the blow was struck on the left side of the back of the head, then problems will also be observed on the left side.
- The child may become absent-minded and have problems concentrating. Which will adversely affect the learning process in kindergarten and school.
- Problems may arise with both short-term and long-term memory.
- The child’s sleep is disturbed, he constantly sleeps poorly, often wakes up, and may even cry or be hysterical.
- The child suffers from constant headaches and possibly problems with blood pressure.
As a rule, if help was provided in a timely manner, almost all possible consequences can be avoided. Of course, if we are talking about a traumatic brain injury, then the child cannot do without tangible consequences; the injury is too severe.
First aid
- The first thing you need to do is calm down and not panic.
- It is important that the baby is at rest after the impact.
- Inspect the site of the injury, check for abrasions and bruises.
- If a hematoma appears, it is necessary to apply a cold or ice object to the site of the bruise, but do not forget to wrap it with cloth first.
- If the bruise is bleeding, you need to disinfect it, for example, with hydrogen peroxide. Use cotton swabs.
- If visual damage is not noticeable, explain to the child that he now needs peace and only quiet games. And monitor his well-being for several days.
- If you identify any symptoms that characterize a complication of the baby’s condition, you need to call an ambulance. This should also be done in case of severe bleeding, fainting and other alarming symptoms.
- It is important to know that if the baby loses consciousness, he must be placed on his side. It is also important to do this if there is vomiting, so that it does not accidentally enter the respiratory system.
- Even if, at first glance, everything is fine with the child, sometimes it is better to play it safe and go to see a doctor.
Prevention
Try to do everything possible to make your baby’s time as safe as possible:
- Take care of special pads on the corners of furniture.
- Wash the floors when the child is not at home or is sleeping.
- When there is ice outside, put on special shoes for your child and yourself that will resist falls.
- Get rid of paths in the apartment that can “ride” across the floor, thereby putting your child in danger.
- If your toddler moves around the apartment with the help of a walker, monitor his movements.
- Do not leave your baby unattended on the bed. If you leave the room, it is better to sit him on the floor. At the same time, you need to be absolutely sure that all corners in the room are safe and nothing poses a threat to the child’s health.
- If your child is learning to skate, roller skate or bike, make sure to purchase special equipment, including a helmet.
You already know that you can’t be completely sure that nothing will ever happen to your baby. Children are very active, love to run, jump, and are not always attentive.
Therefore, no one is safe from a possible fall or hitting the back of the head on a hard surface.
Remember how to behave in the event of such a bruise in order to alleviate the baby’s condition and prevent consequences from developing.
Source: https://zdorovyemalisha.ru/pervaya-pomosch/rebyonok-udarilsya-zatylkom-chto-delat.html
Symptoms of hematoma
There are many vessels on the head that are easily damaged by injury. Blood accumulates under the skin, causing visible bruises.
If a bruise appears on the forehead, but there are no symptoms, then there is no reason to worry, although you can go to the hospital. Sometimes there are signs that cannot be ignored:
- impairment of vision, speech and memory;
- change in pupil size;
- nausea, vomiting;
- severe pain in the forehead or other areas of the head;
- slow movements;
- loss of consciousness;
- pale skin, blue lips;
- convulsions.
Symptoms require immediate medical attention. Take the victim to the hospital or call an ambulance. They may indicate a brain injury, the development of an intracerebral or intracranial hematoma, and this is no longer just a bruise. Such complications can make a person disabled or dead, it all depends on the timeliness and correctness of medical care.
If a bruise or bruise occurs in a child, additional symptoms should alert you:
- unnatural behavior: agitated or calm;
- incessant crying;
- loss of consciousness for a couple of seconds.
Some signs do not appear immediately, so you need to monitor the condition of the injury victim.
Visit your pediatrician if a bruise occurs in an infant who has fallen from a height. A lump may indicate a concussion. It is better to be safe than to overlook and cause harm to the child’s health or lose him.
If you have suspicious symptoms, proceed as follows: provide assistance or call a doctor, and sometimes immediate assistance is required.
General symptoms
A bruise on the back of the head in a child and an adult is usually accompanied by similar symptoms. But for children, even minor damage can be fatal, this is due to the thin and soft structure of the skull of the head.
Each form of injury may exhibit certain symptoms. Typically, in mild cases, the following symptoms are observed:
- fainting (this condition can occur within a few seconds or minutes);
- the person is poorly oriented in space, he may experience confusion of thoughts;
- Memory loss may be observed, it can be retrograde or anterograde;
- after the blow, a sharp pain in the head may immediately appear, and dizziness may occur;
- nausea, which may be accompanied by vomiting;
- there may be noise and buzzing in the ears;
- pain in the eye area.
Treatment of hematoma
How to remove a bruise? You need to act quickly, but carefully. The victim must take a calm position. It is not prohibited to take actions aimed at reducing the hematoma - this reduces the risk of complications.
If there is a bleeding wound, you need to treat the area with an antiseptic and hydrogen peroxide. It is important to apply cold pressure to the bruise. Ideal if it's ice. It should not be applied to bare skin.
If there is no ice, then you can use a cloth soaked in cold water, a metal spoon, a bottle of cold water and other items. Sometimes a piece of meat from the freezer, wrapped in cloth, is used.
If there are no complications, the doctor prescribes ointments, gels and compresses to combat the hematoma. Heparin ointment is often used. It helps to effectively eliminate the consequences of injury. The ointment should be applied in a thin layer, several times a day.
Before applying the next layer, wash off the previous one.
Compress with aloe and honey
A small bump can be removed using folk recipes. They differ in availability:
- Iodine network. Promotes rapid resorption of hematoma. It needs to be updated, it wears out quickly.
- Potato. The vegetable is cut in half and applied to the cone. When the half becomes warm, it is removed and a fresh piece is applied.
- Aloe with honey. Aloe is crushed, mixed with honey and applied to the hematoma as a compress.
- Cabbage leaves. They are crushed (you can use a meat grinder), boiled in milk, then they are wrapped in a napkin and applied to the bruise for an hour twice a day.
- Beets and nuts. An ointment is prepared from these components, which are taken in equal proportions. They are passed through a meat grinder, after which the ointment is applied twice a day for fifteen minutes. This remedy helps get rid of old bruises.
- Onion (1 head), plantain (6 leaves) and honey. Plantain and onion are passed through a meat grinder and mixed with three tablespoons of honey. The compress is used three times a day for twenty minutes.
- Cabbage and horseradish root. Take one hundred grams of each component, crushed in a meat grinder. They are mixed with each other and with one tablespoon of vegetable oil. The compress is used three times a day for fifteen minutes. This remedy helps get rid of a bruise in one or two days.
If a hematoma on the forehead is not associated with complications, it is easy to get rid of it, the main thing is to do it quickly, carefully and correctly.
No matter how hard parents try, rarely does anyone manage to protect their child from all household injuries. A lump on a child’s forehead is not a tragedy. Of course, if the impact force was not high and the damage was only external. Often, even at home and without a visit to the doctor, the consequences of an unpleasant event pass quickly and without complications. The main thing is to know what needs to be done, in what sequence, what symptoms to look for, so as not to miss serious damage.
First aid for injury
A bump on the head resulting from a blow to a hard surface is a hematoma, i.e. accumulation of blood in the thickness of the skin as a result of rupture of numerous small vessels. The tissues are saturated with blood, which causes them to bulge above the level of undamaged areas. In cases where the injury does not lead to a violation of the integrity of the skin, the following should be done:
- It is strictly forbidden to panic or scold the child. Children's crying and hysterics will only accelerate the accumulation of blood in the tissues, and the lump will grow faster.
Advice: In cases where the blow fell on the temple or the back of the head, you should not experiment on a child. It is better to immediately consult a doctor who will conduct the necessary examinations and make sure that nothing critical has happened. The forehead is the strongest part of the head, so if it is damaged, negative consequences occur extremely rarely.
- You need to take something cold and apply it directly to the site of impact. In extreme cases, you can get by with a tablespoon. A compress made from frozen foods wrapped in a thin towel will be much more effective. Do not apply ice or cold directly to the skin; there is a high risk of frostbite. Keep the compress for at least a quarter of an hour.
- What you shouldn't do is pour cold water on your child's head. This will not give the desired therapeutic result, but it can provoke hypothermia and even otitis media.
- If an accident occurs in nature, you need to moisten a clean cloth with cold water and apply it to the place where the bump forms. You shouldn’t dismiss traditional methods either – burdock or plantain will help reduce swelling.
In cases where the integrity of the tissue is compromised, the incision site must be treated with an antiseptic. There is no need to apply a bandage; it will increase the healing time. If the cut is too deep, it is better to go to the medical center. The wound may need to be stitched.
Manipulations that will help you get rid of the lump faster
If you respond to an injury in time, you can prevent the formation of large edema. But most often, parents have to deal with the consequences of the child’s activity in the form of impressive swelling. In this case, the use of cold is no longer useful. Applying a compress 15-30 minutes after an injury will only increase the recovery time.
The most effective in this scenario will be the following procedures:
- You can apply an ointment to help resolve the swelling. Troxevasin, Traumeel, and Rescuer are best suited here. Apply the product directly to the bump and the area around it with light stroking movements. This must be done carefully; usually the bumps are very painful. We carry out the manipulation 2-3 times a day. The duration of treatment should not be more than five days. If the formation has not completely resolved, you need to choose another drug on the recommendation of a doctor or simply wait until it goes away on its own.
- Once the bump has turned into a purple bruise, you can use heat. It will help speed up metabolic processes and quickly eliminate traces of bruises.
- Fans of traditional medicine can try bodyaga. A mass for lotions is prepared from it. Cabbage leaves have a good absorbent effect. It is crushed to a paste, wrapped in a bandage and applied to the affected area.
Depending on the severity of the bruise and the characteristics of the body, the lump can persist from a week to a month.
Alarming symptoms, if they appear, you need to go to the hospital immediately
In some cases, the blow is too strong, which leads to problems not only with external tissues. For this reason, in the first days after a bruise, it is necessary to carefully monitor the child’s condition. If at least one of the following symptoms appears, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- The intensity of the pain syndrome does not decrease, but only increases.
- The child becomes drowsy, lethargic and weak.
- Not a lump, but a dent formed on his forehead.
- The child began to experience nausea and vomiting.
- Bleeding from the nose or ears.
- The baby's consciousness is confused. He loses consciousness, even if only for a few seconds.
- The pupils became different sizes, and squint appeared.
- The blue nasolabial triangle stands out against the background of a pale face.
- The hematoma lasts too long and does not decrease, even if ointment was used.
These symptoms may appear several hours after the impact, so you should not relax. Some of the listed points indicate a concussion, others indicate the need for a puncture.
Associated symptoms and diagnosis
Headaches after hitting your head are often accompanied by other symptoms that you should definitely pay attention to. They will help to find out how serious the damage is and what kind of help it is advisable to provide to the person.
- Nausea.
- Bleeding and clear fluid leaking from the nose or ear canals.
- Drowsiness.
- Uncoordinated body movements.
- Slurred speech or inability to speak.
- Fainting.
- Blue skin under the eyes.
- Loss of sensation or motor ability in any part of the body.
- Sensory organ disorders.
- Inappropriate pupil diameter for lighting level.
- Nervousness.
- Distortion of memory or lapses in it.
- Signs of a coma.
- Epileptic seizures.
For any clinical manifestations that indicate damage to brain structures, an accurate diagnosis of the injury is necessary. For this, X-rays, MRIs, EEGs and other methods are used.
All injuries in a patient can be determined only after a comprehensive consultation with a traumatologist, surgeon, ENT specialist, ophthalmologist, neurologist, or therapist.
Other causes of bumps on the forehead
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to follow every action of a mischievous person. In some cases, a lump on a child’s forehead is not the result of an injury, but one of the following processes and phenomena:
- Hereditary features of the structure of the skull. They do not necessarily appear immediately from birth; often special formations appear with age. In this case, there is no reason to panic; over time, the bulges smooth out, but there is still no cure for them.
- The lump may turn out to be a wen, which is formed when the sebaceous glands are blocked. The formation can grow rapidly, change shape and even color (if suppuration begins). There is no need to delay treatment. Modern techniques allow you to quickly and painlessly remove such formations. Trying to pierce the bulge yourself can cause an infection!
- Sometimes the bumps turn out to be ulcers resulting from the suppuration of an untreated injury. In some cases, they are treated conservatively, by introducing medications into the cavity. Sometimes surgical intervention is unavoidable.
- In addition, some lumps are diagnosed as fibroids. These are benign formations that are not even always treated.
Given such a variety of possible causes for the appearance of a bulge, you should not try to treat the problem yourself unless you know for sure that it is a consequence of an impact.
A lump on the forehead is a common occurrence in children and adults. Usually it appears after an impact, but there are other reasons that cause the appearance of seals. If they occur, it is recommended to consult a doctor, this is due to the location of the growths.
Any suppuration on the head can burst, leading to serious consequences. An experienced surgeon will examine the lump, refer you for the necessary tests, and then explain how to remove the lump. Both conservative treatment and surgical intervention may be prescribed.
Consequences of a bruise
Complications can be different, it depends on the location and severity of the injury. Minor injuries resolve on their own in a short period of time. In case of serious injuries, the development of the following complications cannot be ruled out:
- waking coma (apallic syndrome) - patients are conscious, but they are not able to react to what is happening, and are absolutely indifferent to the people and objects around them. There is a reaction only to pain;
- paresis – partial loss of motor function.
- brain cyst;
- brain abscess - the formation of a cavity with pus during the development of the inflammatory process;
- ICH, or intracranial hypertension syndrome, is increased intracranial pressure;
- constant headache - does not go away for six months or more;
- meningitis is an inflammatory process in the membranes of the brain;
- development of secondary epilepsy;
- death or disability cannot be excluded in case of severe injuries;
Consequences of a bruise on the back of the head:
- decreased performance and concentration;
- deterioration in sleep quality;
- depression;
- regular dizziness;
- the appearance of hallucinations;
- weather dependence.

If you hit the back of your head during a fall, the consequences of the impact can be serious, so it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination.
The success of therapeutic measures depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and treatment and the severity of the injury.
Source

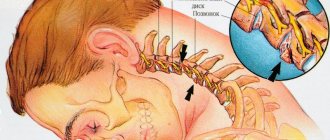
The head is the location of one of the most important human organs – the brain. Therefore, any blow to the skull or neck can lead to the most tragically serious consequences, especially if adequate assistance is not provided in time.
Moreover, unpleasant symptoms can appear both immediately after the incident and an indefinite time after it, and possible injuries can be different and can only be determined accurately in a medical institution. When should you be alarmed if you have a headache after a blow, and how should you behave under these circumstances?
Why do they appear
- Injuries are the main cause of seals. A bump on the forehead from a blow usually appears on the forehead; contusions in other places cause bruises. The fact is that in the forehead area there is a minimum size of the subcutaneous layer. When struck, the blood vessels burst, the blood has nowhere to go and it accumulates between the skin and the skull. When an arm or leg is bruised, blood enters the subcutaneous tissue, resulting in a hematoma. If a person hits his forehead, he will have a bump, not a bruise. The seal after the blow is very painful and swells.
- Blockage of the sebaceous gland. This process causes the appearance of atheroma. It grows slowly, usually appears in adults, but is also found among children. Small balls cause only a cosmetic defect; large atheromas begin to interfere. Atheromas are dense when palpated, the edges are clear, and are located under the skin. As they grow, the skin over them begins to stretch and their integrity is compromised. This may lead to infection.
- Inflammation of the hair follicle. This phenomenon is called furunculosis. A painful boil appears on the forehead. A large pimple on the forehead, like a lump, causes discomfort; the skin above it turns red and swells. The boil is dense to the touch and round in structure. Looks like a ball or bean. If you look closely, you can see a rod in the middle of the boil. It occurs as a result of bacteria entering a microcrack in the skin.
- A lump on the forehead may be an allergic reaction to irritants. The lump, large or small, does not hurt but is very itchy. In parallel, a skin rash may appear.
- Balls sometimes appear due to the proliferation of adipose tissue. They are called lipomas or wen. This is a harmless and safe seal. Lipomas are soft to the touch and grow slowly. Wen does not go away without treatment for several years. If desired, it can be removed surgically. Appears both on the forehead and on other parts of the body.
- Overgrowth of bone tissue or osteoma. This is a bone-hard swelling on the head. The reasons for its appearance are still unknown; doctors mainly believe that it is a hereditary predisposition. Osteomas usually go away on their own and can be removed if they cause cosmetic and psychological discomfort.
- Malignant neoplasm - cancerous tumors on the forehead are painless. They are a red tumor that often bleeds, but can also be a dry red spot. The neoplasms are shapeless and grow quickly. The sooner they are diagnosed, the more likely a positive treatment outcome.
Even if the growth does not bother you or cause discomfort, you should not let the situation take its course. Consult a doctor for diagnosis of lumps.
Symptoms of a contusion on the back of the head
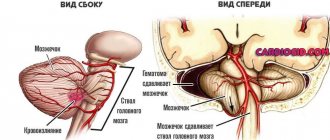
A bruise on the back of the head can cause very serious consequences for the health and life of the victim. The occipital part of the brain is known to contain the visual center, damage to which can lead to blindness or visual impairment.
Symptoms
If the back of the head is severely bruised, the victim may lose consciousness and then feel numbness in the legs. This indicates that the person may have suffered a concussion and should be hospitalized immediately.
But if an infant or young child hits the back of the head hard, in any case you need to call an ambulance. The fact is that even with a severe concussion, children never lose consciousness.
If, as a result of a bruise to the back of the head, an adult has a concussion, then after regaining consciousness he feels:
- memory loss,
- headache,
- dizziness,
- impaired coordination of movements, etc.
In the case where the blow was very strong and there is a brain contusion, the following are observed:
- prolonged loss of consciousness,
- speech disorders,
- paralysis, paresis,
- severe neurological symptoms,
- mental disorders and so on.
A brain contusion is a serious injury. But special attention should be paid to the symptoms of TBI in young children, because even with a brain injury, the symptoms may not be clearly expressed and can be compensated by the child’s body for quite a long time.
If there is only a bruise of the soft tissues of the back of the head, then a hematoma appears in this area of the head, as well as pain, slight drowsiness and a number of other symptoms.
Consequences
In the absence of timely and proper treatment, a victim of a bruised head may experience the following consequences:
- one-sided agnosia, i.e. non-perception or partial perception of part of the space on the side of the head where the injury is located,
- severe irritability and absent-mindedness,
- decreased performance,
- sleep disturbance,
- memory impairment,
- depressive state
- visual and auditory hallucinations,
- prolonged headaches,
- visual impairment, blindness, etc.
After causing a contusion to the back of the head, there may be more serious consequences, including cerebral edema and death, it all depends on the severity of the injury.
First aid
Due to the possible serious consequences after a bruise to the back of the head, it is important to know how to provide first aid to the victim.
If a person loses consciousness after receiving a blow to the back of the head, which may indicate a concussion or bruise of the brain, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Next, you need to carefully lay the victim on his side so that if he vomits, he does not choke on the vomit.
It should be remembered that as a result of a fall and a strong blow to the back of the head, the spine and skull bones can also be damaged, so the victim should be moved with extreme caution. It is forbidden to lift it or move it from place to place yourself.
If the victim is conscious and not vomiting, you just need to apply an ice compress to his head. You can keep the cold for about 20 minutes, and after half an hour repeat this procedure.
While waiting for medical help, it is not recommended to offer analgesics to the victim, because this may further complicate the diagnosis of his head injury.
Other types of cones
Other seals include the following:
- Acne is easy to diagnose. These are small red lumps on the forehead. There is a black rod visible inside. Usually found in teenagers. When squeezing out the blackhead, the ball enlarges slightly and becomes noticeably red. Acne occurs when pores become clogged with sebum and oil.
- A lump on the forehead of a child or an adult can appear due to insect bites - the bite of mosquitoes, bees, wasps leads to the development of edema and the appearance of a red painful tumor, people feel severe itching. At the moment of the bite, an unpleasant prick is felt.
- Warts are benign growths on the skin, sometimes found on the forehead. It is rough to the touch; when examined, the wart looks like a cauliflower fork. The dimensions rarely exceed half a centimeter.
- Hemangioma – This lump occurs due to a congenital abnormality of the blood vessels. It is an irregular interweaving of blood vessels. Hemangioma is usually removed surgically.
- Fibroma is a tumor that comes in two forms. In the first case it is hard, in the second a soft swelling is felt. This is a painless and non-cancerous formation, but the danger is that fibroma can degenerate into fibrosarcoma - a malignant tumor.
Treatment
When lumps appear, people immediately wonder how to quickly get rid of a bump on the forehead and not only, they can appear on, and even on. After all, it not only causes cosmetic discomfort, but can also be dangerous. You should be especially careful when the lump does not go away for a long time.
Treatment depends on the type of compaction and what pathogens it is caused by. Most often, doctors resort to surgical opening of the seals. The incision is then sutured and a course of antibiotics and vitamins is prescribed.
- Surgical intervention. Doctors also cut out fatty tissues, osteomas and fibromas. If we are talking about warts, laser removal is possible.
- Boils are treated in two ways. A large pimple is opened with a scalpel and the pus is cleaned out. If the boil is small, then conservative treatment is possible. These are compresses made from Vishnevsky ointment or ichthyol ointment.
- If an adult or child has a bump on the forehead from a blow, then it is necessary to apply a cold compress to the bruise. The ice pack should be wrapped in a cloth, and the procedure should not exceed fifteen minutes. In the following days, it is necessary to apply compresses from the Bodyaga gel to the site of the injury. Medical assistance is necessary if the child falls and then his condition worsens. Dizziness, nausea, fever appear. Most likely, we are talking about a concussion.
- In case of an allergic reaction, it is necessary to immediately remove the source of irritation and the patient to take a course of antihistamines.
- If we are talking about insect bites, then a cold lotion is applied to the bite site. If the bite site enlarges, the victim should be given an antihistamine.
- The cancerous tumors are excised, and the patient undergoes chemotherapy courses. When cancer is detected at the first or second stage, treatment almost always ends in the patient’s recovery.
If you find lumps, you need to see a surgeon or dermatologist. Doctors diagnose the disease and, if necessary, refer you to a doctor of another specialization. For example, to an oncologist or an allergist.
A blow to the temple: consequences, first aid. Why does a person die from a blow to the temple?
No person is immune from injury. Anyone can, for example, trip and fall or hit their head. But almost any blow to the head in a certain way affects the state of the body; it can cause the development of dangerous pathologies.
Thus, a blow to the temple can have unpredictable consequences, even death. Not everyone knows why this happens. Meanwhile, the temple is the most vulnerable area of the head; it is here that the brain is not sufficiently protected.
That’s why our parents tell us from childhood that hitting us on the head is absolutely forbidden.
Why is this dangerous?
The temporal region is the most vulnerable part of the head. A blow to the temple can have serious consequences, ranging from concussion to death. Many nerve endings pass through this area and lead to other areas of the head, such as the eye sockets. In addition, the temporal bone is quite fragile, so it can break upon impact.
Also in the temporal region passes the temporal artery. A small blow is enough to cause a fracture of the bone plate, as well as a rupture of the artery, which is the most significant of all those that feed the dura mater of the brain.
Why is a blow to the temple dangerous? Trauma can lead to the following consequences:
- Paralysis of limbs.
- Aneurysm.
- Bleeding in the brain.
- Epilepsy.
- Concussion.
- Loss of vision.
- Death.
Thus, the anatomical structure of the human head, in particular the temporal region, suggests the development of health and life-threatening consequences when it is injured. Therefore, the answer to the question of why a person dies from a blow to the temple is obvious.
Symptoms and signs
The consequences of damage to the temporal region may not appear immediately. The first symptoms sometimes appear after two or three days. A person feels a headache, which can be easily relieved with painkillers. But sometimes it can get worse, the medications stop helping, and tinnitus appears.
Over time, the pain is strongly felt in the temporal region, problems arise in the functionality of the neck, bruises appear under the eyes, vision and speech are impaired. A person may feel nauseous and dizzy, and lose consciousness.
These symptoms may indicate a concussion or other health problems, so it is important to seek medical help immediately.
The following signs should alert you:
- Prolonged headaches that do not go away for three days.
- Inability to eliminate pain with medications.
- Noise in ears.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Visual impairment.
- Photophobia.
- The appearance of convulsions, hallucinations.
If immediately after a blow to the temple the consequences begin to appear, you need to urgently call an ambulance.
Diagnostic measures
Even with a light blow to the temple, the consequences can be unpredictable. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo examination by such specialists as a therapist, neurologist, or surgeon. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
The doctor must eliminate the risk of developing dangerous injuries. For this purpose the following is carried out:
- X-ray of the head bones.
- CT or MRI of the brain (the price may vary slightly in different clinics) to exclude internal bleeding and hematoma, identify changes in the brain, and diagnose complications.
The doctor also conducts a study of vision and hearing, tactile sensations, coordination of movements, balance, and reflexes.
In some cases, the doctor may send the victim home under the supervision of relatives.
Relatives should monitor the patient throughout the day, and they should periodically awaken the victim in order to determine whether he wakes up normally.
Adult concussion symptoms and treatment are interrelated. If unpleasant symptoms occur or worsen, hospitalization is required.
While under home observation, the patient must remain in bed, avoid overexertion and physical activity, and do not strain the eyesight.
Therapy
An MRI of the brain (the average price is two thousand rubles) will give an accurate picture of the disease. Depending on this, the doctor will develop a treatment regimen that will focus on:
- To improve metabolic processes in the brain.
- Strengthening vascular walls.
- Prevention of cerebral edema.
- Restoration of blood circulation.
- Relief of pain syndrome.
At the clinic, doctors will eliminate not the symptoms of the pathology, but its causes. Therefore, in case of injuries to the temporal region, it is recommended to remain in a medical facility for treatment. In severe cases, surgery may be required. In some cases, intracranial hematoma is drained.
In the absence of bleeding, conservative treatment is resorted to. The doctor may prescribe sedatives, painkillers, diuretics, muscle relaxants, and analgesics. Antibacterial and antiepileptic drugs are sometimes prescribed.
Complications and consequences
A blow to the temple can have the following consequences:
- Mental and autonomic disorders.
- Impaired sensitivity, rhea, vision and hearing.
- Limitation of mobility.
- Impaired memory and consciousness.
- Parkinson's syndrome, epilepsy.
- Brain atrophy.
- Vascular damage.
- Attachment of a secondary infection.
Forecast
The prognosis will depend on the severity and nature of the injury. In a mild case, the bruise does not lead to serious health problems, so the prognosis will be good. In severe cases, death can occur.
Complications after an injury are also possible. In this case, the victim is often forced to take anticonvulsants throughout his life. Sometimes the consequence of a bruise can be an irreversible mental disorder.
Prevention
A blow to the temple can have life-threatening consequences. In this area, the brain is most vulnerable, since the temporal bone is quite thin (two millimeters). Doctors recommend taking precautions. Do not get into fights, avoid extreme hobbies. Children need to be monitored especially closely, as they are the ones most susceptible to head injuries.
If a bruise does occur, you must immediately call an ambulance. The consequences of a bruise may not appear immediately, but after several days, so it is important to undergo prompt diagnosis and begin therapy to reduce the risk of developing dangerous consequences.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/423147/udar-v-visok-posledstviya-okazanie-pervoy-pomoschi-pochemu-ot-udara-v-visok-chelovek-umiraet
Symptoms of hematoma
The most common symptoms of a hematoma are the appearance of a lump and redness of the bruised area. They do not pose a threat to life, pass quickly, and do not require special hospital treatment.
Alarming symptoms of a hematoma are:
- nausea, vomiting;
- Strong headache;
- dizziness;
- violation of movement coordination;
- difficulty speaking;
- change in pupil size;
- There are circles and spots in front of my eyes.
If alarming symptoms are noticed, the victim should be immediately shown to a doctor. A forehead bruise may be accompanied by a concussion or intracranial, internal cerebral hemorrhage. In this case, to obtain accurate and detailed information, it is best to undergo a brain MRI.
Diagnostics
What tests may be needed for a concussion?
In cases where there are no alarming symptoms, a doctor’s examination is sufficient. If the doctor suspects a more serious injury, a computed tomography (CT) scan is necessary.
When might a CT scan be needed?
CT scan is required in the following cases
- Glasgow Coma Scale score less than 15 points 2 hours after the concussion (the patient is lethargic, does not immediately answer questions, a more detailed assessment is carried out by a doctor)
- suspected open or closed skull fracture
- vomiting 2 or more times
- age over 65 years
- previous amnesia for more than 30 minutes
Is it possible to do an X-ray of the skull instead of a CT scan?
If there are warning signs, a skull x-ray will not be enough, since this study does not show the substance of the brain and may not diagnose serious problems such as traumatic hemorrhage.
First aid for a forehead bruise
If the frontal part of the head is bruised, correct and timely first aid will prevent the formation of a large hematoma. It is necessary to examine the head immediately after the blow. If the victim experiences minor pain only at the site of the bruise, then first aid can be provided independently, without the involvement of medical personnel.
- Place the victim in bed, he should be at rest.
- If an abrasion is noticed, treat it with disinfectants (chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide). A victim with a deep bruised wound should be shown to a doctor; it may need to be stitched up.
- Bandage your head tightly.
- Organize access to fresh air in the victim’s room.
- Apply cold to the injury site. This could be ice wrapped in gauze, a metal spoon, or a handkerchief dipped in water. Keep the cold for 20 minutes, then take a break for half an hour. This procedure must be completed over several days. Cold helps stop bleeding and reduce soft tissue swelling.
Any change in the victim’s condition for the worse is a reason to consult a doctor.
If there are no complications after a forehead bruise, then the bump can be treated at home. The victim is hospitalized if there are signs of a concussion and cerebral hemorrhage. To treat cones, you can use medicinal ointments and traditional medicine methods. In general, there is no need to use medications.
In the first few days, treatment for a lump consists of stopping hemorrhage and reducing swelling of soft tissues using cold. In the future, it is necessary to speed up the resorption process, which helps to eliminate the lump faster.
The doctor removes extensive hematomas in the hospital, making a corner with special needles to remove excess fluid from the soft tissues formed after the hemorrhage.
Medicinal ointments
The following ointments help to cope well with the consequences of hemorrhage:
- "Troxevasin".
- "Lyoton."
- Hepatrin ointment.
- Homeopathic remedy – “Traumel S”.
Medicinal ointments must be applied to the site of the injury several times a day. You can also get rid of the bump using traditional medicine.
ethnoscience
You can speed up the process of resorption of a lump on the forehead using the following time-tested methods:
- Apply finely chopped or beaten plantain leaves to the cone for 10 minutes.
- Combine water and alcohol in equal quantities, wet gauze and apply to the bump for 15 minutes. It is recommended to use this compress 2 days after injury.
- Apply a compress of raw potatoes, grated on a fine grater, to the bump for half an hour in the morning and evening.
- Chop the cabbage leaf and boil it in milk. Cool slightly until warm, wrap in a napkin and apply for an hour 2 times a day.
- An iodine mesh will help quickly eliminate a bump on the forehead.
You can prepare ice cubes with parsley in advance; they will help relieve swelling if your forehead is severely bruised. To do this, pour the leaves of the plant with water, freeze and use as needed.
First aid
In case of a head injury, which is accompanied by loss of consciousness and severe neurological deficit, it is necessary to immediately call emergency doctors. First aid for a mild blow to the head that provoked a concussion is to do the following:
- Place the victim in a horizontal position.
- Perform sanitation (cleaning) of the oral cavity (without raising the head and flexing the spinal column in the cervical region).
- Turn your head to the side to avoid vomit entering your respiratory tract.
- If there is an open wound, treat it with antiseptic treatment and apply a bandage to stop the bleeding.
- Until the doctors arrive, do not let the victim sleep, constantly talking to him.
Features of treatment in children
Even a minor bruise will cause a bruise and bump on the child’s forehead. But injuries under 3 years of age can be dangerous, because the child’s skull is not yet strong and cannot protect the brain from a concussion. After an injury, you need to closely monitor your baby. If he loses consciousness, disturbances in his coordination of movements are noticed, vomiting, or a severe headache are observed, then you need to call an ambulance.
If the injury does not bring great discomfort to the child, then apply cold to the bruise and, if necessary, give an anesthetic (Panadol, Ibufen). There is no reason to worry when the baby is still cheerful and active.
To treat a hematoma in a child, you can use Aibolit ointment. The composition of the drug is safe for children, made on the basis of beeswax. The bruised area should be smeared daily, morning and evening.
The frontal bone is strong, bruises of this part rarely cause complications. Impacts to the temporal and occipital areas of the head are more dangerous. But you still need to be careful. If the lump on the forehead after a bruise does not go away for a long time or has become soft, then consult a doctor immediately.
What to do if you have a head injury. Hitting the back of the head when falling - consequences
Are you having any problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
Find:
Signs of severe injury
Symptoms and signs:
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness, weakness;
- instant loss of consciousness;
- increasing pain.
For those who have received a bruise, it is recommended to create rest (it is forbidden to stand up or walk), apply a cold compress and wait for doctors.
If there are no open wounds and visible damage to the skin, this does not mean that a severe bruise could not provoke a fracture of the skull. Diagnosing the presence of a fracture is extremely difficult; this requires the help of a doctor and an x-ray; only after a comprehensive diagnosis can a final diagnosis be made and treatment prescribed.
The consequences of a severe injury may begin to appear after a few days, so you need to be attentive to any changes that occur in your well-being. https://gidpain.ru/ushib/golovy-delat-pomoshh.html
How can I help you
A head contusion in the occipital region is characterized by the same symptoms.
You need to be able to provide first aid for a head injury and contusion of the back of the head:
- Use a cold compress (apply ice previously wrapped in a cloth or a cold bottle of water). Hold at the site of damage for 10-15 minutes and, after 30 minutes, repeat the compress again.
- Ensure complete rest; in case of nausea or vomiting, turn on side.
- Call an ambulance and monitor the condition of the victim. It is not recommended to give painkillers for a head injury until the ambulance arrives.
The child has
Children under one year of age are at risk because their skulls are not yet fully formed.
Parents should not leave their children unattended and make sure that the baby does not fall off the changing table or suddenly fall out of the stroller.
Children of preschool and school age need to be taught how to behave in public places, playgrounds, and roads in order to prevent accidents.
If, nevertheless, the child is injured, then it is necessary to provide first aid, ensure peace and take him to the emergency room (for minor injuries), or call a team of doctors.
After the examination, take pills and medications prescribed by your doctor.
Basic steps
A hematoma is a hemorrhage in which blood accumulates in the tissues and does not flow out. A hematoma is a consequence of a head injury; it is important to quickly approach the correct treatment.
Treatment is carried out through surgery; incomplete removal of the hematoma leads to consequences - in the worst case, death.
Only a doctor can prescribe and select treatment.
At home, immediately after a minor bruise, apply a cold compress for 10-15 minutes to the site of the impact and apply a compressive bandage. This will block the bleeding vessels and stop the hemorrhage.
We treat at home
A clay compress is used for treatment:
- You can buy ready-made clay in pharmacies, take a cloth (cotton), put film or cellophane under it, and it is also recommended to put something on the clay.
- The compress can be left for 2 hours, applied 2-3 times during the day.
- The same piece of clay can be used many times, by first moistening it before the procedure.
Using salt:
- To do this, you will need to dilute 10 grams of salt in 1/2 glass of water, put a gauze bandage there, and wait until it is completely saturated.
- Then take a bandage and apply it to the bruise, securing it with a bandage or any other fabric.
Possible consequences
The reaction and consequences may vary from person to person.
A number of bruises can end happily, up to the complete recovery of the victim, but there are cases when minor bruises can cause serious harm to health.
It is extremely difficult for older people and young children to recover from injuries (even minor ones), so they are at particular risk and require close attention from doctors providing medical care.
The disorders that arise after injury are very diverse. Here we can distinguish both acute disorders (observed immediately after brain damage) and long-term disorders (manifest over time). The consequences can be very dangerous and may not appear immediately after the injury occurs.
Most often, the consequence of a bruise is a traumatic brain injury, which carries a number of complications.
Even an experienced doctor cannot accurately determine the outcome of the injury. It is necessary to remain calm for several weeks, not to be nervous and monitor your health, since the slightest changes in the functioning of the body can be a consequence of a head injury.
Consequences:
- Mental disorders (from memory impairment, sleep disturbances to severe fatigue).
- Impaired vision and sensitivity.
- Movement violation.
After suffering severe head injuries, patients are advised to see a doctor monthly to prevent the development of serious problems.
By following your doctor's recommendations and undergoing proper treatment, you can improve your health, however, after numerous head injuries, no doctor can guarantee that previously unexposed complications and symptoms may not appear in the future.
You should be attentive to your health, pay special attention to children under one year of age and not leave them unattended in crowded places and on playgrounds, where the child can cause serious injury to himself.
Treatment of trauma to the occipital part of the head
In case of injury in the back of the head, a medical examination and a calm regime are necessary. According to the dynamics of subjective symptoms and objective neurological results, a CT scan is sometimes performed, an examination that can detect increases in brain depression, subdural or epidural hematoma.
In this case, neurosurgical intervention is necessary - elimination of the hematoma. Rare post-traumatic hydrocephalus is usually resolved by inserting a shunt. The cervical spine is secured with a cervical collar.
Appropriate medications are used to suppress other associated symptoms of neck injury:
- symptomatic analgesics;
- weak opioids;
- NSAIDs;
- tricyclic antidepressants.
Rehabilitation treatment is added later.
Important! If you hit the back of your head, a difficult-to-control protracted pseudoneurasthenic syndrome sometimes develops.
If you hit the back of your head and there is a suspicion of damage to the cervical spine, you need to be careful in your actions to prevent deterioration of your general condition during manipulation.
It is advisable to relieve increasing pain from the very beginning with medications from the NSAID group (Brufen, Ibalgin, Ibuprofen). If pain persists, consult a doctor.
If no serious damage is found during the inspection, the following measures may help:
- Massage. After determining the location of the injury, massage of a specific group of muscles in the back of the head effectively eliminates the consequences of the injury. The correct technique of the procedure is important, so massage is performed only by a professional.
- Physiotherapy. The physiotherapist creates a combination of suitable exercises designed to involve all injured muscles and ligaments in the back of the head. Therapeutic exercise improves blood circulation, which provides good results in eliminating and preventing the consequences of injury.
- Physiotherapy. Physiotherapeutic methods include magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, ultrasound or laser treatment.
- Chiropractic. Carrying out this method belongs only to the hands of a specialist!
- Acupuncture. This therapeutic method is advisable when signs of neuralgia appear.
- Regime measures. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is an important part of treating the consequences of neck injuries.
Prescribing treatment without proper examination, determining the causes and localization of damage is unacceptable!