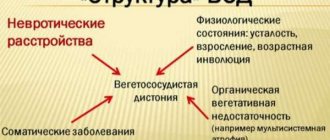
Vegetative-vascular (neurocirculatory) dystonia (autonomic dysfunction, vegetative neurosis, psycho-vegetative syndrome, VSD, NCD) is a common symptom complex that occurs both in childhood (up to 25%) and in adults (about 70%).
The main feature of this polyetiological syndrome is the numerous and varied manifestations of the disease: to date, about 150 clinical symptoms and over 30 syndromes of disorders in VSD have been described.
One of the frequent manifestations and clinical signs of neurocirculatory dystonia is headache.
The cause of all troubles
Dystonia of cerebral vessels
Where do these sometimes unbearable pains come from? Dystonia of cerebral vessels is what is the cause of all troubles. However, it is worth noting that the nature and intensity of pain may differ. This may depend on the type of vegetative-vascular dystonia manifested in the patient. However, be that as it may, in each case the cause of these symptoms is initially vegetative-vascular dystonia.
This disorder is broad enough to be discussed in a nutshell, covering all the points. However, regarding definitions, it is worth noting that vegetative-vascular dystonia is a functional disorder. The dysfunctional functioning of various parts of the autonomic nervous system leads to the fact that the vessels narrow and dilate at the wrong time.
In one case, the cause of headaches is insufficient blood flow to the vessels of the brain during hypertensive type VSD. A different situation may be observed in the case of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the cerebral type. In this case, we are talking about cerebral vascular dystonia, the consequence of which is the occurrence of cephalgic syndrome in the patient.
Symptoms
Heaviness in the head with VSD is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- feeling of squeezing of the head on both sides;
- pulsation in temples;
- nausea, urge to vomit;
- pressure surges;
- noise, whistling, squeaking or ringing in the ears;
- a feeling of instability when walking or when changing the position of the body;
- heat in the face or neck, red spots on the skin;
- numbness of a part of the face or pain when touching a certain area.
We recommend reading: Why do my ears constantly ring?
Also, patients suffering from this symptom often tend to close their eyes, it is difficult for them to look, to keep their gaze on any object. Concentration also deteriorates, irritability and nervousness appear. A person constantly wants to lie down, sleep, relax, he becomes lethargic, apathetic, and feels weak throughout his body.
Provoking factors
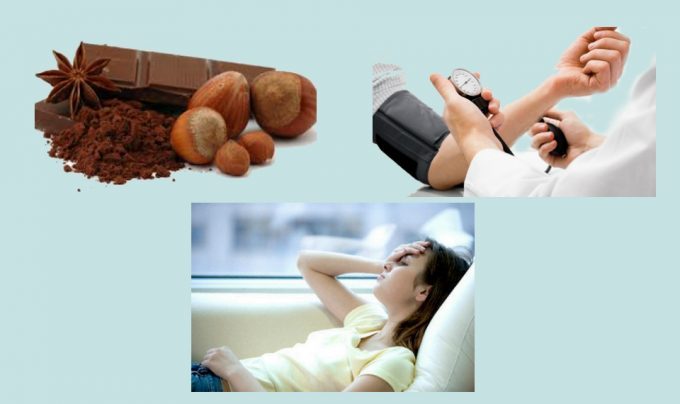

Causes of migraine pain
If we are talking about vegetative-vascular dystonia, then the main provoking factors are psycho-emotional stress, physical overexertion, smoking, and alcohol. If we are talking about migraine pain, then their appearance can be triggered by surges in blood pressure, the premenstrual period, and eating foods such as nuts, chocolate, and cocoa. The occurrence of an attack of migraine pain after taking these products is explained by the high content of tyramine in them.
How to treat
How to relieve a headache with VSD depends on its subtype.
- Pain that occurs after stress and is associated with general tension can be relieved with regular painkillers that are sold over the counter. However, it is necessary to consult a doctor, especially if pain occurs frequently and affects a person’s functioning and performance.
- How to treat migraine will be prescribed by a physician after a thorough neurological examination and determination of the characteristics of the course of the pathology and the condition of the body.
- Clusters have their own treatment methods prescribed by a specialist.
There are also traditional methods, which in some cases can replace and complement pharmacological treatment.
- Exercise helps a lot, it improves vascular tone, stimulates blood circulation and hematopoiesis, improves immunity;
- Yoga, meditation, massages;
- Walks in the open air;
- Herbal decoctions or infusions.
Features of headaches with VSD

Migraine headache
Vegetative-vascular dystonia of the cerebral type can manifest itself in several syndromes, and these are not necessarily headaches. For example, dizziness with VSD may occur if the patient has vestibular syndrome. In addition to dizziness, the patient may complain of fainting, which may also indicate cerebral type VSD. Now let's get back to our main topic. Headache with VSD can be migraine or vascular. Each of these types has its own characteristics and distinctive features.
Headache caused by migraine may have the following symptoms. Migraine is a paroxysmal condition characterized by a sudden onset and an abrupt end. Migraine pain is characterized by pronounced intensity and localization in the area covering the temple, orbit and forehead. As a rule, such pain is localized in one half of the head. They are characterized by the presence of a period of harbingers or the so-called aura. Patients begin to complain of drowsiness and decreased performance.

Marked weakness and fatigue
These symptoms appear suddenly. The pain syndrome can last from one hour to several days. The pain is pulsating in nature. In addition to pain, patients may also be bothered by symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, which are most pronounced at the height of the pain attack. Bright lights and loud noises only aggravate these symptoms. The painful attack is followed by the next period, during which patients complain of severe weakness and fatigue, and severe drowsiness.
There are several forms of migraine: a simple form, which we have already mentioned, associated and special. The associated form means that, along with such a symptom as headache, other manifestations that reflect disorders in other organs and systems come to the fore. There is an ophthalmic form in which patients complain of flashes and white spots in the visual fields, loss of visual fields or short-term loss of vision. The function of the extraocular muscles may also be impaired.

Double vision
Double vision or drooping eyelid are symptoms that the patient may mention along with headache. Associated forms of migraine may also include sensory disturbances or decreased muscle strength on the side opposite the headache. Speech at such moments may be impaired, severe dizziness appears, and gait becomes unsteady.
There are also special forms of migraine. During an attack, blood pressure may rise, heart rate may increase, and tremors may appear. At first glance, it may seem that there is a hypertensive type of vegetative-vascular dystonia here. However, unlike migraine, the hypertensive type is not accompanied by “half” pain.
Special forms also include those when the patient may have pain in various areas of the abdominal cavity, in half of the face. In addition to migraines, vegetative-vascular dystonia can also cause “vascular” headaches. The main reasons for their development are narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels and impaired outflow along the venous bed. They can be felt by patients as spasms, or they can constantly create a feeling of pressure and heaviness.
Why is this happening?
The condition when it seems that the head has become significantly heavier may be due to several reasons.
- High or low blood pressure (hypertension or hypotension). It is known that high blood pressure leads to spasms, which is provoked by the release of adrenaline into the blood, excessive fatigue, intense stress or prolonged experiences. Patients complain of severe heaviness in the head, a feeling as if something is squeezing it from all sides and from the inside. This condition may be accompanied by a feeling as if something is pressing on the eyes, nausea, discomfort and throbbing in the temples. Low pressure, as a rule, provokes vasodilation and, as a result, difficult passage of blood through the capillaries. Patients with hypotension also complain of a very noticeable pulsation in the head.
- Changes in atmospheric pressure. A feeling of intense pressure and heaviness can be caused by low atmospheric pressure. With high blood pressure, the vessels become weak and swell, the brain does not receive enough blood, which also provokes a feeling of a “heavy” head.
- Character accents. Headaches, a “vice-like” feeling, squeezing and heaviness can be felt due to the excessive susceptibility of individuals. Such people tend to think a lot and worry about both past and upcoming events. Of course, such personal characteristics can influence the appearance of various unpleasant physiological symptoms.
Traditional medicine for pain in VSD
Some useful recipes from traditional medicine will help you get rid of cephalea:
- Peony infusion;
- Valerian root decoction;
- Infusions of thyme and St. John's wort;
- Juices from potatoes, black currants, viburnum with the addition of honey;
- Tea from various herbs;
For migraines, contrast showers, hot foot baths or compresses on the forehead from cabbage leaves, burdock, and lilac can help.
Plants for decoctions can be crushed or boiled completely. Strong green tea stimulates blood circulation.
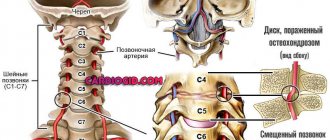
Localization of circulatory pathology
How does a headache hurt with VSD?
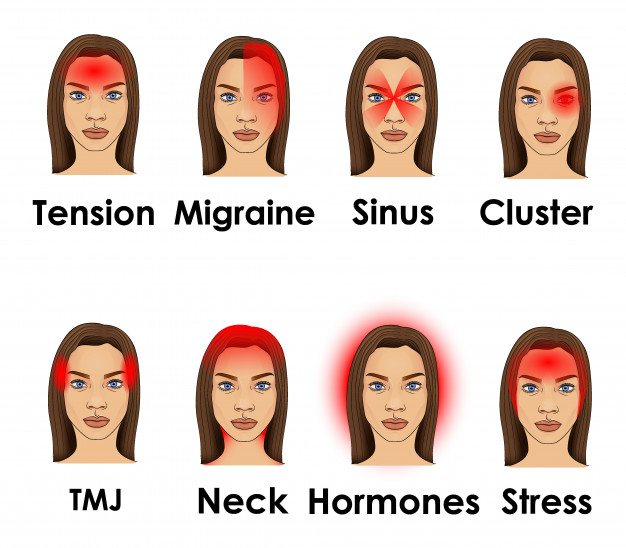
Tension (from the English tension - tension) pain is the scourge of our time, office workers are susceptible to it. A sharp, throbbing pain appears in a separate muscle area of the head: in the back of the head, crown, crown, neck, face, eyes. It can be long-term or short-term (paroxysmal). It occurs sporadically or daily, becoming chronic.
If doctors have not found organic disorders in the vessels and abnormalities in the blood circulation, then headaches are caused by VSD.
Indicators of neurocirculatory dystonia:
- taking drugs that dilate blood vessels (analgesics) is ineffective;
- The patient experiences: anxiety and panic attacks;
- attenuation of pain during sleep and its resumption upon awakening.
Symptoms of migraine include:
- throbbing pain that moves to the eyeball and becomes unbearable;
- pain occurs on both sides, increasing with movement;
- the pain intensifies when bending over, from bright light, noise, music;
- nausea and vomiting occurs;
- the sense of smell is heightened.
Signs of cephalalgia:
- short-term pain (up to 30 minutes);
- feeling of fullness in the head;
- light intolerance;
- intermittent pain;
- load-independent nature of pain;
- anxiety and tearfulness of the patient.
Pain during a vegetative crisis exhausts patients, depriving them of strength and self-control. It is necessary to try to stop the attack. The tactics of assistance are selected taking into account the type of VSD in order to reduce painful symptoms and alleviate the condition.
If the pain is accompanied by cold and tremor of the extremities, tachycardia, overexcitation and anxiety, increased blood pressure (150-180), the patient is recommended:
- breathe deeply, holding the exhale;
- massage the eyeballs and subclavian area;
- place a warm compress on the back of the neck;
- take Corvalol, Valocordin, Diazepam for tachycardia;
- Propranol - for high blood pressure.
If a person complains of pain in the head on one side, dizziness, decreased heart rate (bradycardia), blurred vision, shortness of breath, low blood pressure, you need:
- lay down or make the patient sit down;
- measure blood pressure, pulse;
- try to calm down (give sweet tea, Corvalol);
- rub your ears;
- massage the hollow of the foot.
It is necessary to ensure silence, peace, dim light, try to reduce the symptoms with available means and call a doctor.
Is a headache with vegetative-vascular dystonia dangerous?
A headache in itself with VSD is not dangerous. Of course, provided that the patient has been diagnosed and the doctors have not identified any somatic diseases. Regardless of intensity, cephalalgia is unlikely to cause serious harm to health, but medications used for pain relief can cause harm.
Most of these medications are eliminated through the kidneys and liver. Of course, there will be no serious harm if you take the pills a couple of times a month. Our body is naturally very strong and endowed with the ability to cleanse itself.
But when, with VSD, the head hurts often and you have to take medication every time, this does not have a very good effect on the body. Especially if he is already weakened by a nervous system disorder.
Also, headache with vegetative-vascular dystonia causes serious harm to mental health, worsening the quality of life. A VSD worker always has to carry pills with him, because an attack can strike anywhere. It’s not very pleasant to go to a party or go to the countryside, knowing that a headache may strike at the most inopportune moment. Therefore, regardless of the reasons, it is still necessary to get rid of cephalgia.
Interesting to know!
There are people who are especially sensitive to weather. Air pressure or humidity can cause headaches for them. According to American researchers, another weather phenomenon is to blame: lightning. The scientists found that 31% of people reported more headaches and 28% more migraines when thunderstorms occurred within a 40-kilometer radius. Presumably electromagnetic waves should be responsible for this.
Prevention
In order to relieve headaches, alleviate symptoms and treat the disease, you need to follow some preventive measures:
- Avoid any means that disrupt brain function: nicotine, alcohol, drugs.
- Set a daily routine and stick to it.
- Eat plenty of vegetables and fruits.
- Reduce the intensity of physical activity.
- Frequently be outside, take long walks.
- Learn breathing exercises, or do yoga.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Reduce the use of vasoconstrictor drugs.
Vegetative vascular dystonia can lead to unpleasant consequences if left untreated. It contributes to the formation of pathology of internal organs and worsens the quality of life. But by removing symptoms and preventing new ones, you can ensure a healthy, fulfilling life. The main thing is to strictly follow the doctor's instructions.
Types and symptoms of cephalgia with VSD
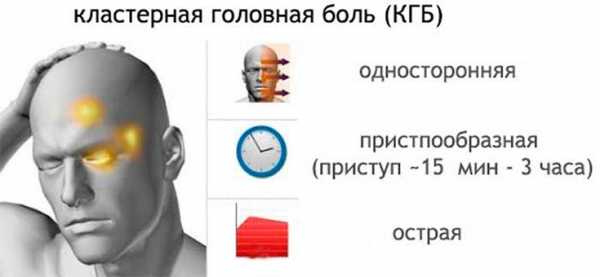
There are several types of headaches that occur with VSD, differing in symptoms. Cephalgia of vascular origin:
- Migraine is a sharp pain that occurs suddenly and has a pulsating character. May be accompanied by an exacerbation of visual and auditory reactions (the patient is irritated by bright lights, loud sounds), dizziness, nausea, vomiting, numbness of half the head and/or body. The pain syndrome is often preceded by the so-called aura - a feeling of flashes before the eyes, or, on the contrary, a short-term darkening in the eyes. Another sign of migraine is obsessive odors that have no real source, and they do not have to be initially unpleasant - it can be the thick aroma of flowers, perfumes, etc. Women are usually prone to migraines; they are rare in men, but their attacks are more severe.
- Tension pain – occurs due to severe mental fatigue or nervous stress. It has a monotonous, aching, oppressive character: the patient complains that his head is being squeezed in a vice, or that he has an imaginary heavy helmet or helmet on his head, covering the skull from all sides.
- Cluster pain is a predominantly male type of cephalalgia. The pain is one-sided - in the left or right half of the head, as a rule, always in the same one. It is localized around the eye, then spreading to the temple, forehead, cheekbone and upper jaw. The pain syndrome is extremely painful.
Factors that provoke VSD and headaches
Cephalgia with VSD also differs by time of day. Migraines usually begin in the morning and can last for several hours, but a recurrence of the attack can be expected no earlier than several weeks or even months later. Attacks of cluster pain are more acute at night and can be repeated several times a night. The duration of this type of pain is short - no more than one or two minutes, but patients perceive it as longer.
With vascular cephalgia, any physical activity becomes impossible - even a slight muscular effort causes a sharp exacerbation of pain, so the patient must be provided with complete rest during the attack, as well as silence and the absence of bright light.
Types of pain syndrome in VSD and their differences
Doctors classify three types of such pain:
Associated with the appearance of strong shocks, tension, and constant worry in a person. This pain is also typical for people whose work involves mental stress and regular concentration of attention and memory. Severe headaches are present in all parts with a feeling of squeezing.
Most often it occurs in women. The cause of its appearance can be affected by strong noise and a person being in a large crowd of people. Being under stress, drinking alcohol, strenuous exercise, and even being in a steam room can cause a migraine. When it occurs, a strong pulsation begins to occur in one side of the head, as well as acute pain in the temporal zone that can spread to the forehead and eyes. This condition is usually accompanied by nausea, vomiting, chills, a feeling of numbness in the limbs, as well as a feeling of irritation to light and noise.
They are mainly observed in men, and manifest themselves in the form of prolonged attacks, especially at night. The most severe pain is observed at the beginning of the attack in the form of acute pain on one side of the head. Pain can also occur in the temporal region, forehead and eyebrows. Pain often occurs in the jaw, chin and cheeks. They are accompanied by such signs as facial redness, increased sweating and lacrimation.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics will help determine the type of VSD and select effective treatment tactics. A cardiologist, neurologist and endocrinologist participate in the diagnosis, and, if necessary, other specialized specialists. An anamnesis is compiled to establish the family heredity of autonomic dysfunction, and the patient’s complaints are recorded. There are many different symptoms of VSD, the disease has many faces.
To exclude possible organ pathology, ECG, ultrasound, MRI and other examinations are performed (individually prescribed for each patient). Then, using modern techniques and tests, the tone and reactivity of the autonomic nervous system are assessed.
The Kerdo index uses a special formula or test to determine vegetative tone (at rest). Autonomic reactivity is checked - the reaction of the nervous system to stimuli.
Tests are carried out with body positions, dosed physical and mental stress, positive and negative emotions to determine the patient’s physiological indicators.