+RU
Consultation with a Phlebologist in Moscow, Articles, Reviews of Clinics
Join us and follow the news on social networks
Treatment of cerebral aneurysm is complicated by the fact that such a pathology may not manifest itself for a certain time. The danger lies not in the formation itself, but in the present risk of its rupture, which is why therapeutic measures should be taken at an early stage of development of the formation. The doctor will advise you on how to treat the pathology and what priority treatment methods in each specific case.
Pathology does not manifest itself for a long time
In medical practice, the term cerebral artery aneurysm refers to the presence of certain neoplasms developing in the blood vessels. The rate of development of the pathology can be different; the aneurysm can remain in a “dormant” state for a long time or grow sharply.
During the growth process, formation can lead to compression of individual tissues and nerve fibers. In this case, the process of supplying blood to certain parts of the brain may be disrupted. There is a risk of local hemorrhages in surrounding tissues. Read the entire article to find out about the treatment of “cerebral aneurysm.”
- Classification of aneurysms Diagnosis
- Clipping
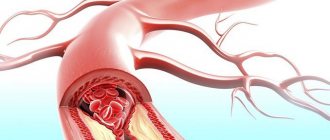
What is an aneurysm
Any artery, from the aorta to the smallest, is a three-layer tube. The inner layer, or intima, is the endothelium (epithelial cells), the middle layer consists of elastic and muscle fibers. The outer one is a mixture of collagen and connective fibers. If one of them becomes thinner or damaged, the vascular wall bulges outward under blood pressure. A bubble forms - an aneurysm - which poses a serious health threat.
Most often, defects in the arterial wall appear at the site of their branches, where the blood pressure is highest. A cerebral aneurysm consists of three structural elements: neck, body, and dome. In the cervical area, the protrusion has a three-layer structure, and its dome consists only of intima. This is where a rupture is most likely. According to statistics, it occurs mainly in patients aged 30 to 50 years, accounting for more than 80% of all cases of cerebral hemorrhages.
Rehabilitation
After the intervention, regardless of the chosen method, the patient faces a long period of rehabilitation. Doctors recommend that such patients go to specialized rehabilitation centers. The competence of employees can significantly increase the likelihood of full recovery.
After the intervention, the patient expects a long recovery period.
Attention! The duration of the rehabilitation course ranges from 1 month to 1.5 years. The progress of the recovery process depends on many factors.
Relatives should provide support to the patient. He faces a long recovery period, which involves the restoration of physical skills and social adaptation (see Dangerous consequences and possible complications of an aneurysm). If the intervention is successful and the patient’s health indicators are normal, the probability of full recovery is 80%.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient must:
- balanced diet;
- hygiene care;
- exercise therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- comfortable psychological environment.
Physiotherapeutic procedures significantly increase the effectiveness of treatment by stimulating the required body functions.
Causes
The pathology can be congenital or acquired. Vascular wall defects due to intrauterine developmental anomalies are often accompanied by other diseases. These include congenital coarctation of the aorta, multiple renal cysts, arteriovenous malformations, and underdevelopment of connective tissue.
Acquired changes are the result of various traumatic brain injuries or previous diseases. Aneurysm of cerebral vessels often develops against the background of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and hyalinosis. If the protrusion is formed after the introduction of an infectious embolus into the artery, it is called mycotic. In addition, aneurysms form due to uneven blood flow or arterial hypertension.
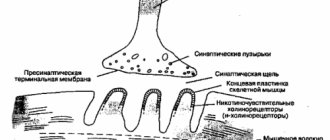
How drugs affect the brain
Vasodilator drugs for the brain in osteochondrosis are divided into two directions: central, peripheral action. When there are changes in the vasomotor system, located in the central part of the brain, medications of group 1 are used. Group 2 drugs that have peripheral effects have 2 directions:
- weakening painful nervous tics. The drugs have a nootropic principle of action: they block impulses, prevent the harmful effects of spasm on muscle tissue;
- drugs that act on vascular walls. The medicine helps to expand the patency of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The need for this therapy appears when there is a spasm of the muscle tissue responsible for the lumen in the channel. If the vessel is narrowed, blood flow worsens and tissue hypoxia occurs.
Only a qualified doctor can prescribe vasodilator medications for cervical osteochondrosis. The neurologist compiles a list of therapeutic measures and selects a medicinal complex that helps stop the development of the pathology. An important condition for taking vasoconstrictor drugs is a strictly defined duration of use.
Symptoms
In most cases, a slight expansion of the artery section does not manifest itself in any way. Such an aneurysm is most often discovered by chance or during a routine examination. When clinical signs appear, they are divided into tumor-like or apoplectic. In the first case, the formation quickly increases in size, compressing nearby brain structures as it grows.
All symptoms add up to the standard clinical picture of the tumor and directly depend on the location of the protrusion. Typically, a tumor-like aneurysm is localized in the cavernous sinus or in the area of the chiasm, the intersection of the optic nerves.
A defect in the arterial wall located in the chiasmal region negatively affects visual function: visual acuity decreases and its fields are disrupted. A long-term and fairly large cerebral aneurysm often leads to nerve atrophy followed by complete blindness. If it is located in the cavernous sinus, which is located at the base of the skull and regulates venous outflow from the eye sockets and brain, cranial nerve palsy occurs. When the 3rd, 4th and 6th pairs are affected, oculomotor disorders such as strabismus and inability to focus on an object occur.
Damage to the branches of the trigeminal nerve is manifested by the characteristic symptoms of its neuralgia. In advanced cases, even the bone tissue of the skull is deformed, which is revealed during an X-ray examination.
When the disease proceeds according to the apoplexy type, any clinical signs are most often absent. An apoplectic aneurysm is discovered only after it has ruptured and hemorrhaged into the brain. Among the symptoms that may precede this, painful sensations in the area of the eye sockets and forehead are occasionally mentioned.
The main types of drugs for osteochondrosis of the neck
The vasodilating effect can be achieved through the use of various forms and variations of drugs. Each medicine has an individual effect on the body, but they all improve conductivity and support metabolic processes. Certain forms of vasodilator drugs prescribed by a doctor as complex therapy for the treatment of neck osteochondrosis must be supervised by a specialist.
It is a mistake to believe that each vasodilator medication has the same effect on the body, regardless of the disease. The vessels in the back and neck have different structures and perform a specific role.
Understanding the mechanism for regulating the tone of smooth muscles and walls allows us to classify vasodilators based on their functional effects on the brain. Medicines are grouped according to the principles of the main components, according to the list of concomitant diseases, and according to the localization of action.
The functioning of drugs for ongoing cervical osteochondrosis is divided into neurotropes, myotropes and calcium channel blockers. Neurotropes have a reflex vasodilatory effect, centrally acting and superficial effects on brain tissue. Myotropes affect the smooth muscle tissue in the middle of the artery. The use of calcium channel blockers is indicated to prevent the formation of the actin-myosin complex, which is responsible for wall contraction. The calcium content in the preparation is necessary to maintain protein compounds in a stable state.
Aneurysm rupture
When the bulge ruptures, the first thing that occurs is a very severe headache. At first, it can be felt locally, where the damage is located. Then gradually the painful sensations become diffuse, covering the entire head. These are accompanied by the following signs of hemorrhage:
- Nausea with repeated vomiting.
- Increased sensitivity and tone of the occipital muscles.
- Kernig's sign is the inability to straighten an elevated leg bent at the knee (in a supine position).
- Brudzinski's symptom complex, when when pressure is applied to different points of the body, the limbs move involuntarily.
- Loss of consciousness for varying periods of time.
- Mental disorders (from minor to severe), seizures of the epileptic type.
Hemorrhage between the meninges - subarachnoid - causes a prolonged spasm of nearby arteries. In most cases, it leads to damage to the brain matter, as in an ischemic stroke.
If, when a cerebral aneurysm ruptures, blood enters its ventricles or substance, focal symptoms are added to the general symptoms. Specific signs depend directly on the location of the damage. When it is located in the area of the bifurcation of the carotid artery, visual function suffers. Damage to the anterior cerebral artery leads to mental disorders with simultaneous paresis of the legs, and damage to the middle cerebral artery leads to speech disorders and paralysis of the opposite side of the body. An aneurysm located in the vertebrobasilar system, as a result of rupture, causes incoordination, dysphagia, frequent eye fluctuations, paresis of the trigeminal and facial nerves.
The incidence of subarachnoid hemorrhages is about 80% of the total. Intracerebral hematomas are less common, but have more pronounced negative consequences. The most dangerous thing is bleeding into the ventricles, since the consequence is most often death. When hemorrhaging into the cavernous sinus, located outside the dura mater, the medulla is not damaged.
Features of pathology in childhood
It should be noted that dilated vessels in the child’s head are also not accompanied by too bright or pronounced symptomatic manifestations. Currently, the pathology occurs equally often in both adult patients and newborns. Despite this, the most common cause of this problem is genetic.
Thus, dilation of the cerebral arteries in newborns is associated with high blood pressure or with a malignant formation, which can develop as a consequence of a disease of infectious origin.
Pronounced signs defined by the instructions may be the following:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- problems with coordination;
- discrepancy between age and level of development.
In addition, dilation of the cerebral vessel in newborns may be accompanied by visual problems. The main sign is that the newborn loses contact with the outside world and people, which indicates an imminent rupture of the aneurysm.
In this situation, coma is quite possible. That is why the most effective control option is considered to be a timely reaction, which consists of eliminating bleeding and reducing the risk of possible complications.
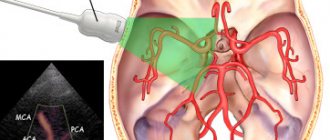
Diagnostics
Detecting a cerebral aneurysm, if it is small in size and does not manifest itself clinically, can only be done by chance. An asymptomatic disease in most cases is detected during special examinations, which are carried out for another reason. If pathological symptoms appear, you need to contact a neurologist.
Diagnosis begins with collecting anamnesis based on the patient’s complaints. A neurological examination is then performed, during which the location of the aneurysm is determined based on specific tests.
The next diagnostic stage is an instrumental examination. It includes the following manipulations:
- X-rays can be used to detect characteristic deformations of the skull bones at its base. Petrified protrusions in which calcium salts are deposited are also visible on x-ray.
- Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are more informative methods of examining the brain, but they may not be enough to confirm the diagnosis.
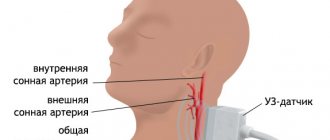
- Angiography provides the most complete picture of the condition of the vessels without introducing contrast agents into them. With its help, a three-dimensional image of the damaged artery is obtained, which allows one to judge the type, size and shape of the protrusion.
Operation
Clipping is the most complex and at the same time effective type of treatment for aneurysms in the brain, performed in an open manner. The difficulty of the neurosurgical operation is that the neck of the aneurysm must be clamped very quickly. The surgeon’s task is also to maintain blood flow in the main and nearby vessels. During the operation, blood clots are also removed from the entire area of the hemorrhage.
Strengthening the walls of the vessel is carried out using surgical gauze, which is wrapped around the area with the blood sac, thereby forming a capsule. However, with this operation the likelihood of subsequent bleeding is quite high.
Endovascular operations are performed without cranial trepanation. Before carrying out such treatment, the patency of adjacent vessels is analyzed. The essence of the operation is to block the affected vessel using special devices - microspirals.
Complications after surgery can include oxygen deprivation and cerebral vascular spasms. But modern treatment can strengthen and expand the vascular walls, regulating the intensity of blood flow in the right places.
The rupture of giant aneurysms on blood vessels in most cases ends in the death of the patient. Therefore, it is so important not to let the situation get worse and carry out timely treatment.
Treatment
An aneurysm is treated primarily surgically, since such a formation requires removal. However, if the protrusion is small in size and does not manifest itself clinically, then the neurologist is limited to systematic observation. A patient with this diagnosis is registered and examined regularly. Additionally, measures are being taken to eliminate the causes that provoked the pathology. If there is an increase in the brain aneurysm with a simultaneously increasing risk of its rupture, surgery is performed using one of the modern techniques.
General recommendations
The leading causes of this disease are atherosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes. If there are chronic pathologies, it is necessary to treat them, as well as adjust your lifestyle. First of all, you should stop smoking and reduce your alcohol consumption. These bad habits have an extremely negative impact on the condition of blood vessels for all of the listed diagnoses.
The transition to a healthy diet is one of the most important conditions for stabilizing the condition and the effectiveness of drug therapy for major diseases. It is necessary to exclude unhealthy fatty foods from the diet, minimize sugar consumption, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits, lean meat, and dairy products. Heat treatment is also important: it is advisable to boil, stew or bake dishes, and avoid fried foods.
Moderate physical activity is required. If sports are contraindicated, you need to move more, walk down the street, climb stairs without an elevator. Special gymnastics are effective in normalizing blood circulation and restoring muscle and vascular tone. In addition, with a cerebral aneurysm, it is very important to maintain a stable emotional background, be less nervous, and avoid stress.
Medicines
It is impossible to cure the pathology itself with tablets or injections, but in most cases drug therapy is necessary. Medicines are prescribed according to the established cause of the aneurysm:
- If the vascular wall becomes thinner due to atherosclerosis, special drugs are used to lower cholesterol levels. These include nicotinic acid, statins, and bile acid sequestrants. By normalizing lipid metabolism, the process of deposition of cholesterol plaques and artery deformation slows down.
- If you have hypertension, you must take medications that lower your blood pressure. They reduce the risk of rupture of an existing brain aneurysm and the formation of new ones.
- Antibiotics are used if the cause of the pathology is an infectious embolus. Antibiotic therapy is intended to treat an infectious-inflammatory process that has caused pathological changes in blood vessels.
In case of rupture with hemorrhage, drug therapy is carried out as for a hemorrhagic stroke. Drugs are used intravenously to stabilize intracranial and arterial pressure, reduce vascular permeability, as well as hemostatic agents and barbiturates. At the same time, the question is raised about the advisability of surgical treatment. Doctors, based on information about the location and volume of hemorrhage, prescribe surgery or continue treatment with medications.
Surgical intervention
The most effective method of treating a cerebral aneurysm is a microsurgical operation to remove it. The following methods of varying degrees of invasiveness are used. Cervical clipping is performed microsurgically after craniotomy. Through a hole with a diameter of no more than 4 cm, the meninges are opened, the aneurysm is isolated, and a special clip is applied to its neck. Thus, the lumen of the protrusion is blocked.
Endovascular occlusion is a less traumatic operation indicated for elderly patients, as well as in the presence of somatic diseases or the deep location of the aneurysm in the brain tissue, its spindle-shaped shape. Through an incision in the femoral artery, a microspiral is inserted into the cavity of the aneurysm, thrombosing it, or a balloon-catheter, blocking the lumen.
If there are malformations, methods of transcranial and radiosurgical removal are indicated. Stereotactic thermocoagulation and artificial thrombosis of the protrusion using coagulants are also used. If the aneurysm ruptures, surgical removal of the hematoma may be required. It is performed by stereotactic aspiration or endoscopic evacuation. In case of ventricular hemorrhage, ventricular drainage is done.
Folk remedies
Using alternative medicine recipes will not help get rid of a cerebral aneurysm. However, it is possible to stabilize blood flow and pressure, reduce the concentration of sugar and cholesterol in the blood using folk remedies. The following are considered the safest and most effective:
- To reduce sugar levels, use a decoction of oat grains or flax seeds, a mixture of ground buckwheat with kefir, lemon juice with chicken eggs. Herbs are also useful - St. John's wort, wormwood, immortelle and others.
- Herbal medicine is also used to reduce cholesterol concentrations (golden mustache, bearberry, ginseng, and dandelion are effective). Honey, bee products, flaxseed oil, garlic, and lemons are especially effective.
- Ginger, milk-garlic drink, and herbal teas with honey will help stabilize blood pressure.
It is important to remember that folk recipes are only an addition to the main treatment. In addition, all home therapy methods must be coordinated with a doctor.
Prevention
To ensure that the vessels are in normal condition, you should adhere to a set of rules for nonspecific prevention:
- Avoiding stress. Balance between work and rest.
- Normal sleep. It is recommended to sleep from 7 to 8 hours a day, but not less than 6. However, the number of hours depends on each individual.
- Balanced diet. The diet should include vegetables, fruits, cereals, herbs, juices - all these products contain vitamins and biologically active substances that affect vascular tone, wall integrity and rheological properties of the blood.
- It is recommended to visit the gym 2 to 4 times. Loads must be dosed. For prevention, you can simply go for a morning jog and do gymnastics.
Source: sortmozg.com
Forecasts
The outlook for a patient with an aneurysm is assessed in many ways. The size, location and nature of the protrusion and its tendency to increase are important. If the formation is small, does not grow and does not manifest itself in any way, you can live your whole life without a rupture or surgery. The presence of chronic diseases that negatively affect the condition of the vascular wall worsens the prognosis. In this case, the risk of rupture or formation of a new aneurysm increases many times.
According to statistics, a ruptured protrusion leads to death in the range of 30 to 50% of all cases. Among survivors, about a third acquire permanent disability, and in a quarter, hemorrhages occur repeatedly. Moreover, the second rupture leads to death much more often - in 70% of cases.
Contraindications
Abuse of vasodilator drugs may not bring the desired result or cause significant harm to the body. Self-prescribing medications for pain is risky and hazardous to health. The drugs are selected individually by the attending physician, assessing the patient’s general condition and taking into account the course of the disease.
Vasodilation drugs actively remove calcium from the body. This side effect can significantly weaken bone strength and reduce the regenerative effect of other drugs aimed at restoring bones and cartilage tissue.
The effect is on damaged vessels and on those in a healthy state. As a result, swelling and varicose veins may appear.
The use of vasodilator medications is strictly contraindicated for:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- epilepsy;
- cardiac disorders;
- hypertension;
- renal failure.
Activation of the performance of the vascular bed in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine using drugs shows excellent results, but it is necessary to approach therapy in a comprehensive manner, simultaneously using other means and medications.
Source: ipozvonochnik.ru