Definition
Dropsy is a pathological condition that occurs during intrauterine development of the fetus and is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in any cavity of the body. There are two types of this disease:
- Immune. The main reason for the development of dropsy of this type is the Rh conflict between mother and fetus. Currently, the pathology is successfully treated, which leads to low mortality.
- Non-immune hydrops fetalis (ICD-10 code P83.2). A more dangerous type of disease that can be caused by many factors. Despite the fact that medicine does not stand still, this pathology has a high percentage of deaths. This is especially true for children born prematurely. With non-immune fetal hydrops, the prognosis will be positive if the pathology is diagnosed at an early stage. This will allow you to identify and eliminate the provoking factor, as well as determine the most effective treatment plan. A photo of non-immune hydrops fetalis (ultrasound) is presented below.
What is fetal hydrocephalus
The condition is characterized by increased intracranial pressure. The disease develops due to exposure to an infectious pathogen or a number of third-party causes.
The disease is formed as follows:
- Excessive amounts of fluid drain from the spinal cord area;
- it begins to gradually accumulate in the brain.
Dropsy in pregnant women can occur due to the abnormal structure of the embryo at the stage of conception.
Pathology has several forms:
- primary;
- secondary.
The first type is a disease caused by congenital defects or genetic mutations. The secondary form develops as a result of exposure to infection.
Fetal hydrocephalus can be closed or open. Closed - when there is an obstacle to the drainage of fluid from the head.
Open - cerebrospinal fluid is not absorbed into the bloodstream, and its circulation in the brain is not impaired.
In addition to the acute and chronic course, doctors distinguish external, internal and mixed types of the disease.
Causes
The causes of non-immune hydrops fetalis are still not fully understood and are characterized only by the repetition of some manifestations. Despite this, the most common factors that provoke the development of pathology are identified:
- Chromosomal pathologies. These include triploidy and Shereshevsky–Turner syndrome.
- Various infections. For example, toxoplasmosis, measles, rubella and others.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system - congenital heart defects, thrombosis of the vena cava and others.
- Genetic diseases. For example, achondrogenesis and Pen-Shockey syndrome.
- Anomalies of the thoracic region. These include hiatal hernia and chest dysplasia.
- Congenital tumors.
- Also, the cause of non-immune fetal hydrops can be malformations of the kidneys and other internal organs.
- Metabolic disorders in a child.
- Pathologies of pregnancy. These include placental transfusion syndrome, cytomegaly, various viruses, placental chorioangioma, anemia and maternal diabetes.
Diagnostic measures
To identify a pathological condition and the nature of its occurrence, a set of diagnostic measures is used. Let's look at them in more detail:
- The main diagnostic measure is ultrasound, which can reveal intrauterine signs of pathology and the degree of their development.
- The blood type and Rh factor are determined. This study is very important to exclude the immune nature of the disease.
- The doctor conducts a survey of the pregnant woman, which clarifies the presence of chronic diseases, infections and surgical interventions performed. Complications that arise during pregnancy and the general course of pregnancy are also important.
- General analysis of urine and blood.
- Blood chemistry.
- ECG.
- Examination of a woman for infections.
Intrauterine examinations of the fetus are prescribed to confirm non-immune hydrops fetalis during pregnancy:
- Examination of amniotic fluid.
- Cordocynthesis.
- PCR for suspected infections.
- Dopplerography.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis is aimed at establishing the provoking factor that caused hydrops fetalis. First, the doctor determines the blood type and Rh factor. This is necessary to remove or confirm immune dropsy and Rh conflict.
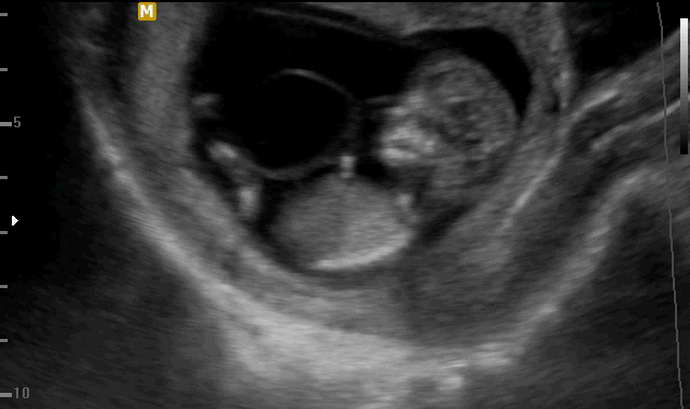
The doctor analyzes past infectious diseases, pathologies and operations, an analysis of the life history, the presence of pathologies associated with gynecology, the course and outcomes of the previous pregnancy, obstetric and gynecological history, a complete description of the current pregnancy, any complications, weight gain, and so on.
Fetal ultrasound is the main diagnostic method. Main signs of ultrasound:
After diagnosis, doctors’ prognoses are often disappointing. According to statistics, the percentage of surviving children does not reach 30%. More often than not, the child dies in the womb. But still, with timely detection of the disease and provision of treatment, there is a chance to save the fetus. But at the same time, there may be the following consequences in the future:
- Heart failure.
- Heart or brain defect.
- Pathology of the respiratory tract.
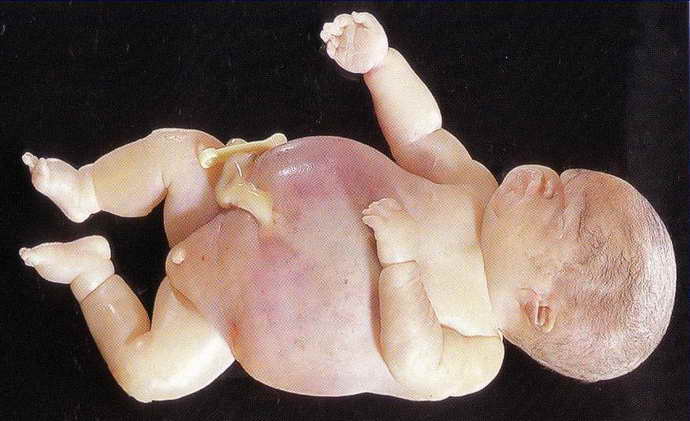
Defects are formed individually in each child due to gender, despite the causes of the disease. Modern medicine makes it possible to recognize non-immune dropsy and provide timely assistance.
The fetus experiences swelling of the head, torso and arms and may have problems with intubation. To be prepared for various types of unforeseen situations and provide timely assistance, you need to purchase tubes of different sizes. You should purchase a guidewire needed for oral intubation.
An equally significant factor is respiratory failure. Most often it is caused by ascites, pulmonary hypoplasia, and hyaline membrane disease. Heart failure is a big deal. It is worth remembering that the first aid that will be provided to a baby with non-immune dropsy will be much more effective if the actions are carried out in an organized and correct manner and if they are prepared for this in advance.
Girls, I’ve been in a disassembled state for two weeks now. An ultrasound was performed at 13 weeks of pregnancy - the diagnosis was non-immune hydrops fetalis and formations in the neck area (which ones were not specified). I went to doctors for two weeks and had ultrasounds three more times to double-check. Subsequent ultrasounds did not improve much - hypertonicity increased due to my moral shock and the child began to “hide” from the doctors. Doctors are talking about termination. There is little information on the Internet, dropsy is a generally unstudied thing, it is not clear where it comes from - I had no infections, not a single doctor found a heart defect in the child, no matter how much he twisted me, the blood supply to me and the baby was normal. The question remains about chromosomal abnormalities. Only an invasive procedure can help figure this out. But the doctors said that there was no point in doing it for me, because even if there is no CA, the child will still not be healthy and the like.
I found a couple of stories with a more or less positive outcome of such situations, but basically everyone goes for an interruption, there is very little information.
Maybe someone has encountered something similar? What were the forecasts? What did they do in the end, were children born with such intrauterine pathologies and what happened to them in reality?
I don’t want stories about “how good everything was,” I want a real picture.
Maybe it will be useful for someone.
Brief background: at week 29, an ultrasound scan revealed large edema in the fetus, diagnosed with non-immune hydrops and sent to the pathology department. They said that they would do Caesarean because... breech presentation. I agreed, but then the test results came back and it turned out that I also had kidney inflammation. The doctors persuaded me to undergo treatment first, but it only got worse and about a week later I was sent to give birth. The boy was born at 30 weeks, weighing as much as 3950 kg, terribly swollen, and lived for about 10 minutes. Today I received the results of the autopsy. No infections. The main diagnosis is hemolytic disease of the newborn. A very rare case of blood type conflict. My first one is positive, my husband’s second one is positive. During pregnancy, tests revealed a slightly increased antibody titer. Also, not everything was in order in the analysis for AFP (there is no analysis on hand now, but one of the indicators was greatly underestimated). Also, during pregnancy, the level of hemoglobin was greatly reduced. My gynecologist was surprised that the geneticist I went to for an AFP test did not send me for cordiocentesis. “Your genetics are fine, but something is wrong with your obstetrics,” that’s all I heard from the geneticist.
I read that in case of Rh conflict, immunoglobulin injections are given, but in case of blood group conflict? Is some kind of prevention and treatment possible? And does anyone know if all this horror will be repeated during the next pregnancy?
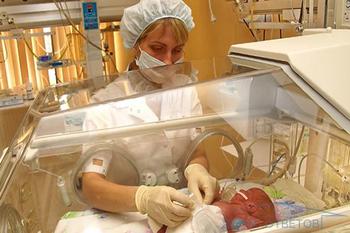
With hydrops fetalis, a pathological condition develops, characterized by the accumulation of fluid in all cavities of the body, followed by the formation of generalized edema (edema of the whole body). This is a fairly rare pathology of pregnancy, which is recorded only once in 14,000 cases. Hydrops fetalis is divided into two forms: immune and non-immune.
The immune form is a severe and more complex form of hemolytic disease of the fetus. At this stage of medical development, this form of dropsy is diagnosed very quickly, so there are chances for successful treatment. The non-immune form of dropsy is provoked by severe intrauterine pathologies (heart defects, infections, chromosomal disorders). It is non-immune dropsy that is difficult to explain, because... It may be impossible to establish the cause and treat it; The prognosis for this form is usually unfavorable.
It is strange that doctors do not agree on the definition of the form of hydrops fetalis. This is of enormous importance, because the prognosis for a successful birth and the specifics of therapy are fundamentally different.
To answer your question regarding pumping out fluid from a fetus inside the womb, then this is unrealistic. Most therapeutic and resuscitation measures are carried out only after the birth of the child. In particular, with immune dropsy, after birth, the pericardial sac is pierced and all the fluid that has accumulated there is removed from it. Using needles and catheters, fluid is pumped out from all systems and cavities of the body where it could appear during the period of intrauterine development.
However, with immune hydrops, therapy can also be provided at the stage of intrauterine development. This increases the chances of normal development of the child. In case of non-immune dropsy, resuscitation measures are also mandatory (puncture of the pericardial sac and removal of fluid from the entire body). However, as mentioned earlier, all activities (with the exception of preparing the necessary equipment and tools) are carried out after the birth of the child. Intrauterine therapy may not be effective enough to minimize all risks and disorders.
The most common complications of hydrops fetalis (regardless of the form of pathology) include:
- Respiratory failure. That is why preparatory measures include the possibility of connecting the child to breathing apparatus and stimulating lung function.
- Cardiovascular failure. As a result of impaired contractile function of the heart, disturbances in intracardiac and pulmonary circulation occur. Often there is a need to “reboot” the heart, as if restarting its work.
- In a fairly large percentage of cases, no resuscitation measures help. The result in this case is the same - death. When specialists in the process of intrauterine development come to the conclusion that the fetus has no chance of normal development, and intrauterine disorders are irreversible, the pregnant woman is offered an abortion or artificial birth.
Clinical picture
The first symptoms of non-immune fetal hydrops can be seen on ultrasound. These include:
- decreased fetal activity;
- subcutaneous edema;
- ascites;
- tachycardia;
- the presence of fluid in the body cavities;
- polyhydramnios;
- enlarged heart;
- the abdomen is enlarged due to ascites.
A woman may experience symptoms such as hypertension and massive edema.
But the most obvious signs are observed immediately after birth. The clinical picture makes it possible to almost accurately identify the disease:
- First of all, the baby’s serious condition is observed.
- The sutures of the skull are open, the fontanelle is protruding.
- Swelling is observed.
- Subcutaneous tissue is poorly expressed, so body temperature is dependent on the environment.
- Suppression of reflexes and low blood pressure are also diagnosed.
- Ascites is often noted.
- Enlarged liver and spleen.
The essence of pathology
Dropsy in pregnant women is the initial stage of gestosis - a condition that occurs as a result of a decrease in the adaptive properties of the woman’s body. The pathological process consists in the retention of a large amount of fluid in the body, its accumulation in soft tissues. This causes the formation of edema, a deterioration in the general well-being of the pregnant woman, and disruption of the heart.
Due to blood thickening, fetal nutritional disturbances occur - hypoxia develops, and the process of intrauterine development slows down.
The main mechanism for the development of dropsy is a change in water-salt balance. Pathology is diagnosed at any stage of pregnancy, but more often at 5-6 months. In 25% of women, dropsy develops into the next form of gestosis – nephropathy.
Pregnancy and childbirth

After the diagnosis is confirmed, the woman is sent to the Center for Surveillance and Surveillance. Non-immune hydrops fetalis is a high-risk pathology that requires high-quality equipment and qualified specialists.
First of all, the compatibility of the diagnosed anomalies with life is determined. The woman must be explained what possible consequences for the child in the future. Non-immune hydrops can provoke serious abnormalities in the development of the fetus, which will cause a significant decrease in the quality of life. If it is not possible to find out the cause of the disease and it is impossible to prescribe effective treatment, then termination of pregnancy is recommended. If a decision is made to keep the child, additional examinations are carried out, the results of which help to decide what in this particular case would be more correct - premature delivery or prolongation of pregnancy. The choice is complicated by the fact that non-immune hydrocele is prone to spontaneous remission.
The decision to give birth is made based on the woman’s condition and the degree of maturity of the baby’s lungs. Before delivery, an ultrasound examination is performed to assess the presence of ascites and effusion. This will prepare you for possible aspiration of fluid. In most cases, a caesarean section is recommended, since with natural childbirth there is a risk of asphyxia.
Hydrocephalus in the fetus - hydrocephalus of the brain
Hydrops fetalis is characterized by an increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system of the brain, internal and external spaces containing cerebrospinal fluid. The prevalence of hydrocephalic syndrome in the neonatal period from birth to the 28th day of extrauterine life is about 4 cases per 1 thousand newborns. Hydrocephalus in the fetus, detected during pregnancy, develops due to impaired production or resorption of cerebrospinal fluid absorption.
As a result of the pathological process, the volume of cerebrospinal fluid increases, which leads to expansion of the ventricles, circulation pathways and spaces filled with cerebrospinal fluid. If hydrocephalus in the fetus develops during the perinatal period, it is accompanied by impaired motor activity and higher mental functions. Infants with congenital hydrocephalus syndrome exhibit delayed motor development. Subsequently, they have difficulty holding their head up and slowly learn to stand and walk, which is often associated with organic damage to the brain matter.
The progression of the disease leads to a decrease in perfusion and permeability of brain tissue, impaired cerebral circulation, and edema. In parallel, pathological conditions and processes develop, such as neuronal degeneration, dysfunction of synapses, and, in the later stages of the course, demyelination of nerve fibers and gliosis.
Pathological changes in the structure of nervous tissue in the early stages of pathology can be reversible due to the high plasticity of the fetal brain tissue. The consequences of a long-term pathological process, expressed in demyelination and gliosis, are irreversible. To prevent serious complications incompatible with the health and life of the child, intrauterine treatment of hydrocephalic syndrome is carried out. In the first case, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the lateral ventricles, the subarachnoid space between the soft and arachnoid mater and the subdural space under the dura mater.
In the occlusive form, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the ventricles against the background of blockage of the ducts through which it is normally drained. Occlusive hydrocephalus comes in several forms:.
Hydrocephalus of the brain in the fetus often correlates with the presence of intracranial space-occupying tumors, cysts, and areas of hemorrhage. Cerebral aqueductal stenosis is also associated with hydrocephalic syndrome. Primary true hydrops fetalis in pregnant women is often caused by a hereditary predisposition provoked by genetic mutations.
The secondary form is the result of a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. The secondary form of hydrops in the fetus during pregnancy occurs as a consequence of many reasons: Cases of maternal infection with infectious agents are especially dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, when brain structures begin to form. Hydrocephalus can develop as a consequence of Arnold-Chiari syndrome, an abnormality in the formation of the skull, in which there is a decrease in size or deformation of the section containing the cerebellum.
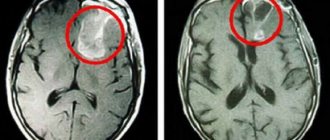
The diagnosis is established based on the results of an instrumental examination, according to the opinions of specialists. At the same time, a mother's blood test is performed, which shows the titer of antibodies to infectious agents to identify latent viral and bacterial infections. The indication for treatment is severe ventriculomegaly, an increase in the size of the ventricles, diagnosed during ultrasound or MRI.
Consultations with a perinatologist, neonatologist, neurosurgeon, and geneticist are required. The results of instrumental studies show the nature of the course of the disease, including the degree of ventricular dilatation and the rate of progression of pathological changes.
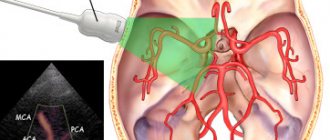
Treatment of the pathology is difficult due to the following reasons: The main methods of therapy include cephalocentesis, ventricular puncture and fetal ventriculoamniotic shunt, which is considered more effective than the installation of shunts and drainage systems after birth. Cephalocentesis is an invasive procedure that punctures the wall of the dilated ventricle and removes excess cerebrospinal fluid. Intrapartum intervention is performed with a puncture needle under sonological ultrasound navigation control during the period of intrauterine development between 25 and 32 weeks of gestation.
Evaluation criteria for the success of cephalocentesis include a reduction in the size of the ventricles and fetal head circumference, which is determined during a control ultrasound examination.
Intrapartum ventriculoamniotic shunting avoids fetal death or the development of serious pathologies in the newborn. The procedure is resorted to if, according to the results of an ultrasound or MRI, hydrocephalus is detected in the fetus, which threatens its normal functioning and development. During the intervention, a shunt is installed - an artificial vessel, drainage, which ensures the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid into the amniotic cavity and amniotic fluid.
The shunt is equipped with a one-way membrane valve that prevents the flow of amniotic fluid back into the ventricular system. Conditions for the operation:. Statistics show that intrauterine minimally invasive treatment of hydrocephalus is more effective than similar operations performed after the birth of the child.
The prognosis for this pathology is relatively favorable. Timely diagnosis and intrauterine treatment significantly increase the baby’s chances of recovery. To prevent the development of a secondary form of pathology, the mother carrying the fetus must give up bad habits: alcohol, smoking, avoid infection, lead a healthy lifestyle, ensure proper nutrition and rest.
Fetal hydrocephalus during pregnancy is a pathology that can cause serious developmental disorders. Intrauterine cephalocentesis can reduce the likelihood of macrocrania, a pathological increase in the diameter of the skull and irreversible changes in the structure of brain tissue.
Intrapartum treatment makes it possible to prolong pregnancy and carry out successful endoscopic minimally invasive intervention after the birth of the child. Hydrocephalus in the fetus is hydrocephalus of the brain. Contents 1 Features of the disease 2 Classification 3 Causes of the pathology 4 Diagnosis 5 Treatment methods 6 Prognosis and prevention. Views: Share with friends:.
Hydrocephalus is the accumulation of fluid from the spinal cord into the brain, including into its ventricles.
Possible treatment
When the causes and consequences of non-immune hydrops fetalis are identified, a decision is made on possible treatment. This takes into account the severity and degree of development of the disease. An umbilical cord blood transfusion may be indicated. This procedure is recommended when the hematocrit decreases below 30 g/l. After 2–3 weeks, the procedure is repeated if necessary. Transfusion is also indicated for severe anemia.
Before the baby is born, the delivery room is carefully prepared, equipped with all the necessary equipment for emergency resuscitation. A team of several neonatologists and resuscitators is being formed.
Immediately after birth, the following procedures are carried out:
- pericardiocentesis, in which accumulated fluid is removed by puncture of the pericardial sac;
- pleural puncture – liquid contents are removed from the pleural cavity;
- laparocentesis - removal of liquid contents from the abdominal cavity.
These therapeutic measures are carried out under ultrasound control.
The following therapy is prescribed as necessary:
- antibacterial;
- anticonvulsant;
- antihemorrhagic;
- metabolic and others.
It should be remembered that only well-organized and coordinated work of the medical staff when providing first aid to a newborn can be crowned with great success. During pregnancy, the woman and child should be under close medical supervision.
Resuscitation in the postpartum period

Intensive care should begin in the delivery room and includes the following actions by neonatologists and resuscitators:
- it is necessary to prepare fresh frozen plasma and red blood cells in advance;
- due to possible swelling of the airways, it is necessary to have ETTs of all sizes in the delivery room, since the breathing method using a mask and bag is ineffective in this case;
- it is necessary to prepare drainages that may be needed to carry out various procedures and remove excess fluid;
- you need to be prepared for an urgent blood transfusion;
- calcium and glucose correction is required;
- a catheter is inserted into the child's umbilical artery;
- They are treated with antibiotics, and, if necessary, treatment for concomitant infectious diseases is performed.
Everything you need to know about hydrocephalus on fetal ultrasound
Consultation with a neurologist, Dr. Consultation with Professor Boyko A. Appointment, consultation with a neurologist, a specialist in cognitive impairment. Initial consultation with a physical therapy doctor. Consultation with a physical therapy doctor, repeated. Consultation with a physical therapy doctor, primary consultation with a physiotherapist.
Repeated consultation with a physiotherapist. Initial consultation with a speech pathologist, including an initial speech therapy examination and the development of a rehabilitation training program. Admission testing, consultation with a psychologist, initial. Appointment testing, consultation with a psychologist, repeated.
Consultation with a neurologist on prescribed prescription drugs, 20 min. Repeated consultation with a psychotherapist. Individual lesson with a neuropsychologist-neurodefectologist as part of a comprehensive program. Advanced neuropsychological testing. Neuropsychological testing. Group clinical and psychological counseling up to 30 minutes. Family clinical and psychological counseling up to 30 minutes.
A comprehensive speech therapist session using hardware techniques. Group lesson with a speech therapist. Individual psychological correction up to 30 min. Correctional session with a speech pathologist-speech therapist on an outpatient basis. Individual lesson on psychological social adaptation.
Individual psychological correction. Cognitive training session up to 30 minutes. Cognitive training session up to 60 minutes. Individual lesson on restoration of speech functions. Correctional lesson with a speech therapist-defectologist 30 min. Speech therapy examination. Lymphatic drainage manual massage. Acupuncture cupping massage. Therapeutic massage as part of a comprehensive program. Therapeutic massage of one anatomical area for up to 15 minutes. Acupuncture session. Individual kinesiotherapy session as part of a comprehensive program up to 30 minutes.
Robotic mechanotherapy as part of a comprehensive program for up to 30 minutes. Individual lesson on restoring walking function using an exoskeleton. Individual kinesiotherapy session up to 30 minutes. Individual outpatient kinesiotherapy session. Individual lesson on the Exart suspension system, 30 min.
Robotic mechanotherapy, including individual occupational therapy session up to 30 minutes. Individual lesson on a verticalizer with walking simulation for up to 30 minutes. Individual kinesiotherapy session using the Biodex Free Step suspension unloading system. Kinesio taping of one zone with the cost of the tape. Individual patronage post 12 hours. Individual patronage post 24 hours. Personal nursing station.
Daily stay of relatives in a hospital room. The overnight stay of relatives in the hospital room is 12 hours.
Newborn examinations
For non-immune hydrops, various examinations begin to be carried out in the delivery room. These include:
- taking blood from the umbilical cord, which reveals bilirubin, blood group, Rh factor, hematocrit and hemoglobin;
- a biochemical blood test is performed to detect urea, creatinine, total protein, ALT and AST;
- blood test to determine glucose levels;
- infection testing;
- plain radiography;
- analyzes of ascitic and pleural fluid, for example, bacterial culture;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and brain;
- additional tests to identify the cause of the disease.
Consequences
With non-immune fetal hydrops, the consequences for the child in the future can be quite serious. Even when diagnosing pathology at an early stage of its development, there is a risk of complications, among which the most common are the following:
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- severe pathologies of the brain and cardiovascular system;
- pathology of the skin;
- cardiovascular failure;
- cryptorchidism in boys;
- death.
Possible complications
Complications of hydrocele depend on the severity of the disease. If the size of the lateral ventricles does not exceed 15 mm, the prognosis is favorable in most cases. In the future, the child often does not have any abnormalities diagnosed.
In severe forms of hydrocephalus, the consequences for the newborn can be disastrous. Complications of cerebral hydrocele include the following pathologies:
- cleft lip;
- Down syndrome;
- atrophic changes in the brain area.
As the size of the head increases, the fetus takes on an incorrect position in the uterus. When the moment of birth arrives, the child presses his legs to the throat, which provokes the development of complications.
In severe cases of pathology, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy. The possibility of having a healthy child is extremely low. A high mortality rate has been recorded for children diagnosed with hydrocephalus in the first year of life.
Prevention
Non-immune dropsy is dangerous because the exact cause of its occurrence is very rarely possible to establish. Preventive measures in this case consist of generally accepted recommendations during pregnancy. These include:
- pregnancy planning, during which the couple undergoes a comprehensive examination to identify and treat chronic, gynecological and hereditary diseases;
- timely registration with the antenatal clinic;
- systematic visits to the obstetrician-gynecologist and compliance with all his recommendations;
- identification and full treatment of infectious, viral and somatic diseases of women during pregnancy;
- a complete and timely examination prescribed during the period of pregnancy.
It is not recommended to neglect routine screenings and ultrasound, because it is with these examinations that developing pathology can be identified.
Diagnostics
During an ultrasound of fetal hydrocephalus, the head of the unborn baby is measured in a transverse position. The main manifestations of pathology during scanning include the width of the lateral ventricles. Normally, this figure should be no more than 10 millimeters.
Diagnostic measures are carried out starting from the 17th week of gestation. Repeated scanning is carried out at 20-22 weeks. Often the disease is detected at 26 weeks.
Another informative way to diagnose edema in the fetus is echography.
Forecast

With non-immune fetal hydrops, the prognosis in most cases is, unfortunately, unfavorable. The number of surviving children is about 30%. Survival depends on how timely the diagnosis of the pathology was, as well as the presence of pathologies accompanying this condition. For example, with heart pathologies, the prognosis will be more disappointing. The degree of influence of infectious diseases on the occurrence of dropsy depends on the duration of pregnancy. The later this condition develops, the more favorable the baby’s prognosis.
With the development of non-immune hydrops in the first half of pregnancy, there is a high risk of spontaneous abortion. At later stages, intrauterine fetal death may occur.
The prognosis will be favorable if the disease is diagnosed at an early stage of its development, and congenital pathologies of the heart and other vital organs have not been identified. Also of great importance is the ability to identify and subsequently eliminate the provoking factor.
Consequences for mother and baby
A reduced level of protein in the blood is detected. Childbirth is difficult due to the abnormal position of the fetus, and this is caused by the increased size of its head.
If an increased accumulation of tansudate is detected in a child in utero, the mother is offered to terminate the pregnancy.
The highest mortality rate for children with this disease is the first 3 months after birth.
When a newborn develops water in the head and the prescribed treatment is ineffective, the following complications are observed:
- gray matter atrophy;
- the appearance of a “cleft lip”;
- Down syndrome;
- decreased level of concentration;
- development of autism;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- memory disorder;
- speech problems;
- visual impairment, up to the formation of blindness.
This causes problems with adaptation, communication, and subsequent education in kindergarten and school.
Life expectancy with hydrocephalus depends on early diagnosis and timely treatment.
Causes
The main cause of the development of immune fetal hydrops is hemolytic disease.
The reason that led to the development of non-immune hydrops fetalis often remains unrecognized, but the following factors are identified:
- chromosomal pathology of the fetus (Down syndrome, mosaicism, trisomy, Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome and others);
- gene diseases: deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, A-thalassemia, Noonan syndrome, achondrogenesis, thanatophoric dwarfism, Pen-Shockey syndrome, multiple pterygium syndrome, achondroplasia;
- malformations of the chest cavity (thoracic dysplasia, diaphragmatic hernia, cystic adenomatous lung defect);
- malformations of the urinary system (congenital nephrotic syndrome, urethral and kidney defects);
- cardiovascular pathology (cardiomyopathy, congenital heart defects, anatomical defects, arterial-venous shunts)
- chorioangioma of the placenta;
- in case of multiple pregnancy (feto-fetal transfusion, acardial twins);
- infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy (cytomegalovirus infection, syphilis, parvovirus infection, toxoplasmosis, Coxsackie viral pancarditis);
- pregnancy complications (preeclampsia, severe anemia, uncorrected diabetes mellitus, hypoproteinemia);
- congenital metabolic disorders (mucopolysaccharidosis type 4, Gaucher disease, neuraminidase deficiency, Morquio disease);
- congenital tumors of the brain and spinal cord, urinary system and digestive tract, liver, sacrococcygeal teratoma, neuroblastoma.
Treatment of hydrops fetalis
If congenital malformations of the fetus are detected that are incompatible with life (1-2 trimester of pregnancy), the woman is offered termination of pregnancy. If termination is refused, the course of pregnancy and the development of the disease continue to be monitored until the time period allows for prenatal (prenatal) therapy.
Treatment of fetal hydrops consists of cordocentesis and blood transfusion into the umbilical cord (in case of severe anemia and a decrease in hematocrit to 30 or below). If necessary, replacement blood transfusion is repeated after 2-3 weeks.
If feto-fetal transfusion of twins is detected, laser coagulation of the vessels connecting the fetuses is performed. If it is not possible to carry out prenatal treatment, the degree of risk of premature birth in relation to antenatal fetal death is assessed and delivery is carried out ahead of schedule with the preliminary prescription of drugs to accelerate the maturation of the fetal lungs. In some cases, maternal administration of cardiac glycosides is indicated to normalize fetal cardiac activity.
Before delivery (it usually occurs as planned), preparations are made for the birth of a child with dropsy. The delivery room must be equipped with equipment for cardiopulmonary resuscitation; a resuscitation team of 2-3 resuscitators and 2-3 neonatologists is formed (after the birth of the child, the child is immediately intubated and artificial ventilation is carried out with 100% oxygen).
Immediately after birth and resuscitation measures, pericardiocentesis (removal of accumulated fluid by puncture of the pericardial sac), pleural puncture (removal of fluid from the pleural cavity) and laparocentesis (suction of fluid from the abdominal cavity) are performed. A catheter is inserted into the umbilical artery for subsequent infusions of red blood cells or blood.
Is it possible to cure the disease and treatment?
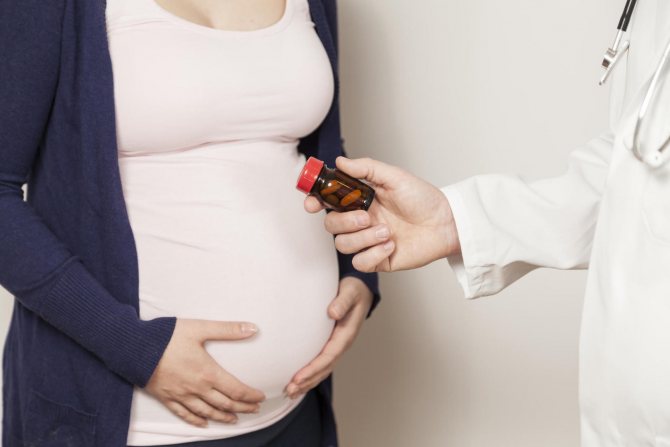

Drug therapy is prescribed for compensated types of pathology. Effective medications for improving the condition of a baby with hydrocephalus are presented in the table.
| Name of the drug | Description | Mode of application |
| Diakarb | The product has diuretic properties, removes excess fluid from the body, and releases potassium. | Used to treat children from 4 months of age at a dose of 50 mg twice a day. |
| Furosemide | Powerful diuretic. Thanks to this property, it is possible to reduce intracranial pressure and normalize the general condition of the patient. | Prescribed from 1 to 3 mg. The dosage is calculated individually based on the body weight of the newborn. In the form of injections from 1 to 1.5 mg per kilogram of body. |
| Mannitol | Diuretic drug. The action of which is to increase the osmotic pressure in the renal tubules. | The product is available in powder form. Before use, it is dissolved in sterile water and administered intravenously |
The information provided in the table is for informational purposes only, so you should consult your doctor before using medications.
Surgical methods of treatment in children
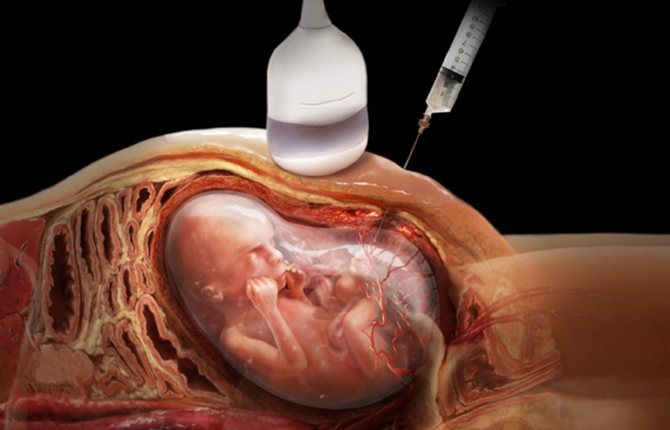
Thanks to a puncture of the anterior abdominal wall of the expectant mother's abdomen, doctors remove fluid from the peri-cerebral space. The procedure is done once. Another effective way to pump fluid out of a baby’s head before birth is bypass surgery. The entire system will remain inside the baby's head until the moment of birth.
Neuroendoscopic operations
A new effective, but at the same time expensive method of surgical treatment of internal hydrocephalus of the fetus. The duration of the operation is no more than 20 minutes.
A special medical device, a neuroendoscope with a built-in small camera, shows the place where the catheter is inserted. It is necessary to quickly remove accumulated cerebrospinal fluid. The doctor makes an additional hole to effectively remove transudate from the enlarged areas of the ventricles of the brain.
Bypass operations
The most effective way to treat true hydrops, but it is carried out only after birth. During the operation, shunts - silicone tubes - are inserted.
They drain excess fluid from the ventricles of the brain into the abdominal region. A special valve regulates the flow volume. The ICP stabilizes and the cerebrospinal fluid does not flow back into the brain cavity.
Several similar procedures are performed throughout the child's life. The tubes can become clogged and break, which leads to mechanical damage and disruption of their operation. Planned surgical interventions are prescribed due to age-related changes in the baby’s body.
Forecasts
The prognosis for non-immune fetal hydrops is unfavorable and the percentage of surviving children is 20-33%. When dropsy develops in the first trimester, pregnancy usually ends in spontaneous abortion; in the second and third trimesters, the risk of antenatal fetal death is high.
With immune dropsy, the prognosis is more comforting; the effect of prenatal and postnatal treatment reaches 80-90%.
Some studies during pregnancy
Important! All materials are for reference purposes only and are in no way an alternative to face-to-face consultation with a specialist.
This site uses cookies to identify site visitors: Google analytics, Yandex metrics, Google Adsense. If this is unacceptable to you, please open this page in anonymous mode.
4 months have passed since such a terrible diagnosis (there was a purge for 12 weeks, the reason is not known). I really want a second child (I have a healthy daughter) and I am very afraid that the situation will not repeat itself, I cannot stand the mental pain that does not go away. I would like to hear advice on how to prepare for a healthy pregnancy. I took tests for infections, everything is fine, and I also want to take Torch.
Symptoms
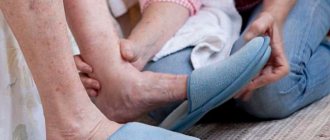
The main symptom of dropsy is swelling. In the initial stages, they appear towards the end of the day. In advanced forms, swelling does not disappear at all.
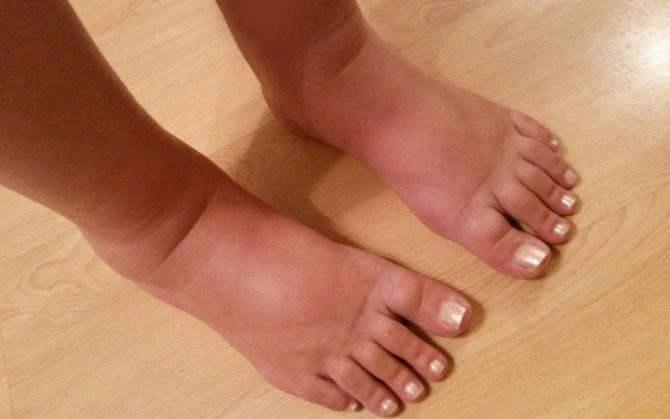

Swelling in the legs during pregnancy
A typical sign that allows one to identify hidden and obvious edema is pathologically rapid weight gain.
During a normal pregnancy, a woman gains no more than 400 grams per week. If the gain reaches 1.5-2 kg, this is a clear sign of dropsy.
Due to improper distribution of fluid, a pregnant woman constantly feels thirsty, which forces her to drink even more water - a vicious circle is formed. As the fluid moves into the tissues, the frequency of urination decreases. The volume of urine excreted also decreases.
The skin of women with dropsy is pale and has a glossy shine - this is due to its stretching due to the accumulation of fluid. When listening to the heart, an increased heart rate is detected. Blood pressure increases.