Praxis, praxis analyzer, praxis center
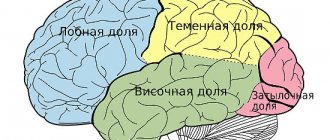
Praxis is the ability to perform purposeful motor acts. Praxis is formed during human life, starting from infancy, and is ensured by a complex functional system of the brain involving the cortical fields of the parietal lobe (inferior parietal lobe) and the frontal lobe, especially the left hemisphere in right-handed people. For normal praxis, the preservation of the kinesthetic and kinetic basis of movements, visual-spatial orientation, programming processes and control of purposeful actions is necessary. The defeat of the praxic system at one level or another is manifested by such a type of pathology as apraxia. The term "praxis" comes from the Greek word "praxis", which means "action". Apraxia is a violation of purposeful action in the absence of muscle paralysis and the preservation of its elementary movements.
Thinking, thinking function
The thinking function is the result of the integrative activity of the entire brain, especially the frontal lobes, which are involved in organizing the purposeful conscious activity of a person, man, woman. Programming, regulation and control take place. Moreover, in right-handed people, the left hemisphere is the basis of predominantly abstract verbal thinking, and the right hemisphere is associated mainly with concrete figurative thinking.
The development of cortical functions begins in the first months of a child’s life and reaches its perfection by the age of 20.
Speech analyzer, Wernicke's center, Broca's center, speech function - sensory center
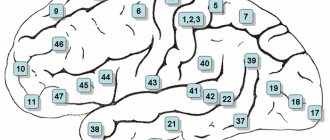
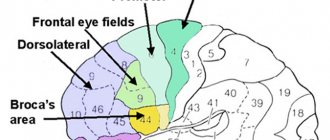
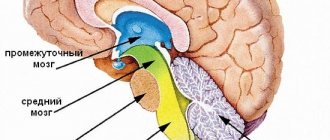
The speech function is provided by the sensory center ( Wernicke's center ), which is located in the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus. When Wernicke's center is damaged, sensory aphasia occurs. The speech function is also provided by the motor center ( Broca's center ), which is located in the posterior parts of the inferior frontal gyrus. When Broca's center is damaged, motor aphasia occurs. With pathology at the junction of the temporal and occipital lobes, amnestic aphasia and semantic aphasia are formed. Speech areas of the cerebral cortex.
Pathophysiology
The traditional theory involves hemodynamic compromise due to repeated episodes of hypotension in the presence of significant arterial stenosis or occlusion.
Some pathological studies highlight the association between border zone infarction and microembolism; In a series of autopsies, embolic material was found in areas of borderline infarctions. The predominant spread of emboli in border zones was also found in experimental studies.
Border zone infarctions can be caused by a combination of two often interrelated processes: hypoperfusion and embolization. Border zones have lower perfusion and thus limited ability to wash out emboli. Severe occlusive disease of the internal carotid artery causes both embolization and decreased perfusion. In addition, cardiac disease is often associated with microembolization from the heart and aorta with periods of decreased systemic and cerebral perfusion. This theory, although it seems reasonable, remains unproven and has been questioned by a number of authors.
Cerebral cortex treatment
Sarclinic uses proprietary methods to restore the functioning of the cerebral cortex. Treatment of the cerebral cortex in Russia in adults, adolescents, children, treatment of the cerebral cortex in Saratov in boys and girls, boys and girls, men and women allows you to restore lost functions. In children, the development of the cerebral cortex and brain centers is activated. In adults and children, atrophy and subatrophy of the cerebral cortex, disruption of the cortex, inhibition in the cortex, excitation in the cortex, damage to the cortex, changes in the cortex, pain in the cortex, vasoconstriction, poor blood supply, irritation and dysfunction of the cortex, organic damage, stroke, detachment are treated , damage, diffuse changes, diffuse irritation, death, underdevelopment, destruction, diseases, perinatal encephalopathy and post-resuscitation encephalopathy, cerebral palsy, minimal cerebral dysfunction, delayed speech development, delayed psychomotor development, FMR, birth trauma. Cells and neurons of the cortex restore their work, structure and function are restored. The structure and activity of the cerebral cortex is restored, polypeptides and their content return to normal, the cortex and subcortex begin to work. In children, age-appropriate maturation of the cerebral cortex occurs. Unfortunately, under certain pathological conditions, death occurs, the death of cells in the cerebral cortex; in this case, it is not possible to restore the functioning of the cortex. On the website sarclinic.ru you can ask a doctor a question online for free. If the cerebral cortex is damaged, then with proper and adequate treatment it is possible to restore its functions.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Text: ® SARCLINIC | Sarclinic.com \ Sarlinic.ru Photo: © MedusArt / Photobank Photogenica / photogenica.ru The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all coincidences are excluded.
Related posts:
Neurologist neuropathologist difference, what is different, what treats what diseases
Agnosia: visual, auditory agnosia, treatment of agnosia
Weber's syndrome HD Weber, alternating peduncular syndrome
Apraxia, treatment of apraxia, treat apraxia in children, adults
I'm afraid to speak, logophobia: treatment of logophobia for stuttering, the child is afraid to speak
Comments ()
Memory, memory function
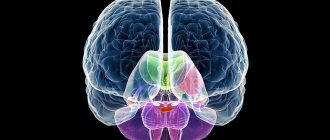
Various areas are involved in the implementation of the memory function. The frontal lobes provide active, purposeful mnestic activity. The posterior gnostic sections of the cortex are associated with particular forms of memory - visual, auditory, tactile-kinesthetic. The speech zones of the cortex carry out the process of encoding incoming information into verbal logical-grammatical systems and verbal systems. The mediobasal regions of the temporal lobe, in particular the hippocampus, translate current impressions into long-term memory. The reticular formation ensures optimal tone of the cortex, charging it with energy.
Function creates the center
According to Ivan Petrovich Pavlov: “Function creates the center!” In early childhood, the boundaries of the cortical centers are diffuse and less differentiated, and only as life experience is gained, a gradual concentration of functional zones occurs, and therefore in children of the first years of life, focal cortical symptoms are weakly expressed and general cerebral symptoms often predominate.
4. Significant differences in the localization of simpler and more complex functions. The simpler the function, the more accurately it is localized. Conversely, the most complex functions are determined by the integrative activity of the entire brain, therefore the concept of “cortical center” (section of the cerebral cortex, fields of the cerebral cortex, areas of the cerebral cortex, parts of the cerebral cortex) is in most cases relative and conditional. Simple cortical functions include sensory function, motor function, visual function, auditory function, vestibular function, olfactory function, and gustatory function. Complex cortical functions include speech, writing, reading, counting, praxis, gnosis, thinking, and memory.