We all consider ourselves quite literate and knowledgeable about almost everything. We all understand that if an atherosclerotic plaque (another blood clot) clogs the vessels responsible for the blood supply to the heart, then a diagnosis may be made that will sound like a heart attack, but if the vessels supplying blood to the brain are clogged, then the pathological condition of a stroke will develop .
Closure of the lumen of a vessel by an atherosclerotic plaque in the lower extremities
However, today few people have heard that when clogged with atherosclerotic plaque, not only the blood vessels located in the head and heart can suffer.
Sometimes the vessels in our legs are susceptible to this problem. Unfortunately, we know little about this problem only because the disease is incredibly difficult to eliminate without complex surgical operations.
Actually, we want to talk about blockage of the vascular bed in the legs (or about the condition of a stroke in the legs, as it is often called popularly), and why, after the primary condition of a stroke, the legs may fail, we want to talk today in this article.
And all because not knowing about this disease or not paying any attention to it does not mean at all that you will not have this disease.
General information about microstroke
Stroke is a pathological condition in which blood flow to the brain is disrupted. This condition necessarily requires the intervention of doctors, otherwise the person faces death. A microstroke is a similar condition in which impaired blood circulation is restored on its own. But this does not mean that this form of pathology is not dangerous to life and health. Even if the body was able to cope with the existing obstacle to blood flow, during all the time it took for it, a significant number of nerve cells could die and the functioning of individual parts of the brain could be disrupted. The duration of an attack can vary from several minutes to a day.
Micro-stroke suffered on the legs occurs in both adults and the younger generation. The majority of cases still occur in persons over 45-50 years of age.
A microstroke is nothing more than a harbinger of a more extensive attack. In every second case, it occurs within the next 5 years after a mini-stroke. Moreover, this can happen even the next day.
Not such a simple micro-stroke on the legs: what threatens it in the short and long term
If the blockage or spasm of the artery supplying the brain is partial, and movement along a small branch is blocked, then the signs of cerebral ischemia are short-lived. Such small forms of acute disturbance of cerebral blood flow (microstroke) can end on their own. In such cases, the patient is not suspected of a vascular accident and does not undergo treatment.
Over time, persistent damage to neurons occurs with the development of a typical stroke, loss of vision, memory impairment, psyche and mental activity.
Is it possible to have a mini-stroke on your feet?
If neurological symptoms are not persistent and go away without taking medications or with treatment for hypertension or coronary artery disease, then patients (and even specialists) may not be aware of the micro-stroke that has occurred. This situation is associated either with the small size of the brain lesion, or with good blood supply, which compensates for the lack of oxygen and cell nutrition.
The latter is typical for relatively young people without systemic atherosclerosis.
As a rule, at the time of contacting a doctor, there are no signs of the disease, so in-depth diagnosis is not carried out, and the patient does not receive adequate treatment. If the cause that led to the micro-stroke is not eliminated, then circulatory disorders progress and a severe stroke is formed.
Increased alertness regarding a possible vascular accident should arise if there are risk factors:
- cardiac ischemia;
- obliterating atherosclerosis of the lower extremities;
- arterial hypertension (an increase in diastolic pressure to 100 mm Hg increases the risk of stroke by 2.5 times);
- previous heart attack, stroke or cerebral ischemia attack, cerebral hypertensive crisis;
- excess cholesterol, triglycerides in the blood;
- old age (after 65 years the risk is 6 times higher compared to 50 years old);
- rhythm disturbances, especially atrial fibrillation;
- smoking and diabetes mellitus increase the possibility of vascular complications by 3 times;
- obesity, physical inactivity, metabolic syndrome;
- alcoholism and drug addiction;
- use of hormonal drugs, including contraceptives;
- abnormal structure of the vessels of the brain, carotid and vertebral arteries, compression from the outside;
- autoimmune diseases with damage to the arteries;
- migraine;
- cardiomyopathy, rheumatism, bacterial endocarditis, congenital and acquired heart defects;
- venous thrombosis;
- Takayasu, Horton's, Moyamoya disease, periarteritis nodosa;
- antiphospholipid syndrome.
Signs
As with ischemic stroke, clinical manifestations consist of focal symptoms and general cerebral disorders. Therefore, they can be divided into several groups:
- general cerebral – sudden acute headache or gradually increasing, general weakness, nausea, vomiting, brief episodes (sometimes imperceptible) loss of consciousness;
- vegetative – hot flashes, redness of the upper half of the body, sweating, cold hands and feet, muscle tremors;
- carotid (spasm or blockage in the area of the carotid artery) - decreased sensitivity (numbness) or tingling of the skin of the arms and legs, half of the face, weakness in the arm or leg, speech impairment, short-term blindness in one eye, convulsions;
- vertebral arteries - dizziness, noise in the head, unsteadiness when walking, flashes of light in the eyes, disturbance of the outlines of objects, loss of part of the visual field, double vision, loss of clarity of speech, difficulty swallowing, headache and dizziness may increase when turning (tilting) the head ;
- stem part - severe dizziness, impaired eye movements, loss of vision and hearing, loss of balance, swallowing and sensitivity in a limited area of the face, difficulty pronouncing words;
- medulla oblongata – brief loss of the ability to move (“freezing in one position”);
- temporal lobes – loss of orientation in space and time, inability to reproduce current events.
Sometimes there is a combination of two or more groups of characteristics. Such an attack can last from a few minutes to 8 - 10 hours. The next day the patient feels satisfactory, or severe weakness remains.
Consequences for women and men
Recent studies have found that long-term consequences for patients who have suffered a mini-stroke are not as safe as previously thought, even with complete restoration of the neurological status.
It is interesting that with conventional diagnostics using CT and MRI, no abnormalities were detected after a month, but when stimulating the cerebral cortex with short magnetic pulses, a disturbance in the processes of neuronal excitation and a longer period of inhibition than normal were detected.
It is assumed that such changes persist for life and are the cause of the appearance in patients who have suffered a transient ischemic attack:
- asthenia – weakness, loss of interest in the environment, weakening of memory;
- neurasthenia – increased irritability, anxiety, insomnia, headache;
- depressive states;
- neurocirculatory dystonia;
- dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Over the course of 5 years after a microstroke, a third of patients develop acute cerebrovascular accident, leading to a permanent neurological defect (loss of speech, paralysis of the limbs, loss of sensitivity, visual impairment).
One consequence, less dangerous for the patient, but quite noticeable for others, is a change in personality traits against the background of a malnutrition of the brain.
The patient becomes extremely uncooperative, loses most social and family contacts, like hypochondriacs, looks for signs of non-existent diseases, and complains of constant pain that cannot be objectively confirmed.
Significant relief of symptoms is observed with neuroprotectors and antidepressants.
What to do if you suspect a microstroke
The first thing that is recommended if you suspect a cerebrovascular accident is to seek emergency medical help.
If the attack occurs against the background of high blood pressure, then it should be gradually reduced, but not allowed to fall below 140/90 mm Hg. Art., as this will lead to an even greater deterioration in the nutrition of brain neurons.
For this purpose, Dibazol, No-spa, Magnesium sulfate is usually used intravenously or intramuscularly.
Before the ambulance arrives, you must:
- take a horizontal position with your head raised;
- apply cold to the head and a warm heating pad to the feet;
- ensure free flow of fresh air;
- You can take an Aspirin tablet or dissolve 10 tablets of 0.1 g of Glycine.
Then, after eliminating the manifestations of a transient cerebrovascular accident, it is imperative to undergo an examination. It includes:
- consultation with an ophthalmologist, neurologist, cardiologist;
- blood tests - general, coagulogram, lipid spectrum, blood sugar;
- Ultrasound with duplex scanning of the vessels of the head and neck;
- rheoencephalography;
- Brain MRI with angiography;
- X-ray or CT scan of the spine (cervical spine);
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart (as recommended by a cardiologist).
Watch the video about the signs of a microstroke, the reasons for its development and consequences:
Treatment and recovery
Patients often undergo treatment on an outpatient basis, since their health remains satisfactory, but given the fact that within a month after the attack it is likely to recur or transform into a stroke, an inpatient course of therapy is considered the most justified.
Medicines can be selected only taking into account diagnostic data, since it is important to eliminate the cause of the micro-stroke. The most common groups of drugs are:
- hypotensive - Prestarium, Arifon;
- antiplatelet agents – Thrombo Ass, Clopidogrel, Curantil;
- anticoagulants (for cardioembolism) – Warfarin, Sinkumar;
- lipid-lowering drugs – Liprimar, Vasilip;
- solutions to improve blood flow - Reopoliglyukin, Glucose, Trisol;
- vasodilators - Cavinton, Sermion, Nimotop, Eufillin;
- neuroprotectors – Semax, Cerebrolysin, Gliatilin, Encephabol.
During the recovery period, patients are prescribed hyperbaric oxygenation, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy on the collar area, radon or pine baths, massage, reflexology, EHF therapy.
If a cholesterol plaque is detected in the carotid artery, which occupies more than 70% of its lumen, surgical treatment is indicated.
Prevention of micro-strokes
To prevent severe cerebrovascular accidents, it is necessary to eliminate or maximally correct the main risk factors for its development. With a persistent increase in blood pressure, lifelong antihypertensive therapy is required. The use of antiplatelet agents and hypocholesterolemic agents is also continued throughout the year.
It is extremely important to give up smoking and alcohol abuse, monitor cholesterol, blood sugar, and blood pressure.
Refusal of contraceptives in tablets, careful use of painkillers, and treatment of concomitant diseases are required.
It is necessary to normalize body weight, and devote at least 30 minutes a day to physical activity. You need to reconsider your diet:
- include at least 400 g of vegetables and fruits per day;
- eat boiled fish more often than meat (only low-fat varieties are allowed);
- give up processed foods, margarine, store-bought sauces, canned food, and offal.
Preventive measures also include timely surgical treatment for impaired patency of the cerebral arteries.
We recommend reading the article about spinal cord stroke. From it you will learn about the causes of the disease and its symptoms, classification of spinal cord stroke, methods of diagnosis and treatment, consequences for the patient.
And here is more information about first aid for a stroke.
A microstroke occurs if cerebral blood flow is disrupted briefly and in a small artery . An attack of transient ischemic attack can be brief, eliminated on its own or by taking medications throughout the day. Therefore, signs of cerebral ischemia remain unattended, and the patient continues to lead his normal lifestyle, suffering a micro-stroke on his feet.
If vascular disorders are suspected, it is necessary to undergo a full examination and a preventive medication course; sometimes surgery is required to prevent a stroke.
Source: https://CardioBook.ru/mikroinsult-na-nogax/
Provoking factors
A microstroke is in no way associated with any infectious pathogens. Impaired blood flow occurs due to existing internal pathologies, mainly of a cardiovascular nature. The risk group includes the following categories of people:
- Having various diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Those who abuse bad habits;
- Hypertensive patients;
- Suffering from diabetes;
- Those suffering from excess weight, especially obesity;
- Not following the principles of healthy eating;
- Having disrupted hormonal levels;
- Those who neglect physical exercise and prefer a passive sedentary lifestyle.
Diabetes mellitus can be a provoking factor for a micro-stroke.
Provoking factors for a micro-stroke on the legs can be severe stress, physical wear and tear of the body due to a long lack of proper rest, a sharp change in weather conditions if the patient has weather dependence, etc.
Treatment and preventive measures
If there are symptoms of a mini-stroke, then you cannot ignore the condition and bear it on your feet. Full assistance from doctors is the key to minimizing the consequences. It is necessary to call an ambulance, agree to hospitalization and comply with all the requirements of medical workers.
The brain is the control center for all functions of the body, and disruption of the nutrition of the cells in this department can lead to an irreparable imbalance for the rest of life.
Treatment of a microstroke is carried out with the same medications as a classic one. If you call an ambulance, the victim will be offered hospitalization in the cardiology department of the hospital. The hospital will conduct an examination: they will do an ECG and X-ray, and take blood and urine for analysis. MRI allows you to diagnose a microstroke; during the examination, the doctor sees altered areas of brain tissue in the form of darkened areas.
The treatment regimen usually includes the following drugs:
angioprotectors - substances that activate blood microcirculation in blood vessels and optimize metabolism; vasodilators; drugs against the formation of blood clots - antiplatelet agents; nootropics to restore brain cell activity.
Preventive actions:
refusal to drink alcohol and cigarettes; normalization of the daily routine; regular proper rest; physical activity; taking vitamins and dietary supplements; minimizing stress.
A number of diseases - hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus - can provoke a mini-stroke, so they should not be neglected; all measures for treatment should be taken. Regular medical examination is a mandatory measure that allows you to identify and treat pathology in a timely manner. Even during a standard examination by doctors at the workplace, serious acute cerebrovascular accidents were diagnosed, and urgent hospitalization helped save the life and health of those examined.
Paying attention to your own health is the key to its safety. No work moments, desire to earn money and “urgent” matters are worth ignoring your poor health and suffering a mini-stroke as usual on your feet. Sharp pain in the back of the head, numbness of the limbs and face, speech impairment, nausea and vomiting are especially dangerous symptoms that require immediate medical attention. If a loved one experiences something similar, call an ambulance. A stroke suffered on the legs is an extremely dangerous phenomenon. A person is in demand as long as he is healthy and prosperous. It sounds cruel, but the plant man, immobilized, with slurred speech, quickly loses his social circle and workplace, despite all his past industrial achievements.
Features and signs of a microstroke suffered on the legs
A microstroke does not always reveal itself, unlike a full-blown attack. Symptoms may be muted, as a result of which people may perceive them as manifestations of other pathologies, for example, severe migraines, chronic fatigue, or viral diseases. There are often cases when, during a micro-stroke, people did not even look up from their work activities. But, despite the fact that the condition, as a rule, stabilizes on its own, various kinds of consequences still remain in the body.
Among women
In women, microstroke rarely occurs at a younger age. In this case, the symptoms in the weaker half, as a rule, are more spontaneous.
The following signs should signal impaired cerebral circulation:
- Headache and dizziness;
- Sudden loss of strength, malaise;
- Nausea;
- Darkening in the eyes;
- Poor breathing;
- Pain in the heart area.
More intense signs of a microstroke in women suffered on the legs include:
- Symptoms of fever: high body temperature and chills;
- Impaired body coordination;
- Unnatural facial expressions;
- Impaired visual function;
- Weakness in the upper and lower limbs.
It is worth pointing out right away that the listed symptoms may or may not be present. The degree of their severity is individual in each case. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the victim’s body, as well as on how severely the blood flow was disrupted and how long the attack lasted.
In men
The signs of a microstroke in men are generally similar to those observed in women, but they are usually more pronounced. Depending on the area of the brain affected, the following symptoms may occur:
- Severe headache;
- Dizziness accompanied by loss of coordination;
- Vision problems;
- Speech impairment.

Just as in the case of women, the severity of possible symptoms depends on many factors.
Stroke on the legs: symptoms of a microstroke and its consequences – Izvilina
A microstroke is a serious pathology in which the death of brain cells occurs due to a blood clot or a sharp spasm of a small vessel.
In this situation, the lesion is small, so people do not always notice that they have been hit. Symptoms appear immediately, and recovery occurs in a short time.
Moreover, the disease is no less dangerous than a regular stroke, because it also leads to necrosis of brain cells.
Sometimes a stroke may be suffered on the legs, and the citizen may not understand what happened to him. A person needs to know if they have had an attack in order to be more careful about their health. Also, if negative symptoms occur, you should know in what cases you need to consult a doctor.
What is the danger of a stroke in the legs?
A stroke on the legs is a negligent attitude towards one’s own health. Even with a common cold, you need to postpone everything, stay in bed, drink a lot of warm liquids and take medications. Otherwise, there is a risk of serious complications and sad consequences. With a stroke, everything is much more serious.
Stroke is a severe disruption of the nutrition of brain tissue that develops due to pathological changes in the vessels of the head. Symptoms develop sharply within 24 hours. The main causes of stroke are a complication of hypertension or atherosclerotic changes in the vessels of the head.
A stroke can be a consequence of stress, physical strain, or overwork. It can develop after a protracted infectious process. With massive hemorrhages, which are accompanied by pathological changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, a fatal outcome is real.
Source: https://fiz-disp.ru/razvitie/insult-na-nogah-simptomy-mikroinsulta-i-ego-posledstviya.html
First aid
If a person nearby exhibits signs similar to a micro-stroke, it is important to react quickly and provide first aid. First of all, you need to call an ambulance or ask someone to do it.
While the team is on the way, the victim must be laid on a flat surface and something placed under his head so that its level is higher than his body. If a person has the urge to vomit, he should be turned to his side. All constricting clothing and accessories must be loosened. You also need to ensure a flow of fresh air into the room.
In general, this is all that a person without medical training can do when providing first aid. If the patient's condition begins to deteriorate sharply, resuscitation may be required in the form of artificial respiration and cardiac massage.
First aid and treatment
It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate. When you recognize the first symptoms, you should immediately call for medical help.
Before the doctors arrive, you can help the patient:
- To do this, you need to place him on a flat surface and turn his head to the side.
- In the room, open all windows to ensure oxygen supply.
- Unbutton your clothes and place a cold, wet cloth on your head. Leave the person completely alone: do not move him or show your panic.
What therapy is needed if a person has suffered a mini-stroke?
To treat circulatory disorders, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Thrombolytics - medications are aimed at dissolving a blood clot and restoring blood flow in the vessels. However, the effect of these medications will be noticeable only if the patient starts taking them in the first 3 days after suffering a stroke. It is important to remember that in case of hemorrhagic stroke, thrombolytics aggravate the situation, so it is necessary to find out the type of stroke.
- Anticoagulants - a medicine aimed at preventing blood clotting and the formation of blood clots.
- Diuretics - help reduce swelling in brain tissue.
- Neuroprotectors are a group of vitamins for the maintenance and restoration of brain cells.
Important! The types of medications and their combination are prescribed by the attending physician.
In addition to taking medications, during the recovery stage the patient is prescribed:
- physical therapy;
- water procedures;
- individual sessions with a speech therapist and rehabilitation specialist;
- physiotherapy;
- diets.
It will be good if the patient can go for sanatorium treatment.
It is important to strictly follow all doctor’s recommendations, control blood pressure, quit smoking and alcohol, and follow a strict diet. Sleep and rest are extremely important for recovery, and don’t forget about walks in the fresh air.
Rehabilitation after a mini-stroke
In order to minimize the consequences of a micro-stroke, the patient should undergo a course of rehabilitation. It is developed individually in each case, depending on the severity of the attack and the patient’s condition.
Traditionally, a rehabilitation course includes:
- Taking medications. Typically, the patient is prescribed drugs that normalize blood flow, prevent the formation of blood clots, and strengthen the walls of blood vessels. But if necessary, medications that restore impaired brain activity can also be recommended. Vitamin complexes will also not be superfluous. They will help saturate the body with all the necessary microelements;
- Physiotherapy. This is a very important block in the rehabilitation course. Special procedures allow you to influence various points where nerve endings are located, thereby stimulating their work. Acupressure, acupuncture, radiocurrents - all these are physiotherapeutic procedures that are often prescribed after a micro-stroke;
- Physiotherapy. This is a special type of physical education that includes specially designed exercises. They are gentle and at the same time affect the necessary areas of the body.
A properly selected rehabilitation program can restore the body with minimal losses and continue your normal lifestyle.
Signs and consequences
With a stroke, acute disturbances in the functioning of the brain and its local functions occur.
This clinical syndrome can last more than a day or lead to death. It can occur due to a disruption in the blood supply to any area of the brain due to decreased blood flow. And also in the presence of thrombosis, embolism, which occurs against the background of pathologies of blood vessels, heart muscle or blood. Ischemic is the most dangerous type of stroke, when a blockage occurs in one of the vessels that supplies blood to a certain part of the brain. Quite often, the cause may be hypertension or another pathology of the heart or blood vessels.
Patients often complain of severe pain in the legs after an ischemic stroke. What to do about this, how to alleviate their suffering? To find out, you need to know about the features of this phenomenon. After all, painful sensations that arise after a stroke cannot be treated with conventional analgesics, since here we are dealing with other mechanisms.
Types of post-stroke pain and their treatment
It occurs in the area of the brain that controls human sensations, in particular pain. It usually occurs three months after a stroke. It begins to be felt in one half of the body, most often in the arm or leg (thalamic), and is long-lasting, strong, and burning in nature.
Antidepressants. The drug amitriptyline is prescribed. In this case, Cymbalta provides a good analgesic effect.
Anticonvulsants. Usually the doctor recommends taking Finlepsin, gabapentin, etc.
Painful sensations often affect paretic limbs. This type of pain occurs a week after the pathology. It is characterized by sharp, cutting-like, burning sensations that intensify when moving the legs or arms.
But in this case, the appearance of such sensations may be an encouraging sign of the beginning of the process of restoring the functions of the limbs. After a stroke, the muscles do not receive impulses coming from the brain for a certain period of time. But the appearance of paretic syndrome may mean that they have begun to receive impulses and respond to this with pain, as their ability to contract is gradually restored.
But there is one trap that many patients fall into. The fact is that these sensations usually appear when the patient is completing a rehabilitation program. But when it becomes very painful, patients often stop activities, which absolutely should not be done.
If you stop rehabilitation, the muscles may no longer recover. Even worse, they may shrink and not unclench at all. That is, the legs and arms will never be able to straighten at all. This phenomenon is called contracture. So keep this in mind and carry out rehabilitation even through severe pain.
— Regular rehabilitation activities. These include regular exercise therapy (physical therapy), a massage course, and possible physiotherapy procedures.
— To reduce pain, the doctor will prescribe analgesics (in this case they bring slight relief).
- Muscle relaxants are prescribed. They are used at the first manifestations of negative sensations. With their help, the muscles relax, which helps reduce soreness. Usually the drugs prescribed are iidokalm, sirdalud. Baclofen has a good effect.
— If necessary, the doctor will prescribe antidepressants and anticonvulsants, which we mentioned above.
But if muscle compression occurs, a contracture occurs, it will not be possible to cope with it, straighten your legs, arms with the help of medications. The only way out is a course of injections with medications that contain botulinum toxin. Such drugs include Botox or Dysport. At the same time, you need to carry out active rehabilitation exercises and also take muscle relaxants. These drugs relieve pain most effectively in the presence of contracture.
From all that has been said, we can conclude that pain in the legs and arms after an ischemic stroke can and should be fought. Only this must be done adequately, depending on its type, and also taking into account the general condition of the patient.
In addition, after overcoming it, you should continue rehabilitation measures and follow all the recommendations of your doctor. This is the only way to literally put the patient back on his feet. Be healthy!
Restoring walking after a stroke occurs in stages. The muscles of the legs and torso are gradually strengthened, the ability to coordinate your movements and maintain balance returns. It takes a lot of time to eliminate movement disorders, but if you put in the effort, you can achieve good results.
A stroke occurs when there is an acute disruption of blood circulation in the brain. As a result, the organ suffers from a lack of oxygen and nutrients, which leads to cell death. After an attack, the following disorders occur:
- The ability to walk is impaired. The patient cannot get out of bed on his own.
- Sudden mood swings occur, positive emotions are replaced by negative ones.
- Cognitive functions become unstable.
- There is no coherent speech.
- Swallowing reflexes are impaired.
If these disorders are present, treatment should begin as quickly as possible, otherwise complete paralysis will occur.
No specialist can say exactly when a person will fully recover from an attack. The rehabilitation program is selected separately for each case. This also applies to the development of exercises to restore the ability to move.
After an acute circulatory disorder in the brain, motor dysfunction can be detected by the following signs:
- An unsteadiness of gait appears, which is not observed in healthy people.
- It is not possible to bend and straighten the leg and arm or fully straighten it. The leg can remain in a straight position at all times.
- The gait becomes uncertain and the steps are incorrect. Can't move quickly.
- It is not possible to fully stand on the sole of the injured foot. Therefore, the patient begins to walk from the toe, and not from the heel, as ordinary people do.
- Each next step can lead to an unexpected fall, as sensitivity decreases.
- The movement of a sick person is similar to a compass.

Basic recommendations for restoring movement
Some patients recover very quickly and learn to walk within 2-3 months after the attack, while others need much more time. Everything depends not only on the degree of damage, but also on the correctness and regularity of home treatment. The use of special exercise equipment speeds up the healing process, but not everyone can afford it. Therefore, many people use homemade devices to train leg and arm movements.
If your legs don’t walk well after a stroke, you need to find out what to do from specialists. The rehabilitation period should begin as early as possible, but only after completion of drug treatment.
First, the patient must learn to sit and only then can he try to get out of bed. At first it will be difficult to even sit, so relatives should make sure that the patient does not fall.
Gradually, the victim will begin to maintain balance and will be able to keep the torso in the correct position, which is necessary for walking.
The ability to bend and straighten your leg and arm should also be restored.
Recovery is facilitated by the use of:
- a special cane with four supports;
- orthopedic shoes with a small heel and wide sole. It is desirable that the fasteners securely secure the ankle joint of the affected limb.
It is necessary to ensure that a person after a stroke develops independence and is able to take care of himself and walk without assistance.
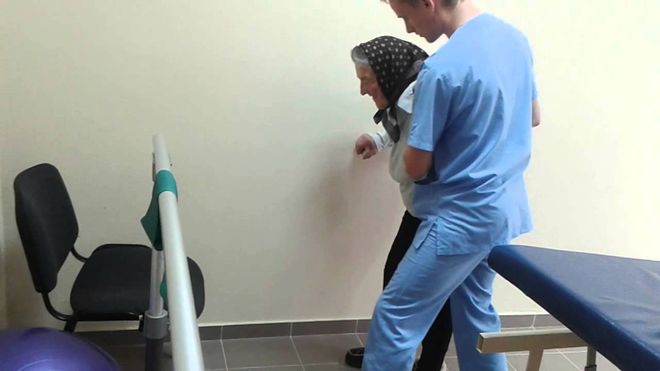
In order for a patient to learn to walk after a stroke, he needs help. In rehabilitation centers they use the technique of drawing a path with footprints in front of the bed. Patients begin to take their first steps along them. This method can also be used at home. It helps to quickly restore motor functions.
It will be easier for the victim to start walking after a stroke if:
- use holders to fix the foot;
- Wear knee pads to prevent the knee from bending and to keep the leg in an upright position.
Once the ability to stand up without assistance has returned, you can connect to a treadmill designed specifically for stroke patients.
It is important that classes are not carried out at a fast pace, as the ankle joint may not work correctly.

The speed of recovery may vary:
- If the stroke manifests itself in the form of a minor ischemic circulatory disorder, then the ability to control the limbs will return to the person within a month.
- The average degree of stroke, which is always accompanied by loss of consciousness, allows only half of the motor activity to be preserved. Therefore, the patient must be gradually taught movements. At first, warming up in a lying position will be enough. Gradually you should move on to more complex exercises.
- A stroke accompanied by severe hemorrhage leaves no chance of recovery. This condition is considered incompatible with life.
Restoration of limb function after a stroke consists of:
- passive gymnastic exercises in bed;
- sitting up in bed;
- getting up and standing still without support;
- walking with legs using technical means of rehabilitation, and later without them.
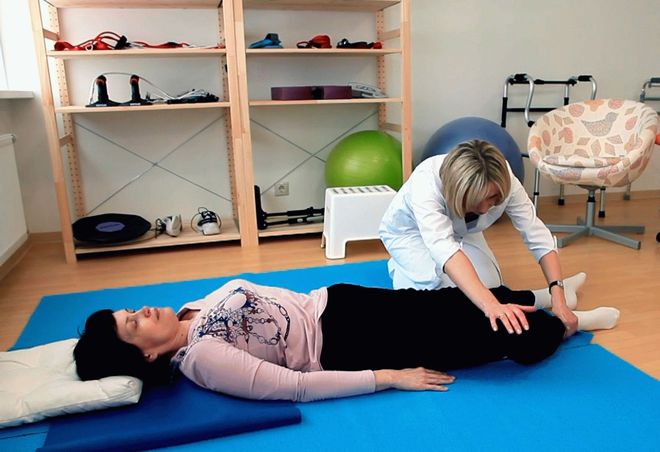
Restoring the vestibular system after a stroke is very important, since with its help a person maintains balance. All training should be carried out gradually increasing the load. You cannot begin to teach a patient to walk if he cannot yet sit up in bed independently or make even the simplest movements.
Exercises for legs after a stroke are developed individually. They should be as physiological as possible.
You need to master the exercises in this order:
- The first group consists of turning from side to side in bed, pushing the body away from the headboard with your legs, trying to get into a sitting position and a lying position without falling.
- The second group consolidates the ability to sit independently. During this period, you can do active gymnastics while sitting, lower your legs from the bed and stand up on your healthy leg.
- The third group can be started when the patient can stand steadily on his healthy leg. In this case, you can already use a walker.
- The fourth group - with the help of a walker you can stand and carefully step from foot to foot.
- Those who have moved to the fifth group can independently develop a stable gait using walkers. The legs can already withstand heavy loads, the patient can walk longer distances than before, and the intensity of the exercises can be increased.
Forecast
If the attack of a microstroke did not last long and the blood flow was able to stabilize within a few minutes, then the patient can hope that areas of the brain will not be severely affected, and there will be no significant consequences. But, unfortunately, this does not always happen. In some cases, a microstroke leads to:
- Concentration of attention decreases;
- Memory deteriorates;
- The emotional background is disrupted. Mood swings become more pronounced.
Whether a microstroke will turn into a full-fledged attack depends on many factors: timeliness of first aid, age, health status, and other things.
Rehabilitation to restore movement after a stroke
Paralysis and paresis are common phenomena in the post-stroke period. If your leg is paralyzed after a stroke, you need to undergo rehabilitation
A stroke leads to paralysis, numbness, paresis and seizures. Therefore, during recovery, it is important to massage your legs after a stroke.
Swelling of the legs after a stroke develops against the background of damage to the right hemisphere of the brain and cerebellum, which are responsible for physical capabilities
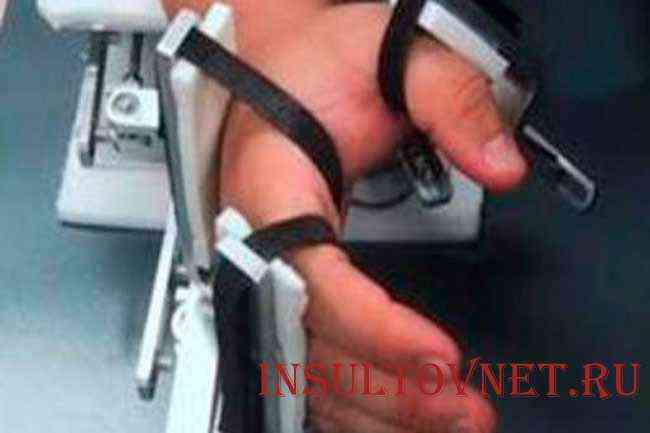
Most often, the consequences after a stroke manifest themselves in the form of paralysis of the limbs. To avoid this, you should do leg exercises after a stroke.
After a primary stroke, there are always consequences and health problems, and this applies not only to pensioners, but even to those who are under 30 years old. The reason lies in the fact that the disease affects the areas of the brain responsible for mental and physical activity.
Often patients are faced with the fact that the leg has paralyzed after a stroke or sensitivity has been lost, paresis, bedsores and ulcers have begun. This is due to the location of the lesions in the right hemisphere of the brain. It is responsible for motor activity, emotions and mental state. Leg paralysis can also develop due to a spinal stroke, hemorrhage in the right hemisphere or cerebellum.
Leg cramps are characterized by sudden contraction and relaxation of muscles, often occurring at night. There are clonic and tonic types of seizures, and the main difference is the duration of the tension. The causes of cramps are stress, decreased water balance, heavy physical activity, and problems with blood circulation.
Therefore, when the brain is damaged by a stroke, one may experience seizures, which is a subsequent effect after paralysis, numbness and loss of sensation. Problems are treated with exercises, taking vitamins, reducing stress levels and going to the pool. It is also necessary to adhere to a diet, give up bad habits and cure chronic diseases.
The most common cause of stroke is a problem of water balance, improper functioning of the kidneys and the genitourinary system. This is affected by brain damage due to stroke, blockage of blood vessels and decreased immunity.
But it is better to prevent leg swelling after a stroke in advance by treating inflammation in the genitourinary system and kidneys with antibiotics.
Also, most patients experience leg pain or cramps after a stroke. This occurs due to damage to the central nervous system and peripheral neurons, from which the type of pain differs: strategic and paretic. Pain usually occurs in the first days after an attack, but can last for one to four weeks, sometimes it is antispasmodic, cutting and acute.
To get rid of the sensations, you need to take hemostatic drugs, painkillers, do massages and rubbing, and go to reflexology. In particularly difficult conditions, it is necessary to put the patient into artificial sleep or coma in order to avoid a recurrent attack of stroke and anaphylactic shock. After all, pain can manifest itself throughout the body or only in a separate part of it.
— No, most often it occurs in older people against the background of poorly treated hypertension and atherosclerosis. In those who are younger, cerebral circulation may be impaired by vasculitis, varicose veins of the legs and thrombophlebitis, as well as by cardiac pathologies, for example, due to atrial fibrillation and inflammatory processes in the heart muscle, which lead to blood clots.
— By what signs can you understand that a person is developing a stroke?
— Before it approaches, a person usually feels numbness in an arm, leg, or part of the face (paresthesia). It is difficult for him to say or formulate something; he cannot even put words in the right order. But if after an attack you ask a person to smile, you will notice that the nasolabial folds have become asymmetrical.
And when you try to raise both hands, one will not cope with the task. Relatives and colleagues should be wary of this. If such phenomena disappear after 10-15 minutes, then a transient ischemic attack has occurred, which indicates that a source of disaster has arisen in the brain and an acute vascular catastrophe is real.

In such cases, the patient must consult a therapist, neurologist or cardiologist in order to begin treatment immediately. With a cerebral hemorrhage (hemorrhagic stroke), only 30-40 people out of a hundred survive. An ischemic stroke gives a greater chance of survival, but after an acute circulatory disorder a person, as a rule, loses his ability to work and becomes disabled.
The fact is that after a stroke, a certain part of the brain dies. Neighboring zones can take over its functions, but are not able to completely replace it. Only with minor strokes, when a small vessel is affected and the body has fully compensated for the damage, defects in movement, speech and memory become almost invisible over time. But this doesn't happen often.
— Lyudmila Ivanovna, resident of the Kyiv region. What methods help people recover after a stroke?
— Previously, patients were prescribed strict bed rest for 21 days. But during this time, a bedridden person, as a rule, developed pneumonia, infections of the genitourinary system, and blood clots. Now, based on scientific data, other methods have been formed. If certain restrictions are needed with a hemorrhagic stroke, then with an ischemic stroke, doctors recommend raising the patient as early as possible in order to avoid complications and enable compensatory mechanisms.
In our department, literally from the third to fifth day after an ischemic stroke, activation of brain functions begins. To do this, we use medications that improve blood supply and metabolic processes, relieve vascular spasms and swelling in the affected area. We also introduce elements of physical therapy (kinesitherapy) so that the brain “remembers” how to control the limbs.
It is very important to accustom the body of such a patient to its usual vertical position, but this must be done gradually. In the morning, patients have a regular toilet with the help of medical staff: washing, brushing teeth, shaving. In order for a person to eat, he is seated with the head of the bed slightly raised. Next, as a rule, IVs are placed and injections are given, which are repeated in the afternoon if necessary.
Then they begin massage, reflexology, and physiotherapeutic procedures. Therapeutic exercise is carried out twice a day. It turns out that during the day six or seven specialists of different profiles work with the patient. If the patient was in a coma and began to regain consciousness, you need to use everything that he previously liked, for example, turn on the TV or put on headphones and let him listen to his favorite music. Positive emotions help you recover earlier.
Many return to their previous jobs. But for people who were managers or engaged in hard work, we usually recommend changing activities: emotional and physical overload can again lead to a stroke. However, it is necessary to work: if there is no daily motivation for activity, the threat of depression increases.
There was a case when, after successful rehabilitation, a man got back on his feet, and a few months later he was brought to us again, lying down. The man had minimal paresis, he could move, but at home his relatives did everything for him and prevented his every desire. Therefore, I always insist: do not bring food to the patient’s bedside if he can get up and walk to the table.
Leg paralysis can be caused by a variety of factors. This may be a sudden disruption of blood circulation in the lower extremities or a malfunction of the motor nerve fibers. It happens that even an experienced doctor is unable to quickly understand the diagnosis and understand why a person’s legs fail. Typically, doctors have to deal with the following diseases:
- alcoholic polyneuropathy;
- diabetic polyneuropathy;
- obliterating endarteritis;
- cerebral stroke;
- diseases of the spine.
These five diseases most often lead to numbness of the lower extremities and impaired motor activity. Regardless of the cause of paralysis of the legs, a person loses the ability to walk - temporarily or permanently. Some diseases can lead to complete loss of the ability to move and cause disability at any age.
Alcoholism is one of the most common causes of polyneuropathy. In the initial stages, this disease makes itself felt with the following symptoms:
- burning pain in the calf muscles;
- numbness and crawling sensation in the legs;
- painful spasms of the lower leg muscles;
- muscle weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- gait disturbances;
- amyotrophy.

All these symptoms do not occur on the same day. In a person who drinks alcohol in excess, signs of polyneuropathy appear gradually. With each new drink, the disease progresses, and one day there comes a moment when the legs simply give out. The person cannot stand up, and any movements are difficult to perform. It also happens that the legs completely stop moving for an indefinite period of time.
Pain, tingling, numbness in the legs is a reason to consult a doctor.
Why do alcoholics' legs fail? It's all about the negative effect of ethyl alcohol on the process of conducting nerve impulses in the legs. In alcoholics, the transport of nutrients and enzymes that ensure the normal functioning of nervous tissue is disrupted. All processes slow down, signal transmission along nerve fibers is disrupted. Ultimately, this leads to muscle weakness, even complete immobility of the legs due to alcohol intake.
- drooping left corner of the mouth;
- drooping outer corner of the left eye;
- partial numbness of the left limbs.
- Disorders of kinesthetics (tactile sensations). As a result, patients become unable to perform many movements. Therefore, at first the victim needs outside participation. You need to start the exercises with the easiest ones, preferably passive in nature.
- Help the patient mentally compare the movements of the healthy and paralyzed sides of the body. When the victim first performs exercises with a healthy limb, and only then tries to do the same on the opposite side.
- Encourage the victim, and also clarify what and how to do, for example, straighten or bend a paralyzed arm or leg. To support the patient, it is necessary to hold his affected limb, quietly directing it in the desired direction. He must perform the remaining movements himself.
- With each introduction of a new exercise, it is important to approach this gradually. Until the victim independently learns to perform at least not the most difficult tasks.
What is a stroke?
Prevention measures
Microstroke is a real scourge of the 21st century. In view of the fact that today people are increasingly tied to sedentary work, neglect proper rest and sleep, abuse unhealthy food, prefer quick snacks to full meals, all this cannot but affect their general condition. With a cumulative effect, all these factors lead to an increasing risk of mini-stroke, which can occur even in young people. That is why prevention of this condition will be useful not for certain categories of the population, but for every person.
In order to protect your body as much as possible from disturbances in the blood flow of the brain, you should take the following measures:
- Keep the body in good shape. It is important to lead an active lifestyle. Even if you have a sedentary job, you can take regular breaks to stretch. Evening walks in the fresh air will be very useful;
- Avoid being overweight. Obesity is a close friend of many diseases, including stroke, heart attack, and atherosclerosis. You shouldn’t exhaust yourself with hunger strikes in pursuit of a slim body. It is enough to stick to a healthy diet and exercise;
- To refuse from bad habits. Together with cigarette smoke and alcohol, toxins enter the body, which clog blood vessels and arteries, which contributes to impaired blood flow - the direct cause of a mini-stroke;
- Avoid stressful situations. It is not always possible to do this, but it is quite possible to control your emotional perception towards them;
- Regularly undergo preventive medical examinations and follow all doctor’s prescriptions in case of certain diseases, especially chronic ones.
In most cases, a microstroke is a consequence of an irresponsible attitude towards one’s health, and with regular preventive examinations, its occurrence can often be avoided.
Andrey Yurievich
How is this condition treated?
Some doctors may dismiss the problem with some skepticism, saying that this is rare and that, in most cases, after problems with the blood vessels of the legs (swelling and soreness), a brain stroke rarely occurs.
This is only half true, since such a development of the disease is really rare, but a brain stroke can still occur against the background of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities.
The optimal treatment option for blockage of blood vessels in the lower extremities is considered to be a high-precision endoscopic operation, which will quickly relieve swelling, pain and other manifestations of the disease. This technique may also be called minimally invasive or catheter-assisted surgery. Unfortunately, there is no other way to eliminate the blockage of blood vessels in the legs.
Types of microstrokes
To better understand the course of treatment and methods of preventing the disease, you should understand a little medical terminology, types of microstrokes and the causes of their occurrence. But first things first.
Doctors, depending on the type of cerebral vascular damage, distinguish 2 types of microstrokes:
- Hemorrhagic. A cerebral vessel ruptures and hemorrhages occur. A ministroke usually affects a small area. However, it is no less dangerous to health. Hemorrhagic microstroke is more common in men and is accompanied by increased blood pressure.
- Ischemic. The blood vessel becomes blocked and blood stops flowing to part of the brain. Without blood supply, cells begin to die. Ischemic microstroke is more common, but is less well diagnosed at the initial stage.