The main function of the recurrent laryngeal nerve is the process of innervation of the laryngeal muscles, as well as the vocal cords, along with ensuring their motor activity, and in addition, the sensitivity of the mucous membrane. Damage to nerve endings can cause disruption of the speech apparatus as a whole. Also, due to such damage, the organs of the respiratory system may be damaged.
Laryngeal nerve dysfunction: clinical manifestations and causes of the disease
Often, damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which in medicine is called neuropathic laryngeal paresis, is diagnosed on the left side as a result of the following factors:
- Previous surgical manipulation of the thyroid gland.
- Previous surgical manipulation of the respiratory system.
- Previous surgical manipulation in the area of the great vessels.
- Viral and infectious diseases.
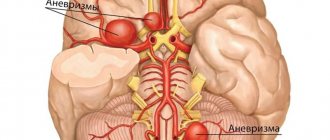
- Vascular aneurysm.
- The presence of oncological tumors of the throat or lungs.
Other causes of paresis of the recurrent laryngeal nerve can also be various mechanical injuries along with lymphadenitis, diffuse goiter, toxic neuritis, diphtheria, tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus. Left-sided lesions are usually explained by the anatomical features of the position of nerve endings, which can be injured due to surgical intervention. Congenital ligament paralysis can be found in children.
Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve: symptoms and treatment
Neuralgia is a lesion of a peripheral nerve. The hallmark of this disease is severe pain.
At the moment, this type of disease has been studied quite well, so making a correct diagnosis is not a problem. There are many types of neuralgia.
In fact, it can hit any area. One of the varieties is neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Description
As the name implies, glossopharyngeal neuralgia affects the nerve of the same name, which is the ninth pair of cranial nerves. This is accompanied by pain in the back of the throat.
The pain radiates to the ear. Most often, the disease attacks men in adulthood. It is easy to confuse this disease with a toothache or think that the problem is in the ear.
Therefore, the patient may first turn to the wrong specialist.
Causes
The main reason why neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve occurs is its coldness. Therefore, this disease is characterized by autumn-spring spread.
The disease can also occur as a complication of other ailments:
- infectious diseases;
- oncology of the larynx;
- inflammation of the membranes of the brain;
- diseases of the nose and ears;
- vascular aneurysms.
Atherosclerosis and damage to the tonsils as a result of injury can lead to this type of neuralgia.
Symptoms
The first signs that characterize neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve resemble short electric discharges. However, the pain is severe. Most often they occur during chewing or swallowing. Pain is also possible when yawning, opening the mouth, or taking a deep breath. As a rule, pain is observed only on one side of the face in the morning.
As the disease develops, the pain radiates to the ear, neck, lower jaw, and soft palate. The patient may experience a bitter taste. Other symptoms characteristic of this disease. – dry throat during an attack and strong salivation after it. The patient may also complain of cough, pain in the throat, Adam's apple and ear, and scratching in the throat.
Due to the large innervation in the mouth, pressure may drop, a collapsing sensation, tinnitus, and dizziness may appear. In severe cases, fainting cannot be ruled out.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease “Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve” is aimed at eliminating or reducing pain. For this purpose, anesthetics are used that are applied to the root of the tongue. This procedure helps relieve pain for up to 7 hours.
If anesthesia does not help, then neuralgia can be treated with novocaine injections. Possible blockade. Along with this method, analgesics in the form of tablets are often prescribed.
Another form of treatment for this type of neuralgia is physical therapy. The procedure is aimed at the nasopharynx, tonsils, and back of the jaw.
An important factor in the treatment of the disease is the general strengthening of the body. Therefore, it is practiced to prescribe multivitamin complexes or aloe extracts.
Folk remedies also help with this disease. For this, willow bark, valerian root, honey, pine branches and cones, black radish, and mint are used. The simplest way is a warming salt compress or a compress made from a mixture of potatoes and horseradish.
If neuralgia is caused by compression, then surgical intervention is possible. During the operation, the nerve is released from pressure on it.
Thus, the treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a complex process. The exact treatment regimen depends on the extent of the lesion and the cause of the disease. Healing may take several years.
Prevention
To avoid a disease such as glossopharyngeal neuralgia, procedures directed against the main factors of its occurrence will help. Therefore, it is important to try to avoid exposure to drafts and not to become overcooled.
To maintain the protective functions of the body, it is necessary to adhere to proper nutrition and do not forget to take vitamins. Moreover, this can be done not only by getting vitamins from food, but also by taking special complexes. This is especially true in the spring, when the body is most weakened and the risk of neuralgia is especially high.
Of course, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle and give up bad habits. This can protect your body not only from neuralgia, but also from many other ailments.
conclusions
Neuralgia can affect almost any human nerve. The disease is characterized primarily by pain in the corresponding area.
For glossopharyngeal neuralgia, this is pain in the throat and ear. When diagnosing the disease, it is advisable to conduct several studies to exclude another type of neuralgia, for example, the pterygopalatine ganglion.
The ear node may also be affected. The symptoms are similar here.
Treatment of the disease involves various techniques and methods. Most often it is a complex of several types of therapy. If there is compression, surgery may be prescribed.
Does your throat hurt badly? Treatment. The most effective remedies for sore throat. Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve. Why does it hurt to swallow? Sore throat and painful to swallow - causes and treatment Facial, glossopharyngeal and trigeminal nerve NEURALGIA OF THE SUPERIOR LARGENY NERVE DIABETIC NEUROPATHY TREATMENT WITH FOLK REMEDIES Elena Malysheva. Symptoms of pharynx cancer NEURALGIA OF THE GLOSPHARYNGEAL NERVE SYMPTOMS NEURALGIA OF THE GLOSPHARYNGEAL NERVE NEURALGIA OF THE GLOSPHARYNGEAL NERVE NEUROLOGY
Source: //medistoriya.ru/nevrologiya/nevralgiya-yazykoglotochnogo-nerva.html
Inflammation of nerve endings
Against the background of pathology of the recurrent laryngeal nerve, the nerve endings become inflamed, which occurs as a result of certain viral and infectious diseases. The cause may be chemical poisoning along with diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis and potassium or calcium deficiency in the body.
Central paresis can also occur due to damage to brain stem cells, which is caused by cancerous tumors. Another reason may be atherosclerotic vascular damage, as well as botulism, neurosyphilis, poliomyelitis, hemorrhage, stroke and severe skull injuries. In the presence of cortical neuropathic paresis, bilateral nerve damage is observed.
During surgical operations in the larynx area, the left recurrent laryngeal nerve can be accidentally damaged by some instrument. Excessive pressure with a napkin during operations, compression of the suture material, and resulting hematomas can also damage the laryngeal nerve. Among other things, a response to anesthetics or disinfectant solutions may occur.

Summary
Neuralgia causes painful symptoms that vary in duration and severity. In addition to pain, neuralgia can cause numbness, muscle weakness and hypersensitivity.
If a person does not receive treatment, neuralgia can interfere with their ability to perform everyday tasks.
Consult with your doctor to determine the best course of treatment for their specific symptoms.
Pharmacodynamics
A medicine is a remedy in the hands of a doctor. Read
Pharmacokinetics
Studies the peculiarities of the drug entering the body.Read
Vitamins
Vitamins have been known to us for more than 100 years. Read
Massage
The term massage came to us from the French language. Read
Symptoms of damage to this nerve
The main symptoms resulting from damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve include the following:
- Difficulties when trying to pronounce sounds, which manifests itself in hoarseness of the voice and a decrease in its timbre.
- The development of dysphagia, in which swallowing food becomes difficult.
- Whistling, and also noisy inhalations of air.
- Complete loss of voice.
- Choking due to bilateral nerve damage.
- Presence of shortness of breath.
- Impaired general mobility of the tongue.
- Loss of sensitivity of the soft palate.
- Sensation of numbness in the epiglottis. In this case, food can enter the larynx.
- Development of tachycardia and high blood pressure.
- With the development of bilateral paresis, noisy breathing may be observed.
- The presence of a cough with the throwing of gastric juice into the larynx area.
- Respiratory disorder.
Symptoms
When the laryngeal nerve is damaged or inflamed, symptoms are often determined by the location of the pathological process. The nature of the clinical picture may change slightly with unilateral and bilateral paralysis. The following general symptoms of damage to the recurrent nerve are distinguished:
- hoarseness and change in voice timbre (the intensity of the symptom gradually increases);
- difficulty breathing when swallowing food (dysphagia);
- noisy, wheezing breathing;
- loss of voice;
- attack of suffocation (typical for bilateral lesions);
- causeless shortness of breath;
- decreased tongue mobility and palate sensitivity;
- a feeling of numbness in the tissues of the epiglottis;
- frequent entry of food into the larynx;
- high blood pressure;
- active heartbeat;
- dry cough, accompanied by the throwing of gastric juice into the mouth;
- breathing disorders of various types.
In case of partial damage to the nerve fiber of the larynx, recovery lasts several weeks (up to six months). During this period, speech and other functions are normalized without outside intervention.
With bilateral damage, the skin becomes pale and the extremities become cold. A few hours after the onset of these symptoms, breathing returns to normal. However, if a person begins to move, these phenomena return. Therefore, for bilateral neuropathy, a tracheotomy is indicated, which involves artificial expansion of the airways.
Features of the condition of patients against the background of damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve
If the recurrent nerve was not cut during surgery, speech can be restored within two weeks. In the case of partial transection of the right recurrent laryngeal nerve, the recovery period usually takes up to six months. Symptoms of numbness of the epiglottis disappear within three days.
Surgery on both lobes of the thyroid gland can lead to bilateral nerve paresis. In this case, paralysis of the vocal cords may form, as a result of which the person will not be able to breathe on his own. In such situations, a tracheostomy, an artificial opening in the neck, may be necessary.
Against the background of bilateral paresis of the recurrent nerve, the patient is constantly in a sitting position, and the skin is pale in color, and the fingers and toes are cold; in addition, the person may experience a feeling of fear. Trying to perform any physical activity only leads to a worsening of the condition. After three days, the vocal cords may take an intermediate position and form a small gap, then breathing returns to normal. But nevertheless, during any movements, the symptoms of hypoxia return.
Cough, along with constant damage to the mucous membranes of the larynx, can lead to the development of inflammatory diseases such as laryngitis, tracheitis and aspiration pneumonia.
Triple pain...
A sharp pain, like an electric shock, takes you by surprise: it “shoots” through your entire face, preventing you from chewing or speaking... Minutes of torment seem like an eternity.
Such attacks are often attributed to migraines, toothache or sinusitis, while the cause lies in the nervous system. The nervous system controls and controls all functions of our body. But sometimes it fails, and then it itself becomes the cause of problems. Neuralgia is one of these problems, both for the central and peripheral nervous systems.
With the first guest of this week’s traditional “Evenings” section “Health” - the head of the neurological department of the Regional Clinical Hospital, a neurologist of the highest category, Lyubov Mikheeva, we talked about trigeminal neuralgia.
A little theory
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth of 12 pairs of cranial nerves. It is located on a person’s face and is responsible for his sensitivity. It got its name because of its shape: three branches extend from the nerve bundle. The superior is the orbital nerve, responsible for the sensitivity of the eye, upper eyelid and forehead.
The middle nerve is the maxillary nerve, which provides sensation to the lower eyelid, cheek, nostrils, upper lip and upper gum. The lower branch is the mandibular nerve. His area of responsibility is the sensitivity of the lower jaw, lower lip, gums and some masticatory muscles.
Together, these three branches provide sensitivity to the tissues of the entire face, most of the soft tissues of the cranial vault, tissues and mucous membranes of the nose and mouth, teeth, as well as parts of the dura mater. Pathologies of the trigeminal nerve disrupt the functioning of the corresponding sensory or motor systems.
Neuralgia can affect one of the branches or the nerve bundle itself. In this case, the pain symptoms will be so different that the person will begin to seek relief from different specialists - a dentist, an ophthalmologist or an ENT specialist...
“Attacks of pain can be spontaneous or provoked by external stimuli,” says Lyubov Mikheeva. – Spontaneous attacks of pain in the depths of the ear and external auditory canal are characteristic of neuralgia of the tympanic nerve. In the area of the eye orbit - with inflammation of the nerve bundle.
With neuralgia of the trigeminal, glossopharyngeal and superior laryngeal nerves, attacks can be spontaneous or they can be provoked by the most common actions - chewing, swallowing, talking.
For pain in the face, it is important to determine whether this complaint is the only one, or whether there are others, in particular the combination of facial pain with pain of another localization.
Roots of the problem
Pain due to trigeminal neuralgia can also be provoked by: touching the skin of the face or head, washing, shaving, brushing teeth, hitting the nose, blowing wind, applying makeup, smiling... But what provokes the development of neuralgia itself?
– Currently, the generally accepted point of view is that the decisive role in the origin of trigeminal neuralgia is compression of the root of the fifth nerve at the point of its entry into the so-called medullary pons (part of the hindbrain - Ed.)
, explains Lyubov Mikheeva.
– The nerve may be compressing an abnormally tortuous blood vessel, a tumor (for example, with a neuroma) or plaques with multiple sclerosis.
In a healthy person, stimulation of the deep sensory nerve fibers inhibits the flow of signals along the superficial sensory fibers, effectively inhibiting pain. When the integrity of the nerve fibers is disrupted, contact occurs between the fibers of the deep and superficial systems.
And the same stimuli, on the contrary, will enhance the pain flow in the sensory nuclei of the trigeminal nerve of the brain stem and subjectively lead to painful sensations.
It is worth mentioning a disease such as Tolosa-Hunt syndrome, which is characterized by pain in the orbital region of the eye and damage to one or more oculomotor nerves.
Often these pains go away on their own.
But the so-called postherpetic neuralgia, which develops after an acute period of herpetic rashes, can lead to constant pain...
The treatment prescribed by the doctor will depend on the causes that provoke trigeminal neuralgia. If neuralgia is caused by external causes, then they can be eliminated (for example, removing a tumor or cyst, slightly “pushing back” the bend of a large vessel pressing on the nerve root).
In this case, the disease is cured. But it happens that even with the most thorough laboratory examination, the causes of trigeminal neuralgia are not detected. Such neuralgic pain can only be alleviated by using anticonvulsants and drugs against neuropathic pain.
What will the doctor prescribe?
“Carbamazepine is an effective drug for the conservative treatment of trigeminal neuralgia,” explains Lyubov Mikheeva. – Its active substance reduces the permeability of the membranes of neurons involved in reactions in nerve fibers, and thereby prevents the occurrence of pain.
The following treatment regimen is usually prescribed: two days of 100 mg three times a day (daily dose 300 mg), two days of 200 mg twice a day (daily dose of 400 mg), two days of 200 mg three times a day (daily dose 600 mg) and three days, 200 mg four times a day (daily dose 800 mg).
If pain symptoms do not go away, the dosage is increased to 1000-1200 mg per day in four to six doses. When the result is achieved, after a month the effective dose is slowly reduced.
Treatment with Carbamazepine must be continued without interruption for six months, and then the body must be transferred to maintenance doses (200-400 mg per day in two doses).
According to Lyubov Mikhailovna, a slightly less effective drug, but also having an analgesic effect, is Phenytoin. It is prescribed 2-3 tablets per day. But this drug has contraindications, which include liver and kidney dysfunction, cachexia (depletion of the body), heart rhythm disturbances, and porphyria.
“During periods of exacerbation of trigeminal neuralgia, specialists practice intravenous administration of sodium hydroxybutyrate,” Lyubov Mikheeva continues the story.
– It is prescribed 5 ml of a 20% solution twice a day, but you should know that a contraindication to its use is a blood disease such as hypokalemia.
Also, during an exacerbation, ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone, laser puncture on pain points, and classical acupuncture are used.
Regarding all the above recommendations, let’s make a reservation right away: you should resort to them only after consultation with your doctor! Otherwise, it will turn out that, trying to cure one thing, you will hurt yourself even more...
Experts say that a complete cure for trigeminal neuralgia is rarely achieved, even with surgical intervention. The effect in which attacks occur much less frequently is considered good.
For example, if before treatment they happened every two to three days, then after treatment they happened once every ten days, and that’s already good...
Meanwhile, upon reaching a certain age (70 years and older), as a rule, attacks of neuralgia become weaker, and in old age they practically disappear.
We don’t think that the latter can serve as a consolation to anyone. But still, with such a disease, it’s worth knowing what you’re facing...
Source: //vr-gazeta.ru/obshchestvo/troekratnaya-bol-/
Methods for diagnosing the disease
The anatomy of the recurrent laryngeal nerve is unique. It will be possible to accurately determine the damage only after consultation with an otolaryngologist. In addition, you will need an examination by specialists such as a neurologist, neurosurgeon, pulmonologist, thoracic surgeon and endocrinologist. Diagnostic examinations against the background of laryngeal paresis are performed as follows:
- Conducting an examination of the patient's larynx, as well as taking an anamnesis.
- Performing computed tomography.
- X-ray of the larynx in direct and lateral projection.
- During laryngoscopy, the vocal cords are in a midline position. During a conversation, the glottis does not increase in size.
- Carrying out phonetography.
- Performing electromyography of the laryngeal muscles.
- Carrying out a biochemical blood test.
As part of additional diagnostic procedures, it may be necessary to perform computed tomography and ultrasound. It would not be superfluous for the patient to undergo X-rays of the brain, respiratory system, thyroid gland, heart and esophagus.
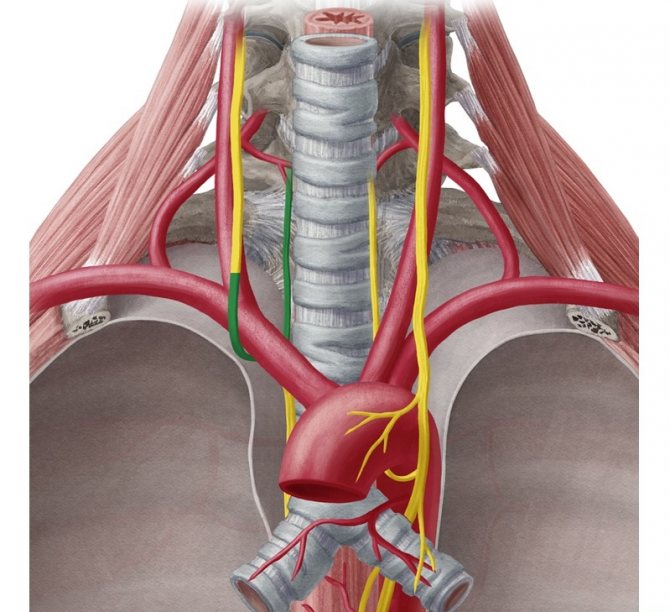
Topography of the subclavian artery.
Subclavian artery, a. subclavia, on the right it departs from the innominate artery, a. anonyma, and to the left - from the aortic arch, arcus aortae, conditionally it is divided into three segments.
The first segment from the beginning of the artery to the interscalene fissure.
The second segment of the artery within the interscalene fissure.
The third segment is at the exit from the interscalene fissure to the outer edge of the first rib, where a already begins. axillaris.
The middle segment lies on the first rib, on which an imprint remains from the artery - the groove of the subclavian artery, sulcus a. subclaviae.
In general, the artery has the shape of an arc. In the first segment it is directed upward, in the second it lies horizontally and in the third it follows obliquely downwards.
A. subclavia produces five branches: three in the first segment and one each in the second and third segments.
Branches of the first segment:
1. A. vertebralis - vertebral artery - arises with a thick trunk from the upper semicircle of the subclavian artery, goes up within the trigonum scalenovertebrale and goes into the foramen transversarium of the VI cervical vertebra.
2. Truncus thyreocervicalis – thyrocervical trunk – extends from the anterior semicircle a. subclavia is lateral from the previous one and soon divides into its terminal branches:
a) a. thyreoidea inferior - lower thyroid artery - goes up, crosses m. scalenus anterior and, passing behind the common carotid artery, approaches the posterior surface of the lateral lobe of the thyroid gland, where it enters with its branches, rami glandulares;
b) a. cervicalis ascendens - ascending cervical artery - goes upward, located outward from n. phrenicus-and behind v. jugularis interna, and reaches the base of the skull;
c) a. cervicalis superficialis - superficial cervical artery - runs in the transverse direction above the clavicle within the fossa supraclavicularis, lying on the scalene muscles and brachial plexus;
d) a. transversa scapulae - transverse artery of the scapula - runs in the transverse direction along the clavicle and, reaching the incisura scapulae, spreads over the lig. transversum scapulae and branches within m. infraspinatus.
3. A. mammaria interna - internal mammary artery - departs from the lower semicircle of the subclavian artery and is directed behind the subclavian vein down to supply blood to the mammary gland.
Branches of the second segment:
4. Truncus costocervicalis - costocervical trunk - departs from the posterior semicircle of the subclavian artery, goes upward and soon divides into its terminal branches:
a) a. cervicalis profunda - deep cervical artery - goes back and penetrates between the 1st rib and the transverse process of the 7th cervical vertebra to the back of the neck, where it branches within the muscles located here;
b) a. intercostalis suprema - superior intercostal artery - goes around the neck of the first rib and goes to the first intercostal space, which supplies blood. It often produces a branch for the second intercostal space.
Branches of the third segment:
5. A. transversa colli - transverse artery of the neck - departs from the upper semicircle of the subclavian artery, penetrates between the trunks of the brachial plexus, runs transversely above the collarbone and at its outer end divides into its two terminal branches:
a) ramus ascendens - ascending branch - goes up along the muscle that lifts the scapula, m. levator scapulae;
b) ramus descendens - descending branch - descends along the vertebral edge of the scapula, margo vertebralis scapulae, between the rhomboid and posterior superior serratus muscles and branches both in the rhomboid muscles and in m. supraspinatus. It is important for the development of roundabout circulation in the upper limb.
The recurrent nerve (vagus), located in the larynx, is responsible for the functioning of the vocal apparatus. Some of its fibers go to the heart. When the recurrent nerve is damaged, speech abilities are impaired; in severe cases, breathing difficulties may occur, which is explained by a decrease in muscle activity in the larynx. Treatment of the pathology is selected based on the complexity of the case.
Differentiation of paresis from other diseases
It is extremely important to be able to differentiate paresis of the laryngeal nerve from other diseases that also cause breathing problems. These include:
- Laryngospasms.
- Blockage of blood vessels.
- The appearance of a stroke.
- Development of multiple system atrophy.
- Attacks of bronchial asthma.
- Development of myocardial infarction.
Against the background of bilateral paresis, as well as in severe conditions in patients and attacks of suffocation, first of all, emergency care is provided, after which diagnostics are carried out and the necessary treatment method is selected.
Classification of symptoms for this disease
Based on the results of diagnostic measures, and in addition, examination of patients, all symptoms of damage to the recurrent nerve are divided into the following conditions:
- The development of unilateral palsy of the left recurrent nerve manifests itself in the form of severe hoarseness, dry cough, shortness of breath when talking and after physical exertion. In addition, the patient cannot talk for a long time, and while eating, he may choke, feeling the presence of a foreign object in the larynx.
- Bilateral paresis is accompanied by difficulty breathing and attacks of hypoxia.
- A condition that simulates paresis is formed against the background of unilateral damage to the laryngeal nerve. In this case, a reflex spasm of the vocal fold may be observed on the opposite side. The patient has difficulty breathing, cannot clear his throat, and chokes on food while eating.
Reflex spasms can develop due to a deficiency of calcium in the blood; a similar condition is often found in people who suffer from thyroid diseases.
What is the treatment for recurrent laryngeal nerve?

How does laryngeal dysfunction manifest?
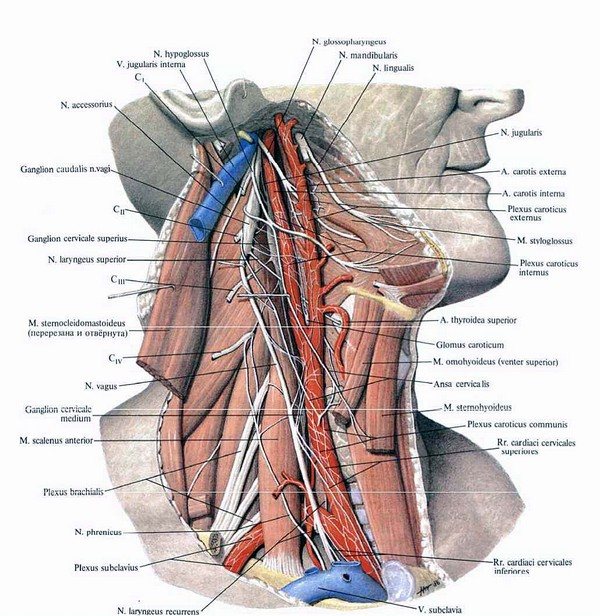
When the vagus nerve and its branches with nuclei are damaged, this leads to paresis of the laryngeal recurrent nerve. This paresis is observed more often and is caused by a pathological process that occurs in the larynx, damage to the NS, and thoracic pathology. And if intercostal neuralgia can be treated at home, then with the laryngeal nerve everything is somewhat more complicated.
Cause
Paresis of the laryngeal zone is often caused by a pathological process with paresis of the left recurrent nerve and the right. Large length n. laryngeus recurrens, its entry into the laryngeal zone from the cavity to the chest, contact with numerous structural components in the anatomy leads to the risk of destruction of nervous tissue in its different zones. The left part of the recurrent nerve endings performs the aortic rounding of the arch; the aneurysm contributes to their compression. And their right part goes near the upper lobe of the lung located on the right, and can be compressed by the adhesions of the pleura in this area. Paresis and other damage to this laryngeal nerve occurs due to the following reasons:
- injury to the laryngeal region;
- pleural inflammation, neoplasms in the pleura;
- inflammation of the pericardium;
- oncological pathology;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- cystic neoplasms in the mediastinal region;
- pathology of the thyroid gland, esophagus.
Laryngeal paresis is also possible with toxic damage, n. The laryngeus recurrens becomes inflamed, damage to this nerve is of a toxic nature during various intoxications.
It can also develop due to diabetes mellitus and infectious pathology. Neuropathic laryngeal paresis occurs as a result of surgical intervention on the thyroid gland with its complete or partial removal. Paresis of the laryngeal area can also be caused by:
- syndrome affecting cranial nerves;
- syphilis, polio lesions of the NS;
- clostridial bacteria;
- formation of cavities in the spinal cord;
- vascular atherosclerosis of the brain;
- strokes;
- traumatic brain injuries.
Paresis of the laryngeal nerve usually occurs on both sides due to the fact that the neuropathways intersect before entering the brainstem area.
Symptoms
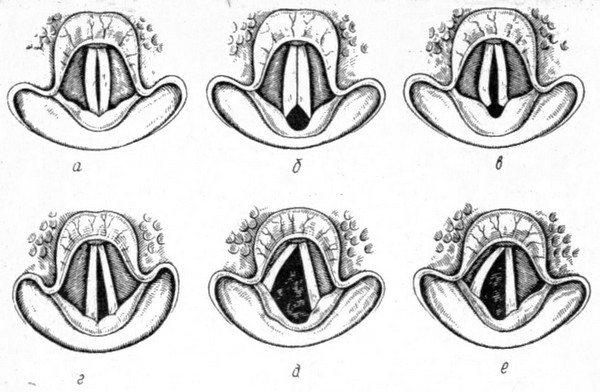
Diagnosis
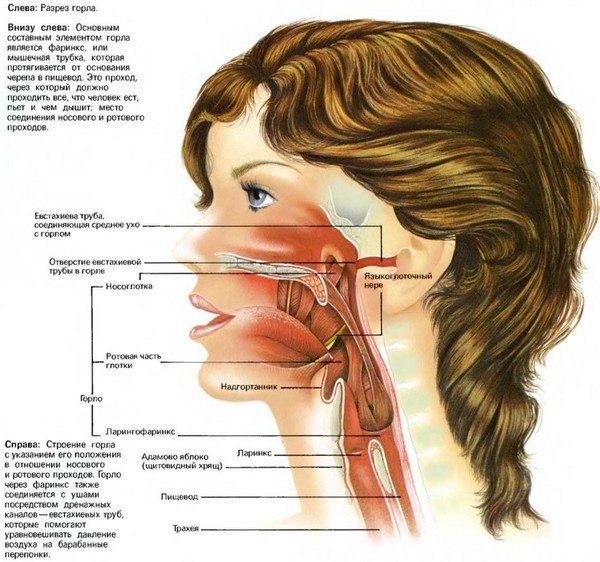
The purpose of diagnostic measures for neuropathic laryngeal paresis is both to make a diagnosis and the reasons for its occurrence. The patient needs the following consultations:
- otolaryngological;
- neurological;
- neurosurgical;
- endocrinological;
- surgical
A patient with this pathology must be thoroughly examined. This is feasible thanks to the following research activities:
- performing computed tomography;
- X-ray, microlaryngoscopic examination of the laryngeal zone;
- diagnostics of voice functions with stroboscopic, electroglotographic, phonetographic studies, as well as determination of the time of maximum voice production;
- electromyographic examination of the muscle fibers of the larynx.
To exclude the cause of laryngeal pathology in diseases in the chest, an X-ray examination of the chest, computed tomography of the mediastinal region, ultrasound cardiac diagnostics, and esophageal radiography are performed. You also need to do an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland. For TBI, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is necessary. Laryngeal paresis is differentiated from myopathological and functional, and it should also be distinguished from inflammation or injury of the arytenocricoid joint, false croup, diphtheria croup, bronchoasthmatic attacks, and congenital wheezing.
Pathology treatment methods
Paresis of the laryngeal nerve is not considered a separate disease, so its treatment begins, first of all, with eliminating the main causes that cause this pathology. As a result of the proliferation of cancerous tumors, the patient requires surgical removal of such tumors. An enlarged thyroid gland is subject to mandatory resection.
Emergency care is required for patients with bilateral paresis, otherwise asphyxia may occur. In such situations, a tracheostomy is performed for the patient. This operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. In this case, a special cannula and tube are inserted into the trachea, which is fixed using a Chassignac hook.
Diagnostic methods
Recurrent neuropathy is diagnosed based on the results of collecting information about the patient's condition. In addition to the medical history, pathologies help in determining the disease:
- external examination of the larynx;
- X-ray in various projections;
- phonetography;
- laryngoscopy;
- electromyography of the laryngeal muscles.
In order to identify the causative factor, ultrasound, CT and other methods of examining the thyroid gland, brain, heart, lungs, and respiratory system are used. Additionally, a biochemical blood test is prescribed to identify the pathogenic agent.
In the case of bilateral laryngeal paralysis, a tracheotomy is first performed, and then the patient is examined. This is explained by the fact that paralysis of this type poses a direct threat to the patient’s life.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment for paresis of the recurrent laryngeal nerve includes taking antibiotics along with hormonal drugs, neuroprotectors and B vitamins. In the event that there is an extensive hematoma, medications are prescribed that accelerate the resorption of bruises.
Reflexology is carried out by influencing sensitive points that are located on the surface of the skin. This therapy restores the functioning of the nervous system, accelerating the regeneration of damaged tissue. Voice and vocal function is normalized through special classes with a phoniatrist.
Against the background of long-term impairment of vocal functions, atrophy may occur along with pathology in the functioning of the laryngeal muscles. In addition, fibrosis of the cricoarytenoid joint may develop, which will interfere with the restoration of speech.
Neuralgia of the superior laryngeal nerve treatment with folk remedies
Neuralgia is a disease that can affect different parts of the body with its location, affecting the peripheral nerve, plexus and vessels of the nerves, pressing on them with surrounding tissues, resulting in severe pain in intensity.
It is important to know that this pain has virtually no effect on the sensitivity and mobility of the affected area; otherwise, it is already a manifestation of another disease, such as neuritis, which are often confused with each other.
The problem is gaining considerable momentum in terms of relevance, so many people are interested in how to get rid of neuralgia at home and is it even possible? It is possible if you pay timely attention to the presence and development of the disease, and provide proper help and support to your own body.
Absolutely any nerve in the structure of the human body is at risk, but there is a group that is most often susceptible to attack by this disease:
- dorsal;
- facial or trigeminal;
- sciatic;
- occipital;
- glossopharyngeal nerve.
The reasons depend on which area has succumbed to the disease; for each type they are characteristic and individual, so let’s find out what causes neuralgia depending on the location of the lesion.
- Identical causes of development provoke spinal neuralgia.
- Pregnancy with significant weight gain (more than 20 kg);
- Infections and inflammations in the pelvic organs, as well as their hypothermia;
- Excessive load on the lower back;
- Physical inactivity (inactivity);
- Overweight;
- Osteochondrosis (damage and sometimes displacement of tissues and cartilage of the vertebral discs);
- Fractures in the pelvis or hips;
- Tumors at the location of the nerve;
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Exposing the back of the head to hypothermia;
- Gout (a metabolic disorder that leads to the accumulation of salt deposits in the joints);
- Tumors of any nature or moderate to severe injuries on the cervical vertebrae and areas near them;
- Osteochondrosis.
- Arterial aneurysm (dilation and accumulation of blood vessels in the form of sacs in the arteries leading to the brain, the diameter of the artery increases, and blood circulation in it slows down);
- Atherosclerosis (blockage and hardening of blood vessels that form fatty tissue around them, lose their elasticity and block the flow of blood to the organ);
- Brain tumors, both benign and malignant;
- Protracted infections that become chronic, as well as purulent inflammation (for example: sinusitis, pulpitis, caries...);
- Hypothermia of any part of the face.
- Infectious diseases (tuberculosis, pneumonia, influenza...);
- Long-term allergic manifestations;
- Intoxication, exhaustion of the body;
- Violation of general metabolism;
- Diabetes;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Sclerosis (hardening and damage to the nervous system and internal organs).
Signs are also individual for any type. To correctly diagnose a disease, you need to clearly understand its symptoms, and ideally have a doctor’s confirmation of the diagnosis. Only in this case can one ask questions about how to treat neurology in general and avoid its relapse in the future. Let's look at the most pronounced symptoms that will help confirm or dispel your suspicions.
- The pain spreads throughout the nerve and feels paroxysmal and shooting.
- Discomfort is felt in one specific part, without going beyond it.
- A burning sensation may occur in the buttocks and lower back.
- There is a feeling that small goosebumps are crawling over the sore spot, especially during sleep, when the body is in a relaxed state.
- A painful sensation on the base of the tongue, in the pharynx and tonsils that occurs during eating, yawning, and coughing.
- Increased production of saliva alternates with absolute dryness of the oral cavity.
- Bitter taste in the mouth when eating any food, even sweets.
- Sudden, sharp attacks of pain when turning the neck or even lightly scratching the circumference of the head.
- Severe pain, reminiscent of a lumbago behind the ears, on the back of the head, as well as on the entire back of the neck.
- Typically, one part is affected, the side of the neck and head, but in rare cases both sides are affected.
- Excessive sensitivity of the skin on the face.
- Attacks of pain are sharp, but short-lived, often go away on their own, lasting from 10 seconds to several minutes, but up to three hundred such pain attacks can occur per day.
- Mostly the area of the face on the right side hurts; very rarely pain can occur on both sides.
- A painful attack can begin suddenly when some physical object is applied to certain points of the face: the wings of the nose, the nasolabial fold, the corners of the eyes. This can happen involuntarily while shaving, applying makeup, as well as while eating or chewing. This type of pain is called trigeminal neuralgia.
- The attack appears spontaneously with intense coughing, a rapid change of position or a deep breath.
- The pain is of a girdling nature and can last for a very long time, from 2-3 hours to three days.
- In the affected, painful part, the sensitivity of the skin almost always decreases, and in some cases it may even disappear altogether.
The pain associated with this disease is very debilitating, analgesics do not act effectively and relieve pain only for a short time, and at some point they stop working altogether, causing addiction to the main substance of the drug. Therefore, information on how to treat neuralgia at home remains popular and in demand.
An effective recipe for the treatment of pain in the back and vertebrae. You need to finely chop the willow bark and boil it under a closed lid for 20 minutes, after cooling, strain and use 1 tbsp internally. three times a day.
indoor geranium
Place several freshly picked leaves of the plant on a cloth, preferably natural one made of flax or other material, and apply it as a compress to the sore spot, apply a bandage over it and wrap it in something warm for two hours, repeat daily every 2-4 hours.
DIY ointment
Boil the lilac buds until the broth becomes thick, strain and combine with fresh pork fat, stir until the consistency of an ointment and rub into the area of pain as needed throughout the day. Store in a cool place or refrigerator.
Garlic oil
You will need pharmaceutical, ready-made oil; you need to make a tincture from it. Pour a tablespoon of oil into 0.5 liters of vodka or cognac, stir until completely combined and dissolved. Lubricate the affected areas no more than 3 times in 24 hours, the duration of treatment varies individually.
Both the root and leaves are used to relieve pain. Grate the root on a fine grater and apply a compress to the area; a horseradish leaf is used in the same way, only in its entirety, well washed under running water, tie the top with cellophane or an elastic bandage and wrap it in a woolen scarf. Keep it on until you feel a noticeable burning sensation, rinse off any remaining residue. Repeat no more than four times in 10 days.
Pass the black radish through a meat grinder or squeeze out the juice using another method and rub it fresh over the entire diseased nerve. It is enough to do it once a day for two weeks.
Mix 100 grams of alcohol and 10 grams of common thyme herb and leave for a day. Take fifteen drops three times a day, at the moments when you experience the most acute pain.
Mix 0.5 liters of liquid honey with the same amount of lemons, grated together with the peel and seeds, and add 40 grams of peeled apricot kernels, stir until smooth. Eat 2 teaspoons every morning and evening (only if you are not overweight) for 1.5 months.
Grind the zest from one large lemon with 30 grams of dry lemon balm leaves, 50 grams of black currant leaves and 600 milliliters of water (boiling water), leave for an hour, filter and consume 70 ml twice, no less than 8 hours after the previous dose, thirty minutes. before meals.

Herbalists consider traditional medicine to be very effective in combating neurological problems. After all, such therapy can have a therapeutic, pain-relieving effect for a long time compared to drug therapy, which is contraindicated for long-term use.
The plant is known for its calming and relaxing effects not only on the central nervous system, but also on all nerve endings in general. Boil 15 grams of dried mint in a glass of boiling water for about 8-10 minutes. Drink one hundred milliliters in the morning and at night.
Birch buds
It is very important to know that the buds are needed to bloom only halfway, so a handful of raw materials is poured with half a liter of vodka or concentrated alcohol; you can use it immediately after dilution in the form of rubbing sore spots or compresses; for the second case, the tincture needs to be diluted with a little water so as not to provoke burnt Do the procedures daily, but not longer than 15 days.
Yarrow
1 tbsp. combine herbs with 250 ml of boiled or thawed water, boil for 5 minutes over high heat, filter and use for pain three to five times a day, regardless of meals.
Will be used for treatment in the form of baths. Boil the bark of young aspen in two liters of water, take enough raw material to form a concentrated decoction, pour it into a bath with main water and steam in this solution for ten minutes. Repeat the procedure every evening an hour and a half before bedtime until you feel relief.
Chamomile tea can generally be considered one of the most healing drinks; in the case of neuralgia, it is also very effective. You just need to pour boiling water over a handful of flowers, let it sit and drink 0.5 cups before meals 3 times every 12 hours.
Collection of herbs
Mix coltsfoot herbs, wormwood and birch leaves in equal proportions, pour 30 ml of kefir or whey into the mixture, grind everything into a paste and apply as a compress, immediately put the product on a bandage, then on the affected part of the body, wrap it with a cloth or secure it bandage, and sleep under a warm blanket. In the morning, wash off the remaining compress with soapy water. Repeat every three to four days until you feel better.
- Physical activity or exercise, warm-up should be done daily, especially if you lead a passive lifestyle.
- The diet must be varied and rich in fiber and protein.
- Oddly enough, it is important to visit the dentist in a timely manner to prevent fermentation, infections, and rotting of teeth and gums.
- Do not spread infectious diseases of any kind, especially the flu and all its complications, as well as infections of the abdominal cavity and hip organs. If you have kidney problems, undergo a medical examination and ultrasound at least once a year, as such a disease increases the chances of developing the disease.
- Avoid hypothermia, dress appropriately for the weather, and do not be under the direct influence of air conditioning and fans for a long time, this especially applies to office workers.
- Do not overwork yourself mentally, avoid stress and nervous situations. After all, it has been scientifically proven that it is the nerves that cause 80% of all existing diseases.
- Sleep is an integral part of the normal functioning of any living organism; monitor the quality and duration of sleep.
- Several times a year, it is recommended to undergo massage therapy lasting 10-15 sessions, affecting the areas most vulnerable to disease, these are the neck and shoulders, back (paying due attention to the spine), legs, knees and feet.
- Take vitamins several times a year, paying special attention to B vitamins.
The time has come to sum up, we have analyzed all the necessary aspects of the knowledge that will be needed in order to diagnose the disease, and also told us the most effective, effective methods and recipes for treating neuralgia at home. Take care of yourself, take care of your health and well-being, so that such an unpleasant problem cannot infiltrate and affect your life.
source
Neuralgia is an inflammatory disease of the peripheral nerves that occurs suddenly and is accompanied by severe pain in the affected area. The cause of the disease is most often hypothermia, which was associated with great physical stress.
Nerve fibers can also be affected due to acute infection, poisoning of the body with toxins or heavy metals. Neuralgia is often caused by osteochondrosis or another disease of the musculoskeletal system. Peripheral nerves can also be damaged by tumors. Neuralgia also develops with diseases such as diabetes, vascular disease, atherosclerosis.
The peculiarity of this disease is that the debilitating pain is poorly relieved by analgesics and can last for a very long time. The area of pain is usually limited. Sometimes there is swelling, loss of sensitivity and redness of the skin.
Treatment of neuralgia is aimed at relieving pain. Classical medicine uses various drugs for this: ointments, thermal procedures, pain-relieving suppositories, tablets, injections. Significant relief from the disease is brought by the appointment of magnetic therapy, UHF and other physical procedures.
Neuralgia can also be treated at home using folk remedies. They will help to effectively relieve or significantly reduce pain. Let's get acquainted with folk recipes for various types of neuralgia in more detail.
Neuralgia has long been treated with geranium. To do this, apply a fresh leaf of the plant to the sore spot and bandage it. You can grind the leaves into a paste and prepare a compress. This will relieve pain and eliminate other symptoms of neuralgia.
For sciatic neuralgia, horseradish leaves should be applied to the affected area. The plant has a local anesthetic and warming effect.
An inflamed peripheral nerve can be treated with this remedy. An infusion is prepared from the rhizome of the autumn crocus. Before this, it is crushed. Take two tablespoons of raw material and pour a glass of water. Leave overnight (8 hours). In the morning, the prepared potion is used for compresses. During the day you need to do two procedures. The top of the compress should be covered with cellophane and insulated. Keep it for one to two hours. Course: two weeks.
For trigeminal neuralgia, you can use this recipe. You should prepare an infusion of chamomile: pour 2 tablespoons of flowers with a glass of hot boiling water. They insist. Take half a glass three times a day 15 minutes before meals.
For peripheral nerve disease, you should take a decoction of white willow bark. 10 grams of crushed raw materials are poured with a cup of boiling water. Place on low heat. After 20 minutes, remove from heat, cool and strain through cheesecloth. Take 2 tablespoons each time before meals.
Peppermint is also considered a good painkiller for neuralgia in folk medicine. For medicinal purposes, prepare the following infusion: take one teaspoon of crushed raw materials per glass of boiling water. Let the drink brew for about 10 minutes. Take 100 ml (half a glass) twice a day.
For any type of neuralgia, salt compresses will help. Salt is diluted with a small amount of warm water. Gauze or cotton cloth is moistened in this solution and applied to the affected area as a compress. It is covered with a warm scarf or handkerchief on top. Keep for at least one hour.
An effective remedy for the treatment of the trigeminal nerve is fir oil. It should be rubbed into the sore spot.
This remedy is no less effective in helping with neuralgia. Church wax (200 g) is melted in a water bath and 200 g are added to it: juice from white lily bulbs, honey and onion juice. This ointment is rubbed into sore spots and used as a compress. It is recommended to do the procedures at night.
For intercostal neuralgia, this traditional medicine recipe is suitable for treatment. Mix turpentine (turpentine oil) and medical Vaseline ointment in a 1:2 ratio. Apply this mixture to the sore spot.
For inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, red beets are used. Grate the root vegetable on a fine grater. The porridge-like mass is wrapped in a bandage, squeezed out a little, and such a tampon is placed in the ear. Cover the top with a dry cloth, fix it and leave the bandage on all night. In the morning, a new tampon is prepared.
This is how you can reduce the pain of neuralgia. A warm boiled egg is peeled, cut into two halves and the yolk is applied to the affected area. The attack of pain will gradually subside.
When the trigeminal nerve is damaged, this traditional method of treatment is used. Buckwheat is placed in a hot frying pan, heated well and poured into a small cloth bag. Apply it to the sore spot and hold until it cools down.
When peripheral nerves are damaged, baths with sage infusion are used for medicinal purposes. For two liters of boiling water, take 4 tablespoons of crushed raw materials. Leave for one hour, filter and pour into a bath of warm water. Add another 3 tablespoons of sea salt. The procedure takes 10 minutes. Take a bath before bed every other day.
Intercostal neuralgia is popularly treated with warm baths with a decoction of pine needles. To do this, take two kilograms of raw material, fill it with water and boil it on the stove for half an hour. After this, the decoction is left to infuse for at least 10 hours. Add pine extract to the bath, after filtering and heating. The procedures are carried out for one week before bedtime. After them, you need to lubricate the sore spot with fir oil and wrap it well in a blanket.
In order to prevent neuralgia, you should try to avoid injuries, drafts and hypothermia. Will help prevent peripheral nerve disease: an active and healthy lifestyle. It is useful to take complex vitamin preparations and do daily exercises. It is necessary to monitor your health and promptly treat diseases that are a factor in the development of neuralgia.
source
Treatment of neuralgia with folk remedies sometimes becomes so effective that even doctors recommend actively using these methods of therapy.
Neuralgia is a severe pathology of peripheral nervous tissue. It manifests itself as strong cramping attacks of unbearable pain, stretching along the entire length of the nerve or even its branches. This disease is also characterized by an inflammatory process in clusters of nerve cells and it develops very rapidly.
Most often, this disease is divided into nerve damage:
- trigeminal;
- occipital;
- intercostal;
- ischial
Treatment of neuralgia with folk remedies is especially important, since the main causes of this serious disease are not always clearly clear, which means it is not possible to directly influence them.
Most often this disease develops after:
- severe hypothermia;
- past infectious respiratory diseases;
- introduction of viruses;
- colds;
- pathological changes in metabolism;
- significant intoxication;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- bruise;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Before starting her treatment, you need to consult a therapist or neurologist.
You also need to undergo a full examination of the body to exclude pathologies that occur with similar symptoms. You need to know that nerve damage is characterized by an increase in local temperature, swelling, and convulsive muscle twitching.
Therefore, it is necessary to make sure that the patient does not have malignant neoplasms, angina pectoris, pancreatitis, paresis or paralysis, muscle rupture, or hemorrhages.
After the doctor conducts an ultrasound scan, an electrocardiogram, an echo-cardiogram, an x-ray, and prescribes a clinical and biochemical blood test, only then will it be possible to say for sure that we are talking about neuralgia.
As a rule, the doctor prescribes painkillers, but they only last a very short time and do not completely help the patient regain good health. In addition, they affect the entire body.
The most commonly used external medications are:
- anti-inflammatory ointments;
- warming gels;
- suppositories with analgesics;
- injections of B vitamins;
- local anesthetics.
Temporary relief for the patient with neuralgia comes from the use of physiotherapeutic procedures. Exposure to magnetic fields, UHF, and ultraviolet radiation effectively helps relieve pain attacks for a long time.
Therefore, treatment with folk remedies becomes a truly effective method of therapy, since its use can combat the main symptoms of neuralgia. Homemade recipes completely relieve pain, eliminate muscle spasms, normalize blood circulation in the affected area, calm the patient, and stabilize the state of his nervous system.
Of course, traditional methods must be connected to the general treatment regimen and be approved by a doctor. It is difficult to overcome any disease using exclusively home methods.
Neuralgia can often be treated with folk remedies. Among them there are proven recipes that are used by everyone who is familiar with this disease. Here are their examples:
- Ten grams of crushed raw material from willow bark must be placed in a container with a volume of a glass of water and boiled for half an hour. Then this decoction should be taken one tablespoon three times a day. This remedy has an excellent anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effect.
- Twenty grams of yarrow raw material should be poured with a glass of boiling water and left for an hour. You need to drink twenty grams of solution four times a day. It strengthens the body, relieves pain, eliminates muscle spasms and reduces inflammation.
- Chamomile is very popular. You need to take eighty grams of dry raw material, add two glasses of water and boil for ten minutes. Then the resulting decoction must be filtered and taken three teaspoons per day. The use of this recipe is intended for a long period of treatment. Chamomile relieves inflammation, eliminates muscle spasms, and has a general calming effect.
- You can take twenty grams of dried mint, place it in a two hundred milliliter container and boil well for at least ten minutes. You need to take one hundred grams of the resulting decoction twice a day. It has a significant calming effect, completely eliminates spasms, relaxes muscles, and well normalizes the overall functioning of nervous tissue.
- Geranium, which grows on almost every windowsill, can have a significant healing effect. You need to take its leaves, bandage it to the affected nerve and make a warm compress. Keep for about two hours. It can help relieve nervous tension, reduce pain, and relax muscles.
Neuralgia is difficult to treat traditionally. Therefore, home methods sometimes come to the fore:
- Many people use black radish juice, which they rub on the affected area. It is able to warm up the diseased nerve, draw out toxins, reduce swelling and eliminate pain.
- Garlic oil, used to prepare a medicinal tincture, has a good effect on neuralgia. Twenty grams of the substance are poured into a bottle of vodka, and then the affected areas are lubricated with this essence. It has a warming, distracting and anti-puffiness effect.
- You can take a handful of lilac buds, grind them and mix them with pork fat. This ointment should be rubbed into the affected nerve. It relieves inflammation, has a muscle relaxant effect and eliminates pain.
- The simplest, but at the same time very effective remedy provides great help. You need to boil an egg, cut it lengthwise and, without waiting for it to cool, apply it to the affected area. This method has a warming effect, eliminates swelling and draws out cellular breakdown products formed during inflammation.
When using these remedies, neuralgia is less likely to manifest itself as painful attacks. The patient's immunity is strengthened, the functioning of nerve cells is normalized, muscles relax, and unpleasant sensations no longer radiate to neighboring areas. They gradually decrease and then disappear completely.
Therefore, a disease such as neuralgia can be treated quite well with home recipes. Unlike pharmacological drugs, they more effectively help to make the pain less severe, stabilize the state of the vascular system, eliminate convulsive manifestations, and calm the nerves.
In order to avoid relapse of the disease, it is necessary:
- take care not to catch a cold;
- dress warmly;
- do not go out sweaty;
- allocate sufficient time for sleep;
- avoid nervous tension;
- take vitamins;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- regularly visit a neurologist;
- promptly treat respiratory infections;
- increase immunity;
- eat a balanced diet;
- avoid obesity;
- do exercises daily;
- take walks in the fresh air more often.
Medicines provide good results, but they are quite expensive, do not last long, are addictive and have a number of side effects. An attack of pain can take the patient by surprise and sometimes there is no time to run to the pharmacy, and even more so, to the doctor for a prescription. Then only a folk recipe allows a person to feel relief.
source
The appearance of paroxysmal or constant pain, which is called neuralgia, is associated with painful changes in the nerve fibers, due to which the receptors themselves that transmit impulses that cause neurological pain suffer.
Painful changes in nerve fibers can appear for various reasons:
- injuries;
- past infectious diseases;
- hypothermia;
- tumors;
- diabetes;
- osteochondrosis;
- atherosclerosis.
Burning, paroxysmal or chronic pain can occur in nerve fibers located throughout the body. Depending on the area of the lesion, neurites are distinguished:
- intercostal (gives in the area of the heart, chest, under the scapula);
- shoulder joint;
- post-herpes;
- lumbar;
- inflammation of the trigeminal (sensitive nerve of the face or trigeminal neuritis), sciatic, ulnar, occipital nerve;
- femoral;
- pterygopalatine node (pain affects the temples, neck, and sometimes spreads to the hands);
- neuroma of the foot (Morton's disease).
How to cure neuralgia as soon as its symptoms appear? The first is the correct diagnosis, because Under the guise of this disease, problems with the heart or blood vessels may be hidden, so it is important to be examined by a doctor for the presence of other diseases with similar symptoms. The main problem of the disease is severe pain that can make you unable to work, and the goal of getting rid of a disease such as neuralgia is to treat the pain syndrome with anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics. At the initial stage, the following may help:
- anti-inflammatory ointments with fir oil;
- acupuncture for local pain relief;
- warming compresses.
Drug treatment alone during an exacerbation may not produce the desired results. The complexity of a syndrome such as neuralgia means treatment must be complex, long-term and combined. The very first cure for neuralgia is painkillers: ointments, tablets, compresses, injections. In combination with pain relief, doctors prescribe medications:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Indomethacin);
- anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Baclofen, Phenytoin);
- muscle relaxants (Clonazepam, Sirdalud, Mydocalm).
Analgesics are often used to relieve the first signs of the disease. Ortofen and Diclofenac are not recommended for use as painkillers for neuralgia. Preparations with ibuprofen and nimesulide have the best effect on the source of pain. A common method of pain relief now is the fentanyl patch. Muscle spasms are well relieved by the drug Lyrica; it is most often used in the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. An analgesic such as Pentalgin is effective at the initial stage.
The most effective pills for neuralgia are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which not only relieve pain, but also relieve inflammation. Such tablets include Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Sulindac, Ketorolac. All these medications are irritating to the kidneys and gastric mucosa, so their use should only be prescribed by a doctor after examination.
To suppress unpleasant symptoms, an ointment for neuralgia will help, the effect of which is to:
- warming tissues and relaxing them;
- improving local blood circulation;
- increasing the elasticity of diseased ligaments;
- activation of local metabolic processes.
The ointments contain anti-inflammatory and analgesic components. Ointments based on bee and snake venoms are effective. Popular ointments that are used to relieve pain and inflammation are Viprosal, Finalgon, Apizartron, Myoton. The main effect is achieved by warming the tissues, improving blood circulation and dilating blood vessels. Before using products with this composition, you should read the instructions. Such ointments, for example, cannot be used during pregnancy and lactation.
What to do with neuralgia if you can’t use ointments, tablets, or they simply don’t help? Drugs for neuralgia that are used for injection are effective. For severe symptoms, analgesic injections are the best way to restore mobility and normal condition to the patient. Injections of Spazgan, Baralgin, Trigan are used. It is important to remember that an injection to numb an inflamed nerve should only be given by a doctor who knows human anatomy well.
During the period when acute pain subsides, it is effective to do acupressure, general or cupping massage to relieve tension in the muscles. Thus, massage for intercostal neuralgia, together with acupuncture, will help improve lymph flow, relieve muscle tension between the ribs, prevent muscle wasting and promote rapid recovery and restoration of mobility. Massage in combination with physiotherapy is effective - physical therapy, which is performed under the guidance of a doctor, will help cope with pain.
How to get rid of neuralgia if you have contraindications for drug treatment? It is possible to treat neuralgia at home using home recipes. Recipes for rubs based on natural ingredients will help you with treatment at home:
- Homemade tincture based on fir cones, dandelions, pine needles - alcohol tinctures with an anti-inflammatory effect are obtained from the listed plant materials. Take 0.5 liters of vodka for a glass of fir cones or dandelions and let the mixture steep. Use as a rub in small quantities before bedtime.
- Warm compress with beeswax. The wax is softened in a steam bath, a warm wax cake is applied to the sore spot, and bandaged with a bandage. The compress can be left overnight.
- Ointment made from dried lilac buds based on pork fat. Grind the dry kidneys into powder and mix with pork fat in a ratio of 1:4. The resulting fat mixture can be used 2 times a day to relieve pain.
Margarita, 48 years old I have been suffering from inflammation of the trigeminal nerve for a long time. After intensive drug treatment, I am saving myself with herbal medicine. With the help of folk recipes, exercises and massage, you can get rid of pain due to inflammation of the facial nerve. The illness arose after suffering from otitis media, so from now on I protect myself from drafts.
Valentina, 45 years old When pain appeared in the area of the heart, which radiated to the shoulder and back, I thought that there was a problem with the heart. After lengthy examinations, it turned out that the nerve between the ribs was pinched. I started taking analgesics and muscle relaxants. Later, the problem began to arise less and less often, because I used folk remedies based on beekeeping products.
Ekaterina, 36 years old The incorrect position in which I was sitting at the computer caused a neuritis that affected the cervical spine. The pain was terrible, at first only strong painkillers helped, I went to the doctor for injections because... I couldn’t even sleep normally. Now I’m saving myself with folk remedies: I make compresses at night, prepare rubs with pine needles.
source