What is inflammation of the sciatic nerve: let’s study where it is located and what its function is? How the disease is diagnosed and treated. Knowledge of anatomy, including the entire human nervous system, is important in understanding the localization of a particular disease, since the manifestation of pain in one place entails the spread of pain throughout the body.
The human nervous system is a morphological and functional integrity of different but interconnected nervous structures. Together with the endocrine system, it regulates the activity of all body systems and the response to changes in the internal and external environment.
In other words, the nervous system plays an integrative role, that is, it combines sensitivity, motor activity and regulatory systems.
The human nervous system is complex, branched throughout the body. This makes it vulnerable to various types of pathologies. From the moment the embryo develops until the end of life, a person is susceptible to various kinds of diseases, which are diagnosed and treated by a neurologist.
The reasons are the following factors: stress, disrupted daily routine, sedentary lifestyle, excessive nervous tension. The human body involuntarily “squeezes” and is in an atmosphere of discomfort.
The fatigue accumulated during the day should go away with a night's rest, but due to all the unfavorable factors, not every person can freely fall into a healthy sleep; rather, they will experience insomnia or restless sleep with frequent awakenings.
With diseases of the nervous system, it becomes difficult for a person to keep the body in balance when walking, to have clear coordination of movements, memory deteriorates, and vision decreases.
There are many reasons for the development of the disease. Thus, hypothermia, infection of the body, injury, diseases of the spine or toxic substances, individually or simultaneously, can lead to a disease such as sciatica - inflammation of the sciatic nerve.
Anatomy
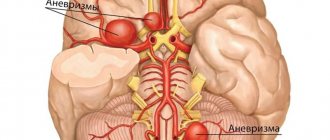
Let's look at where the sciatic nerve is located. In the sacral region, five pairs of spinal nerve roots, connecting with each other, form a thick trunk - the sciatic nerve. It is the longest and most powerful nerve in the human body . It is paired, its fibers exit the pelvic cavity through the infrapiriform opening.
Next it goes along the ischial tuberosity and the greater trochanter of the femur. So, lying at this depth it reaches the thigh. Below the knee, it divides to form the peroneal and tibial nerves, which are responsible for innervation of the leg and foot.
Throughout its entire length, the sciatic nerve branches slightly; the outgoing nerve fibers innervate the surrounding areas .
Due to its power and extensive area of occurrence, the clinical manifestations of the inflammatory process will be pronounced.
What causes a pinched nerve?
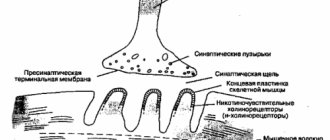
The cause of pinched nerve, which occurs during traumatic, toxic or infectious lesions, is compression of the nerve trunk itself in soft tissues or compression of sensory, motor or sympathetic fibers, which make up the nerve trunk between the soft bones and bony protrusions on the bones of the skeleton.
That is why, when a nerve is pinched, disturbances in movement and organ function occur, and sharp and very severe pain occurs. Most often, a pinched nerve in the spine occurs during physical activity, especially in cases where the load is improperly distributed on the bones and ligaments that form the movable skeleton of the human body.
At the moment of overextension, the nerve root is pinched, and at the site of this microtrauma, reactive edema very quickly grows and a focus of inflammation is formed, which further contributes to compression of the nerve. Thus, a pathological reaction is triggered, requiring measures to eliminate it, which takes considerable time.
Relationship with other bodies
The sciatic nerve has many functions, in particular, it takes on the entire load of the spine and supplies energy to the entire lower limb from the hip to the foot.
Sciatica is an inflammation of the sciatic nerve; translated from Greek ischias means “pelvis.” The disease is characterized by an inflammatory process that causes severe, sharp pain in the entire leg or in a separate area of the limb.
Sciatica is quite easily clinically confused with piriformis syndrome . Painful sensations occur that are caused by the contact of the muscle with the sciatic nerve. This condition cannot be attributed to neuralgia, but the pain that a person experiences can lead to an incorrect diagnosis - sciatica.
With lumbago, pain occurs in the lower back, lower back and pelvis. Unknowingly, some patients perceive this as inflammation of the sciatic nerve.
Innervation zones
The innervation of the muscles of the lower limb by the nervus ischiadicus and its branches is as follows:
Muscle branches n. ischiadicus - semimembranosus, semitendinosus muscles and long head of the biceps femoris; Nervus tibialis - posterior tibialis muscle, long flexors of the fingers and thumb, mm. gastrocnemius, plantaris, soleus, popliteus. Nervus peroneus communis - tibialis anterior muscle, extensor digitorum longus and brevis, extensor pollicis longus.
The innervation of the muscles of the lower limb is presented in more detail in the table below.
A diagram of the cutaneous innervation of the lower limb is presented below.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of sciatica are quite varied and the disease is easily confused with other ailments. To make a diagnosis, instrumental studies are carried out:
- The reflex is tested by hitting the tendon that connects the heel bone to the calf muscle with a hammer. A symptom of sciatica is the absence of a reflex or a sluggish “response”.
- Knee reflex. They also hit the tendon that connects the patella and tibia with a hammer. Normally, the muscle should contract and straighten the leg. If the sciatic nerve is inflamed, the reaction will be weakened or absent. Thus, sciatica manifests itself, which is caused by compression of the nerve plexus by a herniated disc at the level of the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae.
- Plantar reflex. The doctor runs the tip of the hammer along the patient’s foot. When the sciatic nerve is inflamed, flexion of the foot does not occur at all or there is a weak reaction to the stimulus.
- Lasègue's symptom. The patient needs to raise his straight leg while lying down. If pain occurs on the back of the thigh and lower back, this is a sign of sciatica.
- Bonnet's sign. The previous manipulation is carried out, but the doctor raises the leg, not the patient himself.
- Cross syndrome. When checking symptom No. 4, pain also occurs in the second leg.
Treatment of inflammation of the sciatic nerve
One of the main points in treating sciatica is pain relief. For this purpose, complex therapy is prescribed, in which the patient is prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They have an anti-inflammatory effect, reduce fever, pain, and improve general condition. Prescribed, for example, acetylsalicylic acid, Diclofenac, Piroxicam, Ibuprofen.
Interesting! It is worth noting that the high effectiveness of the drugs is combined with side effects.
The patient is prescribed NSAIDs
Taking medications may be complicated:
- stomach or intestinal bleeding;
- renal or liver failure;
- symptoms of central nervous system damage (headache, dizziness, drowsiness);
- nausea, diarrhea;
- allergic reaction.
These drugs have side effects
Each drug has features that are reflected in the manufacturer's instructions. It provides safe ways to take medications. For example, Diclofenac is available in the form of enteric-coated tablets. Therefore, it must be taken during or after meals with a small amount of water, without chewing.
NSAIDs in the form of rectal suppositories bypass the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine. Due to this, the concentration of the drug entering the blood is higher.
Important! The use of suppositories is limited for hemorrhoids and rectal polyps. Exceeding doses and prolonged use of drugs increase the risk of complications.
NSAID dosage regimen
During treatment using NSAIDs, a number of rules must be followed. The safety of therapy is directly related to compliance with the drug dose. Some manufacturers may produce medicines with different contents of the active substance. Before taking the product, you need to carefully study the instructions.
The frequency of taking the drug depends on the time of maintaining the maximum concentration in the blood. Long-acting drugs are available. Reducing the time between doses increases the risk of complications.
Rules for taking NSAIDs
Drugs in the form of tablets are washed down with plenty of water (the volume is indicated in the instructions). They should not be taken on an empty stomach. If the drug is available in capsules, they are not chewed, but swallowed whole. The capsule dissolves in the section where the effect of the drug on the mucosal wall is harmless. Absorption of tablets occurs more actively when maintaining a vertical position. After taking tablets or capsules, you should not lie down for 20-30 minutes.
Important! The combination of several drugs of the same group is possible only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Precautionary measures
Special recommendations are given when using NSAIDs during pregnancy, lactation, and childhood.
Combining such drugs with alcoholic beverages may increase side effects.
Classification of NSAIDs
Modern analogs of anti-inflammatory drugs are selective NSAIDs. They remain highly effective combined with fewer side effects. Let's look at some.
Movalis (meloxicam) is available with a doctor's prescription. Effective as an analgesic and eliminates inflammation. Available in the form of tablets, rectal suppositories, solution for injection.
Important! Despite the improved composition, in rare cases it may cause side effects.
"Movalis"
Tramadol is a centrally acting analgesic that lasts 4-8 hours. Used in complex therapy as prescribed by a doctor.
"Tramadol"
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
When pathogenic microorganisms penetrate tissue, a response in the form of inflammation develops. Biologically active substances are released into the blood and tissues. Each of them, at its own level, supports a defensive reaction.
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Steroids have pronounced anti-inflammatory effectiveness. They affect all phases of inflammation.
Interesting! Their action is similar to hormones that are produced in the body.
Side effects of steroids:
- immunosuppression;
- increased appetite;
- fluid retention in the body;
- steroid osteoporosis (decreased bone mass);
- steroid ulcer.
About some SPVPs
Steroid therapy is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor and with dynamic monitoring on his part.
Ointments with local irritant effect
This group includes “Nicoflex”, “Capsicam”, “Apizartron”, “Efkamon”. They act by irritating the nerve endings of the skin. The blood vessels dilate, the blood supply to the problem area improves, and anti-inflammatory and absorbable effects appear. Patients note a decrease in pain and pleasant warmth.
"Apizartron"
The effect of the drug "Nicoflex" is associated with the irritating effect of capsaicin - the hot component of hot pepper (in "Finalgon" - a synthetic analogue of capsaicin). “Capsicam” combines active substances and camphor, gum turpentine. The action of “Apizartron” is based on the anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antibacterial effects of highly purified bee venom and mustard oil extract.
Important! The drugs act locally, but systemic reactions are possible.
"Nicoflex"
An allergic reaction to the ointment may develop. Manufacturers recommend starting treatment with a small amount of the product. The effect produced may vary between patients.
An overdose of the drug can lead to pain in the form of burning, changes in blood pressure, and increased body temperature. Special instructions apply to use during pregnancy, lactation and childhood.
It is important to follow the dosage of the drug, otherwise complications may occur
Chondroprotective ointments
This group is represented by the drugs “Chondroxid”, “Teraflex M”, “Sofya”, “Chondroitin gel”. The action of these drugs is aimed at restoring joint cartilage in combination with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
"Chondroxide"
“Chondroxide” gel and “Teraflex M” in the form of a cream contain the natural component chondroitin sulfate, which restores the structure of cartilage tissue. The complex cream of the “Sofya” series contains a complex of chondroprotectors in combination with bee venom and an extract of medicinal herbs with anti-edematous and antiseptic effects.
"Teraflex M"
Important! Side effects include an allergic reaction.
NSAIDs in the form of ointments
The group is represented by the drugs “Voltaren Emulgel”, “Butadion”, “Diclovit”, “Fastum Gel”. Drugs can have local and systemic side effects.
Local (in the area of application):
- itching, swelling, rash elements;
- eczema;
- photosensitivity (sensitivity to light).
Skin photosensitivity
Despite the local use of drugs in the form of ointments, systemic side effects may develop:
- hives;
- bronchospasm;
- allergic reaction.
Hives
For successful treatment, the manufacturer's instructions must be carefully followed.
Combined ointments and gels
Such tools perform several functions at once. An example is the Dolobene gel. It has anti-inflammatory, decongestant and local analgesic effects. Contains heparin, as well as dexpanthenol, which is involved in the synthesis of B vitamins.
"Dolobene"
Homeopathic remedies
Homeopathy is an alternative direction in medicine, which is based on the principle of “treat like with like.” Complex homeopathic preparations may contain small doses of minerals, plants, and animal poisons.
For example, homeopathic ointment "Traumel S" contains a complex of active components of medicinal herbs and some chemicals. Used for diseases of the musculoskeletal system in combination with other drugs.
Important! Manufacturers note the possibility of an allergic skin reaction when using the drug.
"Traumeel S"
Drug therapy is supplemented by taking vitamins that accelerate the restoration of nervous tissue.
Examination for sciatica
- Radiography
The method allows you to diagnose inflammation of the sciatic nerve, which is caused by pathology of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. This is a simple and quick diagnosis; the equipment is available in almost every medical institution.
- CT scan
Helps determine the source and location of pain in the sciatic nerve. The method is more informative and accurate, unlike radiography. It is possible to build slices of the lumbar spine in layers or see a three-dimensional model.
- Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI provides a layer-by-layer image of the patient's body, allowing you to obtain clear three-dimensional images of the spine, intervertebral discs and spinal cord.
MRI shows soft tissue, which is effective in diagnosing the causes of sciatica.
- Electroneuromyography
The study is carried out in patients with sciatica to evaluate nerve conduction if there is a disturbance in sensitivity and movement. Electrodes are attached to some muscle groups to record the passage of nerve impulses.
Prevention
Prevention concerns compliance with the regime of optimal loads on the spine, maintaining flexibility and mobility of the joints:
- prevention of hypothermia in the lumbar region, especially in chronic neuralgia;
- compliance with the principles of ergonomics and biomechanics when lifting weights and sudden movements;
- prevention of injuries during sports;
- prevention of postural disorders;
- regular exercise;
- timely seeking medical help for signs of sciatic neuralgia.
It is important to see a doctor immediately if you experience sciatica
Sciatica disrupts all plans, makes a person helpless, dependent on the care of other people. A reasonable attitude towards the health of your spine will protect you from physical suffering and forced abandonment of active life.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment of a pinched sciatic nerve, in consultation with a doctor, can be carried out at home, using folk remedies in parallel.
- Aspen decoction: 1 tbsp. l. Boil aspen leaves in 0.2 liters of water for half an hour. Take 2 tbsp. l. three times a day, and can also be used as hot compresses on the problem area. Store in a cool place.
- St. John's wort infusion: 2 tbsp. l. leave the raw material in 0.4 liters of boiling water for 2 hours. Drink 0.1 liter four times a day.
- Pine bath: take a bath with pine infusion for 20 minutes every day: place 1 kg of pine branches in 3 liters of water and leave for an hour. Filter and pour into the bath (approximate ratio of infusion and water is 1:15). The water in the bathroom should not be hot, but only warm.
- Wax compress: heat a little beeswax so that you can knead it. Apply to the sore spot and insulate it. Keep until the wax cools. Do it at night.
- Radish with honey: grate the black radish along with the peel and squeeze out the juice. Mix with honey, maintaining a 3:1 ratio. Rub the mixture onto the problem area until the medicine is completely absorbed. Warm for an hour. Do it three times a day.
- Rye flour compress: mix 160 g of flour and 20 g of honey. Knead the dough and form into a flat cake. Apply to the affected area, cover with film and insulate. Do it at night, course – a week.
- Cabbage compress: briefly immerse white cabbage leaves in boiling water until they become soft. After cooling, lightly coat with honey and apply to the affected area for 3 hours. Cover with film and insulate. Can be repeated three times a day.
- Turpentine: heat the turpentine in a steam bath to 40ºC. Moisten gauze and apply to the area of inflammation. Cover with film and wrap up. Do it for 10 days.
- Bear lard: rub the problem area with lard daily.
- Agave juice: do daily rubbing with agave juice: cut the thorns from a leaf of the plant, cut it and rub it on the skin. For the first time, test sensitivity on a small area. Do not rub for long, 1-2 times a day.
- Salt compress: dissolve 5-6 tbsp in 3 liters of water. l. sea or regular salt. Dip a sheep's wool scarf there and leave for an hour. Then wring out the scarf and place it on the problem area for 2-3 hours.
- Pine infusion: 1 tbsp. l. Place the tree buds in 0.4 liters of boiling water and leave overnight. Filter and drink 0.1 liter 20 minutes before meals. You can also use the infusion for compresses, increasing its concentration - take 2 tbsp. l. raw materials for the same 0.4 liters of water.