general information
Chest (intercostal) neuralgia can hardly be called an independent disease.
It is a pain symptom that occurs when nerves are pinched. This can happen for many reasons, but the most common is the development of thoracic osteochondrosis. This pathology is accompanied by degenerative-dystrophic processes in the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. Many people believe that to cure neuralgia, you only need to get rid of osteochondrosis. In fact, this opinion is wrong. The thing is that the thoracic spine is the least mobile area of the back. Due to the fact that pain occurs extremely rarely, the body cannot “tell” about the appearance of osteochondrosis in a timely manner. As a result, the disease continues to progress, becomes severe and causes complications, including thoracic neuralgia.
Can there be a cough with thoracic osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis, being a disease of the spine, provokes the development of many unpleasant phenomena, the most common of which is pain. But few people know whether a cough can occur with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region.
And such ignorance, first of all, manifests itself due to the not too high prevalence of this form of the disease.
A cough can indeed accompany osteochondrosis, but in this case the patient must seek medical help to avoid the development of serious pathologies.
How is cough related to osteochondrosis?
With such symptoms, it is almost impossible to correctly diagnose thoracic osteochondrosis on your own.
Due to the fact that the appearance of osteochondrosis provokes compression of the blood artery, there is a significant decrease in the level of oxygen received by the tissues of the chest, as well as the neck and brain.
This causes muscle spasm and increased pressure in the narrowed blood vessels. As a result, the patient experiences a sensation of a lump in the throat and a feeling of constriction in the lungs, which manifests itself as a cough due to osteochondrosis of the thoracic region.
Frequent and prolonged stay of the body in an uncomfortable position, as well as the lack of active sports, aggravate the situation, contributing to further destruction of the spine.
In this case, strong compression of the first six thoracic roots occurs. This provokes serious pain and discomfort in the throat, which reflexively causes the desire to cough.
Therefore, the answer to the question of whether there can be a cough with the thoracic form of osteochondrosis is definitely positive.
Features of cough
Cough with thoracic osteochondrosis contributes to a significant increase in blood vessel pressure. As a result of this, through the narrowed arteries there is a decrease in blood supply to the upper parts of the spinal cord. This phenomenon provokes the development of serious problems in the form of disruption of the heart muscle, brain, stomach and genitourinary system.
The appearance of cough in osteochondrosis is often confused with symptoms of other diseases. At the beginning of its occurrence, the cough is accompanied by a sore throat and is very similar to the development of a sore throat. The cough itself is dry and paroxysmal.
And if left untreated, discomfort increases significantly and is often observed at night. The cough becomes wet and is often accompanied by hoarseness.
A patient in this condition constantly tries to clear his throat and, despite the absence of obstructions in the throat, is afraid of suffocating during sleep, as a result of which rest patterns and mental health are disrupted.
Due to the fact that with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, the main symptom is pain, in combination with cough, these manifestations are often mistaken by patients for signs of tuberculosis or pneumonia.
In addition, depending on the location of pinched roots, pain when coughing can manifest itself in the following way:
- in the chest area, causing a feeling of stiffness;
- near the heart. Often the pain radiates to the arm or under the shoulder blade, as a result of which this symptom can be confused with a heart attack;
- under the ribs;
- in the upper or lower abdomen. In this case, the disease is often confused with pathologies of the digestive system.
With such symptoms, it is almost impossible to correctly diagnose thoracic osteochondrosis on your own.
Confirmation of the relationship between symptoms during diagnosis
Confirmation of the relationship between cough and thoracic osteochondrosis occurs with the diagnostic detection of the following factors:
- unnaturally small distance between the vertebrae;
- the presence of osteophytes on the vertebrae and articular processes;
- hernias and protrusions on intervertebral discs;
- pinched blood vessels and nerve endings;
- inflammatory process in the vertebral area.
Also, one of the confirmations of the nature of the cough is the presence of severe scoliosis.
Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment
The main subgroups of pharmaceutical drugs that help cope with the manifestations of intercostal compression are anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants. The mechanism of their effect on the pathological focus is based on the ability to quickly reduce swelling in the nerve fiber, as well as increase the space in the pinched area.
If the thoracic spine is affected - intercostal neuralgia, treatment usually begins with the following medications:
- Nise;
- Aertal;
- Movalis;
- Mydocalm;
- Baklosan.
Additionally, specialists prescribe subgroup B vitamins - Milgamma, Neuromultivit, Combilipen. They help improve the conduction of nerve impulses in intercostal tissues and reduce the area of inflammation. Sedatives and analgesics, for example, Paracetamol, restore the patient’s well-being.
Traditional medicine methods successfully complement traditional treatment recipes. Various decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants have an equally strong anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, they have virtually no contraindications or restrictions. However, each of these prescriptions should be agreed with your doctor.
There are many treatment options for neuralgia. As a rule, they involve taking anti-inflammatory and painkillers, physiotherapeutic actions and recipes from traditional healers. The main and priority is a timely visit to a doctor, because only a specialist can determine the cause of the pathology and prescribe adequate therapy. How to treat intercostal neuralgia of the chest?
As noted above, therapists primarily prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs (Piroxicam, Ibuprofen) and painkillers (Spazmalgon, Analgin, Sedalgin). They help relieve swelling of inflamed muscles and reduce pain discomfort. The course of treatment usually lasts from 5 to 10 days.
The next stage of treatment is taking muscle relaxants (Baclofen, Clonazepam). These drugs help relax muscle tissue and release peripheral nerves by increasing the intercostal spaces.
When treating intercostal neuralgia, one should not forget about increasing immunity. For this, patients are prescribed multivitamin and mineral complexes to normalize metabolism in the body and improve blood circulation.
Very often, doctors, in the fight against this pathology, combine traditional methods of treatment with folk ones. After a complete examination in a medical facility and determination of the cause of the pinched nerve, you can proceed directly to the therapy itself.
What to drink for chest neuralgia? Traditional healers recommend tinctures of wormwood, elderberries, peppermint, and chamomile. All these plants are characterized by a calming and at the same time analgesic effect, which is extremely necessary during exacerbations of pathology.
At the same time, you can apply compresses to the affected areas. Thanks to their warming effect, they reduce pain discomfort and swelling of muscle tissue. Horseradish, honey, agave leaves, and apricot kernels are perfect for compresses. You can prepare a healing mixture from any ingredient, and then apply it to the affected area and wrap it in a woolen scarf. This treatment should be repeated regularly for two weeks.
You can also prepare a rub. It will require a tablespoon of garlic oil and 0.5 liters of vodka. The ingredients should be mixed and then gently rubbed into the skin.
For neuralgia, it is very important to use not only folk remedies; therapeutic treatment is considered mandatory. It is important to remember that rubbing, ointments and decoction can only be used after consulting a doctor. Treatment at home often worsens the patient’s condition and leads to the development of life-threatening complications.
Non-drug methods can be much more successful in combating the symptoms of intercostal inflammation. After assessing the patient’s condition, the specialist will recommend acupressure massage, physiotherapy, and a course of manual assistance.
Additional methods to improve well-being with neuralgia:
- manual therapy - restoration of the correct position of the vertebrae in the thoracic region, correction of blood circulation in this area, reduction of pain;
- acupressure, cupping, vacuum massage - improving nutrition in tissues, increasing lymph flow in them;
- reflexology - acupuncture, acupuncture to influence reflex zones, relieve spasms from them, eliminate unpleasant sensations;
- the use of special gymnastics in some cases also improves the patient’s well-being - the doctor will determine the indications for its implementation.
After the symptoms of the acute period of intercostal disease subside, the specialist may recommend completing treatment in a sanatorium. Courses of hydrotherapy, mud therapy, hirudotherapy, and therapeutic wraps will help you get rid of neuralgia forever.
If the first signs of the disease occur, you should immediately visit a doctor. Diagnosis is based on the study of symptoms, patient complaints and objective examination data. Instrumental examination methods play an important role:
- MRI;
- computer diagnostics.
X-rays can reveal not only osteochondrosis, but also traces of injury. Neuralgia is diagnosed by palpating painful points located on the patient's ribs. Blood and urine tests are performed at the same time. An effective method is an ECG, which helps to distinguish heart pain from an attack of neuralgia. There is often a need to conduct a fluorographic examination of the lungs to ensure the absence of a tumor.
Myelography detects changes in nerve tissue in the spine. To conduct the study, a contrast agent, oxygen, is used. In some cases, side effects develop after the procedure:
- frequent headaches;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- heartburn;
- nausea.
Causes of pathology
The cause of compression or irritation of the nerves is deformation of the intercostal spaces, which can lead to recent or past injuries, diseases of the spine (curvature, osteochondrosis, herniated intervertebral discs), exposure to bacterial toxins, heavy metals, certain medications, diseases of the nervous system (polyradiculoneuritis, multiple sclerosis), infections (tuberculosis, influenza), allergies, decreased immunity.
Thoracic neuralgia can also appear as a result of cardiovascular pathologies (atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, anemia) due to insufficient oxygen flow to the nerves. The disease can be triggered by inflammatory processes in the ligaments and joints of the spine, changes associated with hormonal imbalances in women during menopause, and salt deposits in the spine.
Often, thoracic neuralgia is a consequence of alcohol abuse, diabetes, hypothermia, and lack of B vitamins in the body, which is often observed with gastritis, colitis, gastric ulcers, hepatitis (it is with these diseases that the metabolism in the nerve tissues suffers first). The development of the disease is possible after suffering a herpetic infection, with diseases of the internal organs, or aneurysm of the thoracic aorta.
However, the most common cause of intercostal neuralgia, which all experts agree on, is an acute muscle spasm, provoked, for example, by an unsuccessful turn or an awkward sudden movement of the body, a long stay in the same position or in a draft, sleeping in an uncomfortable position, unusual physical stress on the spine. It should also be noted that thoracic neuralgia is much more common in older people than in young people.
So, as you probably already understood, there are a lot of causes of pathology, but we have not yet listed a complete list. Under the influence of only one factor, intercostal neuralgia develops extremely rarely; usually several ailments are involved at once. Therefore, sometimes even an experienced doctor cannot determine where one disease ends and another begins.
Very often, the unpleasant sensations intensify when exhaling/inhaling; breathing becomes so difficult that even a slight expansion of the chest during inhalation results in sharp pain.
Signs of thoracic neuralgia should be distinguished from manifestations of other diseases, primarily by the area of pain localization. First, pain is felt in the area of the ribs (in the intercostal spaces), but it can also be observed, for example, in the back, under the shoulder blade, in the lumbar region. Such radiating sensations do not indicate the actual source of nerve damage.
Thoracic neuralgia may have other symptoms. Thus, pain is often accompanied by a distinct twitching (contraction) of individual muscles, a change in skin color (unhealthy pallor or, conversely, redness), and intense sweating. In the area of direct damage to nerve segments, the skin may become numb, that is, lose sensitivity.
Treatment of the disease begins with diagnosis, which only a doctor can correctly carry out, so if the first symptoms occur, you should immediately contact the clinic.
Prevention
Taking preventive measures can reduce the risk of intercostal neuralgia, as well as speed up treatment if it has already appeared. Therefore, it is worth paying attention to the basic rules of prevention and special gymnastics.
Basic Rules
Simple recommendations help reduce the risk of neuralgia, fight it if a person is already sick, and also improve the general condition of the body, allowing you to avoid many different diseases.
Just follow the rules:
- Treat your spine in a timely manner;
- Improve your immunity, take care of your health;
- Try not to get too cold;
- Allow sufficient time for breaks during work;
- Eat right, give up bad habits.
Such rules are especially important for people of retirement age, as well as those who suffer from chronic diseases associated with the spine.
Gymnastics
Special gymnastics shows high effectiveness against thoracic neuralgia. In most cases, it is able to affect even the underlying cause, which makes it very important for general therapy. Therefore, it is recommended to pay special attention to it.
Popular exercises:
- Lie on your back, begin to pull your legs one by one towards your chest, bending your knees. Additionally, you should try to reach your knees with your forehead.
- Roll over onto your stomach with your arms stretched forward. Raise your upper body upward, bending your back.
- Sit on a chair, clasp your hands behind your head, lean forward. After this, stand up and additionally bend or turn 90° with your entire torso.
- Lying on your back, stretch your legs and bend your arms at the elbows perpendicular to the floor. Tightening your chest muscles, slowly move your arms up and down.
- Stand up straight, spread your arms straight to your sides. Using the abdominal and chest muscles, rotate both sides of the body in the shoulder area.
Such exercises can only be performed when you feel normal, because... during an exacerbation, they will not provide any help and will harm the body.
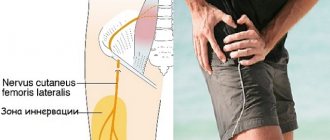
Anatomy of the intercostal nerve
Many nerve bundles extend from the spinal ridge, most of which are localized in the intercostal space. Muscles are attached to the ribs above and below. They are responsible for inhalation and subsequent exhalation. Between them is a thin intercostal nerve. During the next attack, impulses travel along nerve fibers to the brain and spinal cord, and the person feels pain.
As a result of osteochondrosis, scoliosis or displacement of the vertebrae, the intervertebral nerve is reflexively pinched. An unbearable pain occurs that spreads throughout the entire sternum.
Since such discomfort cannot last forever, nerve root atrophy develops. The pain goes away over time, but at the same time the volume of breathing decreases and a characteristic feeling of heaviness appears. Thus, neuralgia of the chest develops, the treatment of which requires a lot of effort.
Neurological spasm of the chest can provoke the development of neuritis, which is characterized by inflammation of the nervous tissue. To avoid these complications, you must follow the following recommendations:
- avoid hypothermia;
- dose physical activity;
- adhere to a balanced diet;
- give up cigarettes and alcohol.
Before starting strength exercises, warm up your muscles well. Persons with osteochondrosis and other pathologies affecting nerve fibers are recommended to regularly undergo a comprehensive examination and go to a sanatorium for treatment every year.
Types of neuralgia and their features
Trigeminal neuralgia is one of the most painful types of this disease. Facial neuralgia is a disease with sharp outbreaks of pain in the areas where the trigeminal nerve transmits nerve impulses. Painful attacks last from 10 seconds to 3 minutes, and are aggravated by sneezing, chewing and talking. Patients experience severe psychological trauma and physical torment, as they are forced to constantly live with pain that interferes with their normal life and function. The main symptoms of facial neuralgia:
- unbearable pain in trigger areas;
- increased lacrimation;
- salivation;
- twitching of the facial muscles.
With cervical neuralgia, pain is caused by the occipital nerves and affects the neck, back of the head, head and eyes. Pain from neuralgia of the neck is often confused with migraine and neuritis. Symptoms of occipital neuralgia are characterized by:
- pain when turning the neck and touching the back of the head;
- photophobia;
- sometimes vomiting and fainting;
- loss of sensation in the neck.
Cervical neuralgia is often confused with cervical osteochondrosis and myositis.
Brachial plexus neuralgia most often affects the right arm, thereby significantly complicating the life of a person, especially a right-handed person. Of all types of neuralgia, this disease occurs most often. Symptoms of shoulder neuralgia are:
- paroxysmal pain in the shoulder and scapula area;
- increased sweating;
- muscle twitching;
- pallor or redness of the skin;
- muscle spasms.
This disease is characterized by breaks between attacks of pain, as in trigeminal neuralgia. If the disease is not treated, neuritis may soon develop, which carries not only unpleasant sensations, but also paralysis of the limb.
With intercostal neuralgia, pain is localized in the ribs. Particularly severe pain occurs when the body is in an awkward position.
Lumbar neuralgia is paroxysmal in nature: the pain either recedes or comes again. This type of neuralgia is often confused with diseases of the kidneys or genitourinary system due to the aching nature of the pain. The main symptoms of neuralgia of the back:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- increased sweating;
- redness or paleness of the skin;
- edema;
- muscle spasms;
- the pain intensifies when pressing on the lower back;
- nausea;
- dizziness.
This type of neuralgia, if left untreated, can also lead to neuritis and, consequently, paralysis of the back.
Damage to the sciatic nerve causes acute pain in the lower back, radiating to the hip and upper leg. This type of neuralgia, which affects the largest nerve in the human body, is called sciatica.
Self-diagnosis
If signs of intercostal neuralgia appear for the first time in a person, it is unlikely that he will be able to correctly identify the disease. Moreover, by misdiagnosing yourself, you can get unwanted complications.
It can be:
- The pain syndrome will become chronic.
- Exacerbation of diseases of the digestive system.
- Ischemic attack, up to stroke.
- Frequent attacks of angina pectoris.
- Hypertensive crisis.
Therefore, it is better not to take risks, but to immediately contact a neurologist.
For an experienced specialist, it is not difficult to diagnose intercostal neuralgia based on characteristic complaints - pain in the intercostal spaces when turning, bending, and also when examining the patient - touching the inflamed tissue increases discomfort.
However, it is imperative to carry out diagnostic procedures in order to exclude the course of other internal diseases in which the clinical manifestations will be similar. Examination of the area of intercostal spaces implies:
- chest x-ray - identification of injuries, cracked ribs, course of degenerative lesions of the vertebrae, curvature of the spine;
- electrocardiogram - to assess the activity of the heart and its parts, the presence of foci of myocardial ischemia;
- a biochemical blood test allows you to timely recognize the course of rheumatoid and gouty processes in the body;
- if oncology is suspected, the specialist will recommend computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging - the images can more clearly examine the localization of the pathological focus, its size, and the involvement of neighboring structures.
After analyzing all the information from the diagnostic measures, the specialist will decide what to do for neuralgia and how to treat it.
Symptoms of pathology
With intercostal neuralgia, pinching of the peripheral nerves is observed. They can be compressed by muscles, ribs or intervertebral discs. There are many reasons for the development of such a pathological process, the main ones among them are the following:
- Diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, scoliosis, lordosis), characterized by deformation, displacement and curvature of the spinal ridge or certain parts of it.
- Pathologies of the central nervous system.
- Problems associated with metabolism and vitamin deficiency in the body (diabetes, gastritis). A lack of B vitamins provokes changes in metabolism and restructuring of all processes in the body, which affects the state of the central nervous system.
- Injuries. With mechanical damage to the chest area, the intercostal spaces change. Any sudden movements cause unbearable pain.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Age-related changes.
- Intoxication. Abuse of alcoholic beverages or poisoning may also develop chest neuralgia.
A weakened immune system is also considered an important factor in the occurrence of this pathology. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend adhering to a healthy lifestyle and monitoring the intake of vitamins into the body, especially in the winter season.
Muscular neuralgia of the chest is similar in its symptoms to heart diseases, because pain discomfort is observed in approximately one area. However, there are proven methods aimed at determining the true causes of unpleasant sensations.
Pain with intercostal neuralgia noticeably intensifies with sudden movements, coughing or breathing. Heart diseases in their manifestations do not depend on bending or turning the body.
The clinical picture of intercostal neuralgia is characterized by a prolonged period of pain. When a nerve is pinched, the discomfort persists for a very long time, sometimes it does not go away even after taking medications. In the case of cardiac pathologies, the pain is short-term and periodic.
Diseases that affect the main muscle of the human body are usually accompanied by an increase in blood pressure and a change in heart rate. With neuralgia of this kind there are no symptoms.
When a nerve is pinched in the thoracic spine, the patient experiences pain of varying degrees of intensity. Symptoms are localized on the left or right side. The pain often acquires a girdling character, radiating to the back, forearm and upper limbs. The intensity of symptoms of chest neurosis increases when the patient makes movements, inhalations or other actions.
Neuralgia is characterized by a decrease in skin sensitivity in this area. Due to damage to the nerve endings, symptoms manifest as stiffness in the chest and inability to take a deep breath.
Another feature of neuralgia is that pain can return in the absence of irritants. So, the patient experiences discomfort in the chest area during sleep or at rest.
The localization of the pain syndrome depends on which part of the nerve plexus has ceased to function normally. If the pathological process affects the fibers lying on the anterior wall of the sternum, symptoms appear in the heart area. When localized near the shoulder blades, the pain syndrome increases with inhalation and exhalation.
The difficulty in identifying the disease lies in the occurrence of symptoms characteristic of other pathologies. At the same time, neuralgia does not pose a serious threat to life and health, while cardiovascular diseases with similar symptoms often cause the death of the patient. Therefore, it is important to exclude concomitant pathologies before the examination begins.
Neuralgia can be differentiated from other diseases by the characteristics of its manifestation. The following symptoms indicate a heart attack and angina:
- intense and squeezing pain localized on the left side of the chest;
- feeling of lack of air;
- paleness of the skin;
- feeling cold;
- nervous and physical tension.
Diseases not associated with heart damage are indicated by:
- dull and aching pain in the left side of the sternum;
- physical and nervous stress.
When intercostal neuralgia is concerned:
- severe, shooting pain that manifests itself along the intercostal nerve;
- increased sweating;
- blood pressure surges;
- increased pain during movement;
- redness or paleness of the skin.
But unlike other pathologies, this disease has a clear external symptom: numerous blistering rashes on the body, the growth of which is accompanied by severe itching.
Pain under the ribs when coughing: understanding the causes
The cough itself is unpleasant. When you add pain under your ribs, the situation becomes complicated. It is impossible to diagnose the causes of discomfort by symptom alone. It can be triggered by a virus, injury, or diseases of the cardiovascular system or internal organs. Nevertheless, let’s try to figure out why my ribs hurt when I cough.
Coughing causes pain in the right or left side: common causes
The spectrum of influence of pathologies in the body in a situation where the ribs hurt when coughing is wide. Let's outline the key points:
- Pneumonia. Among other symptoms, there is pain in the hypochondrium. To reduce discomfort during treatment, try not to provoke attacks; bed rest and reduced physical activity are required.
- Pinched nerve. Pain in the ribs when coughing can be caused by intercostal neuralgia. Unpleasant sensations worsen with movement and become unbearable. You may need the help of an osteopath to get rid of them completely.
- Damage. Violation of the integrity of muscle tissue can be especially pronounced when coughing. An obsessive aching pain in the side intensifies with a sharp muscle contraction.
- Unilateral pleurisy. It can be diagnosed as an independent diagnosis, or as a consequence of a complication. The lateral side of the rib area may hurt, flatulence may be observed, and other symptoms may be associated.
To understand what exactly provokes a cough, you need to listen to the sensations. Feel which side the hypochondrium hurts on, the nature of the pain and the frequency of its occurrence. What disease causes acute processes and how to treat it can only be told by a qualified specialist. Moreover, he will do this after collecting tests and additional examination.
Pain in the right hypochondrium: causes
Many vital organs are located on the right side of a person. To understand why the ribs on the right side hurt when you cough, you need to understand what diseases can affect this.
- Right-sided pneumonia
- the part of the right lung in front hurts. A severe cough is a warning sign. This indicates a progressive course and requires an early examination by a doctor. - Right-sided intercostal neuralgia
– the patient has difficulty coughing, and encircling spasms occur that radiate to one side of the body. This happens if a nerve is damaged. The cause may be advanced osteochondrosis or injury. - Damage to the right hypochondrium
- the main characteristics of the disease are aching pain and shooting attacks. Usually there are no difficulties in diagnosis; the patient himself talks about recently received injuries. Symptoms go away quite quickly after starting treatment. - Right-sided dry pleurisy
- the disease is most often diagnosed as a complication after an acute respiratory infection. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis only after examining the x-ray. - Liver damage
– pain in the side can be caused by an enlarged liver. This is accompanied by other symptoms: high fever, bitter taste in the mouth and problems with stool. Another sign is a yellow tint to the whites of the eyes and skin. - Appendicitis
– the appendix is localized on the right. The inflammatory process that occurs in it will be felt by severe pain on the right, including when coughing.
- Gallstone disease
– pain under the scapula and in the epigastric region. This may be evidence of cholecystitis. Often discomfort associated with the gallbladder is observed in women during pregnancy. Moreover, as the fetus grows, the pain increases. This is due to a violation of the bile ducts. - Pathology of the right kidney
- this is the verdict a doctor can make if, when coughing, the patient experiences discomfort on the right and behind. At the same time, it is physically difficult for him to be in the same position. It’s easy to make sure that you have this particular illness - just lightly hit the area of the lower rib from behind. If an attack of acute pain follows, then the right kidney is not in order. If the spine and lower back react to the blow, then most likely the cause of the discomfort is urolithiasis. - Gastric ulcer
– this disease can cause pain in the anterior hypochondrium. A person feels better when pressing on a painful point. The torment stops if you squat down or lie face down. - Degenerative processes in the pancreas
- they are accompanied by sharp lumbago on the side. They are caused by poor diet, alcohol poisoning, overloading the body with fatty foods, or exacerbation of a chronic disease. - Amebiasis
is an ulcerative disease of the intestines. Causes complications, affecting the liver and lungs. Naturally, this causes pain on the right side of the torso. - Neoplasms on the right side of the chest
- pain can be caused by cancer.
Of course, in some cases you can diagnose it yourself. But most diseases occur with similar symptoms. Therefore, self-medication in this case is useless and even dangerous.
Pain in the left hypochondrium: causes
When the left side of the body begins to hurt, it becomes uneasy. This part contains the heart, one of the most important life-support organs. Therefore, when the left side under the ribs hurts when coughing, you need to recognize the causes of the discomfort as quickly as possible. And, as in the case of the right side, there are a lot of them.
- Heart disease
- despite the fact that any pain on the left side raises suspicion about the work of the heart, confirmation of this is rare. Diseases of the cardiovascular system usually manifest themselves at rest. But it won’t hurt to get checked by a cardiologist.
- Left-sided pneumonia
, unlike right-sided pneumonia, brings more trouble. The fact is that the left lung consists of two lobes, and in place of the third is the heart. Any inflammation can result in a serious illness. - Left-sided pleurisy
- as already mentioned, this is a complication after ARVI that responds well to treatment. - Bronchitis
is a disease caused by a virus. It looks like a cold, the sputum thins gradually. Lack of treatment leads to development into a chronic form. Constant tension in the muscles provokes pain in the hypochondrium. - Gastrointestinal diseases
- pain in the left side under the ribs with cough can be caused by a stomach ulcer, gastritis, inflammation in the intestines. The patient has a history of difficulty breathing and fever and abdominal pain. - Kidney diseases
- degenerative processes cause colic in the lower left hypochondrium, and it is so strong that there is a risk of losing consciousness. In particular, with pyelonephritis, the patient’s temperature rises and difficulty urinating.
- Pancreatitis
- the pancreas is located in the middle of the body, just above the navel. If it cannot cope with the processing of incoming substances, this results in a glut of toxins and an increase in the organ’s size. This may cause discomfort under the ribs. The condition worsens after eating. - Injuries in the left intercostal space
- just as in the case of the right side, mechanical injuries are diagnosed and treated quickly enough. - Tietze syndrome
is an inflammation of the cartilage in the rib area caused by injury. - Diaphragmatic hernia
- the diaphragm separates the thoracic and abdominal sections. When a hernia forms, lumbago appears under the left rib. If a person tries to take a deep breath, it becomes even more painful. - Osteochondrosis
– discomfort when coughing can result from degenerative processes in the joints, as well as injuries to various parts of the spine. - Neoplasms in the lungs
- stabbing lumbago can cause cancer. With metastases, blood appears in the sputum.
Pain in the left side under the ribs when coughing is a controversial, but very serious symptom that cannot be ignored. You need to remember that the sooner you get a professional diagnosis, the sooner you will get rid of unpleasant sensations.
Diagnosis of pain
This review provides general information on what may cause pain in the hypochondrium. Only a specialist can understand the true reasons. It uses modern diagnostic tools:
- Initial examination - the doctor examines the color of the whites of the eyes, skin and tongue, if there is an assumption that the cause of the illness is liver failure.
- Palpation - in case of inflammation of the kidneys, liver or gall bladder, pathology can be detected by pressing on the painful points.
- Studying the medical history for the presence of chronic forms of diseases.
- Laboratory tests - you need to donate mucus, blood, urine and feces.
- Chest X-ray - allows you to identify pathologies in the lungs, heart and spine.
- Electrocardiogram – prescribed for suspected diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Ultrasound examination of organs.
- Fluorography - helps to identify pathology in the lungs.
First, see a therapist. After studying the first results, he will refer you to specialized specialists. In difficult cases, hospitalization is performed. Often both men and women are afraid that treatment will end with surgery. Let us note that surgical intervention is performed in cases of appendicitis, heart disease or damage to the spleen, that is, in cases where life and death are involved.
Acceptable treatments
Frequent use of painkillers can make studying the disease more difficult. But before meeting with a doctor, you need to relieve the pain. You can use antispasmodics, but don’t get carried away. The following medications will help at home:
- No-spa – take 1-3 times a day.
- Nitroglycerin - the pill is placed under the tongue, dissolving.
- Baralgin - prescribed as injections.
Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before taking any drug. For pneumonia, pleurisy, bronchitis, and also if sneezing is added to the cough, doctors prescribe medications:
- antibacterial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- bronchodilators;
- immunomodulators.
Warming ointments are contraindicated for pain in the hypochondrium. But physiotherapy and electrophoresis, on the contrary, have only a positive effect. If you have gallbladder diseases, you do not need to take choleretic drugs; they can cause tissue rupture. If symptoms are observed in a child, you need to call a doctor and feel the tummy.
You can apply a cold compress to the sore side. The main thing to remember is that if the doctor has prescribed bed rest, you need to stick to it until the condition improves. This applies to both children and adults. Routine diagnostics will help avoid illness. Regular ultrasounds and tests will keep the whole family healthy.
After all, as you know, it is better to prevent a disease than to treat it.
Source: //zen.yandex.ru/media/lor/bol-pod-rebrami-pri-kashle-razbiraemsia-v-prichinah-5a88389c168a91266ca8267d
Why do chest pains occur?
A logical question: if everything was relatively in order with health, why do attacks with high intensity immediately occur? In fact, it is rare for anyone to be regularly examined by a cardiologist. Most cases of angina are so-called exertional angina, which occurs after physical or emotional stress. If the attack occurs after sleep, it is angina at rest.
Actually, angina is a violation of the blood supply to the human heart muscle. Such constant oxygen starvation leads to the development of coronary heart disease and heart attack. The main risk factors here are:
- arterial hypertension;
- disorders of fat metabolism and atherosclerosis;
- impaired carbohydrate metabolism and increased blood sugar levels;
- congenital or acquired heart defect.
Intercostal neuralgia is pain running along the trunk and branches of any of the intercostal nerves (there are 11 pairs of them, and the 12th pair are the subcostal nerves). It occurs due to compression, irritation or inflammation of the nerve. There are many reasons for the appearance of neuralgia - problems with the spine (osteochondrosis, displacement and herniation of intervertebral discs), infections (including influenza), radiculitis, neuritis, injuries, hypothermia, and excessive muscle tone...
It's hard when children get sick
Thoracic neuralgia also occurs in children, and the disease is registered even in fetal development.
The symptoms of thoracic neuralgia in a child are the same as in adult patients, and it is difficult to realize that a child has to endure such pain. Factors that cause compression of nerve endings between the ribs in children are determined by doctors separately for children:
- birth injuries;
- stress or depression of the expectant mother;
- excessive physical overload of the child;
- prematurity;
- congenital or acquired diseases of the spine;
- untreated infections;
- weak immune system;
- vitamin B deficiency;
- accidental hypothermia;
- long stay in a drafty room.
The manifestations of the disease in children are the same as the symptoms of thoracic neuralgia in adults. The childhood form of neuralgia is easier to treat, because the rapidly growing body copes with physiological abnormalities, and the regeneration processes in children are strong and fast.
Intercostal neuralgia code according to ICD-10 has M 79.2 and is designated as “neuralgia and neuritis”. It is characterized by symptoms that are also similar to a heart attack, so consultation with a doctor in case of illness is mandatory. In addition, unpleasant anterior chest wall syndrome can be caused by the following ailments:
- stomach ulcer;
- psychological problems;
- myocardial infarction;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- kidney diseases;
- scoliosis;
- thoracic neuralgia;
- kyphosis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- gallbladder pathology;
- thoracic hernia.
Neuralgia of the thoracic spine: symptoms and treatment
Chest pain is the main symptom of this pathology. As mentioned above, the cause is entrapment of the intercostal nerve. As a rule, discomfort is concentrated in a certain area. It is also possible that the pain radiates to the lower back or the area under the shoulder blades.
Neuralgia is often mistaken for heart disease due to similar symptoms. However, in this case, pain discomfort increases with sudden movements or bending. That is why it is best to seek help from a doctor who can make an accurate diagnosis and determine the cause of the discomfort.
A person with neuralgia has changes in posture and posture. He periodically leans to one side, hoping to stretch the intercostal spaces to relieve pressure on the affected area.
The nature and severity of pain may also vary. These indicators depend on the degree of nerve entrapment. Often patients with this diagnosis cannot fully inhale and exhale, and every movement is accompanied by unbearable chest pain. Sometimes the back muscles are involved in the pathological process. They begin to twitch, with profuse sweating, and the skin in the affected area loses normal sensitivity.
When the disease occurs, pain appears in the area of the ribs, which can be sharp, burning, and aching. Moreover, this is observed constantly and only periodically. Soreness becomes noticeable with activity, for example, when sneezing, coughing, or changing body position. There may be pain when palpating the areas, which is noticeable when exhaling or inhaling. It becomes difficult to breathe, which is why any process can cause pain.
Symptoms of thoracic neuralgia must be distinguished from other ailments, which is determined by the area of pain. Discomfort is felt in the ribs, as well as in the back, lower back, and under the shoulder blade. These sensations indicate the presence of nerve damage.
Often pain occurs in only one place. Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia may appear, such as muscle twitching, changes in skin color, and severe sweating. The skin in the area of damage becomes numb. If any signs are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor. Timely treatment is necessary, and then very soon an improvement in the condition will be noticeable.
Causes of pathology
How to treat thoracic neuralgia with cough
According to the ICD, intercostal neuralgia has code M79.2. It belongs to the category of “neuralgia and neuritis”; the malaise is often confused with a heart attack, because their symptoms are largely similar. It can occur after irritation and pinching of the nerves located between the ribs in the chest area, which is accompanied by severe pain.
Risk factors
Under certain circumstances, people may develop neuralgia for no obvious reason. This is caused by the presence of certain factors in life, and the more there are, the higher the likelihood of suffering from damage to the intercostal nerves.
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels;
- Intoxication with harmful substances or alcohol;
- Lack of vitamin B;
- Metabolic failures;
- Poor nutrition;
- Mental stress.
Neuralgia most often occurs in adults and older people. A child can also suffer from such ailment, but this is quite rare.
Causes
The appearance of intercostal neuralgia is always caused by pinched or irritated nerves. This can occur with certain pathologies or disturbances in the normal functioning of the body. In some cases, several reasons are combined at once. Their identification is of great importance, because To get rid of neuralgia, it is important to treat the root cause.
The main reasons for the development of neuralgia:
- Viral or infectious diseases;
- Serious physical activity without preparation;
- Muscle spasms between the ribs;
- Hypertonicity of muscle tissue;
- Inflammation of the intercostal muscles;
- Cervical or thoracic osteochondrosis;
- Intervertebral hernia;
- Injuries and pathologies of the spine;
- Congenital chest defects;
- Development of neoplasms;
- Problems with the cardiovascular system;
- Kidney diseases;
- Poor circulation;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Ulcer, gastritis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Diabetes;
- Excessive salt deposits in the body;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Incorrect posture;
- Colds, decreased immunity.
Often the cause of neuralgia is pregnancy.
Hormonal changes, the appearance of edema, increased stress on the body, compression of internal organs - all this leads to irritation and pinching of the nerves, causing intercostal neuralgia in a woman.
It can also occur in newborns if carried incorrectly by adults. Moreover, any baby can suffer from neuralgia even with a slight draft or the slightest hypothermia.
1 Description and reasons
Thoracic neuralgia occurs due to pinching and irritation of the nerves located between the ribs in the chest area. This condition is accompanied by pain. The disease can occur without obvious reasons, but under the influence of a number of factors. These include:
- pathologies in the functioning of blood vessels;
- vitamin B deficiency;
- hypothermia;
- metabolic problems;
- alcohol intoxication;
- mental stress;
- poor nutrition.
Replacement or pinched nerves can occur as a result of the development of pathological conditions, so treatment for neuralgia should be aimed at eliminating the root cause. Main causes of the disease:
- viral or infectious lesion;
- intervertebral hernia;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- congenital chest defects;
- thoracic and cervical osteochondrosis;
- spinal injury;
- problems with blood circulation;
- multiple sclerosis;
- gastritis;
- ulcer;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- kidney pathologies;
- heavy physical activity without prior preparation;
- hormonal disbalance;
- the presence of excess salt deposits in the body.
Quite often, neuralgia is diagnosed in pregnant women. This is explained by complete hormonal changes in the body, the appearance of edema and a significant increase in the load on the female body.
Clinical picture of the disease
Thoracalgia is a non-independent disease, that is, it is a complication that resulted from the underlying disease or processes that are pathological in nature.
Most often they are associated with pathologies and diseases of the spine. That is, pain caused by MN may be associated with osteochondrosis.
For example, a complication of osteochondrosis (disc hernia) can cause the development of MN and associated pain.
Also, one of the main causes is pathological processes in the spine, accompanied by inflammation, swelling or pinching of the nerve roots of the sternum. In addition to disc hernias, the cause of progression of intercostal neuralgia can be:
- vertebral displacement;
- scoliosis;
- sponditis Definition. This is the destruction of the arches of individual vertebrae;
- growth of bone formations;
- immobile areas in the spinal column;
Often the causes of such diseases are syphilis, tuberculosis, etc. From these statistics it is clear that intercostal neuralgia can begin to develop not only due to diseases and injuries associated with the spine. The above diseases cause irreversible changes that, during development, violate the integrity of organs, tissues and nerve endings.
Another reason is trophic changes in the muscles between the ribs. They can be caused by: problems with the thyroid gland, diseases of the adrenal glands and ovaries, menopause in women. Constant stress, fatigue, strain on the back muscles, spinal injuries, age, alcohol consumption and sternum deformities can play a significant factor.
The main diagnostic symptom is pain, which is characteristic in its manifestation, which makes it possible to distinguish it, for example, from a heart attack or pneumonia. Most often, the pain is acute, but not pulsating, but even, intensifying when exposed to external factors - turning or bending the body, lifting weights, running or actively walking with the involvement of the arms.
Such pain tends to subside if the person is motionless in a comfortable position, and becomes more active during any physical activity, including coughing or sneezing.
When the patient is at rest, discomfort can be detected by palpation of suspected areas of neuralgia.
In this case, the patient will reflexively strive to change body position or hold his breath in order to get rid of pain.
In some cases, there is local numbness of the muscles and skin in the area of pathology, as well as mild hyperemia and the appearance of low-grade fever, along with increased breathing and sweating.
The list of specific symptoms indicating the etiology of the disease looks like this:
- visually detectable curvature of the spine, characteristic signs of vertebral pathology, including hernias, on X-rays and MRI;
- identification of deviations in the condition of the ribs in various injuries (against the background of partial or complete immobilization of the patient);
- the presence in the patient’s blood of signs of an infectious or viral infection that causes inflammation and muscle spasms;
- identification of neoplasms in breast tissue using scanning, analysis of their nature;
- hormonal imbalance, abnormalities in the function of the endocrine system.
Most of the signs related to the clinical picture of the disease (except for chest pain due to neuralgia) are revealed only through additional studies and tests. In some cases, the etiology of the disease is combined, and therefore a mixed set of symptoms is detected.
The main symptom of thoracic neuralgia is pain that occurs in the area where the nerve is compressed. Most often it is localized under the shoulder blades, between the ribs, in the back or lower back. Painful attacks appear quite rarely, but the pinched area constantly ache. The main symptoms of thoracic neuralgia:
- muscle cramps;
- increased pain when coughing, sneezing or bending over;
- numbness of the skin in the area of the pinched nerve;
- pallor or redness of the skin;
- increased sweating.
Prevention
Taking preventive measures can reduce the risk of intercostal neuralgia, as well as speed up treatment if it has already appeared. Therefore, it is worth paying attention to the basic rules of prevention and special gymnastics.
Basic Rules
Simple recommendations help reduce the risk of neuralgia, fight it if a person is already sick, and also improve the general condition of the body, allowing you to avoid many different diseases.
Just follow the rules:
- Treat your spine in a timely manner;
- Improve your immunity, take care of your health;
- Try not to get too cold;
- Allow sufficient time for breaks during work;
- Eat right, give up bad habits.
Such rules are especially important for people of retirement age, as well as those who suffer from chronic diseases associated with the spine.
Gymnastics
Special gymnastics shows high effectiveness against thoracic neuralgia. In most cases, it is able to affect even the underlying cause, which makes it very important for general therapy. Therefore, it is recommended to pay special attention to it.
- Lie on your back, begin to pull your legs one by one towards your chest, bending your knees. Additionally, you should try to reach your knees with your forehead.
- Roll over onto your stomach with your arms stretched forward. Raise your upper body upward, bending your back.
- Sit on a chair, clasp your hands behind your head, lean forward. After this, stand up and additionally bend or turn 90° with your entire torso.
- Lying on your back, stretch your legs and bend your arms at the elbows perpendicular to the floor. Tightening your chest muscles, slowly move your arms up and down.
- Stand up straight, spread your arms straight to your sides. Using the abdominal and chest muscles, rotate both sides of the body in the shoulder area.
Such exercises can only be performed when you feel normal, because... during an exacerbation, they will not provide any help and will harm the body.
4 Preventive measures and complications
To avoid the development of neuralgia, it is necessary to follow simple preventive measures. Physical activity should be distributed carefully. It is important to avoid severe overexertion and injury. Drafts and hypothermia can be dangerous.
It is necessary to lead an active lifestyle, as well as daily perform preventive and therapeutic exercises, which will keep the body in good shape. It is recommended to attend general therapeutic massages several times a year. Timely treatment of colds and infectious diseases helps prevent the development of exacerbations.
Without timely medical care, complications may occur. These include:
- hypoxia of nerves and nerve roots;
- minimal mobility in the affected area;
- chronic neuralgia;
- disruption of the conduction of nerve impulses to organs;
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- stopping breathing.
The chronic form of thoracic neuralgia is that the patient constantly feels pain and has a feeling of heaviness in the chest.
Thoracic neuralgia brings great discomfort. Initially, the doctor relieves pain, and only then prescribes therapeutic treatment. Self-medication can be dangerous and often leads to serious complications. It is important to take not only medications, but also attend prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures. In particularly advanced cases, surgical intervention is performed.
source
Cough with neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia is a collective concept that usually refers to conditions accompanied by pain in the chest area. This type of pain syndrome can be observed in various pathological conditions resulting from damage to various systems and organs.
There are 12 pairs of nerves in the thoracic spinal cord (the same number as the spinal vertebral segments). They are presented in the form of interconnected nerve bundles emerging from the anterior and posterior parts of the spinal cord. The former perform a motor function, while the latter perform a sensitive function.
Source: //aozlmk.ru/kashel/kak-lechit-grudnuyu-nevralgiyu-s-poyavleniem-kashlya/
Doctors will help
If you seek emergency care, doctors will help you navigate this issue by ruling out or confirming heart problems. If you have had an attack of angina, you cannot do without examination by a cardiologist. However, even if the attack turns out to be neuralgia, it is worth visiting a cardiologist.
With neuralgia, the situation is somewhat more complicated - first of all, you need to visit a neurologist, take an x-ray or undergo a tomography. Once the cause is determined, the doctor will be able to make further recommendations for treatment or refer you for consultation to another specialist, such as an osteopath.
Treatment methods depend on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body. Drug treatment is aimed at eliminating the pathological mechanisms that cause inflammation of the nerve roots. Drugs that have an anesthetic effect are of great importance. The drug Mexiletine is an analogue of Lidocaine and has an analgesic effect for neuralgia.
Ointments containing the substance capsacin eliminate discomfort when used topically.
It is necessary to treat neuralgia with drugs that enhance the effect of aminobutyric acid in combination with analgesics. Lamotrigine is used in combination with Finlepsin when other drugs are ineffective. Gabapentin is the best drug to relieve pain from neuralgia.
However, during treatment the patient may experience the following side effects:
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- vomit;
- increase in body weight.
ethnoscience
If you do not have the opportunity to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of thoracic neuralgia, you can use folk remedies to alleviate the condition at first. But remember that with their help you can only temporarily relieve pain, but will not eliminate the main cause of its occurrence. Therefore, the main task is to complete the examination course as quickly as possible and receive qualified help.
So, what traditional medicines can help you? Perhaps the most popular and effective remedy is pepper patch. Before applying it to the painful area, it must be degreased with alcohol and wiped dry. You should wear the patch until you feel warmth spreading throughout your body.
Another good way to relieve chest pain involves the use of turpentine. Pour one hundred milliliters of boiling water into a container and add one hundred grams of turpentine. Stir the mixture thoroughly, then soak gauze or a soft cloth in it, wring it out lightly and apply it to the sore spot. Place film or compress paper on top and cover with a terry towel.
Intercostal neuralgia during pregnancy
During the period of carrying a baby in the womb, thoracic neuralgia is considered a rather dangerous problem. It requires the attention of specialists, otherwise the likelihood of complications for the baby and his mother increases.
Drug therapy is usually not prescribed to such patients, so as not to harm the baby. Treatment is limited to taking multivitamin complexes, using special ointments and dry heat, as well as bed rest.
Of particular importance in the fight against pathology is the course of exercise therapy. Exercises have a positive effect on a woman’s well-being and reduce pain discomfort. Light physical activity does not allow blood to stagnate in the spine.
Diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia
Did you know that...
Next fact
Primary diagnosis is carried out based on the patient's history and complaints. Sometimes such data is enough to determine the disease. In complex cases, additional examination is required, that is, differential diagnosis to exclude diseases with similar symptoms.
The following methods are used:
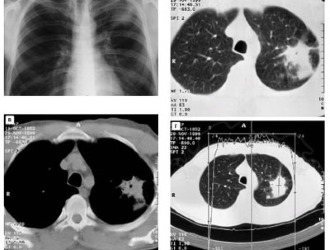
X-ray of the chest and spine in different projections.- MRI and computed tomography to rule out hernias and neoplasms.
- Electrocardiography to make sure there is no heart disease.
- Electroneurography. If a complication after an injury is suspected.
- Ultrasound.
- Gastroscopy. Will allow you to exclude gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Contrasting discography.
- Urine and blood analysis.
Computed tomography will provide more information if done in combination with myelography.
Since intercostal neuralgia can easily be confused with other pathologies, differential diagnosis must be carried out to exclude the following diseases:
- Vascular pathologies.
- Thoracic radiculitis.
- Atypical pneumonia.
- Pleurisy.
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Kidney disease.
Despite the high information content of modern diagnostic methods, they still cannot accurately diagnose in this case. Neuralgia is a functional disorder with a typical symptom that is expressed by pain.
Ultrasound and tomography can only determine:
- Presence of pinched nerve tissue: cyst, neoplasm, inflammatory focus.
- Poor local blood circulation in the area of pain.
This is very important, as it allows you to determine treatment tactics. But in the presence of “classical” neuralgia, which is not a serious illness, such expensive methods are often useless.
Electroneuromyography can be distinguished; the method determines the condition of the nerves. This study (ENMG) is used to detect disturbances in the passage of nerve impulses along a nerve.
How the procedure is carried out:
- The nerve is irritated by electric current, that is, neurostimulation occurs.
- If the nerve is motor, then irritation of the necessary muscles appears. Then the muscle response is analyzed (time, amplitude) and an impulse curve is derived from these indicators.
- In neuralgia, when the nerve is sensitive, the reaction to artificial irritation that causes pain is examined.
The procedure is painless, but is sometimes accompanied by burning or tingling.
You need to know that all instrumental methods are prescribed as an additional measure. The main means of diagnosing neuralgia is a careful medical interview and visual examination by an experienced specialist.
Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment
In order to make a correct diagnosis, a routine physical examination is not enough. First of all, you should determine the cause of the discomfort and the source of the pathology.
The primary sign of neuralgia is pain when palpating the ribs. During a physical examination, any doctor can notice the patient’s unnatural posture, which is characteristic of this pathology. Then laboratory tests are carried out (general and biochemical blood tests). Based on the results of the tests, it is possible to determine the presence of inflammatory diseases and check the functioning of the main systems of internal organs.
The next stage of diagnosis is instrumental research. Neuralgia of the chest on the left is usually perceived as a pathology of the cardiovascular system. To exclude the latter, the patient is prescribed an ECG.
After checking the main muscle, MRI and fluorography are prescribed. Thanks to modern technologies, these devices can examine not only a specific area of the patient’s body, but the entire body.
How to cure the disease
Thoracic neuralgia is treated in various ways. Painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy and traditional medicine are usually prescribed. What is best to use, you need to find out from a specialist.
The patient needs bed rest for 3-4 days. The surface of the bed must be chosen to be hard, since the result of the restoration depends on this. Only then can you use the medications prescribed by your doctor.
Treatment is carried out after establishing the causes. You should not do this yourself, as there is a risk of harm to the body. The doctor prescribes medications to eliminate muscle swelling and reduce pain. Treatment with medications lasts about 5-10 days, everything is determined by the degree of the disease.
Then, to treat the disease, muscle relaxants are used, which have a relaxing effect on the muscles. Physiotherapeutic and magnetic-electronic procedures are effective. Electrophoresis, ultrasound, acupuncture, and massage help with this. If the causes of the disease lie in osteochondrosis or skolitis, then treatment should be performed using manual therapy, therapeutic exercises and massage.
There is no need to take any measures during acute pain, as the condition may worsen. Treatment includes restoration of immunity. It is important to take vitamins and mineral complexes that improve blood circulation and metabolism in a timely manner.
Medical methods
Gels and ointments based on the mentioned products help. Injections are performed with Ketonal, Analgin, Ketorol. Severe pain is eliminated by novocaine blockade. Baclofen and Sirdalud are used to treat muscle spasms. If the disease is caused by an infection, then it needs to be treated urgently.
The disease must be treated comprehensively, so medications are supplemented by taking vitamins B6, B12, B1, which are especially needed for patients with diabetes and gastritis. Ointments with snake and bee venom are excellent help, as they restore blood circulation in the affected area.
Doctors prescribe manual therapy and massage to patients. The procedures must be performed by a specialist, since improper displacement of the vertebrae causes the condition to worsen. Electrophoresis with calcium or novocaine and UV irradiation has an excellent effect.
The disease is eliminated by physiotherapy using infrared and ultrasound radiation, electromagnetic fields. Electrophoresis with medicinal agents has a positive effect. Acupuncture and acupuncture are often prescribed.
Physiotherapy
Various physiotherapeutic procedures can be carried out as prescribed by specialists. Each type of treatment has its own advantages and disadvantages, but the doctor chooses the most effective method.
- Laser therapy involves targeting the painful area. The procedure has an anti-inflammatory effect. After it, regeneration improves, vasodilation appears. About 15 sessions are enough for treatment.
- Electrophoresis with drugs is a procedure in which therapeutic agents are introduced into the skin with a weak electric current. The patient feels a slight tingling sensation, and the entire session lasts 5 minutes.
- UHF therapy also has a healing effect. The body is exposed to an electric field. After the procedure, blood flow improves, tissue swelling is eliminated, and arteries dilate. About 15 sessions are enough for complete recovery.
- Darsonval is an electric current used in physiotherapy. During the procedure, local irritation, improved protective actions, and improved blood flow are observed. Treatment requires about 10 sessions, each lasting about 10 minutes.
Folk remedies
How to treat intercostal neuralgia of the chest with traditional medicine? Often medications are used with home remedies. They can be used only after a diagnosis has been made, since such a medicine has its own properties. Ointments and tinctures made from herbs such as chamomile, lemon balm, and wormwood are effective.
Most of the plants have an analgesic and sedative effect, which is required for thoracic neuralgia. Compresses have a beneficial effect, improving the condition of diseased areas. Although folk remedies will not help with severe forms of the disease, they will perfectly eliminate muscle swelling.
It is better to prepare the tincture from dry herbs. Horseradish, honey and agave leaves are excellent for compresses. The finished product should be applied to the painful area, and also wrapped in a woolen scarf. Treatment with folk remedies should be carried out for at least a week. It is necessary to use traditional medicine methods only after consultation with a doctor. This will prevent complications of the disease.
Folk recipes
There are a lot of medicinal products, but you can use the following recipes presented:
- a chicken egg must be hard-boiled, then rolled on the chest, but you can cut it and apply it to the sore area;
- add hot water (0.5 liters) to salt (2 tablespoons), soak a cloth in the solution and apply it to the problem area;
- the painful area must be degreased with alcohol, wiped, and then apply a pepper plaster;
- you can apply a fresh burdock leaf;
- willow bark (10 g) should be poured with boiling water (1 glass), after which the product should be boiled, cooled, strained, and can be taken by spoon 3 times a day.
Any prescription should be taken after consultation with a doctor, so as not to harm yourself. It is important to complete the entire course of treatment, and then results will definitely appear.
Self-massage
Rubbing and stroking help relieve the patient's condition. And you can do this yourself. Procedures are performed in a sitting position. You need to stretch your back muscles with your hands, and also put your hands in a lock, and do rubbing from the lumbar region to the shoulder blades.
Massage of the reflexogenic zone, located on both sides of the thoracic region between the 1st lumbar and 7th cervical vertebrae, has an excellent effect. It is advisable to massage the areas between the 4th and 5th thoracic vertebrae for about 2 minutes using Golden Star balm. If there is no product, you can perform the procedure with clean hands. You can apply a pepper patch to the sore spots.
Medical massage is very effective in curing illness. Regular procedures restore blood flow in capillaries and arteries, restore nervous tissue, and strengthen the body. The massage should be performed on the back and chest.
The procedures begin with the healthy side, gradually moving to the sick side. All actions must be careful so that the person does not feel rough movements. First, procedures are performed on the back, and then on the chest. For the first time, 15 minutes will be enough, and over time you need to increase the duration of the session. The course consists of 10 procedures in total.
During pregnancy
Illness during pregnancy is a complex problem. She needs special attention, which will prevent complications for the mother and child. In this case, it is important to prescribe the medicine by a doctor who takes into account the individual characteristics of the body.
Many women refuse medications so as not to harm the child. They take vitamins, use ointments, and do exercises. Bed rest is also important. Physical activity improves blood circulation, which is beneficial for the whole body.
- Treatment of chest contusion at home
- Treatment of the sciatic nerve at home with folk remedies, medications, injections, exercises
- Chest CCF - what is it?
- Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine: traditional and folk treatment, diagnosis and rules of prevention
Treatment
Signs of thoracic neuralgia are not specific. Let's talk about the main symptoms of the disease:
- Intensification of the attack while the patient is lying on his side or coughing;
- Intercostal chest pain;
- Possible pain in the heart area, which is not relieved by the use of nitroglycerin;
- High sweating;
- Burning, sharp, aching sensations;
- Pale skin;
- Muscle twitching.
Let's take a closer look at the symptomatic complex of intercostal neuralgia.
Even experienced doctors can confuse this disease with coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction. Only the cardiogram does not show specific changes during neuralgic manifestations.
The intercostal nerves hurt seriously and for a long time. It is not possible to cure the pathology with anti-inflammatory drugs, since the symptoms only go away for a while. The most important thing is to determine when the chest nerves are being irritated and when they are being pinched, as the treatment is different.
Intercostal pain syndrome has different characteristics in different people. Patients describe dull, burning, aching, stabbing, and sharp pains. In this case, the nature of the sensations changes after some time. Increased pain with intercostal neuralgia occurs when coughing, sneezing, moving, inhaling - specific symptoms of the disease.

If in doubt, it is necessary to make a cardiogram, which allows you to accurately differentiate nosological forms. Do not forget about the numerous manifestations: redness of the skin, muscle twitching, loss of sensitivity, excessive sweating, pallor of certain areas.
Symptoms of neuralgia when infected with the herpes virus appear at the prodromal stage of the disease. Itching, burning sensation in the left hypochondrium, pulsating, shooting, paroxysmal pain are manifestations of the disease. It is the changes in symptoms during the course of the disease and the multiplicity of the clinical picture that make it possible to diagnose the disease.
The pain of this type of neuralgia appears at the prodrome stage of the infection. The duration of the pain syndrome is approximately one month. The signs are combined with a reddish rash in the area of the left hypochondrium. The pain syndrome, with a decrease in manifestations, goes away on its own over time.
Despite a certain specificity, the diagnosis is difficult to establish even for an experienced doctor. It is necessary to differentiate with intestinal colic, pancreatitis, appendicitis, pleurisy. Only after the appearance of rashes can a diagnosis be made accurately.
The time between the prodrome and the rash requires the replication of the herpes virus. Neuralgia is explained by the replication of the infection. Reproduction of herpes in the nerve ganglia is explained by subclinical replication. Research has proven the mechanisms of pathogenetic changes during herpes infection. During infection replication, the concentration of neuropeptide “Y” in the nervous tissue increases.
For the treatment of herpes neuralgia, doctors recommend traditional drugs from the group of non-steroidal drugs and analgesics. Local anesthetics (novocaine, lidocaine) are prescribed as pain relievers.
Antiviral therapy is indicated to remove the herpes virus. Medications prevent the appearance of new lesions, reduce the duration of acute pain, and reduce the time of viral shedding. Antiviral treatment is recommended within 70 hours of rash formation.
Pain relief is mandatory not only during herpetic lesions of nerve endings. For any type of treatment for thoracic neuralgia, it is advisable to follow a special scheme:
- Medical analgesic drugs of central action (antidepressants, anticonvulsants);
- Opioid drugs (tramadol);
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, aspirin, paracetamol).
When simple analgesics and anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs are insufficiently effective, it is necessary to use centrally acting drugs. In our country there are some difficulties with prescribing opioid drugs.
This type of neuralgia is treated with five groups of drugs:
- Capsaicin;
- Anticonvulsants;
- Opioid drugs;
- Tricyclic antidepressants;
- Lidocaine patch.
Opioid drugs belong to a strict list, so experts cannot prescribe them to patients with classic thoracic neuralgia. Oxycodone, methadone, and morphine are considered effective drugs for relieving neuropathic pain. The binding of opioid receptors in the brain of the head leads to the relief of even very severe pain.
Inhibition of the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine at nerve synapses leads to the completion of nerve impulses. Test results have proven that when using the drugs, even very acute pain is relieved.
Side effects may occur while using the drugs:
- Drowsiness;
- Decreased appetite;
- Drug addiction;
- Nausea;
- Constipation.
The recommendations of European clinics indicate that the first-line drugs against postherpetic neuralgia are opioid drugs - lidocaine, pregabalin, gabapentin. The second line of drugs is capsaicin.
To cure chest neuralgia, a specific regimen of medications is required.
At the first stage, pregabalin and local anesthetics (lidocaine) are prescribed. If a positive effect is achieved, treatment continues. The weak effectiveness of drugs requires the use of second-line drugs.

Tramadol and capsaicin are sufficient to relieve neurological syndrome. To achieve a better clinical result, physiotherapeutic procedures are required: neurostimulation, acupuncture.
Anticonvulsants are prescribed to relieve neuropathic pain. Gabapentin, pregabalin are medications of the first group to prevent rashes and reduce pain. According to testing, both drugs are effective during neuropathic pain.
At the initial stage, a daily dose of gabapentin is used for therapeutic purposes - 300 mg. Over time, the frequency of use of the medicine increases - the next day 2 times 300 mg, on the third - 3 times 300 mg. On day 5, you can increase the dosage according to the scheme 300/300/600 mg. At the end of the first week, a different combination is used - 300/600/600 mg.
Pregabalin has the same mechanism of action. The medicine does not require slow titration, which is quite convenient for clinical treatment. The drug is prescribed for use 2 times a day. The initial dose of the drug is 80 mg 2 times a day. Over time, the figure increases until the daily dose is reached - 500-700 mg. Studies have proven rapid pain relief within the first week of use.
Antidepressants have proven the importance of using nortriptyline and amitriptyline during postherpetic neuralgia. The mechanism of action of the drugs is inhibition of serotonin-adrenergic systems, which are involved in the mechanism of pain.
The use of amitriptyline and nortriptyline creates anticholinergic effects. having many side effects. Uncontrolled use of drugs leads to heart disease.
Intercostal neuralgia is a rather complex disease that requires timely identification and professional assistance from a doctor. The sooner this disease is identified, the less time a person will suffer from severe pain, which can often be so strong that it can cause the patient to lose consciousness or go into painful shock.
Bulatnikov Alexey Ivanovich
Therapy for intercostal neuralgia includes medication and physiotherapeutic treatment, as well as interventions with surgical intervention. The latter is used quite rarely. Sometimes folk remedies are additionally used.
Medication
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate pain and prevent recurrent attacks. For this, the patient is prescribed various medications. They are available in the form of tablets, ointments or injections.
Doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- “Diclofenac”, “Voltaren” - have an anti-inflammatory effect and are introduced into the body through an injection.
- “Sedalgin”, “Spazgan” - painkillers that help relieve pain and relieve recurrent attacks.
- “Vipratox”, “Apizartron” - special ointments that relieve spasms, help improve well-being and reduce the severity of symptoms.
- “Elenium”, “Realinium” are sedatives that help calm the nervous system and normalize the patient’s condition.
- Vitamin complexes – have a positive effect on the general condition of the body, vitamin B is of particular benefit.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, women are prescribed medications only in the form of ointments. They cannot take pills or give injections, because... this may have a negative impact on the child, whose body will be exposed to medicinal substances that may be dangerous to him.
After prescribing medications, the patient will also be given directions for special physiotherapeutic procedures. They are important for the anatomy of the body, because. restore the position of the spine and relieve unpleasant symptoms. In this case, the patient will be prescribed bed rest for several days.
How to treat neuralgia in the chest with physical therapy:
- Therapeutic exercise – normalizes the condition of the spine, relieves minor pathologies.
- Electrophoresis using special means has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
- Massage – improves blood circulation, normalizes the nutrition of damaged tissues with important substances.
- Acupuncture – improves blood circulation, helps reduce painful manifestations of neuralgia.
In most cases, such procedures are enough to quickly restore your body and improve your well-being.
Surgical
If classical treatment methods do not bring the expected result, the doctor may prescribe surgery. This is only possible with certain diseases of the spine. During the operation, the patient's compressed nerves are released using mechanical force. After this, he will need to undergo light rehabilitation, and the symptoms will disappear almost immediately.