Author of the article: Marina Gennadievna Vasilenko, Head of the Pain Treatment Center, neurologist-algologist, member of the Society of Neurologists and Neurosurgeons, Russian Society for the Study of Pain, Association of Interdisciplinary Medicine, International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP)
Occipital neuralgia is a disease of neurological origin, which is associated with irritation of the nerve roots in the occipital region. The pathology affects pairs of spinal nerves: the lesser and greater occipital nerves. The inflammatory process compresses and irritates these nerves, creating constant pain and reducing the quality of life of patients. Inflammation, according to the degree of origin, can be primary and secondary (against the background of lesions of the cervical vertebrae), and is also divided into neuralgia of the greater occipital nerve and neuralgia of the lesser occipital nerve.
Symptoms
Signs of inflammation of the occipital nerve are the following:
- throbbing pain in the head, ears, temples, lower jaw;
- dizziness and nausea;
- causeless lacrimation;
- discomfort from touching the affected area;
- a haunting feeling of cold;
- change in skin color.
Symptoms of occipital neuralgia:
- paroxysmal shooting pains;
- the duration of the attack is several hours;
- imitation of migraine symptoms;
- localization of pain in the occipital region;
- limitation of head mobility;
- increased sensitivity of the skin at the site of inflammation;
- change in skin color at the site of inflammation.
The pain can be constant, dull or burning.
A distinctive feature of inflammation of the occipital nerve is the presence of trigger points. The slightest pressure on them results in acute pain, so they must be protected from exposure until the disease is completely cured.
Symptoms
Muscles are divided into several large groups, depending on their anatomical location. Damage to different nerves leads to muscle pain in different parts of the body:
- with pathology of the intercostal nerves, pain occurs in the anterior or posterior part of the chest;
- pathology of the sciatic nerve causes pain in the lower back, buttocks, and legs;
- damage to the cranial nerves leads to pain in the face and scalp;
- Infectious nerve damage, especially herpetic, causes long-term pain in various parts of the body.
Vitamin deficiency, diabetes, alcoholism lead to muscle pain in the legs, loss of sensitivity and impaired nutrition of muscles and skin. The general clinical picture of muscular neuralgia is an attack of pain that suddenly appears and suddenly disappears. Each person can describe the nature of pain in their own way. This will depend on many factors:
- characteristics of the body;
- pain threshold;
- localization of nerve pathology;
- extent of damage;
- cause of damage.
With muscular neuralgia, the symptoms are quite varied, and those that are not directly related to nerve damage can also be observed.
Due to herpes infection
Herpetic damage to nerve fibers has special symptoms. In fact, the pain in this case is not muscular, but it is so strong that the person feels that everything hurts - muscles, skin, sometimes even bones. This intensity of pain is due to the fact that the herpes virus destroys the sheath of the nerve fiber. It takes a very long time to recover, so the pain syndrome can persist for months.
Intercostal neuralgia
The condition occurs due to damage to the intercostal nerves. The extent of pain will depend on the number of affected nerve fibers - from the neck to the costal arch. The pain is of a girdling nature. The pain syndrome intensifies when changing body position, making movements, or physical activity. When pressing on the intercostal spaces, the pain intensifies.
Painful sensations occur in attacks. Attacks of intercostal neuralgia can last from several hours to several days. They can be combined with sensory disturbances in the form of goosebumps and numbness of the skin. Due to the pain, it becomes difficult for a person to breathe; he spares the painful area of the chest.
If neuralgia is localized in the left half of the chest, it can be confused with an attack of angina or myocardial infarction. Taking nitroglycerin helps differentiate these conditions, which stops angina. To exclude myocardial infarction, electrocardiography is required.
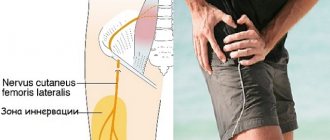
Due to damage to the sciatic nerve
A fairly common pathology in older people. The nature of the pain is usually one-sided. The pain starts from the lower back, covers the tailbone and thigh and can radiate to the popliteal region.
The pain is constant, of moderate intensity. With certain movements, increased pain occurs, called lumbago. In this case, a burning sensation occurs, intensifying with the slightest movement. They weaken when lying down.
Trigeminal neuralgia
This nerve innervates the skin and muscles of the face. If it is damaged, pain will occur in this area. Pain occurs suddenly, under the influence of so-called trigger factors. They can be overwork, light or sound irritation.
More often the pathology is unilateral. The pain is extremely intense, stabbing in nature. At the same time, numbness of the facial skin and small muscle twitches are observed. The attack lasts no more than ten minutes, then the pain also suddenly stops.
Pain may radiate to the ear or jaw. Often after the attack stops, heaviness in the head, a feeling of pulsation and fullness appears.
Diagnostic methods
If inflammation of the occipital nerve is suspected, the following is carried out:
- initial examination;
- collection of clinical picture information;
- collection of patient complaints;
- clarification of the conditions for the appearance of symptoms of inflammation of the occipital nerve;
- identification of concomitant diseases.
Instrumental diagnostics are based on the use of MRI, CT and radiography.
Seeking help from a doctor
It is always easier to get rid of the root cause of a disease than to fight the consequences for a long time. Therefore, at the first signs of inflammation of the occipital nerve, treatment will be prescribed by a neurologist. At the Academician Roitberg Clinic, experienced specialists will provide you with the necessary assistance in eliminating the symptoms of occipital neuralgia and treating any type and etiology.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of the occipital nerve involves relieving muscle tone, inflammatory processes and pain impulses. It has several directions:
- medications are used to relieve pain, muscle spasms and inflammation, such groups of medications as anti-inflammatory, muscle relaxants, anticonvulsants (if necessary), steroids, analgesics, B vitamins are used;
- physiotherapy is aimed at warming;
- therapeutic and physical training complex of exercises;
- massage;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- Surgery is a last resort method of treatment when all other methods have not had the desired effect.
An important step in treating inflammation is treating the root cause of the disease. Such an integrated approach to the symptoms and treatment of occipital neuralgia brings the maximum positive effect.
How can you fight the disease using traditional methods?
How to treat occipital neuralgia with folk recipes? This treatment takes place at home and is aimed at reducing severe pain. You can use the following folk remedies:
- ointment from lilac buds - a thick decoction of lilac mixed with pork fat, rubbed into areas of inflammation on the neck and head;
- dream herb infusion – brew 2 tablespoons of dry herb with a glass of boiling water and leave for 24 hours, you need to drink it in one day;
- Take 1 tbsp of willow bark decoction. l. from 3 to 5 times a day;
- alcohol compresses.
Can neuralgia develop from stress?
The human body is an inextricable unity of two regulatory systems: nervous and humoral.
The humoral regulation system carries out its work through the blood - through the release of substances into it that force organs and tissues to perform some function.
For example, the production of insulin causes sugar to leave the blood and glucagon to appear in the blood. Enkephalins and endorphins are called “hormones of joy and happiness.”
Features of nervous regulation
Nervous regulation is the second type of communication, built according to a vertical type with bilateral connections. The highest command center is the cerebral cortex.
If pain is analyzed in ancient centers that exist even in the spinal cord (primary pain analyzers), then in the cerebral hemispheres pain takes on an emotional connotation.
In addition, a change in a person’s emotional background can change the duration of pain, and even turn the bright interval during which pain is expected into suffering.
The impact of stress on health
There are many studies showing that chronic stress worsens the course of all diseases without exception - from mental disorders to a bruised finger.
Each of us can remember many similar cases: for example, long-awaited friends have come to visit you, you are happy and happy, and now, you are bringing a treat to the table, everyone is hungry, there is a wonderful boat ride ahead, or a hike to beautiful places - and suddenly you accidentally stubbed your little toe on the door frame.
Most likely, you will forget about the pain in a few minutes, switching to more pleasant and entertaining things.
Now imagine: you lost your job, your wife (husband) left you. Opening the door to your apartment, you discover that you have been robbed. You rush inside and, in the same way, hurt your little finger. The pain will seem a hundred times stronger and longer lasting. Sensitive subjects may even burst into tears, and strong-willed people will try to overcome the sudden onset of despair, and think that the sky itself is against you.
Until the evening you will remember this soul-shaking episode, and your finger will hurt much longer.
In the case of neuralgia, negative pain impulses are consolidated, transmitted to higher analytical centers, where the pain impulse can remain for a longer time, due to the self-induction of neural networks.
In addition, the “border zone” expands - the moments of the onset of pain, before its full development, are lengthened, and the period of pain subsidence is also lengthened. It is due to this that the duration of light intervals is shortened.
If special measures are not taken, the pain can reach such intensity that a person, in search of a way out, will resort to the last resort - suicide. This is all the more possible because in our world you can find a large number of people who are ready to do this against the background of complete physical health.
Exchange of serotonin in the human body
The state of the system of neurotransmitters (mediators) in the brain: serotonergic, cholinergic and GABAergic plays a great role in the development of such a chronic stress state. Each of these systems is responsible for its own “area of work,” but in modern medicine, most antidepressant drugs regulate serotonin metabolism.
It turned out that the longer serotonin remains in the synaptic cleft between neurons and, without being destroyed, continues to exert its effect, the better a person’s mood, the less important painful stimuli are.
As a result of taking such drugs, the actual level of pain remains the same, but, due to the fact that its perception is changed, it becomes less significant, occupies less thoughts, and, in the end, “survives” from memory.
This explains the use of antidepressants during fasting. They promote weight loss, since a person acquires an “indifferent attitude” to the urges of a hungry stomach, and is able to endure much longer.
On the other hand, there is no evidence that depression or stress can directly cause neuralgia at this point in time for the first time.
Thus, an added stress or depressive state has a negative impact on existing neuralgia, and in the opposite situation - the first attack of neuralgia will still be caused by local reasons, but still, its intensity and duration will be experienced much more painfully.
Source: //nevralgia24.ru/obshhie-voprosy/mozhet-li-razvitsya-nevralgiya-ot-stressa/
Disease prevention
Preventive measures should be permanent:
- rational organization of the work process;
- systematic physical exercise;
- avoid injuries and hypothermia;
- improving the diet with the addition of the maximum amount of vitamins and minerals;
- maintaining the correct neck position while working;
- timely treatment of respiratory and infectious diseases;
- rational distribution of physical activity;
- preventive treatment of concomitant diseases if present.
In our clinic, consultations are conducted by highly qualified neurologists. You can make an appointment with them on the website or by phone. JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberag) is located at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10, Mayakovskaya metro station.
Non-drug therapy
Treatment of muscular neuralgia also involves non-drug therapy, including:
- physical therapy;
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- use of magnet and electrophoresis.
Various types of physical exercises, such as race walking, swimming and yoga, can also be beneficial. Non-drug therapy should be carried out regularly, as it helps reduce the number and intensity of attacks.
Muscular neuralgia is a fairly serious and dangerous disease, which is much easier to prevent than to treat over a long period of time.