A pinched nerve in the hand is a pathological condition in which the nerve fiber begins to poorly transmit impulses to the tissues of the hand. After damage to the nerve endings, the patient's limb below the lesion site becomes numb, pain occurs, and sensitivity decreases. In severe cases, motor function becomes impossible. Treatment of the pathology includes painkillers, vitamins and other agents are used to restore the integrity of the nerve. Traditional medicine methods are also allowed.
Causes of pinched nerve fibers
The brachial, radial, or ulnar nerve may be damaged. The localization of the lesion depends on the reasons:
- untreated injuries (knife and gunshot) or untimely identified fractures, dislocations;
- incorrectly performed surgical intervention;
- habitual joint dislocation;
- heavy load on joints when playing sports;
- excessive and prolonged tension in the muscular system of the arm;
- occupational injuries, bruises;
- carrying very heavy objects;
- “wedding night” syndrome (the partner lies on her partner’s arm for a long time);
- improper use of crutches;
- uncomfortable posture during sleep, sleeping at the table;
- compression by tumor formation;
- scars where the nerve passes;
- violation of injection technique.
Before starting treatment, the doctor must find the exact cause of the nerve compression. Analysis of symptoms, as well as anamnestic data, will help in diagnosis; additional examination methods are also needed.
Benefits of procedures
By influencing the skin and muscle tissue during massage, it warms up. As a result, the blood vessels dilate, which ensures the outflow of excess accumulated fluid in the tissues. Also, the circulatory system begins to deliver oxygen as normal, as well as vitamins and microelements. This is what allows not only to significantly relieve pain symptoms, but also to reduce swelling.
During therapeutic massage sessions, complete restoration of motor function occurs quite quickly. However, the patient can do the massage independently, acting on the damaged area with simple rubbing movements. In this case, it is recommended to additionally use warming ointments in the form of Arpizartron, Chondroxide or Voltaren gel.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of hand nerve compression depends on the location of the lesion. Damage to the nerve fiber of the arm occurs at the level of the shoulder joint, shoulder, elbow or wrist.
Ulnar and radial nerve entrapment
Pinching of the ulnar nerve is manifested by numbness, tingling, and loss of sensitivity. Unpleasant sensations may be in the hand at the level of the forearm and in the finger. Numbness is found in the little finger, as well as in the lower half of the ring finger. Paralysis of the adductor apparatus and muscles that flex the thumb is possible.
If the ulnar nerve fiber is completely damaged, the patient loses sensation in the ring and little fingers.
In patients, you can see the typical appearance of the hand with damage to the ulnar nerve - a “bony hand”. The special position of the fingers is explained by paralysis of the interosseous muscles of the palm. In patients, atrophy of the muscular system is detected in the interdigital space of the 1st and 2nd fingers on the hand.
Pinching of the radial nerve in the hand is accompanied by numbness, loss of sensitivity, tingling, and pain.
The radial and ulnar nerves are often injured in the elbow joint. If the radial nerve is affected in the area of the elbow joint, then the arm hurts throughout the entire forearm and hand. Atrophy of the muscles innervated by the ulnar nerve is possible. In patients, the sensitivity of the index, middle and half of the ring finger, as well as the thumb (on the palm side), is impaired. Sensitivity is impaired in the inner part of the palm. On the back of the hand, the distal (in the area of the nail plates) phalanges of the little finger, index finger, middle finger, half of the ring finger, and thumb are affected. Patients with nerve damage are unable to grasp objects. Patients have a characteristic symptom of a hanging limb. The abduction of the thumb and the turning of the hand with the palm up are impaired.
Nerve entrapment in the shoulder joint
Pinched brachial nerve has the following symptoms: impaired sensitivity, stiffness of movement, complete or partial numbness of the fingers. After sleep, the patient often cannot move his arm. The movement of the arm in the articular joints is impaired. The patient's palms folded together do not fit tightly.
Patients with brachial nerve damage experience constant muscle pain that worsens after sleep. Possible paleness of the skin on the hand, involuntary contractions of the muscle system.
Pinched nerve in the hand
A pinched nerve in the hand often occurs when the nerve fiber at the level of the wrist joint is affected. This pathology is very rare.
Patients experience the following symptoms:
- the hand goes numb;
- arm hurts.
The patient's hand may hang parallel to the body. It is impossible to grasp objects, retract the thumb, and muscle strength in the hand decreases. Atrophy (reduction in muscle size) of the arm is visible on the surface.
Nerve damage at the level of the wrist joint can occur with:
- prolonged pressure on the nerve fiber;
- bruises, dislocations of the wrist joint;
- lesions of the articular apparatus (deformation);
- constant work on the computer, when the brush lies on the edge of the table.
Symptoms: how does pathology manifest itself?
The pinched nerve of the wrist does not affect the motor function of the entire arm; the limb rises and falls freely and is abducted to the sides.
In the area of the wrist joint there is a section of the nerve branch that provides sensitivity and moves the limb. If the nerve is pinched, the following signs appear:
- aching, persistent, shooting pain radiating to the shoulder, elbow or fingers;
- muscle weakness, especially when trying to grasp or hold an object;
- partial or complete loss of motor functions;
- a feeling of numbness of the skin or tingling in the phalanges.
Diagnosis of compression of the brachial nerve
Diagnostic measures include physical examination and additional examination techniques. During the appointment, the doctor collects a complete medical history: how long ago the symptoms appeared, the causes of the disease, the presence of chronic pathologies, the type of activity of the patient, and asks where it hurts.
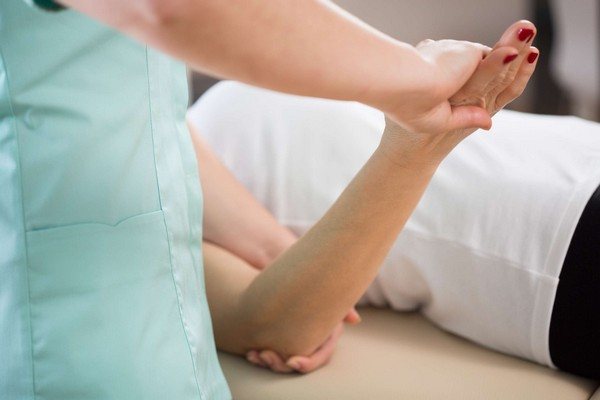
During a physical examination, the specialist performs several diagnostic tests. He compares the muscle strength of the affected and healthy arm, checking:
- pronation (inward rotation of the hand), supination (outward rotation of the hand);
- clasping palms together;
- fixing the arms in an extended position,
- symmetry of muscle function,
- holding a glass.
The doctor conducts tests to determine sensitivity in all fingers, forearm and shoulder. Sensitivity is tested by touching the patient's skin or using a needle.
During the examination, the doctor prescribes general and biochemical blood and urine tests.
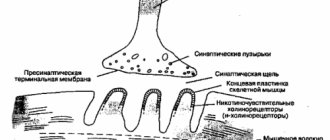
Electromyography allows a diagnosis of nerve entrapment to be made. The technique allows you to see the electrical activity of the muscle system in the hand. An electromyograph helps detect areas of poor muscle innervation. For a complete examination, the patient is referred for examination to an endocrinologist, orthopedist, or surgeon. An x-ray of the shoulder joint, upper arm, forearm, and hand is also necessary.
Diagnostic methods
A pinched radial nerve in the hand is diagnosed by a surgeon. The doctor finds out the cause of the condition, the presence or absence of previous injuries or bone diseases, and evaluates motor functionality. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a number of diagnostic procedures such as:
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- radiography;
- electromyography;
- Nerve conduction test.
The study will determine the condition of soft and bone tissues.
Using these methods you can get the following results:
- condition of the joints on the hand;
- the nature of the damage to the surrounding soft tissues, which could lead to pinching;
- speed of movement of nerve impulses;
- muscle contractility.
Therapeutic measures for nerve compression in the hand
Treatment for pinched nerves includes drug therapy, physiotherapeutic techniques, physical therapy, massage, and the use of traditional medicine. Treatment is carried out almost the same regardless of the location of the lesion.
Drug therapy
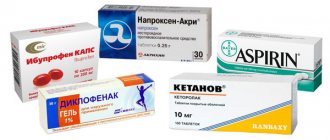
Drug therapy includes analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin complexes, as well as drugs that enhance the conduction of impulses. To reduce the intensity of pain, non-steroidal drugs are used:
- Diclofenac;
- Nimesulide;
- Ibuprofen.
Execution Rules
Pinched sciatic nerve is a pathology that will require a lot of time for diagnosis and treatment. During the period of acute inflammation, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed. Massage for this disease is indicated for both men and women only during remission and after completing a course of drug treatment.
Massage for inflammation of the sciatic nerve helps improve blood flow in the pathological area, relieve spasms and muscle tension. You should undergo treatment only in special massage rooms with experienced specialists.
The course of therapeutic massage ranges from 10 to 15 sessions. The massage is performed using a special technique using massage creams and oils based on bee or snake venom, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory drugs or using honey. In this case, the patient is on a hard couch, in a prone position. The body is as relaxed as possible, arms lie along the body. For the greatest relaxation effect, you can use a bolster or pillow placed under your stomach.
Massage
Massage procedures can be performed independently or go to a massage therapist. One session should last 10-20 minutes. The course of treatment includes 10-15 sessions.
Massage manipulations help improve blood flow in tissues. And activation of blood circulation stimulates nutrition of damaged nerve fibers, affected muscles and accelerates rehabilitation.
Medicinal herbs
Traditional medicine is not the main method of treatment for a pinched nerve in the hand. Herbal treatment is best combined with medications and physiotherapy. You should consult a doctor before using herbs.
Eleutherococcus root
Eleutherococcus stimulates metabolic processes in tissues. More often a decoction is prepared from the plant. To prepare the remedy, take a tablespoon of crushed root, add 500 ml of water, boil for 30 minutes, and pass through cheesecloth. Some of the liquid will evaporate, so water must be added to the original volume of the solution. You can add 2 teaspoons of lemon juice or honey to the finished decoction.
Blue clay
Blue clay accelerates the restoration of nerve tissue, reduces swelling and inflammation. The clay needs to be crushed and dried. After this, it is diluted with water and stirred until it becomes a homogeneous thick mass. After preparation, the clay slurry is applied to a piece of gauze folded several times. A gauze bandage is applied to the affected area and held until completely dry. For each manipulation, fresh clay is taken.
Lemon
Lemon peel should be peeled from the pulp and applied to the skin at the site of nerve damage before going to bed. The scabs should be secured well with a bandage (plain or elastic) and the bandage should be left until the morning. You can also apply olive oil to your skin.
Herbal cocktail
Warm herbal baths are recommended for recovery after nerve damage. For the herbal “cocktail” you will need sage, Jerusalem artichoke, and oregano. For 10 liters of boiling water you need 15 tablespoons of each component. Keep your hand in the liquid for 15-20 minutes.
Alcoholic cocktail
An alcoholic “cocktail” is used as a compress. Ingredients of the remedy:
- 150 g of ammonia;
- 50 g camphor;
- 250 g alcohol;
- 250 g sea salt.
All ingredients are added to a 3-liter jar, and then 1 liter of water is poured. The solution needs to sit for a day. After settling, soak gauze with the solution and apply to the affected area. The procedure is carried out 3 times a day. The solution must be shaken before use.
Dates
Dates are pitted and crushed in a blender. The prepared mass should be eaten 3 teaspoons 3 times a day. Take date pulp after meals. If necessary, you can pour milk into the slurry. Course therapy takes 30 days.
Burdock
Burdock root should be finely chopped. To prepare a medicinal solution you will need 1 tablespoon of root and 200 ml of red wine. The root is poured with wine and left for 2 hours in the refrigerator. You should take 60-70 ml 2 times a day.
Carnation
Pour 15 g of dried cloves into a thermos and pour 500 ml of boiling water. The solution must be infused for 2 hours. You should drink the medicine 200 ml 3 times a day. Therapy lasts 15 days. After 10 days you need to take a break, and then continue treatment again. Clove therapy lasts 6 months.
Elecampane
A decoction is made from elecampane. To do this, you need to take 15 g of dry plant, pour 200 ml of boiling water over it. Infuse the solution and pass through several layers of gauze. The medication should be taken 100 ml twice a day. Drink the solution after meals. Course therapy lasts 30 days.
Rosemary
Rosemary leaves are poured with vodka and left for 3 weeks in the refrigerator. The medicinal solution must be shaken periodically. After standing, the medicine is passed through several layers of gauze. Rub the solution over the affected area before going to bed.
Turpentine
Turpentine is mixed with warm water (ratio 2:3). The solution is poured onto a slice of rye bread (2 cm thick). The soaked bread is applied to the damaged area of the hand for 7-8 minutes. After the procedure, you need to lie down and cover yourself with a blanket. Treatment is repeated for 2-3 days.
Treatment
If the radial nerve is pinched, treatment must be timely and professional. First you need to find out the cause and area of the pinching. Treatment is divided into conservative and surgical methods. The conservative method is to relieve pain and restore the damaged area itself. Before prescribing medications, or better yet at the first sign, avoid physical activity. The healing and restoration process takes a long time. Treatment should begin with the very first signs of pinching.
During drug treatment, anti-inflammatory drugs, decongestants and painkillers, vitamin therapy, and drugs that prevent scar formation are prescribed. Physiotherapy, acupuncture, and massages are often added to the treatment complex.
If within three months there is no effectiveness from the drug treatment, then a decision is made to undergo surgery.
If the ends of the nerve tissue are torn, it is stitched together. If a tumor is detected during pinching diagnosis, it is recommended to remove it. Surgeries are carried out with the release of scars, that is, the nerves are isolated, released and, due to better conditions, restored, this method is called neurolysis. Neuroraphy is a surgical method of treatment; its essence lies in the fact that the ends of the nerves are compared and sutured using microneurosurgical techniques. During surgery, adhesions adjacent to the tissues may be detected. In this case, their dissection and prevention of pinching of the nerve in the arm are indicated.

A pinched hand can be treated at home, but always after consulting a doctor. To do this, the doctor may prescribe exercises to restore the functionality of the arm. Physical exercises will be aimed at flexing and extending the fingers. Massage as the pain progresses; you can rub in warming ointments. You can take herbal baths based on sage, Jerusalem artichoke and oregano. But before that, you should make sure that you are not allergic to herbs. Dates are good for neuralgic ailments; you need to take them in small quantities after meals for a month. But remember, dates have a lot of fructose, so this option may not be suitable for everyone.
Nerve pinching of the hand is a fairly common occurrence and at the first symptoms you should pay attention to it and consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If treatment was carried out adequately and on time, the following results can be achieved:
- first of all, relieving pain at the pinched site and along the nerve;
- absence of relapses or long remission;
- increased performance, physical activity;
- improvement of blood circulation at the site of infringement;
- complete or at least partial restoration of impulse transmission through nervous tissue;
- if there was an inflammatory process, then completely exclude it.
Prevention
Prevention of a pinched nerve in the hand is timely treatment of injuries, fractures, and dislocations. If an infectious disease occurs, therapy must be taken with particular seriousness. A herpetic infection does not need to be treated on its own, as the virus can severely damage nerve endings.
If a person’s work involves stress on the hands, one must constantly do physical exercises to strengthen the ligaments and muscles.
Obese patients should try to lose weight. This will reduce the chance of joint damage.
It is important not to overcool and avoid injury. The right approach to nutrition, a healthy lifestyle, and vitamin therapy stimulate the strengthening of bones, joints, cartilage, and improve the condition of the nerves.
We recommend reading similar articles:
Treatment: how to proceed correctly?
Drug therapy
If a nerve is pinched in the wrist joint, doctors recommend the following medications to relieve neuralgic pain and inflammation:
To stimulate metabolic processes in nerve cells, it is recommended to consume B vitamins. It is useful to take chondroprotectors, which help restore the cartilage tissue of the joints of the hand. All medications must be prescribed by a doctor; self-medication is dangerous. If drug treatment is ineffective, surgery is prescribed to free the pinched nerve.
Physiotherapy methods
You can eliminate a pinched nerve in your hand or finger using the following physiotherapeutic procedures:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- thermal wraps with ozokerite or paraffin;
- inductothermy;
- massage;
- osteopathy - finger pressure on active points;
- manual therapy.
The effectiveness of therapeutic effects on the wrist nerve is as follows:
- relieves muscle spasm;
- eliminates pain and inflammation;
- promotes regeneration of damaged tissues;
- restores mobility;
- saturates tissues with oxygen;
- improves blood circulation and metabolic processes.
Reflexology procedures should only be performed by a specialist; self-medication can cause complications.
Physiotherapy
During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to perform simple exercises:
- clenching and unclenching fingers into a fist;
- flexion-extension of the wrist;
- rotational movements of the brush;
- spreading the phalanges to the sides and bringing them together;
- thumb rotation;
- alternately raising the phalanges when the palm lies on a hard surface;
- imitation of playing the piano;
- pulling the wrist towards the distal phalanges, imitating the movements of a caterpillar.
Clinical picture
Patients are concerned about pain and a tingling sensation, burning sensation in the fingers and back of the forearm, weakness in the muscles of the hand. Gradually, numbness of the back of the hand appears, adduction and abduction of the thumb is impaired, and extension of the hand and forearm becomes difficult.
An objective examination of the patient reveals:
- paresthesia and hypoesthesia in the area of the rear of the I, II, III fingers, the posterior surface of the forearm (70%);
- weakness in the extensor muscles of the hand and fingers, weakness of the supinator, brachioradialis muscle (60%);
- inability to abduct and adduct the thumb (70%);
- decreased carporadial reflex (50%);
- muscle atrophy (40%);
- the appearance of pain during supination of the forearm with overcoming resistance and in the test with extension of the middle finger (50%);
- pain on palpation along the radial nerve (60%).