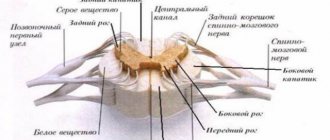
Central paresis
In this disease, spasticity develops due to a reduction in inhibitory effects (IT) on spinal neurons (their type: motor- and inter). As a result, the number of impulses reaching alpha motor neurons increases. This is a response to muscle stretching.
A decrease in TV is a consequence of cumulative defects in the pyramidal canals inside the brain (both spinal and cerebral). Most often, muscle spasticity develops due to damage to the cortico-reticular-spinal tract.
If the brain is affected, the TV is also weakened, but this is most reflected in the gamma motor neurons. They set the movement of the anti-gravity muscles. As a result, characteristic post-stroke spastic hemiparesis appears:
- The shoulder and hip are adducted.
- Elbow and wrist joints bend
- The knee extends.
When spinal spasticity develops, TVs to interneurons located in the area decrease. Because of this, excitations spread along nerve fibers to other levels, and pathological symptoms appear.
Outwardly, this most often manifests itself in convulsions and uncontrolled movements.
To put it differently, when muscle spasticity occurs in cerebral palsy, energy accumulates in them, and communication with the brain is disrupted or absent. They misunderstand his commands and contract chaotically at any time. This is how the accumulated energy is spent.
If central paresis cannot be cured for a long time, for example, more than six months, then the segmental apparatus of the spinal cord changes structurally. This manifests itself in disruption of connections between nerve fibers and the functioning of paretic muscles, tendons and joints. Because of this, there is an increase in movement disorders and resistance that forms in the muscle when it is stretched. Doctors must take this into account when analyzing muscle tone in paretic or paralyzed arms and legs.
Spasticity treatment
Treatment methods for spasticity can be different, some of them can be distinguished:
- Physiotherapy is used to stretch muscle groups and maintain joint mobility, while reducing the risk of injury. When muscle mobility is low, physiotherapy can be used as a means of gradually and smoothly stretching them. In some cases, it may be advisable to undergo minor surgery to increase the length of the ligament by making an incision in the leg;
- Drug therapy is used in cases where it is necessary to take medications to relieve increased tension in the leg muscles. The mechanism of action may be different; some drugs affect the spinal cord, others affect brain receptors;
- Botulinum toxin is a remedy that provides the appropriate effect when used when it is necessary to relax a spastic muscle for a short time. Ethanol or phenol can be considered an alternative, despite the fact that these drugs are suitable for short-term innervation of large and strong muscles, which may cause pain in certain nerves.
Exercise for spasticity
Spasticity manifests itself as a violation of motor activity, manifested in partial or complete immobility, increased muscle tone, as well as involuntary movements. There are certain exercises that can reduce spasticity, restore motor activity and eliminate synkinesis in paralyzed limbs.
Performing exercises requires a certain synchronicity, and both affected limbs participate in them, moving in the same direction at different or the same speed. You can do the exercises yourself, or you can use someone else’s help. Execution involves an average and slow pace, the number of repetitions is limited to four. You can rest by placing your arm or leg in a position that relaxes the muscles most effectively.
Massage for spasticity
For spasticity, the following massage methods can be used. The arms are joined on the chest, the legs are pulled towards the abdominal area, the body bends slightly and in this position you can carry out free light rocking, which ensures a decrease in muscle tone after a certain time. The time during which a decrease in muscle tone occurs should be used to provide high-quality stimulation for the restoration of certain motor functions that were impaired as a result of muscle spasm. When muscle tone increases, it is recommended to repeat the described massage method. This technique is most effective when applied to children aged from one month to seven years.
You can use a form of massage that normalizes muscle tone using a ball. To do this, you need to lie on the ball with your chest and stomach, then make a series of movements in different planes, then change the position of your body and lie on your back on the ball, subsequently repeating the entire listed set of movements. Depending on the muscle tone at the time of the exercise, the duration of the exercise should be determined. On average, this type of massage takes no more than fifteen minutes a day.
Folk remedies
For spasticity of the lower extremities, the following traditional medicine is recommended for use. It is necessary to sew bags according to the shape of the legs and the area of the torso up to the lumbar spine, which are subsequently filled with birch leaves torn from the tree. Immediately before going to bed, the patient should be placed with his feet in these bags and kept in them for some time, while ensuring that the leaves fit the person’s body in a dense layer on all sides as tightly as possible. This is necessary to create the necessary temperature environment in the bags so that the person sweats well. At the same time, your feet sweat just as profusely as they would when using a steam bath. It is recommended to stay in this position all night. In some cases, it may be advisable to replace the leaves around midnight if they become very wet. After completing several such sessions, spastic manifestations in the lower extremities will cease to bother you.
Spasticity level
Different scales are used to analyze it. The most common is the Ashworth product. The scoring system for muscle tone here is as follows:
- 1 – it is slightly elevated, the condition quickly improves;
- 1a – slight excess, muscles tense in less than 50% of the total number of passive movements;
- 2 – moderate development during 100% range of movements (passive actions are easily implemented);
- 3 – significant growth (movements are problematic);
- 4 – the paretic part of the limb does not straighten or bend completely.
Treatment measures
The main goal in the treatment of muscle spasticity is to improve the potential and function of the affected limbs.
Doctors decide how increased tone affects the patient's functional abilities. In people suffering from central paresis, the limbs are less active when compared with patients with 1-2 points on the designated scale.
Some patients with high levels of leg muscle spasticity walk and stand more easily. And when its degree decreases, they move much worse.
Before starting therapy, doctors identify a treatment plan in a particular case (improving movement, reducing negative spasms, etc.) and coordinate it with patients or their relatives.
The specifics of treatment are largely determined by the period from the moment of illness and the level of paresis. The shorter the time since the onset of the disease, the greater the chances of effective therapy.
To achieve a positive result, the following methods are used:
- Physiotherapeutic.
- Pharmacological.
- Surgical.
Cerebral palsy - briefly about the essence
Cerebral palsy (abbreviated as cerebral palsy) is an extensive symptom complex that combines motor, neurological, and brain disorders and occurs in the perinatal period (from any period of gestation to 4 weeks of the baby’s life). The degree of impairment varies greatly and depends on the strength and duration of exposure to traumatic factors. The development mechanism is caused primarily by hypoxia, the death of neurons in certain areas of the brain. The disease often affects intellectual, physical and motor development, leads to mental disorders, pathologies of the organs of vision and hearing. Patients with cerebral palsy need lifelong rehabilitation, constant medication, sometimes surgical treatment, and physical therapy.
According to statistics, cerebral palsy accounts for 1.5-1.7% of cases per 1 thousand children born under 12 months; the risk increases with extreme prematurity of the baby. According to WHO, more than 50% of cases of cerebral palsy develop as a result of pathological and premature births, violations of obstetric care tactics in women in labor, and severe cerebral hypoxia.
REFERENCE . Cerebral palsy in children occupies a special place in pediatrics and child neurology, since every year the rate of those born with a neurological symptom complex only increases. This is due not only to general factors (ecology, lifestyle, pregnancy pathologies), but also to advances in neonatology, which make it possible to care for babies from 450-500 g and maintain their viability.
Physiotherapy
Its main task is to train movements in problematic limbs and prevent complications.
During the course of this therapy, patients are taught to sit, stand and walk. For this purpose additional means are used.
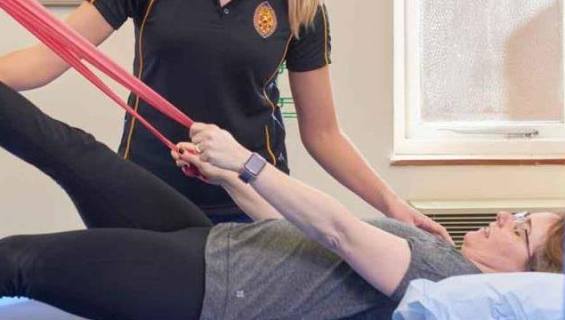
Patients’ limbs are also bandaged, orthopedic equipment is used, and spastic muscles are exposed to thermal radiation.
To effectively relieve muscle spasticity, specialists perform electrical stimulation of problem areas.
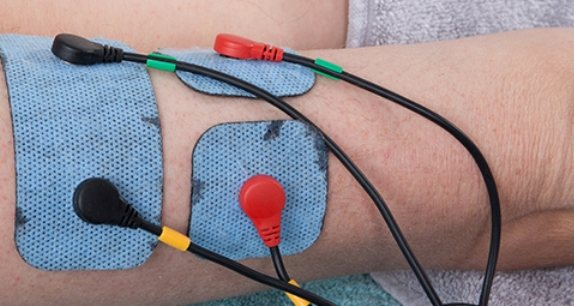
As a rule, these are extensors of the fingers or the anterior tibialis muscle.
Diagnostic measures
During the diagnostic process, the specialist first of all studies the medical history, as well as what medications the patient is taking and whether any of the patient’s close relatives suffer from neurological disorders.
Spasticity is diagnosed using tests, the essence of which is to assess limb movements and muscle activity during active and passive movements.
When examining the patient, the specialist determines whether there is resistance to the limbs during passive flexion and extension. If resistance is present, this is a sign of spasticity, and increased ease of movement may be a sign of paresis.
Pharmacology
Here central muscle relaxants have the greatest effect. Patients take them orally. These drugs have the following advantages:
- reduce muscle tone;
- improve motor potential;
- relieve painful spasms;
- enhance the effect of therapeutic exercises;
- facilitate the care of paralyzed patients;
- prevent the appearance of contractures.
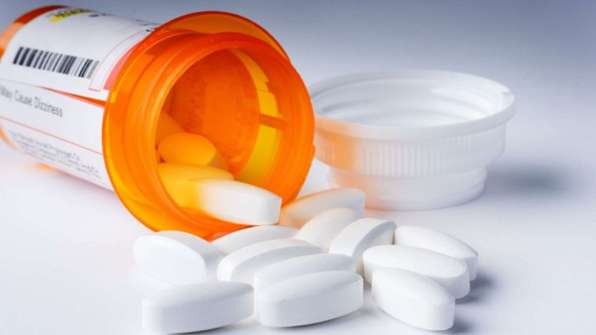
If muscle spasticity is mild, muscle relaxants have a rapid positive effect. For complicated diseases, they are used in large doses. This is fraught with negative side effects.
Treatment with these drugs begins with a minimum dosage. It gradually evolves to achieve the required task.
Combinations of drugs against this disease are not allowed.
In Russia, the following tablets for muscle spasticity are also most often used:
- "Sirdalud". Suppresses polysynaptic reflexes in the spinal cord and has a moderate central analgesic effect. Particularly effective in the treatment of cerebral and spinal muscle spasticity. The minimum daily dose is 3 times 6 mg, the average is 12-24 mg, the maximum is 36 mg. Side effects: drowsiness, slight drop in blood pressure.
- "Baclofen." Mainly used to treat spinal spasticity. It effectively suppresses the generation of tonic amino acids and has a central analgesic effect. Minimum daily dosage: 15 mg x 3. Gradually it increases daily by 5 mg. Maximum – 60-75 mg. Side effects: nausea, constipation, diarrhea, hypertension. Therefore, the drug should be used with caution in older people.
- "Tolperisone". Powerfully suppresses spinal reflex activity, has a mild vasodilator and central analgesic effect. Reduces spasms. It is used in the fight against two types of spasticity: spinal and cerebral. The initial dose per day is 150 mg. It develops systematically up to 300-450 mg. Side effects: drowsiness, muscle weakness, arterial hypotension.
Massage techniques and techniques
The choice of massage technique, duration and intensity of the course, as well as the number of sessions per week is determined only by the attending physician. The doctor also selects a complex of several types of treatment procedures, which must be followed.
Relaxing and stimulating techniques
Massage procedures should be started immediately after the diagnosis is confirmed. Children with cerebral palsy are deprived of the ability to move normally, so sessions are aimed at strengthening weak and relaxing tense muscles.
Basic relaxation techniques include:
- all types of stroking;
- wallow;
- light pops and labile vibrations.
To stimulate muscle activity, use:
- deep stroking;
- rubbing with weights;
- kneading;
- sawing carried out with the edge of the palm.
If segmental massage is performed, then techniques are used to work the deep paravertebral muscles of the back.
Classical technique
The purpose of classical massage for cerebral palsy is to normalize muscle tone and improve the physical and psychological condition of the child. The procedure is carried out using classical massage techniques - stroking, kneading, rubbing and shaking, vibrating pats, and all movements should be smooth and not cause pain.
The session begins with massaging the neck, back, buttocks and thighs. The child is first placed on his stomach so that he is comfortable. Particular attention is paid to the subscapular region, because this area is weakened due to spasm of the pectoralis major muscle. After working on the back of the legs, the baby is turned onto his back. Work continues with the front surface of the legs, stomach, chest and arms.
In the presence of diplegia, a deeper impact on the joints is used. On the first day, only the back and legs are worked, the second session includes additional work on the stomach, chest and arms.
The classic technique for babies is used from the first months of life without any massage creams or oils. Cosmetics are allowed to be used only from 3-4 months. The course includes up to 20 procedures, each lasting about 60 minutes. After working, the baby is given 10-15 minutes to rest.
Speech therapy technique
You can perform speech therapy exercises and massages at home. The session begins with stroking from the central point of the forehead to the temples. Then the technique is performed above the eyebrows and from the bridge of the nose along the wings of the nose to the nostrils. Lightly rub along the chin and the area above the ears, and then stroke again from the corners of the mouth to the earlobes. Each technique is repeated 4 times, and massaging can be done up to 5 times a day.
For speech impairment
Speech therapy massage for cerebral palsy with speech impairment helps not only to relax the muscles, but also stimulates metabolic processes in tissues, increases the mobility of muscle fibers, and improves their conductivity.
Begin the session by pressing on the junction of the upper and lower jaws. Then they apply on the nasolabial fold, cheekbones and chin muscles.

Exercises with a toothbrush can be performed up to 5 times. First, it is passed along the edge of the tongue, drawing the letter U and Z, and then several circular movements are made. After this, draw the letter V on the surface of the tongue with your finger and brush along the edges again.
For face
Facial massage should be started as early as possible to achieve maximum effect. It is carried out in the following sequence:
- massage the lips with light circular movements for a minute;
- The index fingers are placed at the wings of the nose, and the middle fingers are drawn along the contour of the lips;
- press on the corners of the mouth, then apply light pressure over the lips;
- massage the earlobes;
- lightly stroke the entire face.
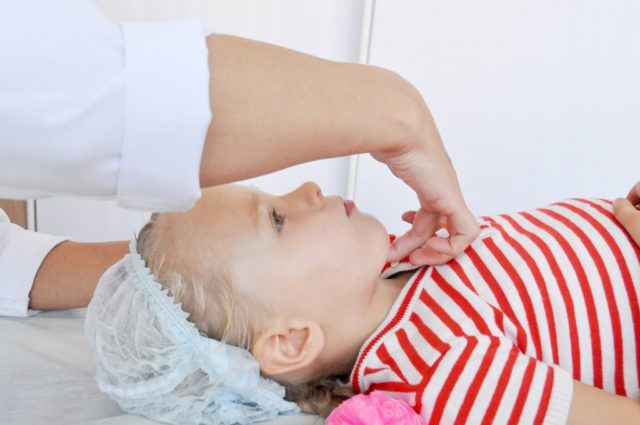

To improve brain function, at the end of the session, stretch your hands. Daily massage stimulates the functioning of the brain hemispheres and internal organs. Both palms and fingers are worked in circular movements with gentle pressure. Up to 10 soft pressures are applied to the fingertips, and a sun is drawn in the center of the palm with the index finger.
Massage to improve breathing
To restore the functioning of the respiratory system during paralysis, children with cerebral palsy are prescribed a special technique, including general massage techniques.
The technique is as follows:
- lightly stroking and kneading the chest, oblique and rectus abdominal muscles;
- Using targeted techniques, massage the ribs and the areas where the diaphragm is attached to them;
- intensive kneading, squeezing and pinching are performed on the trapezius muscle;
- kneading massage the vertebrae of the neck and thoracic region.
The benefits of massage in activating blood circulation: weak muscles do not receive enough oxygen, which leads to the accumulation of under-oxidized metabolic products. Improving the movement of blood and lymph not only saturates cells with essential nutrients, but also helps eliminate toxins. This massage method stimulates the pectoralis major and minor muscles, intercostal and diaphragmatic muscles, which leads to free and complete breathing.
Botulinum toxin class A injection
This is an additional measure when there is increased muscle activity without contracture, but with severe pain and spasms. The drug reduces range of motion and normalizes motor function. It is administered intramuscularly.
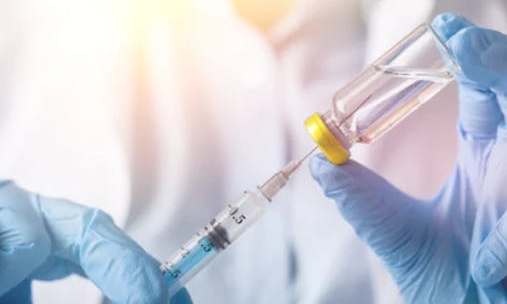
The clinical effect after the injection appears after 2-4 days and lasts for 2-6 months. Then, if necessary, the injection is repeated.
The duration of the effect is determined by the dosage of the drug itself and the complexity of the disease.
As a result of its use, the muscles contract normally. This is explained by this. That the injected toxin destroys proteins. Gradually they are restored, and nerve endings grow, leading to the generation of new synapses.
Side effects of the injection: itching and pain at the injection site, significant muscle weakness.
Living with a disease
Spasticity of the upper extremities interferes with the normal functioning of the arms. The severity of this disorder depends on symptoms and health status. The person may need help with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, and eating. Activities such as writing or driving become inaccessible in most cases.
Massage for spastic paralysis (as a result of spinal cord injury, acute cerebrovascular accident)
1. Decreased reflex excitability of muscles in a spastic state.
2. Strengthening paretic muscles.
3. Restoration of impaired motor functions.
4. Prevention of contracture formation.
5. Increase in general psychophysiological tone.
1. Lying on your back, a cushion under the knee joints.
2. Lying on your stomach, a bolster under your ankle joints, a pillow under your stomach.
1. Massage of the anterior surface of the lower limb.
2. Massage the anterior chest on the affected side.
3. Massage of the upper limb.
4. Massage of the back surface of the lower limb.
5. Massage the back area.
Surgical intervention
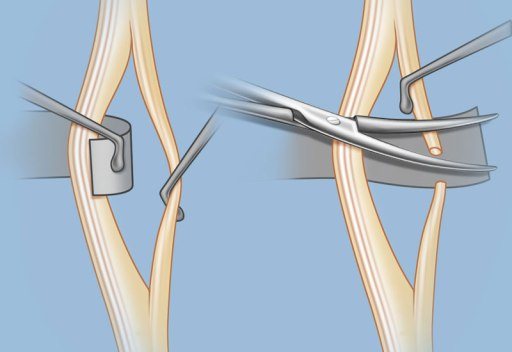
To reduce muscle spasticity, it can occur at any of these levels:
- brain;
- dorsal;
- peripheral nerves;
- muscles.
The brain is operated as follows: electrocoagulation of the globus pallidus or cerebellum is turned on. A stimulator is implanted on the surface of the latter.
These operations are quite complex and dangerous. Therefore they are used extremely rarely.
Treatment of the spinal cord can be arranged as follows: the cone is dissected along the longitudinal line. This breaks the reflex arc separating the posterior and anterior horn of this brain.
The operation is performed only in the most extreme cases and with spasticity of the leg muscles. It requires enormous skill of the surgeon and implies a high risk of serious complications.
To eliminate spasticity, peripheral nerves can be cut. Because of this operation, severe pain and dysesthesia develop. After this, orthopedic procedures are carried out. For this reason, it is practically not used today.
And the most common surgical intervention is carried out as follows: the tendon of the muscle is lengthened, or it moves. This reduces the activity of its intrafusal fibers and, as a result, spasticity.
The effect of this method is difficult to predict. In difficult cases, a series of operations is performed. If contracture develops, this method remains the only treatment measure.
In children
Spasticity in children most often manifests itself after injuries and illnesses. At the first signs of such an illness, you should not waste time and begin treatment as soon as possible. Very often, spasticity in childhood occurs in children with disabilities, with cerebral palsy and various spinal injuries. In such cases, the treatment process is much more complicated. Spasticity in children usually consists of involuntary muscle contractions and spasms. It can appear for no reason. The signals sent by the brain are perceived by the muscles completely incorrectly, which causes their sudden contraction.
The situation after a stroke or head injury
This is where physical therapy comes to the fore. She gets comfortable from the first days of illness and trains lost movements. The patient begins to stand and walk independently.

The most commonly prescribed medication is Sirdalud. The doctor correctly determines and develops its dosage to prevent sedation.
When muscle spasticity occurs during a stroke, motor function can be seriously impaired. In this case, botulinum toxin is injected. Optimal results are achieved if its injections are made in the early period (less than a year) of the disease and a modest level of paresis.
Multiple sclerosis
In patients with this disease, muscle spasticity is often found. The reason for this is damage to the spinal cord.
The greater negative impact occurs on the lower extremities. And about a quarter of patients experience serious problems with motor functions.
To improve the condition, use Sirdulud or Baclofen. Debilitating muscle spasms are relieved with diazepam. Therapy begins with minimal dosages. They gradually increase
Surgical measures for such a diagnosis are used for two purposes:
- reduce spasticity;
- improve the functionality of the pelvic organs.
If the patient suffers from local spasticity in the legs, botulinum toxin is injected into the muscles of the thigh and lower leg.
Complex of reasons
The main cause of spasticity is an imbalance in the signals traveling from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles.
In addition, reasons may be:
- spinal and spinal injuries;
- transferred ;
- accompanied by inflammatory processes in the brain (,);
- (damage associated with lack of oxygen);
- Availability .
Aggravating factors
If a patient has spasticity, the following factors can aggravate the situation:
- constipation and intestinal infection;
- skin infectious diseases that are accompanied by inflammation;
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- clothing that restricts movement.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, these factors can cause the condition to worsen.