Relatively recently, the actively used English word “ bullying ” appeared in the Russian-speaking space, which means bullying, intimidation of one person by another, or several persons.
A new term is not always a new phenomenon. And in the case of bullying, everything is as old as time. Who hasn't heard of hazing? Everyone has encountered something like this at least once in their life - some as a witness, and others have tried on the role of instigator or victim.
In any case, bullying has always been perceived as just an annoying incident, an unpleasant episode in life, but never as something that needs to be fought.
There will be people who will say that the fact of oppression or bullying that once took place in their lives only strengthened their character and taught them to survive.
Someone even thanks the enemies who once turned his life into hell, because, wanting to get away from bullying, he changed himself and his life for the better: he quit his hated job, found himself, and climbed the career ladder. Oh, if only everything ended so well for victims of bullying!
Experience shows that people who are victims of bullying carry lifelong scars in the form of suicidal thoughts, depression, anxiety and low self-esteem.
School is a very fertile ground for the growth of hateful sentiments. The grading system, the social status of each child, the lack of empathic skills in children and other factors make the atmosphere of goodwill in the classroom very fragile.

Forms and characteristics
The peculiarity of bullying is that negative influence from the aggressor is regularly exerted. These could be attacks from a group of children (not necessarily classmates) or from one child. Bullying occurs from a group of teachers or from one teacher.
Bullying can occur in elementary school, among teenagers, and in high school. This doesn't change the essence. Only the intensity of the manifestation differs. It is directly proportional to the strength and capabilities of the aggressors.
There are 6 types of bullying:
- Verbal . These are insults, intimidation, threats. Signs: the child becomes withdrawn, is capricious a lot, and changes in appetite are noticeable. Sometimes children directly ask their parents about what their peers accuse them of. For example, if a child is called fat, he may ask the following questions: “Mom, am I really fat?”, “Mom, am I fat?”, “Mom, how can you lose weight?”
- Physical . These are kicks, pushes, trips, blows, grabs, unpleasant touches. Signs: complaints of abdominal pain or headache, general poor health, frequent bruises or other signs of physical impact, dirty or torn clothing.
- Social . This is what we mean when we talk about outcasts in the classroom. With this type of bullying, the aggressors do not want to be on the same team as the victim, sit at the same desk with her, communicate or engage in other activities. Signs: abnormal craving for solitude, mood swings, refusal to meet and play with peers, hatred of group work.
- Economic . This is damage to property, extortion, taking money, coercion to steal. Signs: loss or loss of things, theft of money from parents or a sharp and strong desire to find a part-time job, isolation.
- Sexy . These are slaps on the butt, grabbing the breasts or other parts of the body, vulgar hints, direct coercion for intimacy. Sexual bullying usually combines emotional, physical, social, and economic. And sometimes it is associated with another type - cyberbullying. Signs: isolation, change in clothing preferences (craving for closed things), change in appetite.
- Cyberbullying . This is cyberbullying: threats in messages, insults in comments, hacking a page or creating a fake page and spreading bad or dangerous information on behalf of the victim, beating a child and posting entries on the Internet. Signs: the child begins to spend more time on the Internet, after communicating on the Internet he becomes sad or anxious, the child’s interests change or the craving for previous hobbies disappears, problems with sleep are noticeable.
Please note: when it comes to cyberbullying, anyone can become an aggressor. A person of any age, gender and from anywhere in the world. However, more often cyberbullying is combined with other types of bullying and comes from someone in the environment.
Social
What it is? Social threat or exclusionary harassment involves someone being deliberately excluded from participating in a group activity, whether it be lunch, play, sports, or social work.
Example: A group of girls in a dance class are talking about a weekend party and exchanging pictures, while focusing little or no interest on the girl they decided not to invite, pretending she doesn't exist.
Characteristics: Watch for mood swings, avoidance of socializing with peers, and greater than usual desire for solitude. Girls, more than boys, feel social isolation and nonverbal or emotional threat. The mental pain from this type of bullying can be as powerful as that from physiological violence, and last much longer.
What should I do? Use the evening time to talk with your child about his day. Help him find positive moments in absolutely everything, focus on his good qualities and make sure he understands that there are people who love him very much and are ready to help him in everything. Focus on building your child's abilities and interests in music, art, sports, reading, and extracurricular activities so that he or she has the opportunity to build relationships outside of school.

Danger and consequences

The dangerous consequences of bullying include:
- low self-esteem, complexes and self-doubt;
- depressive and suicidal tendencies;
- neuroses and other mental illnesses.
Bullying is chronic stress. It disables all body systems, undermines physical and mental health, and leads to emotional exhaustion. Because of bullying, a child considers himself unworthy, defective, and superfluous. It is difficult for a person with such “baggage” to realize himself in life, get an education after school, find a job, start a family, or make friends.
However, the further development of events depends on the tactics chosen by the child. Stress triggers animal reactions. There are 3 possible responses: flight, retaliatory attack, freezing.
In the first case, the child gets used to being patient, being invisible, and running away. In the second, he himself becomes an aggressor. In the third, he turns into a robot. It’s as if he turns off the emotional sphere, loses the ability to feel.
The choice of strategy depends on a number of factors, for example, on temperament and characteristics of family upbringing. But all 3 scenarios trigger a chain of problems in adult life.
Who, why and for what can bully a child?

When schoolchildren bully another child, it is about their weakness. This is how they try to divert attention from their problems and shortcomings and gain authority in the class. And some take it out on a weaker child, taking revenge on their parents for regular humiliation and beatings. In this case, bullying brings relief to the aggressor.
What can cause child bullying? Anything:
- external, mental or physiological characteristics of the child;
- standard of living and family composition;
- interests and preferences in clothing, hobbies;
- behavioral characteristics;
- thirst for knowledge (bullies often punish those who remind the teacher about homework and answer best at the blackboard);
- any funny incident, for example, an unsuccessful public performance.
If we are talking about bullying on the part of teachers, then it is purely a matter of professional incompetence. In order not to lose authority in the eyes of the students, the teacher takes it out on one of the students. For example, he lowers grades for someone who regularly violates discipline. Or, trying to pacify the student, he gets personal.
This is how an incompetent teacher tries to maintain authority. It happens that a teacher initiates or supports bullying of a child by classmates. But this behavior of the teacher has the same reasons.
Why a teacher can bully a child:
- outstanding abilities or, conversely, academic failure, falling behind the school curriculum;
- family dysfunction or, conversely, a high standard of living for the family;
- nationality, clothing, other external or internal characteristics;
- violation of discipline, aggression towards the teacher;
- informal leadership in the classroom.
The intensity and strength of bullying directly reflects the degree of inferiority (weakness) of the one who bullies. Bullying can be caused by envy, revenge, hostility, the struggle for power, the desire to neutralize a competitor, sadistic tendencies, the desire to assert oneself, the desire to be the center of attention.
Who is the most likely victim of bullying?
There is no specific characteristic of a person who can become a victim of bullying.

At risk are:
- Silent, unsociable children, especially if they have no friends. Also not making contact, preferring to spend time alone;
- People who have an unusual appearance, red hair, freckles, or are overweight. Also, children with deviations in terms of speech or behavior, the child may stutter or limp;
- Capable children, superior to everyone in the team in skills and knowledge. Especially if teachers single them out and forgive them a lot. Or, conversely, those who are not interested in their own achievements, but use successful parents as an example;
- Sneaters who report every step of the team to teachers or parents;
- Physically weak, unable to stand up for themselves;
- Children who attract attention with jokes and tomfoolery. They deliberately make a fool of themselves, getting into ridiculous situations, laughing at their shortcomings. They often flirt, which provokes serious attacks from the team;
- Children with modern innovations, from clothes to technology. Or, on the contrary, poorly, poorly dressed;
- Sloppy children who cause hostility in appearance.
Especially if they answer provocative questions too vigorously. Even teachers who make comments about their appearance can have a negative attitude towards them.
Aggressors easily identify people who are unsure of themselves, those whom no one will help. Often introverts, immersed in the world of their own experiences, and sad children become victims of bullying. They do not like themselves, depend on the opinions of those around them, without having their own position, they look scared and anxious.
How to understand that a child is being bullied
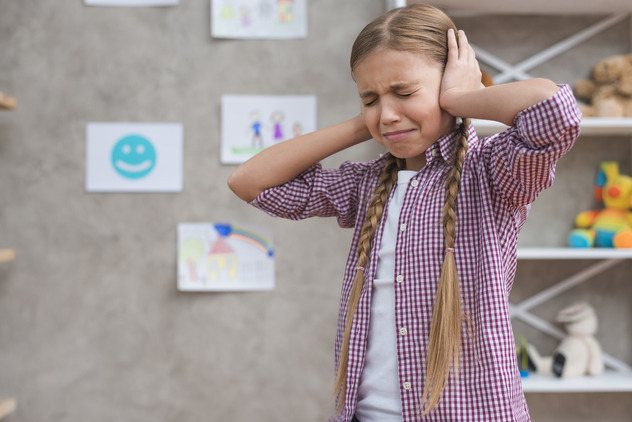

We have already looked at specific signs of bullying for certain types. Now let's talk about the common signs of bullying at school:
- self-isolation, isolation, distance from children and adults;
- stubbornness and negativism when discussing school, relationships with peers, and the topic of bullying as such;
- outbursts of aggression and irritability;
- anxiety and tension that increase in the presence of specific people or in certain conditions;
- mood swings and touchiness or, conversely, excessive restraint;
- reluctance to go to school, coming up with “excuses”;
- lethargic and depressed state;
- frequent colds and complaints of poor health.
The main sign is sudden changes in the child’s behavior, mood, thinking, reactions, and preferences. Children react to bullying in different ways, much depends on the primary characteristics of the individual.
Only together, only with the whole world
Without adult influence, children can only interact as an archetypal pack, united on the basis of dislike for someone else, be it a teacher, another child, or someone else. Preventing and preventing violence in schools cannot occur through a system of prohibitory measures, increased security and an increase in the number of video cameras. These are all external “bells and whistles” that can be easily bypassed if desired.
Violence in school can only be defeated through the joint efforts of all stakeholders: teachers, parents and children themselves.
Not only trying to protect your child from violence, but eliminating the problem of violence in school altogether - this is the task we all need to set. Otherwise, nothing will work! There will be another traumatized sound student who will come to school with a weapon in order to shoot his classmates.
What to do
Let's consider the action plan from two positions: aggressors-students and aggressors-teachers.
Aggressors – students

How to protect your child from bullying at school:
- Contact your teacher. You need to work with the whole class and at the adult level.
- Connect with a school psychologist or contact a private psychologist. Invite him to participate in a meeting of conflicting parties.
- If the teacher doesn't see the problem or brushes it off, then move on. Contact the director. If necessary, go to the administration.
- Involve the parents of the aggressor and the parents of other children. Explain to them that witnesses to bullying also suffer psychological trauma.
- If it comes to beatings, then remove them and write a statement. For any type of bullying, collect as much evidence as possible. For example, save screenshots of correspondence if we are talking about threats on the Internet.
- Teach your child to fight back. It is important to explain that bullying cannot be kept silent. You must always fight back (calmly and decisively), involve teachers and parents. Talk about the consequences of bullying so that the child has no doubts.
- Support your child. No “It’s your own fault,” “Stop provoking them,” “Don’t pay attention.” And under no circumstances make the child appear to be an even greater victim: “What are you Herods doing to him.”
- Don't run away from problems and don't transfer your child to another school.
All adult participants in proceedings must make it clear to children that what they are doing is not fun. It is a crime. Don't ignore the laws, especially when it comes to bullying teenagers.
Criminal penalties are provided for threats, blackmail, extortion, insults and other elements of bullying.
Aggressors are teachers
Journalist and psychologist Olga Zolotkov experienced the problem of bullying a child by a teacher. She managed to resolve the situation, on the basis of which Olga drew up an action plan:
- Ring all the bells. Contact the teacher himself, the head teacher or the school director. If necessary, go to the administration. You can’t do anything worse, your child is already in bad shape.
- Write down every little thing. Collect as much evidence of bullying as possible, then you will not be accused of slander and bias.
- Clearly define what you want to achieve: dismissal of a teacher, change of class teacher, public apology. This will allow you not to be distracted from the essence and not respond to excuses.
- Make appointments. It is best if both parents come to the meeting with the teacher. To resolve the conflict, you can connect a mediator.
- Never, under any circumstances, give in to your emotions. Be a team with your child, don’t let them quarrel. Keep your child informed of events, but spare him from negativity and active proceedings.
- Don't rely on other parents for support, but don't give up on it. Go all the way, make the incident as public as possible. However, remember that you can stop at any time if the teacher finds the strength and wisdom to compromise.
If peaceful ways do not help, there is only one thing left - filing a complaint with the police and the Ministry of Education. It is important to substantiate your claims in detail and with reference to the laws of the Russian Federation. Main assistants: the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Law on Education and the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Contacting Digital Sharks is the right solution to the problem of cyberbullying
When patience is at its limit, moral strength is rapidly running out, and cyberbullies just can’t close up shop and leave your pages, it’s logical to turn to specialists. This:
- will save your nerves;
- will save time;
- will protect you from reading a stream of insults.
If you expected to see a description of a typical solution to the problem, there will not be one: each case is individual, and we work with each separately. Only one thing remains the same: you send a link to the bullying and forget about the problem. We are solving it. Afterwards, we report on successful work and return you to restful sleep.
Get rid of the cyberbully once and for all
How to deal with the consequences of bullying

Children, especially teenagers, prefer to be guided by the opinions of their peers or those who are a little older. They also like to search for information themselves and watch videos on the Internet. So the best option is to provide your child with a list of useful resources. These could be books about bullying, websites and helplines, stories from bloggers or stars about their experiences of overcoming bullying.