Reasons why a headache behind the right ear
The head behind the right ear can hurt both due to diseases of the hearing organ and due to many other disorders. Painful sensations spread from the ear to the surface of the head and vice versa. It is important to correctly determine the cause of discomfort in order to select the most effective treatment regimen.
Diseases of the hearing organ
Ear disease is the most common cause of unilateral headaches in this area. If the mucous membrane undergoes inflammatory changes, this leads to the development of otitis media. The disease can be expressed to a greater or lesser extent, but is always accompanied by discomfort and pain. Otitis media can be identified by the following signs:
- ear pain that spreads to part of the head - it can be aching, throbbing, acute or chronic;
- increased body temperature;
- hearing impairment.
Otitis externa is considered the least dangerous because it is easier to treat. The mucous membrane is easy to clean from exudate and treat with anti-inflammatory drugs. Inflammation of the middle and inner ear is a more dangerous pathology. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease manifests itself as acute throbbing pain on the entire right surface of the head. The patient cannot sleep, eat, and in the future, otitis media is dangerous due to intoxication and the spread of infection to the membranes of the brain.
Headache behind the right ear - muscle disease
Pain in the neck muscles can also radiate to the area behind the right ear. They are sharp, constant, and intensify when turning the head and when pressing on the problem area. Their cause is mechanical damage or inflammation of muscle tissue. Soreness can be caused by the following factors:
- hypothermia of the neck;
- intense loads on the damaged area;
- careless movements, which result in micro-tears of muscle fibers.
Myogelosis is another muscle disease that is accompanied by pain behind the right ear. It is characterized by the appearance of compactions due to impaired blood supply and tissue nutrition. The causes of myogelosis include osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, lack of physical activity, infectious processes and hypothermia. The disease is accompanied by decreased mobility of the neck, shoulder girdle and upper limbs, as well as acute headache, nausea and vomiting.
Neuralgia
An acute, throbbing, one-sided headache is a typical sign of nerve inflammation. Most often, the process affects the trigeminal nerve, which gives branches to the membranes of the brain, facial muscles, upper and lower jaws. The exacerbation lasts several minutes, the rest of the time the pain is aching. Home treatment is not possible, but painkillers may provide temporary relief. After examination by a doctor, a nerve block using anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs may be necessary.
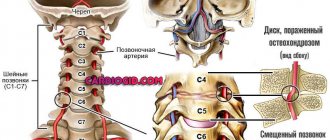
Diseases of the cervical spine
In the cervical spine there are nerves and vessels that go to the membranes of the brain. Normally, they are located in special holes in the vertebrae, so they are reliably protected from compression and injury. However, in some diseases they are under pressure from bone tissue, pathological growths and neoplasms. This leads to a deterioration in blood supply and innervation to certain areas of the head, which is accompanied by local pain.
- Osteochondrosis is a chronic degenerative disease of intervertebral cartilage, as a result of which they become less elastic and gradually deform. The clearance between adjacent vertebrae decreases, which leads to deterioration of the patency of the canals. The process is accompanied by acute pain in the neck and right side of the head, which intensifies when it turns.
- Protrusions and herniations of intervertebral discs are a dangerous disease that, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to the need for surgical intervention. At the initial stage, protrusion is a slight protrusion of the intervertebral cartilage in any direction. Then the changes become irreversible; if the dense outer shell of the disc (fibrous ring) is damaged and its contents leak out, a hernia is indicated.
- Neoplasms, pathological growths of bone tissue, spondylosis (fusion of adjacent vertebrae with limited mobility) also disrupt conduction through blood vessels and nerves. The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of the disease and the type of disorder.
Headache symptoms are accompanied by additional signs characteristic of a particular disease. The diagnosis is confirmed by the results of x-rays, ultrasound and additional examinations.
Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is an inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone caused by a bacterial infection. With this disease, a characteristic swelling with redness and fever appears behind the left or right ear. Bacteria, often pneumococcus, multiply in the synovial fluid and can provoke the development of purulent inflammation. It can spread to the eardrum or to the periosteum, resulting in the formation of abscesses.
Mastoiditis causes acute headache, symptoms of inflammation of the middle ear and an increase in general body temperature. It is important to start treatment in the first stages, since advanced stages can lead to deterioration and even loss of hearing and perforation of the eardrum. To eliminate the infection, antibiotics, painkillers and symptomatic medications are prescribed.
Injuries and their consequences
One of the causes of headaches is a history of traumatic brain injury. As a result of a fall or blow, blood circulation in certain areas of the brain is disrupted, which leads to frequent headaches even long after the injury. In addition, such injuries are characterized by increased arterial and intracranial pressure and migraines. They are accompanied by nausea and vomiting, redness or pallor of the mucous membranes, and fainting. Headache attacks can be triggered by physical exertion, bruises, as well as changes in weather conditions and atmospheric pressure.
Vascular diseases
Changes in blood pressure are one of the causes of unilateral headaches. It can spread to the temples and back of the head, as well as to the area behind the ears. High blood pressure can be diagnosed by the following signs:
- pressing, throbbing headache, often one-sided;
- tinnitus, blurred vision;
- weakness, drowsiness, lack of coordination of movements.
When pressure decreases, rapid pulse, weakness, drowsiness, and throbbing headache are observed. Both of these conditions are dangerous to health because they can cause ischemic stroke. After consultation, the doctor will prescribe medications for a course of treatment and also recommend preventive examinations.
Common diseases and symptoms
As medical practice shows, most often painful sensations appear with tonsillitis or sore throat. As such diseases progress, the pain intensifies while swallowing food. In this case, other symptoms also arise, namely:
- weakness;
- sore throat;
- poor appetite.
Painful sensations in the process of opening the mouth are diagnosed with “mumps,” a malignant formation in the larynx or other part of the mouth. With otitis media, pain occurs not only in the ears, but also in the jaw. In this case, it is not recommended to self-medicate, as this will only harm your health.
Diagnostic methods
Timely diagnosis of a headache behind the right ear is the key to successful treatment. It is impossible to determine its cause at home, since this will require consultations with specialized specialists and special examinations. After a visual examination and medical history, the doctor may recommend the following tests:
- otoscopy - examination of the external auditory canal and eardrum using a special instrument (otoscope);
- audiometry - a technique for measuring hearing acuity and sensitivity to sounds of different frequencies;
- if necessary, bacterial culture of discharge from the ear to determine the type of infection;
- X-ray is the main method of examining the cervical spine for osteochondrosis, vertebral displacement, protrusions and hernias;
- Ultrasound - ultrasound diagnostics will allow you to determine the presence of subcutaneous formations, and with the help of a contrast agent you can examine blood circulation in the main vessels;
- additional techniques (MRI, CT) are recommended if neoplasms are suspected, as they allow you to obtain a complete three-dimensional picture of the disease.
At the Clinical Institute of the Brain, it is possible to undergo a complete diagnosis, including in a hospital setting. Our center has modern equipment and a staff of broad and specialized specialists.
Rules for safe phone use
To avoid complications, people are advised to use their cell phone correctly:
- The safest way to talk on a mobile phone is on the street. In such conditions, the waves do not linger, which reduces the possibility of negative effects on the human body.
- During a conversation, it is strictly forbidden to press the phone tightly to your ear. The tube must be located at a certain distance from the auricle, which will ensure normal operation of the internal antenna and reduce the negative impact on the body.
- Talking on the phone while lying down is strictly prohibited. The tube should not be placed in a horizontal position, as the transmitting and receiving devices will not work properly, which will lead to increased negative influence.
- It is recommended to avoid listening to beeps and music on the handset. The conversation should begin after the interlocutor has picked up the phone.
- If the patient has epilepsy, neurosis, or psychopathic disorders, then telephone communication should be kept to a minimum. Children, elderly people and women during pregnancy are not recommended to communicate on mobile phones for long periods of time.
- Using a mobile phone simultaneously with other sources of electromagnetic waves, which include household appliances, is prohibited. This is due to a significant increase in load.
- It is recommended to hold the phone by the lower part of the case. It is not recommended to block the surface with your palm, as this leads to a decrease in the quality of signal transmission. The device operates as powerfully as possible, which causes radiation.
- When talking on the phone, it is recommended to take a break of 15 minutes.
- If the quality of signal reception is poor, this leads to an increase in the radiation of the device.
A mobile phone emits electromagnetic waves, which negatively affect the functioning and condition of the brain. Patients are diagnosed with headaches with frequent use of the device. To avoid the development of symptoms, a person is recommended to use a cell phone in accordance with certain rules.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen for headaches is selected individually. It depends on the type of pain, the frequency and nature of its manifestation, as well as the age of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases. Treatment may include the following steps:
- antibiotic therapy - administration of antibacterial drugs orally or in the form of injections, if the bacterial cause of inflammation is confirmed;
- drug treatment - an individual regimen that includes painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants and other drugs;
- methods of recovery from injuries, including physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises and massage - they are also effective in the initial stages of osteochondrosis;
- specific drugs to increase or decrease blood pressure;
- Surgical treatment is prescribed only when conservative methods are insufficiently effective, including abscesses, hernias, and purulent diseases of the hearing organ.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the treatment of headaches. General and individual diagnostic and therapy programs have been developed here, which are adapted separately for each patient. Modern equipment, competent specialists, the possibility of round-the-clock observation in a hospital setting - these advantages make it possible to timely identify pathology and carry out its comprehensive treatment.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 1 votes
Share article on social networks
Secondary signs
Discomfort is observed with any form of otitis. In addition, additional symptoms arise, which manifest themselves as:
- increased body temperature;
- a sharp decrease in hearing levels;
- pain in the ear when chewing;
- malaise and severe pain inside the ear.
If one of the symptoms of otitis occurs, you should immediately visit a doctor. If treatment is not timely, the disease will develop into a more severe form - purulent. As a result, the pain will become unbearable and sharp, and pus and bloody discharge will begin to come out of the ear canal. As pathology develops, body temperature rises significantly.
Migraine
The most common localization of cephalgia is a headache from above in one place, most often in the parietal region. The nature of the pain is aching. Mostly, the pain syndrome is quite long-lasting and does not go away for several weeks, and in some cases, months.
The causes of migraines are the release of certain substances into the blood, as well as changes in the body’s nervous system. This human condition is accompanied by the following symptoms:
Migraines often occur due to alcohol abuse, overeating and stress.
Pathogenesis
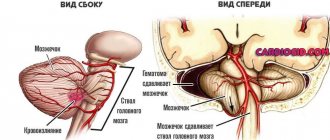
Mechanical damage to the skull is accompanied by various types of pathological processes (mixture, infringement) that cause the development of intravenous pressure. In response to serious damage, the body reacts acutely, in the form of subcellular, cellular and tissue disorders.
In the process of mixing or pinching, compression of the stem formations in the cerebellum area is possible. The cerebellum is one of the parts of the brain that is responsible for the regulation and coordination of movements. Any violation of brain structures entails the development of pathological processes.